Oxfordshire
Oxfordshire (abbreviated Oxon, from Oxonium, the Latin name for Oxford) is a county in South East England. The ceremonial county borders Warwickshire to the north-west, Northamptonshire to the north-east, Buckinghamshire to the east, Berkshire to the south, Wiltshire to the south-west and Gloucestershire to the west.
| Oxfordshire | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceremonial county | |||
| |||
| Motto: Sapere Aude ('Dare to be Wise')[1] | |||
 | |||
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom | ||
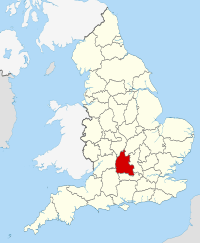
| Constituent country | England | ||
| Region | South East England | ||
| Ceremonial county | |||
| Lord Lieutenant | Tim Stevenson OBE | ||
| High Sheriff | Mrs Amanda Ponsonby MBE [2] (2020–21) | ||
| Area | 2,605 km2 (1,006 sq mi) | ||
| • Ranked | 22nd of 48 | ||
| Population (mid-2018 est.) | 687,524 | ||
| • Ranked | 35th of 48 | ||
| Density | 264/km2 (680/sq mi) | ||
| Ethnicity | 95.1% White - 1.7% S. Asian | ||
| Non-metropolitan county | |||
| County council | |||
| Executive | Conservative | ||
| Admin HQ | Oxford | ||
| Area | 2,605 km2 (1,006 sq mi) | ||
| • Ranked | 15th of 26 | ||
| Population | 687,524 | ||
| • Ranked | 17th of 26 | ||
| Density | 264/km2 (680/sq mi) | ||
| ISO 3166-2 | GB-OXF | ||
| ONS code | 38 | ||
| NUTS | UKJ14 | ||
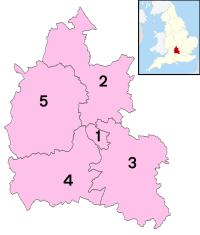 Districts of Oxfordshire | |||
| Districts |
| ||
| Members of Parliament | |||
| Time zone | Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | British Summer Time (UTC+1) | ||
The county has major education and tourist industries and is noted for the concentration of performance motorsport companies and facilities. Oxford University Press is the largest firm among a concentration of print and publishing firms; the University of Oxford is also linked to the concentration of local biotechnology companies.
As well as the city of Oxford, other centres of population are Banbury, Bicester, Kidlington and Chipping Norton to the north of Oxford; Carterton and Witney to the west; Thame and Chinnor to the east; and Abingdon-on-Thames, Wantage, Didcot, Wallingford and Henley-on-Thames to the south. The areas south of the Thames, the Vale of White Horse and parts of South Oxfordshire, are in the historic county of Berkshire, as is the highest point, the 261 metres (856 ft) White Horse Hill.[4]
Oxfordshire's county flower is the snake's-head fritillary.[5]
History
Oxfordshire was recorded as a county in the early years of the 10th century and lies between the River Thames to the south, the Cotswolds to the west, the Chilterns to the east and the Midlands to the north, with spurs running south to Henley-on-Thames and north to Banbury.
Although it had some significance as an area of valuable agricultural land in the centre of the country, it was largely ignored by the Romans, and did not grow in importance until the formation of a settlement at Oxford in the 8th century. Alfred the Great was born across the Thames in Wantage, Vale of White Horse. The University of Oxford was founded in 1096, though its collegiate structure did not develop until later on. The university in the county town of Oxford (whose name came from Anglo-Saxon Oxenaford = "ford for oxen") grew in importance during the Middle Ages and early modern period. The area was part of the Cotswolds wool trade from the 13th century, generating much wealth, particularly in the western portions of the county in the Oxfordshire Cotswolds. Morris Motors was founded in Oxford in 1912, bringing heavy industry to an otherwise agricultural county. The importance of agriculture as an employer has declined rapidly in the 20th century though; currently under one percent of the county's population are involved due to high mechanisation. Nonetheless, Oxfordshire remains a very agricultural county by land use, with a lower population than neighbouring Berkshire and Buckinghamshire, which are both smaller.
Throughout most of its history the county was divided into fourteen hundreds, namely Bampton, Banbury, Binfield, Bloxham, Bullingdon, Chadlington, Dorchester, Ewelme, Langtree, Lewknor, Pyrton, Ploughley, Thame and Wootton.
The Oxfordshire and Buckinghamshire Light Infantry, the main army unit in the area, was based at Cowley Barracks on Bullingdon Green, Cowley.
The Vale of White Horse district and parts of the South Oxfordshire administrative district south of the River Thames were historically part of Berkshire, but in 1974 Abingdon, Didcot, Faringdon, Wallingford and Wantage were added to the administrative county of Oxfordshire under the Local Government Act 1972. Conversely, the Caversham area of Reading, now administratively in Berkshire, was historically part of Oxfordshire as was the parish of Stokenchurch, now administratively in Buckinghamshire. The areas of Oxford city south of the Thames such as Grandpont were transferred much earlier, in 1889.
Geography
Oxfordshire includes parts of three Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty. In the north-west lie the Cotswolds, to the south and south-east are the open chalk hills of the North Wessex Downs and wooded hills of the Chilterns. The north of the county contains the ironstone of the Cherwell uplands. Long-distance walks within the county include the Ridgeway National Trail, Macmillan Way, Oxfordshire Way and the D’Arcy Dalton Way.
Extreme points
- Northernmost point: 52°10′6.58″N 1°19′54.92″W, near Claydon Hay Farm, Claydon
- Southernmost point: 51°27′34.74″N 0°56′48.3″W, near Thames and Kennet Marina, Playhatch
- Westernmost point: 51°46′59.73″N 1°43′9.68″W, near Downs Farm, Westwell
- Easternmost point: 51°30′14.22″N 0°52′13.99″W, River Thames, near Lower Shiplake
Rivers
The central part of Oxfordshire contains the River Thames with its flat floodplains; the river forms the historic county boundary with Berkshire. The Thames Path National Trail parallels the river as it crosses Oxfordshire, continuing towards London. There are many smaller rivers that feed into the Thames such as the Thame, Windrush, Evenlode and Cherwell. Some of these rivers have trails running along their valleys. The Oxford Canal follows the Cherwell from Banbury to Kidlington.
Green belt
Oxfordshire contains a green belt area that fully envelops the city of Oxford, and extends for some miles to afford a protection to surrounding towns and villages from inappropriate development and urban growth. Its border in the east extends to the Buckinghamshire county boundary, while part of its southern border is shared with the North Wessex Downs AONB. It was first drawn up in the 1950s, and all the county's districts contain some portion of the belt.
Economy
This is a chart of trend of regional gross value added of Oxfordshire at current basic prices published by the Office for National Statistics with figures in millions of British pounds sterling.[6]
| Year | Regional gross value added[7] | Agriculture[8] | Industry[9] | Services[10] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 7,607 | 120 | 2,084 | 5,404 |
| 2000 | 10,594 | 80 | 2,661 | 7,853 |
| 2003 | 12,942 | 93 | 2,665 | 10,184 |
Politics
The Oxfordshire County Council, since 2013 under no overall control, is responsible for the most strategic local government functions, including schools, county roads, and social services. The county is divided into five local government districts: Oxford, Cherwell, Vale of White Horse (after the Uffington White Horse), West Oxfordshire and South Oxfordshire, which deal with such matters as town and country planning, waste collection, and housing.
In the 2016 European Union referendum, Oxfordshire was the only English county as a whole to vote to remain in the European Union by a significant margin, at 57.06% (70.27% in the City of Oxford), despite Cherwell (barely) voting to leave at 50.31%.
Education

Oxfordshire has a completely comprehensive education system with 23 independent schools, including the notable Radley College, and 35 state secondary schools. Only eight schools do not have a sixth form; these are mostly in South Oxfordshire and Cherwell districts.
The county has two universities: the ancient University of Oxford and the modern Oxford Brookes University, which are both located in Oxford. In addition, Wroxton College, located in Banbury, is affiliated with Fairleigh Dickinson University of New Jersey.
Buildings

The "dreaming spires" of the buildings of the University of Oxford are among the reasons for Oxford being the sixth most visited city in the United Kingdom for international visitors.[11] Among many notable University buildings are the Sheldonian Theatre, built 1664–68 to the design of Sir Christopher Wren, and the Radcliffe Camera, built 1737–49 to the design of James Gibbs.
Blenheim Palace close to Woodstock was built by the great architect John Vanbrugh for John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, after he had won the battle of Blenheim. The gardens, which can be visited, were designed by the landscape gardener "Capability Brown", who planted the trees in the battle formation of the victorious army. In the palace, which can also be visited by the public, Sir Winston Churchill was born in 1874.
Chastleton House, on the Gloucestershire and Warwickshire borders, is a great country mansion built on property bought from Robert Catesby, who was one of the men involved in the Gunpowder Plot with Guy Fawkes. Stonor Park, another country mansion, has belonged to the recusant Stonor family for centuries.
Mapledurham House is an Elizabethan stately home in the far south-east of the county, close to Reading.
The Abbey in Sutton Courtenay is a medieval courtyard house. It has been recognised by the Historic Building Council for England (now Historic England) as a building of outstanding historic and architectural interest.[12] It is considered to be a ‘textbook’ example of the English medieval manor house,[13] and is a Grade I-listed building.[14]
Settlements in Oxfordshire

- Abingdon-on-Thames (in Berkshire until 1974)
- Banbury
- Bicester
- Burford
- Carterton
- Charlbury
- Chinnor
- Chipping Norton
- Didcot (in Berkshire until 1974)
- Faringdon (in Berkshire until 1974)
- Henley-on-Thames
- Islip
- Kidlington
- Oxford
- Thame
- Wallingford (in Berkshire until 1974)
- Wantage (in Berkshire until 1974)
- Watlington
- Witney
- Woodstock
Emergency services
- Oxfordshire Fire and Rescue Service
- South Central Ambulance Service
- Thames Valley Air Ambulance
- Thames Valley Police
- British Transport Police
Settlements by population
| Rank | Town | Population | Year | Definition | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Oxford | 150,200 | 2011 | Oxford non-metropolitan district | |
| 2 | Banbury | 46,853 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 3 | Abingdon-on-Thames | 33,130 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 4 | Bicester | 32,642 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 5 | Witney | 27,522 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 6 | Didcot | 25,140 | 2011 | Civil parish | 200 dwellings in the south-east of the town lie in neighbouring East Hagbourne parish. |
| 7 | Carterton | 15,769 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 8 | Kidlington | 13,723 | 2011 | Civil parish | Does not include Gosford. |
| 9 | Henley-on-Thames | 11,619 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 10 | Wallingford | 11,600[15] | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 11 | Thame | 11,561 | 2011 | Civil parish | Includes hamlet of Moreton |
| 12 | Wantage | 11,327 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 13 | Grove | 7,178 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 14 | Faringdon | 7,121 | 2011 | Great Faringdon civil parish | |
| 15 | Chipping Norton | 6,337 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 16 | Chinnor | 5,924 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 17 | Benson | 4,754 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 18 | Eynsham | 4,648 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 19 | Wheatley | 4,092 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 20 | Kennington | 4,076 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 21 | Woodstock | 3,100 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 22 | Charlbury | 2,830 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 23 | Watlington | 2,727 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 24 | Bampton | 2,564 | 2011 | Civil parish | |
| 25 | Deddington | 2,146 | 2011 | Civil parish |
Places of interest
| Key | |
| Abbey/Priory/Cathedral | |
| Accessible open space | |
| Amusement/Theme Park | |
| Castle | |
| Country Park | |
| English Heritage | |
| Forestry Commission | |
| Heritage railway | |
| Historic House | |
| Mosques | |
| Museum (free/not free) | |
| National Trust | |
| Theatre | |
| Zoo | |
- Bicester Village



.svg.png)

.svg.png)
.svg.png)





- Harcourt Arboretum, Nuneham Courtenay

- Hook Norton Brewery – working Victorian "tower" brewery that offers guided tours




.svg.png)


.svg.png)
.svg.png)


.svg.png)

- Rollright Stones – megalithic stone circle and Whispering Knights burial chamber, near Little Rollright

- Rycote chapel – 15th-century chapel with original furnishings
- St Katharine's church, Chiselhampton – 18th-century parish church with original furnishings (no website, limited access)
- St Mary's church, Iffley – 12th-century Norman parish church[20]



.svg.png)
See also
- Lord Lieutenant of Oxfordshire
- High Sheriff of Oxfordshire
- Oxfordshire Artweeks, an annual art festival each May
- Oxford University (including links to the individual colleges)
- Oxford Canal
References and notes
- "Camelot International, Britain's heritage and history". Camelotintl.com. Archived from the original on 3 May 2012. Retrieved 9 November 2011.
- "No. 62943". The London Gazette. 13 March 2020. p. 5161.
- "Homepage". Archived from the original on 23 November 2002. Retrieved 16 November 2002.
- Edwardes, Simon (2001). "County and Unitary Authority Tops". The Mountains of England and Wales. Archived from the original on 22 December 2015. Retrieved 14 December 2015.
- "Fritillary (Fritillaria meleagris)". Plantlife. Archived from the original on 30 January 2012. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- "unknown" (PDF). pp. 240–253. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 July 2011.
- Components may not sum to totals due to rounding
- includes hunting and forestry
- includes energy and construction
- includes financial intermediation services indirectly measured
- "Economic Statistics". Oxford City Council. Archived from the original on 17 December 2015. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- The Abbey, Sutton Courtenay archives.
- Currie 1992, p. 225.
- Historic England. "The Abbey (1052729)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- Service, District Data. "District Data Service - South Oxon Census 2011 summary leaflet". www.oxford.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 5 August 2018. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- Christopher Gale (7 July 2012). "Abingdon County Hall Museum". Abingdonmuseum.org.uk. Archived from the original on 13 August 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- "Home page". Chipping Norton History Society and Museum. Archived from the original on 16 May 2017. Retrieved 27 June 2017.
- "Home". Combemill.org. Archived from the original on 10 September 2014. Retrieved 23 August 2014.
- "Oxfordshire". Milton Manor House. Archived from the original on 9 July 2014. Retrieved 23 August 2014.
- Pevsner, Nikolaus; Sherwood, Jennifer (1974). The Buildings of England: Oxfordshire. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0300096392.
- Glitz. "Wheatley Windmill Website". Wheatleymill.co.uk. Archived from the original on 24 July 2014. Retrieved 23 August 2014.
Further reading
- Currie, Christopher Richard John (1992). "Larger Medieval Houses in the Vale of White Horse" (PDF). Oxoniensia. 57: 81–224. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- Powell, Philip (2005). The Geology of Oxfordshire. Dovecote Press. ISBN 1-904349-19-6.
External links
| Look up Oxfordshire in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Oxfordshire. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Oxfordshire. |
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. 20 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 415–418.
- Oxfordshire County Council
- Thisisoxfordshire Oxfordshire news, sport & information
- The Oxfordshire Association
- Flags of Oxfordshire
- Visit South Oxfordshire
- Banbury & District National Trust Association
- Images of Oxfordshire at the English Heritage Archive
- Oxfordshire at Curlie