Acacia confusa
| Acacia confusa | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Clade: | Mimosoideae |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. confusa |
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia confusa | |
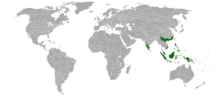 | |
| Range of Acacia confusa | |
| Synonyms | |
Acacia confusa is a perennial tree native to South-East Asia. Some common names for it are acacia petit feuille, small Philippine acacia, Formosa acacia (Taiwan acacia) and Formosan koa. It grows to a height of 15m. The tree has become very common in many tropical Pacific areas, including Hawaii, where the species is considered invasive.[3]
Uses
Its uses include chemical products, environmental management and food and drink. The bark may be ground into a powder and saturated into water to create a tea, or may be spread onto various foods as a spice and taste enhancer. The wood has a density of about 0.75 g/cm³.[4] In Taiwan, its wood is used to make support beams for underground mines. The wood is also converted to charcoal for family use. The plant is used in traditional medicine[5] and is available from herbal medicine shops (草藥店) in Taiwan, but there has been no clinical study to support its effectiveness. It is also frequently used as a durable flooring material.



Phytochemicals
Phytochemicals found in Acacia confusa:
Root bark
- N-Methyltryptamine, 1.43%[6]
- N,N-Dimethyltryptamine, 1.15%[6]
Seeds
- Oxalyldiaminopropionic acid (α-amino-β-oxalylaminopropionic acid),[7] which can cause neurological damage, paralysis, and death.
Stems
- N-Methyltryptamine, 0.04%[6]
Varieties
- Acacia confusa var. inamurai Hayata
See also
References
- ↑ World Conservation Monitoring Centre (1998). "Acacia richii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 3 May 2014.
- ↑ International Legume Database & Information Service (ILDIS)
- ↑ Pacific Island Ecosystems at Risk (PIER)
- ↑ FAO Appendix 1
- ↑ Li, Thomas S. C. Taiwanese Native Medicinal Plants: Phytopharmacology and Therapeutic Values, CRC Press (2006), ISBN 0-8493-9249-7, p.2. online GoogleBooks preview
- 1 2 3 Arthur, HR; Loo, SN; Lamberton, JA (1967). "Nb-Methylated tryptamines and other constituents of Acacia confusa Merr. Of Hong Kong". Australian Journal of Chemistry. 20 (4): 811. doi:10.1071/CH9670811.
- ↑ Quereshi, M.Yasin; Pilbeam, David J.; Evans, Christine S.; Bell, E.Arthur (1977). "The neurolathyrogen, α-amino-β-oxalylaminopropionic acid in legume seeds". Phytochemistry. 16 (4): 477. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)94332-2.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Acacia confusa. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Acacia confusa |
- Erowid Acacia vault
- Acacia confusa Merr. Medicinal Plant Images Database (School of Chinese Medicine, Hong Kong Baptist University) (in traditional Chinese) (in English)