2014 SR349
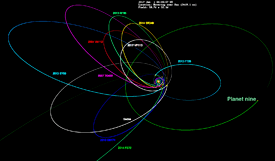 The orbits of 2014 SR349 (yellow) and other detached objects, along with the hypothetical Planet Nine's orbit on the right. | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Scott Sheppard and Chad Trujillo |
| Discovery date | 19 September 2014 |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | 2014 SR349 |
|
TNO · E-SDO (detached object) | |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Epoch 2017-Feb-16 (JD 2457800.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 5 | |
| Observation arc | 738 days (2.02 yr) |
| Aphelion |
549 AU (barycentric)[1] 535 AU |
| Perihelion | 47.57 AU |
|
299 AU (barycentric)[1] 292 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.8369 |
|
5157 yr (barycentric)[1] 4981 years | |
| 357.3° | |
| 0.00019622°/day | |
| Inclination | 17.98° |
| 34.75° | |
| 341.35° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | ~200 km |
| 6.6 | |
|
| |
2014 SR349 is a trans-Neptunian object and scattered disc object in the outermost part of the Solar System. It was first observed on 19 September 2014, by astronomers Scott Sheppard and Chad Trujillo at Cerro Tololo Observatory, Chile, and revealed on 29 August 2016.[2] It currently has a magnitude of 24.18.[3]
References
- 1 2 3 Horizons output. "Barycentric Osculating Orbital Elements for 2014 SR349". Retrieved 2017-02-08. (Ephemeris Type:Elements and Center:@0)
- ↑ "Hunt for Planet 9 reveals extremely distant solar system objects". Astronomy Now. August 29, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2016.
- ↑ "Asteroid 2014 SR349". Theskylive. Retrieved October 16, 2016.
External links
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.