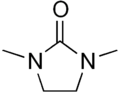
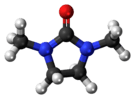
1,3-Dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,3-Dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone | |||
| Other names
Dimethylethyleneurea N,N'-Dimethylimidazolidinone | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| Abbreviations | DMI | ||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.187 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H10N2O | |||
| Molar mass | 114.1457 | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Melting point | 8.2[1] °C (46.8 °F; 281.3 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
1,3-Dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone (DMI) is a cyclic urea used as a high-boiling polar aprotic solvent.[2] It is colourless, highly polar solvent has high thermal and chemical stability. It is a homolog of the related solvent DMPU. It can be prepared from 1,2-dimethylethylenediamine by reaction with phosgene.
Solvent
DMI has excellent solvating ability for both inorganic and organic compounds. In many applications, DMI (as well as DMPU) can be used as a substitute or replacement for the carcinogenic solvent HMPA.[3]
DMI is used in a variety of applications including detergents, dyestuffs, electronic materials and in the manufacture of polymers.
DMI is toxic in contact with skin.[4]
References
- ↑ DMI at Mitsui Chemicals
- ↑ Leahy, Ellen M. "1,3-Dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone" e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (2001),doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd342
- ↑ Lo, C.-C.; Chao, P.-M. (1990). "Replacement of carcinogenic solvent HMPA by DMI in insect sex pheromone synthesis". Journal of Chemical Ecology. 16 (12): 3245–3253. doi:10.1007/BF00982095.
- ↑ DMI at TCI
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.