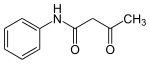
Acetoacetanilide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Oxo-N-phenylbutanamide | |
| Other names
Acetoacetylaminobenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.725 |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 177.20 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless solid |
| Melting point | 83 to 88 °C (181 to 190 °F; 356 to 361 K) |
| low | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Acetoacetanilide is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2C(O)NHC6H5. It is the acetoacetamide derivative of aniline. It is a white solid that is poorly soluble in water. It and many related compounds (prepared from various aniline derivatives) are used in the production of organic pigments called arylide yellows.
Preparation and reactions
Acetoacetanilide is prepared by acetoacetylation of aniline using diketene.
To make the dyes, acetoacetanilides are coupled to diazonium salts, "azo coupling".[1]
References
- ↑ K. Hunger. W. Herbst "Pigments, Organic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_371
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.