Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes which alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol (opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene.[2]
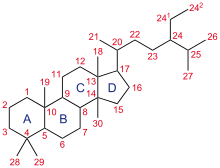
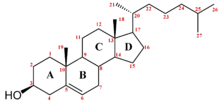
The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four "fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cholestane.[1]:1785f[3] Steroids can also be more radically modified, such as by changes to the ring structure, for example, cutting one of the rings. Cutting Ring B produces secosteroids one of which is vitamin D3.
Examples include the lipid cholesterol, the sex hormones estradiol and testosterone,[4]:10–19 and the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone.[5]

Nomenclature
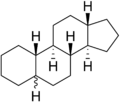
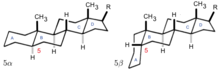
Gonane, also known as steran or cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene, the simplest steroid and the nucleus of all steroids and sterols,[6][7] is composed of seventeen carbon atoms in carbon-carbon bonds forming four fused rings in a three-dimensional shape. The three cyclohexane rings (A, B, and C in the first illustration) form the skeleton of a perhydro derivative of phenanthrene. The D ring has a cyclopentane structure. When the two methyl groups and eight carbon side chains (at C-17, as shown for cholesterol) are present, the steroid is said to have a cholestane framework. The two common 5α and 5β stereoisomeric forms of steroids exist because of differences in the side of the largely planar ring system where the hydrogen (H) atom at carbon-5 is attached, which results in a change in steroid A-ring conformation. Isomerisation at the C-21 side chain produces a parallel series of compounds, referred to as isosteroids.[8]
Examples of steroid structures are:
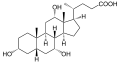 Cholic acid, a bile acid, showing the carboxylic acid and additional hydroxyl groups often present
Cholic acid, a bile acid, showing the carboxylic acid and additional hydroxyl groups often present Dexamethasone, a synthetic corticosteroid drug
Dexamethasone, a synthetic corticosteroid drug Lanosterol, the biosynthetic precursor to animal steroids. The number of carbons (30) indicates its triterpenoid classification.
Lanosterol, the biosynthetic precursor to animal steroids. The number of carbons (30) indicates its triterpenoid classification. Progesterone, a steroid hormone involved in the female menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis
Progesterone, a steroid hormone involved in the female menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis Medrogestone, a synthetic drug with effects similar to progesterone
Medrogestone, a synthetic drug with effects similar to progesterone β-Sitosterol, a plant or phytosterol, with a fully branched hydrocarbon side chain at C-17 and an hydroxyl group at C-3
β-Sitosterol, a plant or phytosterol, with a fully branched hydrocarbon side chain at C-17 and an hydroxyl group at C-3
In addition to the ring scissions (cleavages), expansions and contractions (cleavage and reclosing to a larger or smaller rings)—all variations in the carbon-carbon bond framework—steroids can also vary:
- in the bond orders within the rings,
- in the number of methyl groups attached to the ring (and, when present, on the prominent side chain at C17),
- in the functional groups attached to the rings and side chain, and
- in the configuration of groups attached to the rings and chain.[4]:2–9
For instance, sterols such as cholesterol and lanosterol have a hydroxyl group attached at position C-3, while testosterone and progesterone have a carbonyl (oxo substituent) at C-3; of these, lanosterol alone has two methyl groups at C-4 and cholesterol (with a C-5 to C-6 double bond) differs from testosterone and progesterone (which have a C-4 to C-5 double bond).
 Cholesterol, a prototypical animal sterol. This structural lipid and key steroid biosynthetic precursor.[1]:1785f |
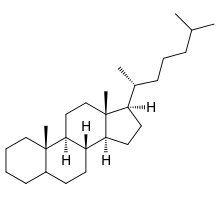 5α-cholestane, a common steroid core |
Species distribution and function
In eukaryotes, steroids are found in fungi, animals, and plants.
Fungal steroids
Fungal steroids include the ergosterols, which are involved in maintaining the integrity of the fungal cellular membrane. Various antifungal drugs, such as amphotericin B and azole antifungals, utilize this information to kill pathogenic fungi.[9] Fungi can alter their ergosterol content (e.g. through loss of function mutations in the enzymes ERG3 or ERG6, inducing depletion of ergosterol, or mutations that decrease the ergosterol content) to develop resistance to drugs that target ergosterol.[10] Ergosterol is analogous to the cholesterol found in the cellular membranes of animals (including humans), or the phytosterols found in the cellular membranes of plants.[10] All mushrooms contain large quantities of ergosterol, in the range of tens to hundreds of milligrams per 100 grams of dry weight.[10] Oxygen is necessary for the synthesis of ergosterol in fungi.[10] Ergosterol is responsible for the vitamin D content found in mushrooms; ergosterol is chemically converted into provitamin D2 by exposure to ultraviolet light.[10] Provitamin D2 spontaneously forms vitamin D2.[10] However, not all fungi utilize ergosterol in their cellular membranes; for example, the pathogenic fungal species Pneumocystis jirovecii does not, which has important clinical implications (given the mechanism of action of many antifungal drugs).[10] Using the fungus Saccharomyces cerevisiae as an example, other major steroids include ergosta‐5,7,22,24(28)‐tetraen‐3β‐ol, zymosterol, and lanosterol.[10] S. cerevisiae utilizes 5,6‐dihydroergosterol in place of ergosterol in its cell membrane.[10]
Animal steroids
Animal steroids include compounds of vertebrate and insect origin, the latter including ecdysteroids such as ecdysterone (controlling molting in some species). Vertebrate examples include the steroid hormones and cholesterol; the latter is a structural component of cell membranes which helps determine the fluidity of cell membranes and is a principal constituent of plaque (implicated in atherosclerosis). Steroid hormones include:
- Sex hormones, which influence sex differences and support reproduction. These include androgens, estrogens, and progestogens.
- Corticosteroids, including most synthetic steroid drugs, with natural product classes the glucocorticoids (which regulate many aspects of metabolism and immune function) and the mineralocorticoids (which help maintain blood volume and control renal excretion of electrolytes)
- Anabolic steroids, natural and synthetic, which interact with androgen receptors to increase muscle and bone synthesis. In popular use, the term "steroids" often refers to anabolic steroids.
Plant steroids
Plant steroids include steroidal alkaloids found in Solanaceae[11] and Melanthiaceae (specially the genus Veratrum),[12] cardiac glycosides,[13] the phytosterols and the brassinosteroids (which include several plant hormones).
Prokaryotes
In prokaryotes, biosynthetic pathways exist for the tetracyclic steroid framework (e.g. in mycobacteria)[14] – where its origin from eukaryotes is conjectured[15] – and the more-common pentacyclic triterpinoid hopanoid framework.[16]
Types
By function
The major classes of steroid hormones, with prominent members and examples of related functions, are:
- Corticosteroids:
- Glucocorticoids:
- Cortisol, a glucocorticoid whose functions include immunosuppression
- Mineralocorticoids:
- Aldosterone, a mineralocorticoid which helps regulate blood pressure through water and electrolyte balance
- Glucocorticoids:
- Sex steroids:
- Progestogens:
- Progesterone, which regulates cyclical changes in the endometrium of the uterus and maintains a pregnancy
- Androgens:
- Testosterone, which contributes to the development and maintenance of male secondary sex characteristics
- Estrogens:
- Estradiol, which contributes to the development and maintenance of female secondary sex characteristics
- Progestogens:
Additional classes of steroids include:
- Neurosteroids such as DHEA and allopregnanolone
- Aminosteroid neuromuscular blocking agents such as pancuronium bromide
As well as the following class of secosteroids (open-ring steroids):
- Vitamin D forms such as ergocalciferol, cholecalciferol, and calcitriol
By structure
Intact ring system
Steroids can be classified based on their chemical composition.[17] One example of how MeSH performs this classification is available at the Wikipedia MeSH catalog. Examples of this classification include:

| Class | Example | Number of carbon atoms |
|---|---|---|
| Cholestanes | Cholesterol | 27 |
| Cholanes | Cholic acid | 24 |
| Pregnanes | Progesterone | 21 |
| Androstanes | Testosterone | 19 |
| Estranes | Estradiol | 18 |
The gonane (steroid nucleus) is the parent 17-carbon tetracyclic hydrocarbon molecule with no alkyl sidechains.[18]
Cleaved, contracted, and expanded rings
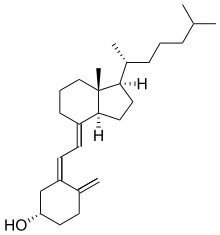
Secosteroids (Latin seco, "to cut") are a subclass of steroidal compounds resulting, biosynthetically or conceptually, from scission (cleavage) of parent steroid rings (generally one of the four). Major secosteroid subclasses are defined by the steroid carbon atoms where this scission has taken place. For instance, the prototypical secosteroid cholecalciferol, vitamin D3 (shown), is in the 9,10-secosteroid subclass and derives from the cleavage of carbon atoms C-9 and C-10 of the steroid B-ring; 5,6-secosteroids and 13,14-steroids are similar.[19]
Norsteroids (nor-, L. norma; "normal" in chemistry, indicating carbon removal)[20] and homosteroids (homo-, Greek homos; "same", indicating carbon addition) are structural subclasses of steroids formed from biosynthetic steps. The former involves enzymic ring expansion-contraction reactions, and the latter is accomplished (biomimetically) or (more frequently) through ring closures of acyclic precursors with more (or fewer) ring atoms than the parent steroid framework.[21]
Combinations of these ring alterations are known in nature. For instance, ewes who graze on corn lily ingest cyclopamine (shown) and veratramine, two of a sub-family of steroids where the C- and D-rings are contracted and expanded respectively via a biosynthetic migration of the original C-13 atom. Ingestion of these C-nor-D-homosteroids results in birth defects in lambs: cyclopia from cyclopamine and leg deformity from veratramine.[22] A further C-nor-D-homosteroid (nakiterpiosin) is excreted by Okinawan cyanobacteriosponges. e.g., Terpios hoshinota, leading to coral mortality from black coral disease.[23] Nakiterpiosin-type steroids are active against the signaling pathway involving the smoothened and hedgehog proteins, a pathway which is hyperactive in a number of cancers.
Biological significance
Steroids and their metabolites often function as signalling molecules (the most notable examples are steroid hormones), and steroids and phospholipids are components of cell membranes.[24] Steroids such as cholesterol decrease membrane fluidity.[25] Similar to lipids, steroids are highly concentrated energy stores. However, they are not typically sources of energy; in mammals, they are normally metabolized and excreted.
Steroids play critical roles in a number of disorders, including malignancies like prostate cancer, where steroid production inside and outside the tumour promotes cancer cell aggressiveness.[26]
Biosynthesis and metabolism
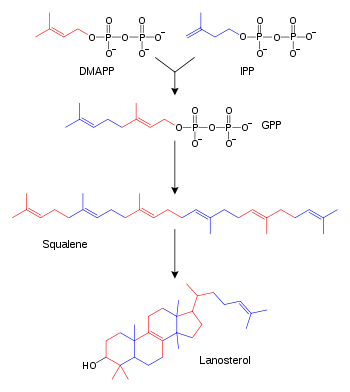
The hundreds of steroids found in animals, fungi, and plants are made from lanosterol (in animals and fungi; see examples above) or cycloartenol (in plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol derive from cyclization of the triterpenoid squalene.[2]
Steroid biosynthesis is an anabolic pathway which produces steroids from simple precursors. A unique biosynthetic pathway is followed in animals (compared to many other organisms), making the pathway a common target for antibiotics and other anti-infection drugs. Steroid metabolism in humans is also the target of cholesterol-lowering drugs, such as statins.
In humans and other animals the biosynthesis of steroids follows the mevalonate pathway, which uses acetyl-CoA as building blocks for dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) and isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP).[27] In subsequent steps DMAPP and IPP join to form geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP), which synthesizes the steroid lanosterol. Modifications of lanosterol into other steroids are classified as steroidogenesis transformations.[28]
Mevalonate pathway
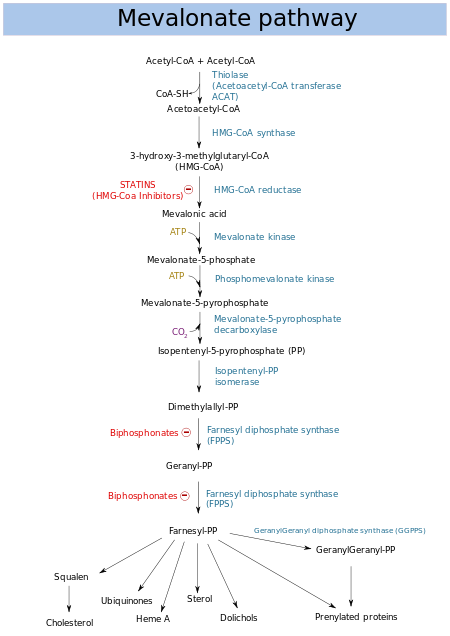
The mevalonate pathway (also called HMG-CoA reductase pathway) begins with acetyl-CoA and ends with dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) and isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP).
DMAPP and IPP donate isoprene units, which are assembled and modified to form terpenes and isoprenoids[29] (a large class of lipids, which include the carotenoids and form the largest class of plant natural products.[30] Here, the isoprene units are joined to make squalene and folded into a set of rings to make lanosterol.[31] Lanosterol can then be converted into other steroids, such as cholesterol and ergosterol.[31][32]
Two classes of drugs target the mevalonate pathway: statins (like rosuvastatin), which are used to reduce elevated cholesterol levels,[33] and bisphosphonates (like zoledronate), which are used to treat a number of bone-degenerative diseases.[34]
Steroidogenesis
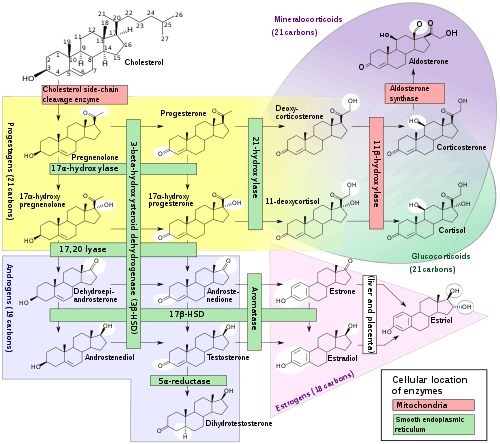
Steroidogenesis is the biological process by which steroids are generated from cholesterol and changed into other steroids.[36] The pathways of steroidogenesis differ among species. The major classes of steroid hormones, as noted above (with their prominent members and functions), are the Progestogen, Corticosteroids (corticoids), Androgens, and Estrogens.[37] Human steroidogenesis of these classes occurs in a number of locations:
- Progestogens are the precursors of all other human steroids, and all human tissues which produce steroids must first convert cholesterol to pregnenolone. This conversion is the rate-limiting step of steroid synthesis, which occurs inside the mitochondrion of the respective tissue.[38][37]
- Cortisol, corticosterone, aldosterone, and testosterone are produced in the adrenal cortex.[37]
- Estradiol, estrone and progesterone are made primarily in the ovary, estriol in placenta during pregnancy, and testosterone primarily in the testes (some testosterone is also produced in the adrenal cortex).[37]
- Estradiol is converted from testosterone directly (in males), or via the primary pathway DHEA - androstenedione - estrone and secondarily via testosterone (in females).[37]
- Stromal cells have been shown to produce steroids in response to signaling produced by androgen-starved prostate cancer cells.[39]
- Some neurons and glia in the central nervous system (CNS) express the enzymes required for the local synthesis of pregnenolone, progesterone, DHEA and DHEAS, de novo or from peripheral sources.[37]
Alternative pathways
In plants and bacteria, the non-mevalonate pathway uses pyruvate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate as substrates.[29][40]
During diseases pathways otherwise not significant in healthy humans can become utilized. For example, in one form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia a deficiency in the 21-hydroxylase enzymatic pathway leads to an excess of 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP) – this pathological excess of 17-OHP in turn may be converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT, a potent androgen) through among others 17,20 Lyase (a member of the cytochrome P450 family of enzymes), 5α-Reductase and 3α-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.[41]
Catabolism and excretion
Steroids are primarily oxidized by cytochrome P450 oxidase enzymes, such as CYP3A4. These reactions introduce oxygen into the steroid ring, allowing the cholesterol to be broken up by other enzymes into bile acids.[42] These acids can then be eliminated by secretion from the liver in bile.[43] The expression of the oxidase gene can be upregulated by the steroid sensor PXR when there is a high blood concentration of steroids.[44] Steroid hormones, lacking the side chain of cholesterol and bile acids, are typically hydroxylated at various ring positions or oxidized at the 17 position, conjugated with sulfate or glucuronic acid and excreted in the urine.[45]
Isolation, structure determination, and methods of analysis
Steroid isolation, depending on context, is the isolation of chemical matter required for chemical structure elucidation, derivitzation or degradation chemistry, biological testing, and other research needs (generally milligrams to grams, but often more[46] or the isolation of "analytical quantities" of the substance of interest (where the focus is on identifying and quantifying the substance (for example, in biological tissue or fluid). The amount isolated depends on the analytical method, but is generally less than one microgram.[47] The methods of isolation to achieve the two scales of product are distinct, but include extraction, precipitation, adsorption, chromatography, and crystallization. In both cases, the isolated substance is purified to chemical homogeneity; combined separation and analytical methods, such as LC-MS, are chosen to be "orthogonal"—achieving their separations based on distinct modes of interaction between substance and isolating matrix—to detect a single species in the pure sample. Structure determination refers to the methods to determine the chemical structure of an isolated pure steroid, using an evolving array of chemical and physical methods which have included NMR and small-molecule crystallography.[4]:10–19 Methods of analysis overlap both of the above areas, emphasizing analytical methods to determining if a steroid is present in a mixture and determining its quantity.[47]
Chemical synthesis
Microbial catabolism of phytosterol side chains yields C-19 steroids, C-22 steroids, and 17-ketosteroids (i.e. precursors to adrenocortical hormones and contraceptives).[48][49][50] The addition and modification of functional groups is key when producing the wide variety of medications available within this chemical classification. These modifications are performed using conventional organic synthesis and/or biotransformation techniques.[51][52]
Precursors
Semisynthesis
The semisynthesis of steroids often begins from precursors such as cholesterol,[50] phytosterols,[49] or sapogenins.[53] The efforts of Syntex, a company involved in the Mexican barbasco trade, used Dioscorea mexicana to produce the sapogenin diosgenin in the early days of the synthetic steroid pharmaceutical industry.[46]
Research awards
A number of Nobel Prizes have been awarded for steroid research, including:
- 1927 (Chemistry) Heinrich Otto Wieland — Constitution of bile acids and sterols and their connection to vitamins[54]
- 1928 (Chemistry) Adolf Otto Reinhold Windaus — Constitution of sterols and their connection to vitamins[55]
- 1939 (Chemistry) Adolf Butenandt and Leopold Ruzicka — Isolation and structural studies of steroid sex hormones, and related studies on higher terpenes[56]
- 1950 (Physiology or Medicine) Edward Calvin Kendall, Tadeus Reichstein, and Philip Hench — Structure and biological effects of adrenal hormones[57]
- 1965 (Chemistry) Robert Burns Woodward — In part, for the synthesis of cholesterol, cortisone, and lanosterol[58]
- 1969 (Chemistry) Derek Barton and Odd Hassel — Development of the concept of conformation in chemistry, emphasizing the steroid nucleus[59]
- 1975 (Chemistry) Vladimir Prelog — In part, for developing methods to determine the stereochemical course of cholesterol biosynthesis from mevalonic acid via squalene[60]
See also
- Adrenal gland
- Batrachotoxin
- List of steroid abbreviations
- List of steroids
- Membrane steroid receptor
- Pheromone
- Reverse cholesterol transport
- Steroidogenesis inhibitor
- Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein
- Steroidogenic enzyme
References
- Moss GP, the Working Party of the IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature (1989). "Nomenclature of steroids, recommendations 1989" (PDF). Pure Appl. Chem. 61 (10): 1783–1822. doi:10.1351/pac198961101783. Also available with the same authors at Carlson P, Bull JR, Engel K, Fried J, Kircher HW, Loaning KL, Moss GP, Popják G, Uskokovic MR (Dec 1989). "IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature (JCBN). The nomenclature of steroids. Recommendations 1989". European Journal of Biochemistry / FEBS. 186 (3): 429–58. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15228.x. PMID 2606099.; Also available online at "The Nomenclature of Steroids". London, GBR: Queen Mary University of London. p. 3S–1.4. Retrieved 10 May 2014.
- "Lanosterol biosynthesis". Recommendations on Biochemical & Organic Nomenclature, Symbols & Terminology. International Union Of Biochemistry And Molecular Biology. Archived from the original on 2011-03-08. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- Also available in print at Hill RA, Makin HL, Kirk DN, Murphy GM (1991). Dictionary of Steroids. London, GBR: Chapman and Hall. pp. xxx–lix. ISBN 978-0412270604. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Lednicer D (2011). Steroid Chemistry at a Glance. Hoboken: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-66084-3.
- Rhen T, Cidlowski JA (Oct 2005). "Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids--new mechanisms for old drugs" (PDF). The New England Journal of Medicine. 353 (16): 1711–23. doi:10.1056/NEJMra050541. PMID 16236742.
- Victor A. Rogozkin (14 June 1991). Metabolism of Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids. CRC Press. pp. 1–. ISBN 978-0-8493-6415-0.
The steroid structural base is a steran nucleus, a polycyclic C17 steran skeleton consisting of three condensed cyclohexane rings in nonlinear or phenanthrene junction (A, B, and C), and a cyclopentane ring (D).1,2
- Klaus Urich (16 September 1994). Comparative Animal Biochemistry. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 624–. ISBN 978-3-540-57420-0.
- Greep 2013.
- Bhetariya PJ, Sharma N, Singh P, Tripathi P, Upadhyay SK, Gautam P (2017-03-21). "Human Fungal Pathogens and Drug Resistance Against Azole Drugs". In Arora C, Sajid A, Kalia V (eds.). Drug Resistance in Bacteria, Fungi, Malaria, and Cancer. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-48683-3.
- Kavanagh, Kevin, ed. (8 September 2017). Fungi: Biology and Applications. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN 9781119374312.
- Wink M (Sep 2003). "Evolution of secondary metabolites from an ecological and molecular phylogenetic perspective". Phytochemistry. 64 (1): 3–19. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(03)00300-5. PMID 12946402.
- Wink, Michael; van Wyk, Ben-Erik (2008). Mind-altering and poisonous plants of the world. Portland (Oregon USA) and Salusbury (London England): Timber press inc. pp. 252, 253 and 254. ISBN 978-0-88192-952-2.
- Wink, Michael; van Wyk, Ben-Erik (2008). Mind-altering and poisonous plants of the world. Portland (Oregon USA) and Salusbury (London England): Timber press inc. pp. 324, 325 and 326. ISBN 978-0-88192-952-2.
- Bode HB, Zeggel B, Silakowski B, Wenzel SC, Reichenbach H, Müller R (Jan 2003). "Steroid biosynthesis in prokaryotes: identification of myxobacterial steroids and cloning of the first bacterial 2,3(S)-oxidosqualene cyclase from the myxobacterium Stigmatella aurantiaca". Molecular Microbiology. 47 (2): 471–81. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03309.x. PMID 12519197.
- Desmond E, Gribaldo S (2009). "Phylogenomics of sterol synthesis: insights into the origin, evolution, and diversity of a key eukaryotic feature". Genome Biology and Evolution. 1: 364–81. doi:10.1093/gbe/evp036. PMC 2817430. PMID 20333205.
- Siedenburg G, Jendrossek D (Jun 2011). "Squalene-hopene cyclases". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 77 (12): 3905–15. doi:10.1128/AEM.00300-11. PMC 3131620. PMID 21531832.
- Zorea, Aharon (2014). Steroids (Health and Medical Issues Today). Westport, CT: Greenwood Press. pp. 10–12. ISBN 978-1440802997.
- Edgren RA, Stanczyk FZ (Dec 1999). "Nomenclature of the gonane progestins". Contraception. 60 (6): 313. doi:10.1016/S0010-7824(99)00101-8. PMID 10715364.
- Hanson JR (Jun 2010). "Steroids: partial synthesis in medicinal chemistry". Natural Product Reports. 27 (6): 887–99. doi:10.1039/c001262a. PMID 20424788.
- "IUPAC Recommendations: Skeletal Modification in Revised Section F: Natural Products and Related Compounds (IUPAC Recommendations 1999)". International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). 1999.
- Wolfing J (2007). "Recent developments in the isolation and synthesis of D-homosteroids and related compounds". Arkivoc: 210–230.
- Gao G, Chen C (2012). "Nakiterpiosin". In Corey E, Li JJ (eds.). Total synthesis of natural products: at the frontiers of organic chemistry. Berlin: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-34065-9. ISBN 978-3-642-34064-2.
- Uemura E, Kita M, Arimoto H, Kitamura M (2009). "Recent aspects of chemical ecology: Natural toxins, coral communities, and symbiotic relationships". Pure Appl. Chem. 81 (6): 1093–1111. doi:10.1351/PAC-CON-08-08-12.
- Silverthorn, Dee Unglaub, 1948- (2016). Human physiology : an integrated approach. Johnson, Bruce R., Ober, William C., Ober, Claire E., Silverthorn, Andrew C. (Seventh ed.). [San Francisco]. ISBN 9780321981226. OCLC 890107246.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Sadava D, Hillis DM, Heller HC, Berenbaum MR (2011). Life: The Science of Biology (9th ed.). San Francisco: Freeman. pp. 105–114. ISBN 978-1-4292-4646-0.
- Lubik AA, Nouri M, Truong S, Ghaffari M, Adomat HH, Corey E, Cox ME, Li N, Guns ES, Yenki P, Pham S, Buttyan R (2016). "Paracrine Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Contributes Significantly to Acquired Steroidogenesis in the Prostate Tumor Microenvironment". Int. J. Cancer. 140 (2): 358–369. doi:10.1002/ijc.30450. PMID 27672740.
- Grochowski LL, Xu H, White RH (May 2006). "Methanocaldococcus jannaschii uses a modified mevalonate pathway for biosynthesis of isopentenyl diphosphate". Journal of Bacteriology. 188 (9): 3192–8. doi:10.1128/JB.188.9.3192-3198.2006. PMC 1447442. PMID 16621811.
- Chatuphonprasert, Waranya; Jarukamjorn, Kanokwan; Ellinger, Isabella (2018-09-12). "Physiology and Pathophysiology of Steroid Biosynthesis, Transport and Metabolism in the Human Placenta". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 9: 1027. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.01027. ISSN 1663-9812. PMC 6144938. PMID 30258364.
- Kuzuyama T, Seto H (Apr 2003). "Diversity of the biosynthesis of the isoprene units". Natural Product Reports. 20 (2): 171–83. doi:10.1039/b109860h. PMID 12735695.
- Dubey VS, Bhalla R, Luthra R (Sep 2003). "An overview of the non-mevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis in plants" (PDF). Journal of Biosciences. 28 (5): 637–46. doi:10.1007/BF02703339. PMID 14517367. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-04-15.
- Schroepfer GJ (1981). "Sterol biosynthesis". Annual Review of Biochemistry. 50: 585–621. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003101. PMID 7023367.
- Lees ND, Skaggs B, Kirsch DR, Bard M (Mar 1995). "Cloning of the late genes in the ergosterol biosynthetic pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae--a review". Lipids. 30 (3): 221–6. doi:10.1007/BF02537824. PMID 7791529.
- Kones R (December 2010). "Rosuvastatin, inflammation, C-reactive protein, JUPITER, and primary prevention of cardiovascular disease--a perspective". Drug Design, Development and Therapy. 4: 383–413. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S10812. PMC 3023269. PMID 21267417.
- Roelofs AJ, Thompson K, Gordon S, Rogers MJ (October 2006). "Molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates: current status". Clinical Cancer Research. 12 (20 Pt 2): 6222s–6230s. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0843. PMID 17062705.
- Häggström M, Richfield D (2014). "Diagram of the pathways of human steroidogenesis". WikiJournal of Medicine. 1 (1). doi:10.15347/wjm/2014.005. ISSN 2002-4436.
- Hanukoglu I (Dec 1992). "Steroidogenic enzymes: structure, function, and role in regulation of steroid hormone biosynthesis". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 43 (8): 779–804. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(92)90307-5. PMID 22217824.
- Miller WL, Auchus RJ (February 2011). "The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders". Endocrine Reviews. 32 (1): 81–151. doi:10.1210/er.2010-0013. PMC 3365799. PMID 21051590.
- Rossier MF (Aug 2006). "T channels and steroid biosynthesis: in search of a link with mitochondria". Cell Calcium. 40 (2): 155–64. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2006.04.020. PMID 16759697.
- Lubik AA, Nouri M, Truong S, Ghaffari M, Adomat HH, Corey E, Cox ME, Li N, Guns ES, Yenki P, Pham S, Buttyan R (2016). "Paracrine Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Contributes Significantly to Acquired Steroidogenesis in the Prostate Tumor Microenvironment". International Journal of Cancer. 140 (2): 358–369. doi:10.1002/ijc.30450. PMID 27672740.
- Lichtenthaler HK (Jun 1999). "The 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants". Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology. 50: 47–65. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.47. PMID 15012203.
- Witchel SF, Azziz R (2010). "Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia". International Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology. 2010: 1–11. doi:10.1155/2010/625105. PMC 2910408. PMID 20671993.
- Pikuleva IA (Dec 2006). "Cytochrome P450s and cholesterol homeostasis". Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 112 (3): 761–73. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.05.014. PMID 16872679.
- Zollner G, Marschall HU, Wagner M, Trauner M (2006). "Role of nuclear receptors in the adaptive response to bile acids and cholestasis: pathogenetic and therapeutic considerations". Molecular Pharmaceutics. 3 (3): 231–51. doi:10.1021/mp060010s. PMID 16749856.
- Kliewer SA, Goodwin B, Willson TM (Oct 2002). "The nuclear pregnane X receptor: a key regulator of xenobiotic metabolism". Endocrine Reviews. 23 (5): 687–702. doi:10.1210/er.2001-0038. PMID 12372848.
- Steimer T. "Steroid Hormone Metabolism". WHO Collaborating Centre in Education and Research in Human Reproduction. Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
- "Russell Marker Creation of the Mexican Steroid Hormone Industry". International Historic Chemical Landmark. American Chemical Society.
- Makin HL, Honor JW, Shackleton CH, Griffiths WJ (2010). "General methods for the extraction, purification, and measurement of steroids by chromatography and mass spectrometry". In Makin HL, Gower DB (eds.). Steroid analysis. Dordrecht; New York: Springer. pp. 163–282. ISBN 978-1-4020-9774-4.
- Conner AH, Nagaoka M, Rowe JW, Perlman D (Aug 1976). "Microbial conversion of tall oil sterols to C19 steroids" (PDF). Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 32 (2): 310–1. PMC 170056. PMID 987752.
- Hesselink PG, Vliet Sv, Vries Hd, Witholt B (1989). "Optimization of steroid side chain cleavage by Mycobacterium sp. in the presence of cyclodextrins". Enzyme and Microbial Technology. 11 (7): 398–404. doi:10.1016/0141-0229(89)90133-6.
- Sandow J, Scheiffele E, Haring M, Neef G, Prezewowsky K, Stache U (2000). Hormones. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_089. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- Leigh HM, Meister PD, Weintraub A, Reineke LM, Eppstein SH, Murray HC, Peterson DH (1952). "Microbiological Transformations of Steroids.1 I. Introduction of Oxygen at Carbon-11 of Progesterone". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 73 (23): 5933–5936. doi:10.1021/ja01143a033.
- Capek M, Oldrich H, Alois C (1966). Microbial Transformations of Steroids. Prague: Academia Publishing House of Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences. doi:10.1007/978-94-011-7603-3. ISBN 9789401176057.
- Marker RE, Rohrmann E (1939). "Sterols. LXXXI. Conversion of Sarsasa-Pogenin to Pregnanedial--3(α),20(α)". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 61 (12): 3592–3593. doi:10.1021/ja01267a513.
- "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1927". The Nobel Foundation.
- "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1928". The Nobel Foundation.
- "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1939". The Nobel Foundation.
- "The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1950". The Nobel Foundation.
- "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1965". The Nobel Foundation.
- "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1969". The Nobel Foundation.
- "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1975". The Nobel Foundation.
Bibliography
- Russel CA (2005). "Organic Chemistry: Natural products, Steroids". In Russell CA, Roberts GK (eds.). Chemical History: Reviews of the Recent Literature. Cambridge: RSC Publ. ISBN 978-0-85404-464-1.
- "Russell Marker Creation of the Mexican Steroid Hormone Industry - Landmark -". American Chemical Society. 1999.
- Lednicer D (2011). Steroid Chemistry at a Glance. Hoboken: Wiley. doi:10.1002/9780470973639. ISBN 978-0-470-66085-0. A concise history of the study of steroids.
- Yoder RA, Johnston JN (Dec 2005). "A case study in biomimetic total synthesis: polyolefin carbocyclizations to terpenes and steroids". Chemical Reviews. 105 (12): 4730–56. doi:10.1021/cr040623l. PMC 2575671. PMID 16351060. A review of the history of steroid synthesis, especially biomimetic.
- Han TS, Walker BR, Arlt W, Ross RJ (Feb 2014). "Treatment and health outcomes in adults with congenital adrenal hyperplasia". Nature Reviews. Endocrinology. 10 (2): 115–24. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2013.239. PMID 24342885. Adrenal steroidogenesis pathway.
- Greep, Roy O., ed. (22 October 2013). "Cortoic acids". Recent Progress in Hormone Research: Proceedings of the 1979 Laurentian Hormone Conference. Elsevier Science. pp. 345–391. ISBN 978-1-4832-1956-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bowen RA (October 20, 2001). "Steroidogenesis". Pathophysiology of the Endocrine System. Colorado State University. Archived from the original on February 28, 2009.
.svg.png)