AEX index
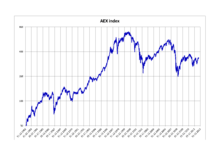 AEX index performance between 1982 and 2012 | |
| Foundation | 1983 |
|---|---|
| Operator | Euronext |
| Exchanges | Euronext Amsterdam |
| Constituents | up to 25 |
| Type | Large cap |
| Market cap | €490.85 billion (Begin March 2015)[1] |
| Weighting method | Capitalization-weighted |
| Related indices | AMX index, AScX index |
| Website |
www |
The AEX index, derived from Amsterdam Exchange index, is a stock market index composed of Dutch companies that trade on Euronext Amsterdam, formerly known as the Amsterdam Stock Exchange. Started in 1983, the index is composed of a maximum of 25 of the most frequently traded securities on the exchange. It is one of the main national indices of the stock exchange group Euronext alongside Brussels' BEL 20, Paris's CAC 40 and Lisbon's PSI-20.
History
The AEX started from a base level of 100 index points on 3 January 1983 (a corresponding value of 45.378 is used for historic comparisons due to the adoption of the Euro).[2] The index's peak to date is 703.18, reached on 5 September 2000 at the height of the dot-com bubble.[3] The index value more than halved over the following three years before recovering in line with most global financial markets.
The AEX index enjoyed its second largest one-day loss on September 29, 2008, when the index closed down almost 9%. The decade between 1998 and 2008 has been bad for the AEX index, as it has been the worst performing stock index except for the OMX Iceland 15.[4] The preceding years were a lot better compared to the rest of the world.
Rules
Selection
As of 2011, the AEX index composition is reviewed four times a year - a full "annual" review in March and interim "quarterly" reviews in June, September and December. Any changes made as a result of the reviews take effect on the third Friday of the month.[5] Previously reviews were held in March and September only.[6] Prior to 2008, index changes were made only annually in March.
At the main March review date, the 23 companies listed on Euronext Amsterdam's regulated market with the highest share turnover (in Euros) over the previous year are admitted to the index.[5] Of the companies ranked between 24th and 27th, a further two are selected with preference given to existing constituents of the index. Companies which have fewer than 25% of shares considered free float on Euronext Amsterdam are, however, ineligible for inclusion.[5] Unlike some other European benchmark equity indices (such as the OMXS30), if a company has more than one class of shares traded on the exchange, only the most frequently traded of these will be accepted into the AEX.[5] If a company or companies are removed from the index due to delisting, acquisition or another reason, no replacements are made until the next review date.[5]
At the three interim reviews in June, September and December, no changes are made to the AEX unless either the index has seen one or more constituents removed, or a non-constituent possesses a share turnover ranked 15th or higher overall over the previous 12 months.[6] If vacancies are to be filled, the highest-ranking non-AEX companies are selected to join the index.[6]
Weighting
The AEX is a capitalization-weighted index. At each main annual review, the index weightings of companies in the index are capped at 15%,[7] but range freely with share price subsequently. The index weights are calculated with respect to the closing prices of the relevant companies on March 1. At the interim reviews, weightings after adjustment are left as close as possible to those of the previous day and are not re-capped.[5]
Calculation
The index comprises a basket of shares, the numbers of which are based on the constituent weights and index value at the time of readjustment. The value of the index at any given time, It, is calculated using the following formula:[5]
with t the day of calculation; N the number of constituent shares in the index (usually 25); Qi,t the number of shares of company i on day t; Fi,t the free float factor of share i; fi,t the capping factor of share i (exactly 1 for all companies not subject to the 15% cap); Ci,t the price of share i on day t; and dt the index divisor (a factor calculated from the base capitalisation of the index, which is updated to reflect corporate actions and other index changes.
Composition
The index is composed of the following listings as of 1 April 2017.[8]
| Company | ICB Sector | Ticker symbol | Index weighting (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aalberts Industries | industrial goods and services | AALB | 0.72 |
| ABN AMRO | banks | ABN | 1.32 |
| Aegon | insurance | AGN | 1.73 |
| Ahold Delhaize | food retailers and wholesalers | ADRNY | 5.21 |
| Akzo Nobel | chemicals | AKZA | 3.99 |
| Altice | telecommunications | ATC | 2.35 |
| ArcelorMittal | basic resources | MT | 3.20 |
| ASML | technology | ASML | 9.50 |
| Boskalis | construction and materials | BOKA | 0.56 |
| DSM | chemicals | DSM | 2.35 |
| Gemalto | technology | GTO | 0.80 |
| Heineken | food and beverage | HEIA | 3.76 |
| ING Group | banks | INGA | 11.11 |
| KPN | telecommunications | KPN | 1.98 |
| NN Group | insurance | NN | 2.11 |
| Philips | industrial goods and services | PHIA | 5.70 |
| Randstad Holding | industrial goods and services | RAND | 1.32 |
| RELX Group | media | REN | 3.42 |
| Royal Dutch Shell | oil and gas | RDSA | 15.27 |
| SBM Offshore | oil and gas | SBMO | 0.53 |
| Unibail-Rodamco | real estate | UL | 4.44 |
| Unilever | personal and household goods | UNA | 15.17 |
| Vopak | industrial goods and services | VPK | 0.58 |
| Wolters Kluwer | publishing | WKL | 2.27 |
See also
- AMX index, the market index of the next 25 largest funds on Euronext Amsterdam.
- AScX index, market index of 25 small caps on Euronext Amsterdam.
References
- ↑ This is the actual total free-float market cap of the AEX constituents. Because the index uses a basket model which does not include the total number of shares, the market cap of the index per se is significantly less than this. "AEX Executive Presentation - January 2011" (PDF). NYSE Euronext. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 June 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2011.
- ↑ "Amsterdam AEX Stock Index". Global Financial Data. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- ↑ Its record close was 701,56 on 4 September 2000 "AEX Index Breaks Through Magic 500 Threshold". NIS News. 3 January 2007. Archived from the original on 28 December 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- ↑ In the long run, we're all dead, amsterdamtrader.com, January 7, 2009
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Rules for the AEX, AMX and AScX" (PDF). NYSE Euronext. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 June 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2011.
- 1 2 3 "Announcement Rules Change AEX-index, AMX-index and AScX-index - Introduction of Interim Review and Revised Eligibility Rule" (PDF). Euronext. June 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-20. Retrieved 2008-05-14.
- ↑ "AEX-Index profile". Euronext. Archived from the original on 2008-02-02. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- ↑ "AEX-INDEX Market Information". Euronext AEX. Retrieved 2017-04-01.