< Introduction to Mathematical Physics < Continuous approximation
We assume here that external forces are described by and that internal strains are described by tensor .
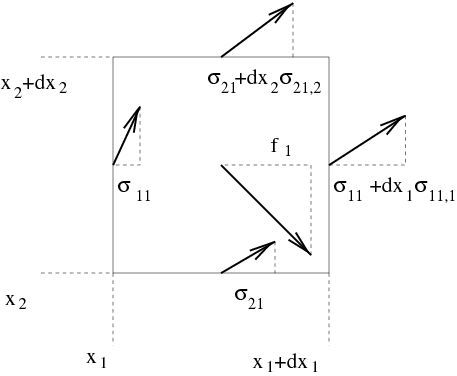
This integral equation corresponds to the applying of Newton's law of motion\index{momentum} over the elementary fluid volume as shown by figure figconsp.

Momentum conservation law corresponds to the application of Newton's law of motion to an elementary fluid volume.}
figconsp
Partial differential equation associated to this integral equation is:
Using continuity equation yields to:
Remark: Momentum conservation equation can be proved taking the first moment of Vlasov equation. Fluid momentum is then related to repartition function by the following equality:
Later on, fluid momentum is simply designated by .
This article is issued from
Wikibooks.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.