Sirenia
The Sirenia, commonly referred to as sea-cows or sirenians, are an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit swamps, rivers, estuaries, marine wetlands, and coastal marine waters. The Sirenia currently comprise the families Dugongidae (the dugong and, historically, Steller's sea cow) and Trichechidae (manatees) with a total of four species. The Protosirenidae (Eocene sirenians) and Prorastomidae (terrestrial sirenians) families are extinct. Sirenians are classified in the clade Paenungulata, alongside the elephants and the hyraxes, and evolved in the Eocene 50 million years ago. The Dugongidae diverged from the Trichechidae in the late Eocene or early Oligocene.
| Sirenia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| West Indian manatees (Trichechus manatus) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Superorder: | Afrotheria |
| Clade: | Paenungulata |
| Clade: | Tethytheria |
| Order: | Sirenia Illiger, 1811 |
| Families | |
|
Dugongidae | |
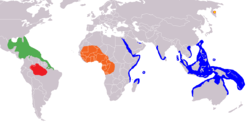 | |
| West Indian in green, Amazonian in red, African in orange, dugong in blue, Steller's sea cow circled (yellow) | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
List of synonyms
| |
Sirenians grow to between 2.5 and 4 metres (8.2 and 13.1 feet) in length and 1,500 kilograms (3,300 pounds) in weight. The now extinct Steller's sea cow was the largest sirenian to have lived, and could reach lengths of 8 metres (26 feet) and weights of 8 to 10 tonnes (8.8 to 11.0 short tons). Sirenians have a large, fusiform body to reduce drag through the water. They have heavy bones that act as ballast to counteract the buoyancy of their blubber. They have a thin layer of blubber and consequently are sensitive to temperature fluctuations, which cause migrations when water temperatures dip too low. Sirenians are slow-moving, typically coasting at 8 kilometres per hour (5.0 miles per hour), but they can reach 24 kilometres per hour (15 miles per hour) in short bursts. They use their strong lips to pull out seagrasses, consuming 10–15% of their body weight per day.
While breathing, they hold just their nostrils above the surface, sometimes standing on their tails to do so. Sirenians typically inhabit warm, shallow, coastal waters, or rivers. They are mainly herbivorous, but have been known to consume animals such as birds and jellyfish. Males typically mate with more than one female (polygyny), and may participate in lek mating. Sirenians are K-selected, and display parental care.

The meat, oil, bones, and skins are valuable items sold in markets. Mortality is often caused by direct hunting by humans or other human-induced causes, such as habitat destruction, entanglement in fishing gear, and watercraft collisions. Steller's sea cow went extinct due to overhunting in 1768.
Taxonomy
Etymology
Sirenia, commonly sirenians, are also referred to by the common name sirens, deriving from the sirens of Greek mythology.[2][3] This comes from a legend about their discovery, involving lonely sailors mistaking them for mermaids.[4] Seekoei (sea cow) is also the name for a hippopotamus in Afrikaans.[5]
Classification
Sirenians are classified within the cohort Afrotheria in the clade Paenungulata, alongside Proboscidea (elephants), Hyracoidea (hyraxes), Embrithopoda, Desmostylia, and Afroinsectiphilia.[6][7][8][9] This clade was first established by George Gaylord Simpson in 1945 based on anatomical evidence, such as testicondy and similar fetal development. The Paenungulata, along with the Afrotheria, are one of the most well-supported mammalian clades in molecular phylogeny.[10] Sirenia, Proboscidae, and Desmotylia are grouped together in the clade Tethytheria. Based on morphological similarities, Tethytheria, Perissodactyla, and Hyracoidea were considered to be grouped together as the Altungulata, but this has been invalidated by molecular data.[7]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A cladogram of the Sirenia within Afrotheria based on molecular evidence[6] |
Sirenia Families († = Extinct) |
|---|
|
Family Dugongidae[11] — View by clicking [show] —
Family Trichechidae[14] — View by clicking [show] —
†Family Protosirenidae[15] — View by clicking [show] —
†Family Prorastomidae[16] — View by clicking [show] —
|
| Extant Order Sirenia – two genera, four species | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Genus Trichechus (manatees) Linnaeus, 1758 – three species | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common name | Scientific name | Status | Distribution | Picture | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| West Indian manatee | T. manatus Linnaeus, 1758 List of synonyms[1]
|
VU IUCN | 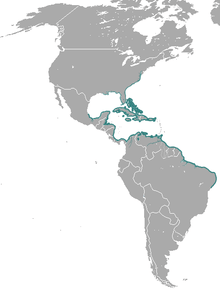 |
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| African manatee | T. senegalensis Link, 1795 |
VU IUCN | 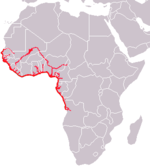 |
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amazonian manatee | T. inunguis Natterer, 1883 | VU IUCN |  |
.jpg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Genus Dugong de Lacépède, 1799 – one species | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common name | Scientific name | Status | Distribution | Picture | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dugong | D. dugon Müller, 1776 List of synonyms[1]
|
VU IUCN |  |
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Evolution
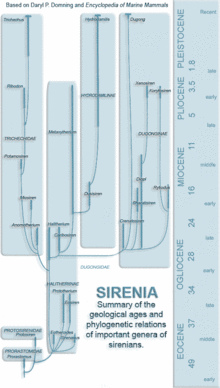
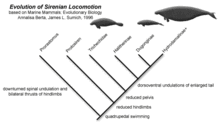
The evolution of sirenians is characterized by the appearance of several traits, which are found in all sirenians (monophyly). The nostrils are large and retracted, the upper-jaw bone contacts the frontal bone, the sagittal crest is missing, the mastoid fills the supratemporal fenestra (an opening on the top of the skull), a drop-like ectotympanic (a bony ring that holds the ear drum), and pachyosteosclerotic (dense and bulky) bones.[7]
Sirenians first appeared in the fossil record in the Early Eocene and significantly diversified throughout the epoch. They inhabited rivers, estuaries, and nearshore marine waters.[17] Sirenians, unlike other marine mammals such as cetaceans,[18] lived in the New World. One of the earliest aquatic sirenians discovered is Prorastomus which dates back to 40 million years ago, and the first known sirenian, the quadruped Pezosiren, lived 50 million years ago.[17] An ancient sirenian fossil of a petrosal bone was found in Tunisia, dating back to approximately the same time as Prorastomus.[19] This is the oldest sirenian fossil to be found in Africa and supports molecular data suggesting that sirenians may have originated in Africa.[19] Prorastomidae and Protosirenidae, the earliest sirenian families, consisted of pig-like amphibious creatures who died out at the end of the Eocene. When the Dugongidae appeared at this time, sirenians had evolved the characteristics of modern variety, including an aquatic streamlined body with flipper-like front legs with no hind limbs, and a powerful tail with horizontal caudal fins which uses an up-and-down motion to move them through the water.[20]
The last of the sirenian families to appear, Trichechidae, apparently arose from early dugongids in the late Eocene or early Oligocene. It is a monophyletic taxon. In 1994, the family was expanded to include not only the subfamily Trichechinae (Potamosiren, Ribodon, and Trichechus),[21] but also Miosireninae (Anomotherium and Miosiren). The African manatee and the West Indian manatee are more closely related to each other than to the Amazonian manatee.[7]
Dugongidae comprises the subfamilies Dugonginae and Hydrodamalinae (which are both monophyletic) and the paraphyletic Halitheriinae. The tusks of modern-day dugongs may have originally been used for digging, but they are now used for social interaction. The genus Dugong probably originated in the Indo-Pacific area.[7]
Description
Adaptations


The tail fluke of a dugong is notched and similar to those of dolphins, whereas the tail fluke of manatees is paddle-shaped.[7] The fluke is raised up and down in long strokes to move the animal forward, or twisted to turn. The forelimbs are paddle-like flippers which aid in turning and slowing.[20][22] Unlike manatees, the dugong lacks nails on its flippers, which are only 15% of a dugong's body length.[23] Manatees generally glide at speeds of 8 kilometres per hour (5 mph), but can reach speeds of 24 kilometres per hour (15 mph) in short bursts.[24] The body is fusiform to reduce drag in the water. Like cetaceans, the hind limbs are internal and vestigial. The snout is angled downwards to aid in bottom-feeding.[25] Sirenians typically make two- to three-minute dives,[26] but manatees can hold their breath for up to 15 minutes while resting[24] and dugongs up to six minutes. They may stand on their tail to hold their head above water.[27]

.jpg)
Much like elephants, manatees are polyphyodonts, and continuously replace their teeth from the back of the jaw. Adults lack incisors, canines, and premolars, and instead have 8 to 10 cheek teeth in their mouth. Manatees have an infinite supply of teeth moving in from the back and shedding in the front, which are continuously formed by a dental capsule behind the tooth-row. These teeth are constantly worn down by the abrasive vascular plants they forage, particularly aquatic grasses. Unlike in manatees, the dugong's teeth do not continually grow back via horizontal tooth replacement.[28] The dugong has two tusks which emerge in males during puberty, and sometime later in life for females after reaching the base of the premaxilla.[23] The number of growth layer groups in a tusk indicates the age of a dugong.[29]
Sirenians exhibit pachyostosis, a condition in which the ribs and other long bones are solid and contain little or no bone marrow. They have among the densest bones in the animal kingdom, which may be used as ballast, counteracting the buoyancy effect of their blubber and help keep sirenians suspended slightly below the water's surface.[30] Manatees do not possess blubber, per se, but rather have thick skin, and, consequently, are sensitive to temperature changes. Likewise, they often migrate to warmer waters whenever the water temperature dips below 20 °C (68 °F). The lungs of sirenians are unlobed;[31] they, along with the diaphragm, extend the entire length of the vertebral column, which help them control their buoyancy and reduce tipping in the water.[32][33]
Extant sirenians grow to between 2.5 and 4 metres (8.2 and 13.1 ft) in length and can weigh up to 1,500 kilograms (3,300 lb). Steller's sea cow was the largest sirenian to have lived, and could reach lengths of 9 metres (30 ft),[31] and could weigh in at 8 to 10 tonnes (8.8 to 11.0 short tons).[34] A dugong's brain weighs a maximum of 300 grams (11 ounces), about 0.1% of the animal's body weight.[23] The body of sirenians is sparsely covered in short hair (vibrissae), except for on the muzzle, which may allow for tactile interpretation of their environment.[35] Manatees are the only creatures to exhibit corneal avascularity, and lack blood vessels in the cornea, which prevents optical clarity and vision. This may be the result of irritations from or protection against their hypotonic freshwater environment.[36]
Diet

Sirenians are referred to as "sea cows" because their diet consists mainly of seagrass. Dugongs sift through the seafloor in search of seagrasses. Dugongs use their sense of smell to find the seagrass because their eyesight is poor making it difficult to use their sense of sight to find food.[37] They ingest the whole plant, including the roots,[38] although they will feed on just the leaves if this is not possible.[29] Manatees, in particular the West Indian manatee, are known to consume over 60 different freshwater and saltwater plants, such as shoalweed, water lettuce, muskgrass, manatee grass, and turtle grass. Using their divided upper lip, an adult manatee will commonly eat up to 10–15% of their body weight, or 50 kilograms (110 lb), per day, which requires the manatee to graze for several hours per day.[39] However, 10% of the diet of the African manatee is fish and mollusks.[40] Manatees have been known to eat small amounts of fish from nets.[41] As opposed to bulk feeding, dugongs target high-nitrogen grasses to maximize nutrient intake, and, although almost completely herbivorous, dugongs will occasionally eat invertebrates such as jellyfish, sea squirts, and shellfish. Some populations of dugongs, such as the one in Moreton Bay, Australia, are omnivorous, feeding on invertebrates such as polychaetes[38] or marine algae when their supply of seagrasses decrease. In other dugong populations in western and eastern Australia, there is evidence that dugongs actively seek out large invertebrates.[29] Populations of Amazonian manatees become restricted to lakes during the July–August dry season when water levels begin to fall, and are thought to fast during this period. Their large fat reserves and low metabolic rates—only 36% of the usual placental mammal metabolic rate—allow them to survive for up to seven months with little or no food.[42]
Reproduction
Despite being mostly solitary, sirenians congregate in groups while females are in estrus. These groups usually include one female with multiple males. Sirenians are K-selectors, so, despite the longevity, females give birth only a few times during their life and invest considerable parental care in their young. Dugongs generally gather in groups of less than a dozen individuals for one to two days. Since they congregate in turbid waters, little is known about their reproductive behavior. The males are often seen with scars, and the tusks on dugongs grow in first for males, suggesting they are important in lekking. They have also been known to lunge at each other. The age when a female first gives birth is disputed, ranging anywhere from six to seventeen years.[23] The time between births is unclear, with estimates ranging from 2 to 7 years.[43][29] Though, in Sarasota, Florida 113 manatee were observed of known gender. Of these 113, there were 53 females that produced at least 55 calves during a five-year period of observation.[44]
Manatees can reach sexual maturity as early as two to five years of age.[44] Manatee gestation length is around one year, and then they lactate for one to two years. West Indian manatees and African manatees can breed year-round, and a female will mate with multiple male partners.[45] Amazonian manatees have a breeding season, usually mating when the river levels begin to rise, which varies from place to place.[46]
Manatees in Captivity
Manatees, in comparison to other marine species, tend to do well in a captive environment. In 1875, there started to be success in keeping manatees thriving in captivity.[47] It is not only about keeping them alive but making sure they get everything they need without having to be in their natural environment. It is extremely difficult to replicate a natural environment in an enclosed setting but places that work in conservation, rescue, attraction, and rehabilitation do their best to get as close as they can to a natural environment.[48] It is not only difficult for these places to make an enclosure like their natural environment but also provide the food they would have there. Manatees in a captive environment, due to what they eat and the quantities of which they eat, cannot consume the diet they would in a natural environment. The amount of food and what they specifically eat is not cost effective for places to provide for them.
Manatees that are in captivity for rehabilitate purposes or simply can not survive in the wild due to injury or illness benefit from being in these programs. When captivity is not beneficial is when healthy manatees are being pulled out of their natural environments to be put on display for human enjoyment. In some cases, the entertainment industry does not provide the best care for them like a conservation rescue would. Their main priority is the amount of money they make from people wanting to see the manatees.[49] Manatee population numbers are lower than they should be, so it is not helping the conservation efforts when manatees are being taken out of nature for monetary reasons. Rehabilitation places for manatees are beneficial for the conservation of manatees despite them being in captivity. The rescue injured or sick manatees and bring them back to health. During this time, they collect as much information they can before releasing them back into the wild. They use this information to learn about manatees in the wild and better protect them injuries or illness.
Threats and conservation

The three extant manatee species (family Trichechidae) and the dugong (family Dugongidae) are rated as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List of endangered species. All four are vulnerable to extinction from habitat loss and other negative impacts related to human population growth and coastal development.[40][50][51][52] Steller's sea cow, extinct since 1786, was hunted to extinction by humans.[53]
The meat, oil, bones, and skin of manatees are valuable items. In some countries, such as Nigeria and Cameroon, African manatees are sold to zoos, aquariums, and online as pets, sometimes being shipped internationally. Though illegal, lack of law enforcement in these areas induce poaching. Some residents of West African countries, such as Mali and Chad, depend on the oil of the African manatee to cure ailments such as ear infections, rheumatism, and skin conditions.[40] Hunting is the largest source of mortality in Amazonian manatees, and there are no management plans except for in Colombia.[54] Amazonian manatees, especially calves, are sometimes illegally sold as pets, but there are several institutions that care for and rescue these orphans, with the possibility of their releasing into the wild.[50] The body parts of dugongs are used as medicinal remedies across the Indian Ocean.[29]
Manatees have also faced threats in Cuba, an area that is not always known for its manatee population. Manatees in Cuba have faced poaching, entanglement and pollution. The area has some of the most extensive and best manatee habitat in the Caribbean, but the population has been unable to thrive there for numerous reasons.[55] Existing information about manatees in Cuba is limited and scarce, this makes it difficult to spread awareness which therefore enhances the situation of illegal poaching and entanglement within fishing nets in a majority of the coastal communities.[56] Poaching of the manatees has been a significant issue since the 1970s when it was initially reported that the hunting was taking its toll on the manatee population in Cuba.[55] In 1975 it was recorded that the manatees' status in Cuba was rare and declining at an alarming rate due to pollution and hunting. In 1996 manatees were placed under protection through the Fishery Decree law 164. This law provided penalties against those that manipulated, harm, or injured manatees. However, it was seen that the hunting of manatees in Cuba in the 1990s may have been the result of economic hardships in this country and the manatees were an alternative source of protein.[55] Although there have been efforts made to protect the population of manatees in Cuba, it has not proven to be helpful or as impactful as those working to protect the population had hoped. Many of these areas are seen as "paper parks" or parks or protected areas that only exist due to their name and nothing else, and they do not have a significant impact on conversation and protections.[57]

Environmental hazards induced by humans also puts sirenians at risk. Sirenians, especially the West Indian manatee, face high mortality from watercraft collision, and about half of all West Indian manatee deaths are caused by watercraft collisions. An increased usage of hydroelectric power and subsequent damming of rivers increase waterway traffic, which can lead to vessel collisions, and manatees may become entangled in navigational locks. The urbanized coastline of areas such as the Caribbean and Australia can result in the decline of seagrass populations. Reliable areas of warm water in Florida are generally the result of discharge from power plants, but newer plants with more efficient cooling systems may disrupt the pattern of warm water refuges, and an increased demand for artesian springs for water, the natural source of warm water, decreases the number of warm water refuges. Sirenians can be caught as bycatch from fisheries, and they can be seen as pests with the interference of local fishermen and the destruction of their nets.[40][50][51][52] African manatees have also been known to venture into rice paddies and destroy the crops during the rainy season, and these confrontations with locals may lead to intentional culling of the manatees.[58] Red tide, scientifically known as Karenia brevis is a harmful algae bloom that releases toxins into the water killing many marine species. In 1982, numerous sick manatees were accounted for and researchers believe this was due to the accumulation brevetoxins in filter-feeding organisms attached to seagrass blades, which are a popular diet for manatees. Manatee die-offs from exposure to red tide toxins were recorded by the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission in southwest Florida in 2002, 2003, 2005, 2007, and most recently in 2013. As of June 20, 2018 the current red tide bloom spreads from Pasco county to Collier County off the West coast of Florida.[59] As of January 2018 there have been a total of 472 manatee deaths caused by this red tide along with water crafts, cold stress, and other factors.[60]
Weather disasters and other natural occurrences are also sources of mortality. The West Indian manatee and Dugong face risks from hurricanes and cyclones, which are predicted to increase in the future. These storms may also damage seagrass populations.[52][51] Exposure to brevetoxin from Karenia brevis during a red tide event are also sources of mortality; they may be able to be exposed to brevetoxin after a red tide has subsided, as it could settle on seagrasses.[51] African manatees can become stranded during the dry season when rivers and lakes become too small or dry up completely.[40]
All sirenians are protected by the Marine Mammal Protection Act of 1972 (MMPA), the Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA), and the Convention on the International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES).[61] In addition to this, the four species are further protected by various specialty organizations. The Dugong is listed in the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), the Convention on Migratory Species, and the Coral Triangle Initiative.[52] In Florida, manatees are protected by the Florida Manatee Sanctuary Act of 1978, which implements actions such as the limitation or prohibition of watercraft speeds where manatees exist.[62] Marine mammal rehabilitation programs have been underway and regulated in the United States for more than 40 years. In 1973 injured and distressed manatees were rescued or aided within Florida. Eventually, the program was formalized into the Manatee Rescue, Rehabilitation, and Release Program managed by the USFWS. In 2012 the program became the Manatee Rescue/Rehabilitation Partnership (MRP) with permitting and oversight by the USFWS. From 1973 through 2014, this program rescued 1,619 manatees and 526 Florida manatees have been released.[63]
See also
- Dwarf manatee
- Cetacea
- Marine mammal
References
- Shoshani 2005.
- "Sirenia Illiger, 1811". Integrated Taxonomic Information System.
- What are sirenians? Archived 2012-07-20 at the Wayback Machine Sirenian International - Manatee & Dugong Research, Education, & Conservation
- Berta 2005, p. 103.
- "English to Afrikaans Meaning: hippopotamus". Afrikaans.English-Dictionary.Help. Retrieved 27 August 2017.
- Tabuce, R.; Asher, R. J.; Lehmann, T. (2008). "Afrotherian mammals: a review of current data" (PDF). Mammalia. 72: 2–14. doi:10.1515/MAMM.2008.004.
- Berta 2005, pp. 89–100.
- Svartman, M.; Stanyon, R. (2012). "The Chromosomes of Afrotheria and Their Bearing on Mammalian Genome Evolution". Cytogenetic and Genome Research. 137 (2–4): 144–153. doi:10.1159/000341387. PMID 22868637.
- Simpson, G. G. (1945). "The principles of classification and a classification of mammals". Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 85: 1–350.
- Rose, Kenneth D.; Archibald, J. David (2005). The Rise of Placental Mammals: Origin and Relationships of the Major Extant Clades. Johns Hopkins University. p. 99. ISBN 978-0-8018-8022-3.
- "Classification of the family Dugongidae". Fossilworks. Retrieved 1 January 2017.
- Vélez-Juarbe, Jorge; Domning, Daryl P. (2015). "Fossil Sirenia of the West Atlantic and Caribbean region. XI. Callistosiren boriquensis, gen. et sp. nov". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35: e885034. doi:10.1080/02724634.2014.885034.
- Vélez-Juarbe, Jorge; Domning, Daryl P. (2014). "Fossil Sirenia of the West Atlantic and Caribbean region. X. Priscosiren atlantica, sp. nov". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 34 (4): 951. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.815192.
- "Classification of the family Trichechidae". Fossilworks. Retrieved 1 January 2017.
- "Classification of the family Protosirenidae". Fossilworks. Retrieved 1 January 2017.
- "Classification of the family Prorastomidae". Fossilworks. Retrieved 1 January 2017.
- Domning, D. P. (2001). "The Earliest Known Fully Quadrupedal Sirenian". Nature. 413 (6856): 625–627. Bibcode:2001Natur.413..625D. doi:10.1038/35098072. PMID 11675784.
- Thewissen, J. G. M.; Bajpai, Sunil (2001). "Whale Origins as a Poster Child for Macroevolution". BioScience. 51 (12): 1037–1049. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[1037:WOAAPC]2.0.CO;2.

- Benoit, Julien; Adnet, Sylvain; El Mabrouk, Essid; Khayati, Hayet; Ben Haj Ali, Mustapha; Marivaux, Laurent; Merzeraud, Gilles; Merigeaud, Samuel; Vianey-Liaud, Monique (2013-01-16). "Cranial Remain from Tunisia Provides New Clues for the Origin and Evolution of Sirenia (Mammalia, Afrotheria) in Africa". PLoS ONE. 8 (1): e54307. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...854307B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054307. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3546994. PMID 23342128.
- Berta, Annalise (2012). "Diversity, Evolution, and Adaptations to Sirenians and Other Marine Mammals". Return to the Sea : The Life and Evolutionary Times of Marine Mammals. Berkeley, CA: University of California. p. 127. ISBN 978-0-520-27057-2.
- Trichechinae at fossilworks.org (retrieved 28 July 2017)
- Berta 2005, p. 250.
- Marsh, Helene (1987). "Chapter 57: Dugongidae" (PDF). Fauna of Australia. 1B. CSIRO. ISBN 978-0-644-06056-1. Archived from the original on 2013-05-11.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
- "Manatee". National Geographic. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- Feldhamer, G. A.; Drickamer, L. C.; Vessey, S. H.; Merritt, J. F.; Krajewski, Carey (2015). Mammalogy: Adaptation, Diversity, Ecology (4th ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 402–418. ISBN 978-1-4214-1588-8.
- Louise Chilvers, B.; Delean, S.; Gales, N. J.; Holley, D. K.; Lawler, I. R.; Marsh, H.; Preen, A. R. (2004). "Diving behaviour of dugongs, Dugong dugon". Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology. 304 (2): 203. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2003.12.010.
- "Dugong". National Geographic. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- Self-Sullivan, Caryn, Evolution of Sirenia (PDF), sirenian.org, archived from the original (PDF) on 31 December 2006, retrieved 10 March 2007
- Marsh, H.; Eros, C.; Hugues, J. (2002). Dugong: status reports and action plans for countries and territories (PDF). International Union for Conservation of Nature. p. 7. ISBN 978-92-807-2130-0.
- Waller, Geoffrey; Dando, Marc (1996). Sealife: A Complete Guide to the Marine Environment. Smithsonian Institution. pp. 413–420. ISBN 978-1-56098-633-1.
- Eldredge, Neal (2002). Life on Earth: An Encyclopedia of Biodiversity, Ecology and Evolution. ABC-CLIO. p. 532. ISBN 978-1-57607-286-8.
- Domning, Daryl; Vivian Buffrenil (1991). "Hydrostasis in the Sirenia: Quantitative Data and Functional Interpretations". Marine Mammal Science. 7 (4): 331–368. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1991.tb00111.x.
- Rommel, Sentiel; John E. Reynolds (2000). "Diaphragm structure and function in the Florida manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris)". The Anatomical Record. Wiley-Liss, Inc. 259 (1): 41–51. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(20000501)259:1<41::AID-AR5>3.0.CO;2-Q. PMID 10760742.
- Scheffer, Victor B. (November 1972). "The Weight of the Steller Sea Cow". Journal of Mammalogy. 53 (4): 912–914. doi:10.2307/1379236. JSTOR 1379236.
- Reep, R.L.; Marshall, C.D.; Stoll, M.L. (2002). "Tactile Hairs on the Postcranial Body in Florida Manatees: A Mammalian Lateral Line?" (PDF). Brain, Behavior and Evolution. 59 (3): 141–154. doi:10.1159/000064161. PMID 12119533. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 January 2012.
- Ambati, B. K.; Nozaki, M.; Singh, N.; Takeda, A.; Jani, P. D.; Suthar, T.; Albuquerque, R. J. C.; Richter, E.; Sakurai, E.; Newcomb, M. T.; Kleinman, M. E.; Caldwell, R. B.; Lin, Q.; Ogura, Y.; Orecchia, A.; Samuelson, D. A.; Agnew, D. W.; St Leger, J.; Green, W. R.; Mahasreshti, P. J.; Curiel, D. T.; Kwan, D.; Marsh, H.; Ikeda, S.; Leiper, L. J.; Collinson, J. M.; Bogdanovich, S.; Khurana, T. S.; Shibuya, M.; Baldwin, M. E. (2006). "Corneal avascularity is due to soluble VEGF receptor-1". Nature. 443 (7114): 993–997. Bibcode:2006Natur.443..993A. doi:10.1038/nature05249. PMC 2656128. PMID 17051153.
- "Dugong dugon Dugong". Mammals of Africa : Introductory Chapters and Afrotheria. 2013. doi:10.5040/9781472926913.0013. ISBN 978-1-4729-2691-3.
- Berta 2005, pp. 438–444.
- Siegal-Willott, Jessica L.; Harr, Kendal; Hayek, Lee-Ann C.; Scott, Karen C.; Gerlach, Trevor; Sirois, Paul; Reuter, Mike; Crewz, David W.; Hill, Richard C. (2010). "Proximate Nutrient Analyses of Four Species of Submerged Aquatic Vegetation Consumed by Florida Manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris) Compared to Romaine Lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. longifolia". Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine. 41 (4): 594–602. doi:10.1638/2009-0118.1. JSTOR 40962301. PMID 21370638.
- Keith Diagne, L. (2015). "Trichechus senegalensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T22104A97168578. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T22104A81904980.en.{{cite iucn}}: error: |doi= / |page= mismatch (help)
- Powell, James (1978). "Evidence for carnivory in manatee (Trichechus manatus)". Journal of Mammalogy. 59 (2): 442. doi:10.2307/1379938. JSTOR 1379938.
- Best, Robin C. (1983). "Apparent Dry-Season Fasting in Amazonian manatees (Mammalia: Sirenia)". Biotropica. 15 (1): 61–64. doi:10.2307/2388000. JSTOR 2388000.
- Berta 2005, p. 502.
- Koelsch, J. K. (2001). "Reproduction in Female Manatees Observed in Sarasota Bay, Florida". Marine Mammal Science. 17 (2): 331–342. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2001.tb01274.x.
- Best, Robin (1984). Macdonald, D. (ed.). The Encyclopedia of Mammals. New York: Facts on File. pp. 292–298. ISBN 978-0-87196-871-5.
- Best, R. C. (1982). "Seasonal Breeding in the Amazonian Manatee, Trichechus inunguis (Mammalia: Sirenia)". Biotropica. 14 (1): 76–78. doi:10.2307/2387764. JSTOR 2387764.
- Bossart, Gregory D. "Manatees." CRC handbook of marine mammal medicine. CRC Press, 2001. 989-1010.
- Mignucci-Giannoni, ANTONIO A. "Marine mammal captivity in the northeastern Caribbean, with notes on the rehabilitation of stranded whales, dolphins and manatees." Caribbean Journal of Science 34.3-4 (1998): 191-203.
- Parente; Leite, Cristiano; Einhardt Vergara-Parente, Jociery; Lima, R. P. (2004). "Strandings of Antillean manatees, Trichechus manatus manatus, in northeastern Brazil". Latin American Journal of Aquatic Mammals. 3 (1): 69–75. doi:10.5597/lajam00050.
- Marmontel, M.; de Souza, D. & Kendall, S. (2016). "Trichechus inunguis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22102A43793736. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T22102A43793736.en.
- Deutsch, C.J.; Self-Sullivan, C. & Mignucci-Giannoni, A. (2008). "Trichechus manatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T22103A9356917. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T22103A9356917.en.
- Marsh, H. & Sobtzick, S. (2015). "Dugong dugon". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T6909A43792211. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T6909A43792211.en.
- Domning, D.; Anderson, P.K.; Turvey, S. (2008). "Hydrodamalis gigas". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008. Retrieved 16 January 2017.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Reeves, Randall R.; Leatherwood, Stephen; Jefferson, Thomas A.; Curry, Barbara E.; Henningsen, Thomas (1996). "Amazonian Manatees, Tricheus inunguis, in Peru: Distribution, Exploitation, and Conservation Status" (PDF). Interciencia. 21 (6).
- Alvarez-Alemán, Anmari; García Alfonso, Eddy; Forneiro Martin-Vianna, Yanet; Hernández Gonzalez, Zaimiuri; Escalona Domenech, Raisa; Hurtado, Andrés; Powell, James; Jacoby, Charles A; Frazer, Thomas K (2017). "Status and conservation of manatees in Cuba: historical observations and recent insights". Bulletin of Marine Science. doi:10.5343/bms.2016.1132. ISSN 0007-4977.
- "Antillean Manatee Conservation in Cuba | Sea to Shore Alliance". Sea to Shore Alliance. Retrieved 2018-07-22.
- Alvarez-Alemán, Anmari; Angulo-Valdés, Jorge A.; Alfonso, Eddy García; Powell, James A.; Taylor, Cynthia R. (April 2017). "Occurrence of the Endangered Antillean manatee Trichechus manatus manatus in a marine protected area, Isla de la Juventud, Cuba". Oryx. 51 (2): 324–331. doi:10.1017/S0030605315001143. ISSN 0030-6053.
- "African manatee (Trichechus senegalensis)". Wildscreen. Archived from the original on 2011-11-30. Retrieved 24 January 2017.
- “Red Tide Current Status.” Facts About Horseshoe Crabs, myfwc.com/redtidestatus
- “2018 Manatee Mortalities.” Facts About Horseshoe Crabs, myfwc.com/research/manatee/rescue-mortality-response/mortality-statistics/2018/
- "Marine Mammals". U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- "The 2016 Florida Statutes". Online Sunshine. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- Rescue, rehabilitation and release of Florida manatees: Analysis of factors affecting survival By: Adimey, N. M.; Rauschenberger, H.; Reid, J. P.; et al. P 18 BIENN C BIOL MA Published: December 2009
Further reading
- Daryl P. Domning. "Bibliography and Index of the Sirenia and Desmostylia". Archived from the original on 2013-11-03.
- Shoshani, J. (2005). Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 92–93. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- Berta, A.; Sumich, J. L.; Kovacs, K. M. (2015). Marine Mammals: Evolutionary Biology (3rd ed.). Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-397002-2.
- Garrison, Tom. Oceanography, 5th Ed., Brooks Cole, 30 July 2008. ISBN 978-0-495-55531-5
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sirenia. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Sirenia |
| The Wikibook Dichotomous Key has a page on the topic of: Sirenia |
