< Calculus
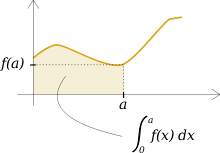

The definite integral of a function f(x) from x=0 to x=a is equal to the area under the curve from 0 to a.
Basics of Integration
4.1 Definite integral 4.2 Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 4.3 Indefinite integral 4.4 Improper Integrals
Integration Techniques

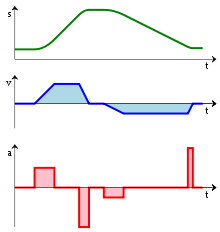
From bottom to top:
- an acceleration function a(t);
- the integral of the acceleration is the velocity function v(t);
- and the integral of the velocity is the distance function s(t).
4.5 Infinite Sums 4.6 Derivative Rules and the Substitution Rule 4.7 Integration by Parts 4.8 Trigonometric Substitutions 4.9 Trigonometric Integrals 4.10 Rational Functions by Partial Fraction Decomposition 4.11 Tangent Half Angle Substitution 4.12 Reduction Formula 4.13 Irrational Functions 4.14 Numerical Approximations 4.15 Exercises
Applications of Integration
4.16 Area 4.17 Volume 4.18 Volume of solids of revolution 4.19 Arc length
This article is issued from
Wikibooks.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.