< USMLE Step 1 Review 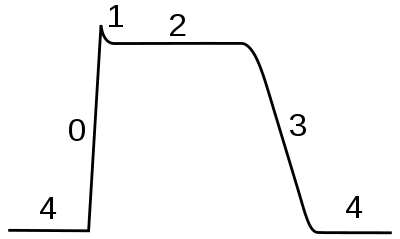
Basic science
Heart anatomy
.svg.png)
Cardiac cycle
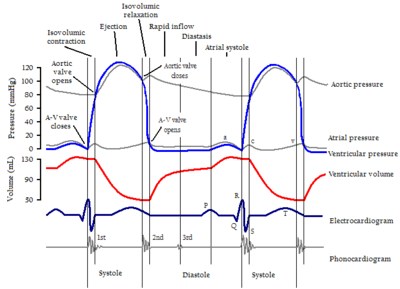
Heart sounds
Physiologic splitting of S2
Inspiration → ↓intrathoracic pressure →
- ↑Stretch pulmonary capacitance vessels → ↓LV filing → ↓length of LV systole →
- Earlier closure of aortic valve → earlier A2
- ↑RV filling → ↑length of RV systole →
- Delayed closure of pulmonic valve → delayed P2
- S1: MV/TV closure
- S2: AV/PV closure
- Physiologic splitting of S2 on inspiration (see inset)
Heart electrophysiology
Conducting system of heart
Sinoatrial (SA) node in right atrium → atrioventricular (AV) node → His bundle → Purkinje fibers → ventricular myocardium
Myocardial action potentials

Ventricular action potential.
Ventricular action potential
- Phase 4
- outward potassium leak (resting membrane potential)
- Phase 0
- inward sodium (rapid depolarization)
- Phase 1
- outward potassium (partial repolarization)
- Phase 2
- balance of inward sodium/calcium and outward potassium (plateau)
- Phase 3
- outward potassium (repolarization)

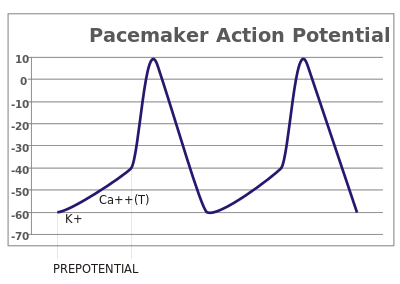
Pacemaker potential (SA and AV nodes).
Pacemaker potential
- Phase 4
- inward sodium/calcium (slow depolarization; SA/AV cells have no resting membrane potential)
- Phase 0
- inward calcium (rapid depolarization)
- Phase 3
- outward potassium (repolarization)
Cardiovascular pathology
Arrhythmias
- Atrial fibrillation: irregularly irregular rhythm (no p waves), rate often >100 (a type of supraventricular tachycardia), can result in heart failure, thrombus formation; treat with rate control (beta-blockers, non-DHP calcium channel blockers) or rhythm control (dofetilide, sotalol, amiodarone), and anticoagulation (warfarin).
- Atrial flutter: p waves present in "sawtooth" pattern, often at rate of 300 and ventricular rate of 150 (often 2:1 conduction, but can vary); often resistant to rate control; treat refractory cases with ablation (maze procedure).
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: supraventricular impulses conducted along accessory pathway leading to early and nonuniform depolarization of ventricles, causing QRS widening with a delta wave.
Endocarditis
Endocarditis stigmata
- Roth spots
- nonspecific retinal hemorrhages (cotton-wool spots)
- Osler nodes
- painful lesions on fingers/toes due to immunologic phenomena
- Janeway lesions
- painless lesions on fingers/toes due to immunologic phenomena
- Splinter haemorrhages
- speculated to be caused by vasculitis in nail bed in IE
- finger clubbing
- mechanism unknown
Fever, malaise, embolic phenomena (eg, stroke), new murmur; vegetation on echocardiography, positive blood cultures, elevated ESR/CRP. Treat with empiric antibiotics, using culture results to guide more specific antibiotic selection.
Rheumatic fever
Diagnosis[1]
- J♥NES
- Joints (migratory polyarthritis)
- ♥ (pancarditis)
- Subcutaneous Nodules
- Erythema marginatum
- Syndenham's Chorea - face, tongue, upper-limb chorea
References
- ↑ Baddour LM, Wilson WR, Bayer AS, et al. (June 2005). "Infective endocarditis: diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, and the Councils on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke, and Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, American Heart Association: endorsed by the Infectious Diseases Society of America". Circulation 111 (23): e394–434. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.165564. PMID 15956145. http://circ.ahajournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=15956145.
This article is issued from
Wikibooks.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.