chromosome
English
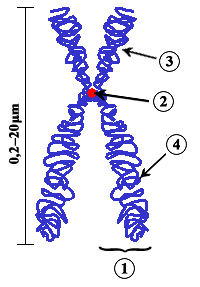
An illustration of chromosome, with its parts. (1) Chromatid. One of the two identical parts of the chromosome after S phase. (2) Centromere. The point where the two chromatids touch, and where the microtubules attach. (3) Short arm (4) Long arm.
Etymology
19th century: from German Chromosom, ultimately from Ancient Greek χρῶμα (khrôma, “colour”) + σῶμα (sôma, “body”) (because they are stained under the microscope).
Pronunciation
Noun
chromosome (plural chromosomes)
Derived terms
Translations
structure in the cell nucleus
|
|
Further reading
- chromosome in Webster’s Revised Unabridged Dictionary, G. & C. Merriam, 1913.
- chromosome in The Century Dictionary, New York, N.Y.: The Century Co., 1911.
- chromosome at OneLook Dictionary Search
French
Etymology
19th century: chromo- + -some, from German Chromosom, ultimately from Ancient Greek χρῶμα (khrôma, “colour”) + σῶμα (sôma, “body”) (because they are stained under the microscope).
Pronunciation
- IPA(key): /kʁɔ.mo.zom/
Audio (file) - Homophone: chromosomes
- Hyphenation: chro‧mo‧some
Meronyms
Holonyms
Derived terms
- chromosomique
- hétérochromosome
Further reading
- “chromosome” in le Trésor de la langue française informatisé (The Digitized Treasury of the French Language).
This article is issued from
Wiktionary.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.