homocysteine
See also: homocystéine
English
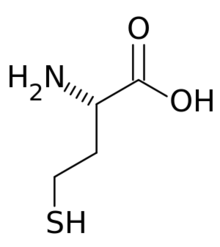
Structure diagram of homocysteine
Noun
homocysteine (countable and uncountable, plural homocysteines)
- (biochemistry) An amino acid which is monitored in the blood to estimate risk of cardiovascular disease.
- 1989, L. A. Smolin, N. A. Benevenga, Chapter 8: Methionine, Homocyst(e)ine, Cysteine—Metabolic Interrelationships, Mendel Friedman, Absorption and Utilization of Amino Acids, Volume 1, CRC Press, page 170,
- One possible explanation for the low plasma cystine in homocystinuric patients who are given sufficient dietary cystine is the high plasma concentration of the cysteine-homocysteine mixed disulfide.
- 2000, Donald W. Jacobsen, 3. Biochemistry and Metabolism, Killian Robinson (editor), Homocysteine and Vascular Disease, Kluwer Academic, page 15,
- Homocysteine, a metabolite of the methionine cycle, is a strong independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
- 2017, Himadri Panda, Handbook on Small & Medium Scale Industries (Biotechnology Products), Asia Pacific Business Press, page 224,
- The amino acids produced from L-methionine and substituted thiols were identified as the corresponding S-substituted homocysteines, e.g., 2-mercaptoethanol and cysteamine produced S-(β-hydroxyethyl) homocysteine and S-(β-aminoethyl) homocysteine, respectively.
- 1989, L. A. Smolin, N. A. Benevenga, Chapter 8: Methionine, Homocyst(e)ine, Cysteine—Metabolic Interrelationships, Mendel Friedman, Absorption and Utilization of Amino Acids, Volume 1, CRC Press, page 170,
Usage notes
Not to be confused with homocystine (a different compound whose relationship with homocysteine is analogous to that of cystine with cysteine).
Derived terms
See also
- homocystine
This article is issued from
Wiktionary.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.