tomatine
English
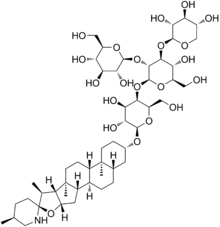
Structure diagram of α-tomatine
Noun
tomatine (countable and uncountable, plural tomatines)
- (organic chemistry) A toxic glycoalkaloid with fungicidal properties, found in the stems and leaves of tomato plants.
- 2006, John R. Stommel, 6: Genetic Enhancement of Tomato Fruit Nutritive Value, Maharaj K. Razdan, Autar K. Mattoo (editors), Genetic Improvement of Solanaceous Crops, Volume 2: Tomato, page 208,
- Tomato accumulates the glycoalkaloids a-tomatine and dehydrotomatine in a 10 : 1 ratio (Madhavi and Salunkhe 1998).
- 2012, Cheryll Williams, Medicinal Plants in Australia, Volume 3: Plants, Potions and Poisons, page 156,
- In addition, the level of tomatine in transgenic tomatoes (190–280 mg/100 g fresh weight) was increased substantially from that of the parent (35 mg/100 g) and the standard transgenic tomato (12 mg/100 g).
Derived terms
Anagrams
This article is issued from
Wiktionary.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.