In this section, an example of the calculation of a partition function is presented. The Ising model [ma:equad:Schuster88], [ph:physt:Diu89] \index{Ising} is a model describing ferromagnetism\index{ferromagnetic}. A ferromagnetic material is constituted by small microscopic domains having a small magnetic moment. The orientation of those moments being random, the total magnetic moment is zero. However, below a certain critical temperature , magnetic moments orient themselves along a certain direction, and a non zero total magnetic moment is observed[1] . Ising model has been proposed to describe this phenomenom. It consists in describing each microscopic domain by a moment (that can be considered as a spin)\index{spin}, the interaction between spins being described by the following hamiltonian (in the one dimensional case):
partition function of the system is:
which can be written as:
It is assumed that can take only two values. Even if the one dimensional Ising model does not exhibit a phase transition, we present here the calculation of the partition function in two ways. represents the sum over all possible values of , it is thus, in the same way an integral over a volume is the successive integral over each variable, the successive sum over the 's. Partition function can be written as:
with
We have:
Indeed:
Thus, integrating successively over each variable, one obtains:
eqZisi
This result can be obtained a powerful calculation method: the renormalization group method[ph:physt:Diu89], [ma:equad:Schuster88]\index{renormalisation group} proposed by K. Wilson[2]. Consider again the partition function:
where
Grouping terms by two yields to:
where
This grouping is illustrated in figure figrenorm.
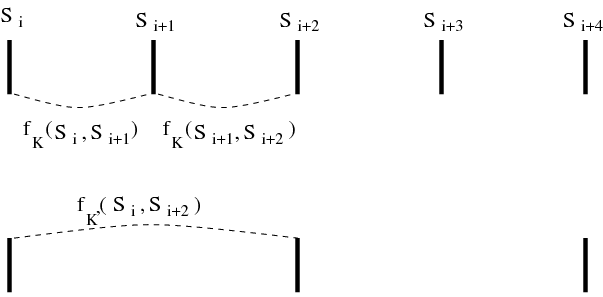
Calculation of sum over all possible values of yields to:
Function can thus be written as a second function with
Iterating the process, one obtains a sequence converging towards the partition function defined by equation eqZisi.
- ↑
Ones says that a phase transition occurs.\index{phase transition}
Historically, two sorts of phase transitions are distinguished [ph:physt:Diu89]
- phase transition of first order (like liquid--vapor transition) whose characteristics are:
- Coexistence of the various phases.
- Transition corresponds to a variation of entropy.
- existence of metastable states.
- second order phase transition (for instance the ferromagnetic--paramagnetic transition) whose characteristics are:
- symmetry breaking
- the entropy S is a continuous function of temperature and of the order parameter.
- phase transition of first order (like liquid--vapor transition) whose characteristics are:
- ↑ Kenneth Geddes ilson received the physics Nobel price in 1982 for the method of analysis introduced here.