46 Aquilae
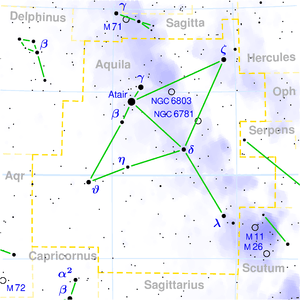 46 Aquilae near the star Tarazed (γ Aql) | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aquila |
| Right ascension | 19h 42m 12.81267s[1] |
| Declination | 12° 11′ 35.7383″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.321[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B9III[3] |
| U−B color index | −0.42[4] |
| B−V color index | −0.08[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −24.70 ± 1.6[3] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −0.32[1] mas/yr Dec.: −8.70[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 4.53 ± 0.79[1] mas |
| Distance | approx. 700 ly (approx. 220 pc) |
| Details[5] | |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.7 cgs |
| Temperature | 12900 K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 1.0 ± 0.5 km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
46 Aquilae (abbreviated 46 Aql) is a seventh-magnitude star in the constellation of Aquila. 46 Aquilae is its Flamsteed designation. It is located approximately 700 light years from Earth, based on parallax.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 van Leeuwen, F.; et al. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
- ↑ Høg, E.; et al. (2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355: L27–L30. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H.
- 1 2 "* 46 Aql". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2010-07-24.
- 1 2 Crawford, D. L. (February 1963), "U, b, v, and Hβ Photometry for the Bright B8- and B9-TYPE Stars", Astrophysical Journal, 137: 530, Bibcode:1963ApJ...137..530C, doi:10.1086/147526.
- ↑ Bailey, J. D.; Landstreet, J. D. (2013). "Abundances determined using Si ii and Si iii in B-type stars: Evidence for stratification". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 551: A30. arXiv:1301.3050. Bibcode:2013A&A...551A..30B. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201220671.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.