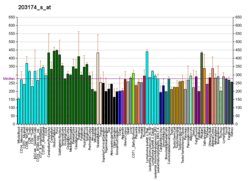
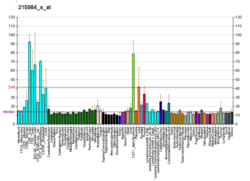
ARFRP1
ADP-ribosylation factor-related protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARFRP1 gene.[5][6]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a membrane-associated GTP-ase and localizes to the plasma membrane. It is related to the ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) and ARF-like (ARL) genes. The gene is located in a gene cluster that includes the a gene (M68) that is overexpressed in some tumors.[6]
Interactions
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000101246 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000038671 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Schurmann A, Massmann S, Joost HG (Jan 1996). "ARP is a plasma membrane-associated Ras-related GTPase with remote similarity to the family of ADP-ribosylation factors". J Biol Chem. 270 (51): 30657–63. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.51.30657. PMID 8530503.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: ARFRP1 ADP-ribosylation factor related protein 1".
- ↑ Schürmann A, Schmidt M, Asmus M, Bayer S, Fliegert F, Koling S, Massmann S, Schilf C, Subauste MC, Voss M, Jakobs KH, Joost HG (April 1999). "The ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF)-related GTPase ARF-related protein binds to the ARF-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor cytohesin and inhibits the ARF-dependent activation of phospholipase D". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (14): 9744–51. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.14.9744. PMID 10092663.
Further reading
- Zahn C, Hommel A, Lu L, et al. (2007). "Knockout of Arfrp1 leads to disruption of ARF-like1 (ARL1) targeting to the trans-Golgi in mouse embryos and HeLa cells". Mol. Membr. Biol. 23 (6): 475–85. doi:10.1080/09687860600840100. PMID 17127620.
- Shin HW, Kobayashi H, Kitamura M, et al. (2005). "Roles of ARFRP1 (ADP-ribosylation factor-related protein 1) in post-Golgi membrane trafficking". J. Cell Sci. 118 (Pt 17): 4039–48. doi:10.1242/jcs.02524. PMID 16129887.
- Barrios-Rodiles M, Brown KR, Ozdamar B, et al. (2005). "High-throughput mapping of a dynamic signaling network in mammalian cells". Science. 307 (5715): 1621–5. doi:10.1126/science.1105776. PMID 15761153.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Behnia R, Panic B, Whyte JR, Munro S (2004). "Targeting of the Arf-like GTPase Arl3p to the Golgi requires N-terminal acetylation and the membrane protein Sys1p". Nat. Cell Biol. 6 (5): 405–13. doi:10.1038/ncb1120. PMID 15077113.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Deloukas P, Matthews LH, Ashurst J, et al. (2002). "The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 20". Nature. 414 (6866): 865–71. doi:10.1038/414865a. PMID 11780052.
- Coppola T, Magnin-Luthi S, Perret-Menoud V, et al. (2001). "Direct interaction of the Rab3 effector RIM with Ca2+ channels, SNAP-25, and synaptotagmin". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (35): 32756–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100929200. PMID 11438518.
- Bai C, Connolly B, Metzker ML, et al. (2000). "Overexpression of M68/DcR3 in human gastrointestinal tract tumors independent of gene amplification and its location in a four-gene cluster". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (3): 1230–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.3.1230. PMC 15578. PMID 10655513.
- Schürmann A, Schmidt M, Asmus M, et al. (1999). "The ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF)-related GTPase ARF-related protein binds to the ARF-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor cytohesin and inhibits the ARF-dependent activation of phospholipase D.". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (14): 9744–51. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.14.9744. PMID 10092663.
External links
- ARFRP1 human gene location in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- ARFRP1 human gene details in the UCSC Genome Browser.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.