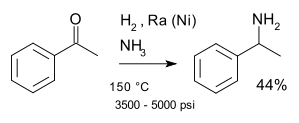1-Phenylethylamine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Phenylethan-1-amine | |
| Other names
(±)-1-Phenylethylamine (±)-α-Methylbenzylamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.588 |
| KEGG | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H11N | |
| Molar mass | 121.18 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.94 g/mL |
| Melting point | -65 C |
| Boiling point | 187 °C (369 °F; 460 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Corrosive |
| Related compounds | |
Related stereoisomers |
(R)-(+)- (CAS [3886-69-9]) (S)-(–)- (CAS [2627-86-3]) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
1-Phenylethylamine is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH(NH2)CH3. Classified as a monoamine, this colorless liquid is often used in chiral resolutions. Like benzylamine, it is highly basic and forms stable ammonium salts and imines.
This compound may be prepared by the reductive amination of acetophenone under various standard conditions for this type of reaction. One major route for this chemical uses the Mignonac reaction, a one-pot protocol using hydrogen gas as the reducing agent:[2]
The Leuckart reaction, using ammonium formate, is another method for this transformation.[3][4]
See also
References
- ↑ 1-Phenylethylamine - PubChem Public Chemical Database
- ↑ John C. Robinson, Jr. and H. R. Snyder (1955). "α-Phenylethylamine". Organic Syntheses. ; Collective Volume, 3, p. 717
- ↑ Mann, F. G.; Saunders, B. C. (1960). Practical Organic Chemistry, 4th Ed. London: Longman. pp. 223–224. ISBN 9780582444072.
- ↑ A. W. Ingersoll (1937). "α-Phenylethylamine". Organic Syntheses. ; Collective Volume, 17, p. 76
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.