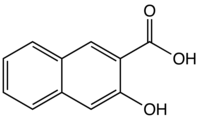
3-Hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
3-Hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid BON acid β-Hydroxynaphthoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 744100 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number | 202-180-8 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number | QL1755000 |
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 188.18 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow solid |
| Melting point | 222 °C (432 °F; 495 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS signal word | Warning |
| H302, H312, H317, H319, H361, H371, H402, H412 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P272, P273, P280, P281, P301+312, P302+352, P305+351+338, P308+313, P309+311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P333+313, P337+313, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid is an organic compound with the formula C10H6(OH)(CO2H). It is one of the several carboxylic acids derived from 2-naphthol. It is a common precursor to azo dyes and pigments. It is prepared by carboxylation of 2-naphthol via the Kolbe–Schmitt reaction.[1]
3-Hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid is a precursor to many anilides, such as Naphthol AS, which are reactive toward diazonium salts to give deeply colored azo compounds. Azo coupling of 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid gives many dyes as well.
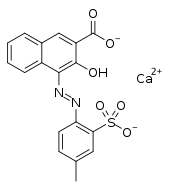 Lithol Rubine BK is one of many dyes made from 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid. Notice that the coupling occurs adjacent to the hydroxy group.
Lithol Rubine BK is one of many dyes made from 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid. Notice that the coupling occurs adjacent to the hydroxy group.
References
- ↑ Gerald Booth (2005). "Naphthalene Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_009. .
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.