< Fractals < Iterations in the complex plane %3Dz%5E2_%2B_mz_where_p_over_q%3D1_over_3.svg.png)
Gallery
- directions
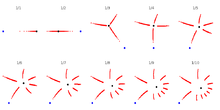 critical orbits for internal angle from 1/1 to 1/10. True attracting directions
critical orbits for internal angle from 1/1 to 1/10. True attracting directions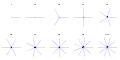 Q-th arm stars for q from 1 to 10. Schematic directions
Q-th arm stars for q from 1 to 10. Schematic directions perturbation of parabolic critical orbit
perturbation of parabolic critical orbit
Theory
dimension one means here that f maps complex plain to complex plain ( self map )[1]
z + mz^d
Class of functions :[2]
where :
Simplest subclass :
simplest example :
W say that roots of unity, complex points v on unit circle
are attracting directions if :
mz+z^d
%3Dz%5E2_%2B_mz_where_p_over_q%3D1_over_3.svg.png)
Critical orbit and directions for for complex quadratic polynomial and internal angle 1/3
On the complex z-plane ( dynamical plane) there are q directions described by angles:
where :
- is a internal angle ( rotation number) in turns [3]
- d = r+1 is the multiplicity of the fixed point [4]
- r is the number of attracting petals ( which is equal to the number of repelling petals)
- q is a natural number
- p is a natural number smaller then q
Repelling and attracting directions [5] in turns near alfa fixed point for complex quadratic polynomials
| Internal angle | Attracting directions | Repelling directions |
|---|---|---|
| 1/2 | 1/4, 3/4 | 0/2, 1/2 |
| 1/3 | 1/6, 3/6, 5/6 | 0/3, 1/3, 2/3 |
| 1/4 | 1/8, 3/8, 5/8, 7/8 | 0/4, 1/4, 2/4, 3/4 |
| 1/5 | 1/10, 3/10, 5/10, 7/10, 9/10 | 0/5, 1/5, 2/5, 3/5, 4/5 |
| 1/6 | 1/12, 3/12, 5/12, 7/12, 9/12, 11/12 | 0/6, 1/6, 2/6, 3/6, 4/6, 5/6 |
| - | - | - |
| 1/q | 1/(2q), 3/(2q), ... , (2q-2)/(2q) | 0/q, 1/q, ..., (q-1)/q |
References
This article is issued from
Wikibooks.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.