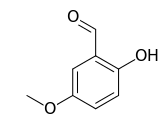
2-Hydroxy-5-methoxybenzaldehyde
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Hydroxy-5-methoxybenzaldehyde | |
| Other names
5-Methoxysalicylaldehyde; 2-Formyl-4-methoxyphenol; 6-Hydroxy-m-anisaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.537 |
| EC Number | 211-589-0 |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 152.15 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow to yellow-green liquid |
| Density | 1.219 g/mL |
| Melting point | 4 °C (39 °F; 277 K) |
| Boiling point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.578 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Hydroxy-5-methoxybenzaldehyde is an organic compound and an isomer of vanillin.
Chemical synthesis
The chemical is produced by the Reimer-Tiemann reaction on 4-methoxyphenol with a 79% yield.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Wynberg, Hans; Meijer, Egbert W. (2005). "The Reimer–Tiemann Reaction". Wiley Online Library: pg.16. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or028.01. ISBN 9780471264187. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.