6-APA
 | |
.gif) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
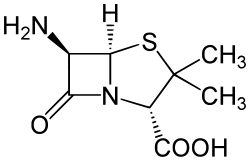
| IUPAC name
(2S,5R,6R)-6-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4- thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2- carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.177 |
| EC Number | 208-993-4 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H12N2O3S | |
| Molar mass | 216.257 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Melting point | 198 °C (388 °F; 471 K) |
| Boiling point | 207 °C (405 °F; 480 K) decomp |
| 0.4 g/100 mL | |
| log P | 0.600 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
6-APA is the chemical compound (+)-6-aminopenicillanic acid.[1]
Use
6-APA is the core of penicillins. It is obtained from the fermentation brew of the Penicillium mold and used as the main starting block for the preparation of numerous semisynthetic penicillins.
History
In 1958, Beecham scientists in the UK discovered the penicillin nucleus, 6-APA. From that starting material, a large number of new semisynthetic penicillins could be designed, whose activity was directed against problem infections.[2]
References
- ↑ Synthesis of Penicillin: 6-Aminopenicillanic Acid in Penicillin Fermentations - F. R. Batchelor, F. P. Doyle, J. H. C. Nayler & G. N. Rolinson. Nature 183, 257-258 (24 January 1959) doi:10.1038/183257b0
- ↑ F.P. Doyle, J.H.C. Nayler, G.N. Rolinson US Patent 2,941,995, filed July 22, 1958, granted June 21, 1960. Recovery of solid 6-aminopenicillanic acid.
External links
See also
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.