Overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish from a body of water at a rate that the species cannot replenish in time, resulting in those species either becoming depleted or very underpopulated in that given area. According to a highly contested 2006 article in the journal Science, if fishing rates continue unchanged, all the world's fisheries will have collapsed by the year 2048.[1] In a Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations 2018 report, the FAO estimates that one-third of world fish stocks were overfished by 2015.[2]

Overfishing can occur in water bodies of any sizes, such as ponds, rivers, lakes or oceans, and can result in resource depletion, reduced biological growth rates and low biomass levels. Sustained overfishing can lead to critical depensation, where the fish population is no longer able to sustain itself. Some forms of overfishing, such as the overfishing of sharks, has led to the upset of entire marine ecosystems.[3]
The ability of a fishery to recover from overfishing depends on whether the ecosystem's conditions are suitable for the recovery. Dramatic changes in species composition can result in an ecosystem shift, where other equilibrium energy flows involve species compositions different from those that had been present before the depletion of the original fish stock. For example, once trout have been overfished, carp might take over in a way that makes it impossible for the trout to re-establish a breeding population.
Global scale

Overfishing has stripped many fisheries around the world of their stocks. The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization estimated in a 2018 report that 33.1% of world fish stocks are subject to overfishing.[4] Significant overfishing has been observed in pre-industrial times. In particular, the overfishing of the western Atlantic Ocean from the earliest days of European colonisation of the Americas has been well documented.[5]
The fraction of fish stocks that are within biologically sustainable levels has exhibited a decreasing trend, from 90% in 1974 to 66.9% in 2015. In contrast, the percentage of stocks fished at biologically unsustainable levels increased from 10% in 1974 to 33.1% in 2015, with the largest increases in the late-1970s and 1980s.
In 2015, maximally sustainably fished stocks (formerly termed fully fished stocks) accounted for 59.9% and underfished stocks for 7% of the total assessed stocks.[6] While the proportion of underfished stocks decreased continuously from 1974 to 2015, the maximally sustainably fished stocks decreased from 1974 to 1989, and then increased to 59.9% in 2015.[6]
In 2015, among the 16 major statistical areas, the Mediterranean and Black Sea had the highest percentage (62.2%) of unsustainable stocks, closely followed by the Southeast Pacific 61.5% and Southwest Atlantic 58.8%. In contrast, the Eastern Central Pacific, Northeast Pacific (Area 67), Northwest Pacific (Area 61), Western Central Pacific and Southwest Pacific had the lowest proportion (13 to 17%) of fish stocks at biologically unsustainable levels.[6]
Daniel Pauly, a fisheries scientist known for pioneering work on the human impacts on global fisheries, has commented:[7]
It is almost as though we use our military to fight the animals in the ocean. We are gradually winning this war to exterminate them. And to see this destruction happen, for nothing really – for no reason – that is a bit frustrating. Strangely enough, these effects are all reversible, all the animals that have disappeared would reappear, all the animals that were small would grow, all the relationships that you can't see any more would re-establish themselves, and the system would re-emerge.
Evidence
Examples of overfishing exist in areas such as the North Sea, the Grand Banks of Newfoundland and the East China Sea.[8] In these locations, overfishing has not only proved disastrous to fish stocks, but also to the fishing communities relying on the harvest. Like other extractive industries such as forestry and hunting, fisheries are susceptible to economic interaction between ownership or stewardship and sustainability, otherwise known as the tragedy of the commons.
- The Peruvian coastal anchovy fisheries crashed in the 1970s after overfishing and an El Niño season[9] largely depleted anchovies from its waters.[10][11] Anchovies were a major natural resource in Peru; indeed, 1971 alone yielded 10.2 million metric tons of anchovies. However, the following five years saw the Peruvian fleet's catch amount to only about four million tons.[9] This was a major loss to Peru's economy.
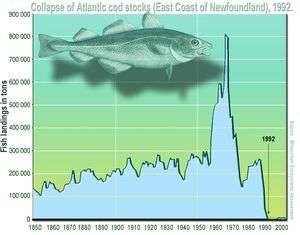
- The collapse of the cod fishery off Newfoundland,[12] and the 1992 decision by Canada to impose an indefinite moratorium on the Grand Banks, is a dramatic example of the consequences of overfishing.[13]
- The sole fisheries in the Irish Sea, the west English Channel, and other locations have become overfished to the point of virtual collapse, according to the UK government's official Biodiversity Action Plan. The United Kingdom has created elements in this plan to attempt to restore the fishery, but the expanding global human population and the expanding demand for fish has reached a point where demand for food threatens the stability of these fisheries, if not the species' survival.[14]
- Many deep sea fish are at risk, such as orange roughy and sablefish. The deep sea is almost completely dark, near freezing, and has little food. Deep sea fish grow slowly because of limited food, have slow metabolisms, low reproductive rates, and many do not reach breeding maturity for 30 to 40 years. A fillet of orange roughy at the store is probably at least 50 years old. Most deep sea fish are in international waters, where there are no legal protections. Most of these fish are caught by deep trawlers near seamounts, where they congregate for food. Flash freezing allows the trawlers to work for days at a time, and modern fishfinders target the fish with ease.[15]
- Blue walleye became extinct in the Great Lakes in the 1980s. Until the middle of the 20th century, the walleye was a commercially valuable fish, with about a half million tonnes being landed in the period from about 1880 to the late-1950s, when the populations collapsed, apparently through a combination of overfishing, anthropogenic eutrophication, and competition with introduced rainbow smelt.
- The World Wide Fund for Nature and the Zoological Society of London jointly issued their "Living Blue Planet Report" on 16 September 2015 which states that there was a dramatic fall of 74% in worldwide stocks of the important scombridae fish such as mackerel, tuna and bonitos between 1970 and 2010, and the global overall "population sizes of mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish fell by half on average in just 40 years."[16]
- Overfishing of the critically endangered Pacific bluefin tuna has resulted in the few still caught selling for astronomical prices. In January 2019, a 278 kilogram (612 pound) tuna sold for 333.6 million yen, or over US$3 million, US$4,900 per pound. Fishers, driven by the fish's high value, use extraordinary techniques to catch them, leaving the population on the verge of collapse.[17]
In management
Several countries are now effectively managing their fisheries. Examples include Iceland and New Zealand.[18] The United States has turned many of its fisheries around from being in a highly depleted state.[19]
Consequences
According to a 2008 UN report, the world's fishing fleets are losing US$50 billion each year due to depleted stocks and poor fisheries management. The report, produced jointly by the World Bank and the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), asserts that half the world's fishing fleet could be scrapped with no change in catch. In addition, the biomass of global fish stocks have been allowed to run down to the point where it is no longer possible to catch the amount of fish that could be caught.[20] Increased incidence of schistosomiasis in Africa has been linked to declines of fish species that eat the snails carrying the disease-causing parasites.[21] Massive growth of jellyfish populations threaten fish stocks, as they compete with fish for food, eat fish eggs, and poison or swarm fish, and can survive in oxygen depleted environments where fish cannot; they wreak massive havoc on commercial fisheries. Overfishing eliminates a major jellyfish competitor and predator, exacerbating the jellyfish population explosion.[22] Both climate change and a restructuring of the ecosystem have been found to be major roles in an increase in jellyfish population in the Irish Sea in the 1990s.[23]
Types
There are three recognized types of biological overfishing: growth overfishing, recruit overfishing, and ecosystem overfishing.
Growth overfishing
Growth overfishing occurs when fish are harvested at an average size that is smaller than the size that would produce the maximum yield per recruit. A recruit is an individual that makes it to maturity, or into the limits specified by a fishery, which are usually size or age.[24] This makes the total yield less than it would be if the fish were allowed to grow to an appropriate size. It can be countered by reducing fishing mortality to lower levels and increasing the average size of harvested fish to a size that will allow maximum yield per recruit.[25][26]
Recruitment overfishing
Recruitment overfishing occurs when the mature adult population (spawning biomass) is depleted to a level where it no longer has the reproductive capacity to replenish itself—there are not enough adults to produce offspring.[25] Increasing the spawning stock biomass to a target level is the approach taken by managers to restore an overfished population to sustainable levels. This is generally accomplished by placing moratoriums, quotas, and minimum size limits on a fish population.
Ecosystem overfishing
Ecosystem overfishing occurs when the balance of the ecosystem is altered by overfishing. With declines in the abundance of large predatory species, the abundance of small forage type increases causing a shift in the balance of the ecosystem towards smaller fish species.
Acceptable levels
The notion of overfishing hinges on what is meant by an "acceptable level" of fishing. More precise biological and bioeconomic terms define acceptable level as follows:
- Biological overfishing occurs when fishing mortality has reached a level where the stock biomass has negative marginal growth (reduced rate of biomass growth), as indicated by the red area in the figure. (Fish are being taken out of the water so quickly that the replenishment of stock by breeding slows down. If the replenishment continues to diminish for long enough, replenishment will go into reverse and the population will decrease.)[27]
- Economic or bioeconomic overfishing additionally considers the cost of fishing when determining acceptable catches. Under this framework, a fishery is considered to be overfished when catches exceed maximum economic yield where resource rent is at its maximum. Fish are being removed from the fishery so quickly that the profitability of the fishery is sub-optimal. A more dynamic definition of economic overfishing also considers the present value of the fishery using a relevant discount rate to maximise the flow of resource rent over all future catches.
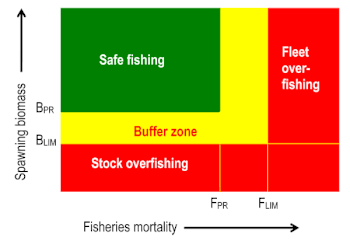
Harvest control rule
A model proposed in 2010 for predicting acceptable levels of fishing is the Harvest Control Rule (HCR),[28] which is a set of tools and protocols with which management has some direct control of harvest rates and strategies in relation to predicting stock status, and long-term maximum sustainable yields. Constant catch and constant fishing mortality are two types of simple harvest control rules.[29]
Input and output orientations
Fishing capacity can also be defined using an input or output orientation.
- An input-oriented fishing capacity is defined as the maximum available capital stock in a fishery that is fully utilized at the maximum technical efficiency in a given time period, given resource and market conditions.[30]
- An output-oriented fishing capacity is defined as the maximum catch a vessel (fleet) can produce if inputs are fully utilized given the biomass, the fixed inputs, the age structure of the fish stock, and the present stage of technology.[31]
Technical efficiency of each vessel of the fleet is assumed necessary to attain this maximum catch. The degree of capacity utilization results from the comparison of the actual level of output (input) and the capacity output (input) of a vessel or a fleet.
Mitigation
In order to meet the problems of overfishing, a precautionary approach and Harvest Control Rule (HCR) management principles have been introduced in the main fisheries around the world. The Traffic Light color convention introduces sets of rules based on predefined critical values, which can be adjusted as more information is gained.
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea treaty deals with aspects of overfishing in articles 61, 62, and 65.[32]
- Article 61 requires all coastal states to ensure that the maintenance of living resources in their exclusive economic zones is not endangered by over-exploitation. The same article addresses the maintenance or restoration of populations of species above levels at which their reproduction may become seriously threatened.
- Article 62 provides that coastal states: "shall promote the objective of optimum utilization of the living resources in the exclusive economic zone without prejudice to Article 61"
- Article 65 provides generally for the rights of, inter alia, coastal states to prohibit, limit, or regulate the exploitation of marine mammals.
According to some observers, overfishing can be viewed as an example of the tragedy of the commons; appropriate solutions would therefore promote property rights through, for instance, privatization and fish farming. Daniel K. Benjamin, in Fisheries are Classic Example of the 'Tragedy of the Commons', cites research by Grafton, Squires and Fox to support the idea that privatization can solve the overfishing problem: According to recent research on the British Columbia halibut fishery, where the commons has been at least partly privatized, substantial ecological and economic benefits have resulted. There is less damage to fish stocks, the fishing is safer, and fewer resources are needed to achieve a given harvest."[33]
Another possible solution, at least for some areas, is quotas, restricting fishers to a specific quantity of fish. A more radical possibility is declaring certain areas of the sea "no-go zones" and make fishing there strictly illegal, so the fish have time to recover and repopulate.
In order to maximise resources some countries, e.g., Bangladesh and Thailand, have improved the availability of family planning services. The resulting smaller populations have a decreased environmental footprint and reduced food needs.[34]
Controlling consumer behavior and demand is critical in mitigating action. Worldwide, a number of initiatives emerged to provide consumers with information regarding the conservation status of the seafood available to them. The "Guide to Good Fish Guides" lists a number of these.[35]
Government regulation
Many regulatory measures are available for controlling overfishing. These measures include fishing quotas, bag limits, licensing, closed seasons, size limits and the creation of marine reserves and other marine protected areas.
A model of the interaction between fish and fishers showed that when an area is closed to fishers, but there are no catch regulations such as individual transferable quotas, fish catches are temporarily increased but overall fish biomass is reduced, resulting in the opposite outcome from the one desired for fisheries.[36] Thus, a displacement of the fleet from one locality to another will generally have little effect if the same quota is taken. As a result, management measures such as temporary closures or establishing a marine protected area of fishing areas are ineffective when not combined with individual fishing quotas. An inherent problem with quotas is that fish populations vary from year to year. A study has found that fish populations rise dramatically after stormy years due to more nutrients reaching the surface and therefore greater primary production.[37] To fish sustainably, quotas need to be changed each year to account for fish population.
Individual transferable quotas (ITQs) are fishery rationalization instruments defined under the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act as limited access permits to harvest quantities of fish. Fisheries scientists decide the optimal amount of fish (total allowable catch) to be harvested in a certain fishery. The decision considers carrying capacity, regeneration rates and future values. Under ITQs, members of a fishery are granted rights to a percentage of the total allowable catch that can be harvested each year. These quotas can be fished, bought, sold, or leased allowing for the least cost vessels to be used. ITQs are used in New Zealand, Australia, Iceland, Canada, and the United States.
In 2008, a large-scale study of fisheries that used ITQs compared to ones that didn't provided strong evidence that ITQs can help to prevent collapses and restore fisheries that appear to be in decline.[38][39][40][41]
China bans fishing in the South China Sea for a period each year.[42]
Removal of subsidies
Several scientists have called for an end to subsidies paid to deep-sea fisheries. In international waters beyond the 200 nautical mile exclusive economic zones of coastal countries, many fisheries are unregulated, and fishing fleets plunder the depths with state-of-the-art technology. In a few hours, massive nets weighing up to 15 tons, dragged along the bottom by deep-water trawlers, can destroy deep-sea corals and sponge beds that have taken centuries or millennia to grow. The trawlers can target orange roughy, grenadiers, or sharks. These fish are usually long-lived and late maturing, and their populations take decades, even centuries to recover.[43]
Fisheries scientist Daniel Pauly and economist Ussif Rashid Sumaila have examined subsidies paid to bottom trawl fleets around the world. They found that US$152 million per year are paid to deep-sea fisheries. Without these subsidies, global deep-sea fisheries would operate at a loss of US$50 million a year. A great deal of the subsidies paid to deep-sea trawlers is to subsidize the large amount of fuel required to travel beyond the 200 mile limit and drag weighted nets.[43]
"There is surely a better way for governments to spend money than by paying subsidies to a fleet that burns 1.1 billion litres of fuel annually to maintain paltry catches of old growth fish from highly vulnerable stocks, while destroying their habitat in the process" – Pauly.[43]
"Eliminating global subsidies would render these fleets economically unviable and would relieve tremendous pressure on over-fishing and vulnerable deep-sea ecosystems" – Sumaila.[43]
Minimizing fishing impact
Fishing techniques may be altered to minimize bycatch and reduce impacts on marine habitats. These techniques include using varied gear types depending on target species and habitat type. For example, a net with larger holes will allow undersized fish to avoid capture. A turtle excluder device (TED) allows sea turtles and other megafauna to escape from shrimp trawls. Avoiding fishing in spawning grounds may allow fish stocks to rebuild by giving adults a chance to reproduce.
Aquaculture
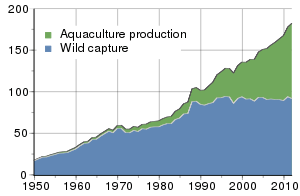
Aquaculture involves the farming of fish in captivity. This approach effectively privatizes fish stocks and creates incentives for farmers to conserve their stocks. It also reduces environmental impact. However, farming carnivorous fish, such as salmon, does not always reduce pressure on wild fisheries, since carnivorous farmed fish are usually fed fishmeal and fish oil extracted from wild forage fish.
Aquaculture played a minor role in the harvesting of marine organisms until the 1970s. Growth in aquaculture increased rapidly in the 1990s when the rate of wild capture plateaued. Aquaculture now provides approximately half of all harvested aquatic organisms. Aquaculture production rates continue to grow while wild harvest remains steady.
Fish farming can enclose the entire breeding cycle of the fish, with fish being bred in captivity. Some fish prove difficult to breed in captivity and can be caught in the wild as juveniles and brought into captivity to increase their weight. With scientific progress, more species are being made to breed in captivity. This was the case with southern bluefin tuna, which were first bred in captivity in 2009.[44]
Consumer awareness
As global citizens become more aware of overfishing and the ecological destruction of the oceans, movements have sprung up to encourage abstinence[45]—not eating any seafood—or eating only "sustainable seafood".
Sustainable seafood is a movement that has gained momentum as more people become aware of overfishing and environmentally destructive fishing methods. Sustainable seafood is seafood from either fished or farmed sources that can maintain or increase production in the future without jeopardizing the ecosystems from which it was acquired. In general, slow-growing fish that reproduce late in life, such as orange roughy, are vulnerable to overfishing. Seafood species that grow quickly and breed young, such as anchovies and sardines, are much more resistant to overfishing. Several organizations, including the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC), and Friend of the Sea, certify seafood fisheries as sustainable.
The Marine Stewardship Council has developed an environmental standard for sustainable and well-managed fisheries. Environmentally responsible fisheries management and practices are rewarded with the use of its blue product ecolabel. Consumers concerned about overfishing and its consequences are increasingly able to choose seafood products that have been independently assessed against the MSC's environmental standard. This enables consumers to play a part in reversing the decline of fish stocks. As of February 2012, over 100 fisheries around the world have been independently assessed and certified as meeting the MSC standard. Their where-to-buy page lists the currently available certified seafood. As of February 2012, over 13,000 MSC-labelled products are available in 74 countries around the world. Fish & Kids is an MSC project to teach schoolchildren about marine environmental issues, including overfishing.
The Monterey Bay Aquarium's Seafood Watch Program, although not an official certifying body like the MSC, also provides guidance on the sustainability of certain fish species.[46] Some seafood restaurants have begun to offer more sustainable seafood options. The Seafood Choices Alliance[47] is an organization whose members include chefs that serve sustainable seafood at their establishments. In the US, the Sustainable Fisheries Act defines sustainable practices through national standards. Although there is no official certifying body like the MSC, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has created FishWatch to help guide concerned consumers to sustainable seafood choices.
In September 2016, a partnership of Google and Oceana and Skytruth introduced Global Fishing Watch, a website designed to assist citizens of the globe in monitoring fishing activities.[48][49][50]
Barriers to effective management
The fishing industry has a strong financial incentive to oppose some measures aimed at improving the sustainability of fish stocks.[5] Recreational fisherman also has an interest in maintaining access to fish stocks. This leads to extensive lobbying that can block or water down government policies intended to prevent overfishing.
Outside of countries' exclusive economic zones, fishing is difficult to control. Large oceangoing fishing boats are free to exploit fish stocks at will.
In waters that are the subject of territorial disputes, countries may actively encourage overfishing. A notable example is the cod wars where Britain used its navy to protect its trawlers fishing in Iceland's exclusive economic zone. Fish are highly transitory. Many species will freely move through different jurisdictions. The conservation efforts of one country can then be exploited by another.
While governments can create regulations to control people's behaviors this can be undermined by illegal fishing activity. Estimates of the size of the illegal catch range from 11 to 26 million tonnes, which represents 14-33% of the world's reported catch.[51] Illegal fishing can take many forms. In some developing countries, large numbers of poor people are dependent on fishing. It can prove difficult to regulate this kind of overfishing, especially for weak governments. Even in regulated environments, illegal fishing may occur. While industrial fishing is often effectively controlled, smaller scale and recreational fishermen can often break regulations such as bag limits and seasonal closures. Fisherman can also easily fish illegally by doing things such as underreporting the amount of fish they caught or reporting that they caught one type of fish while actually catching another.[52] There is also a large problem with the surveillance of illegal fishing activity. In 2001, the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), passed the International Plan of Action to Prevent, Deter and Eliminate Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated Fishing (IPOA-IUU). This is an agreement with the intention to stop port states from allowing boats to dock that participated in illegal, unreported or unregulated fishing. It also gives details for port states on effective measures of inspecting and reporting illegal fishing.[53] Some illegal fishing takes place on an industrial scale with financed commercial operations.
The fishing capacity problem is not only related to the conservation of fish stocks but also to the sustainability of fishing activity. Causes of the fishing problem can be found in the property rights regime of fishing resources. Overexploitation and rent dissipation of fishermen arise in open-access fisheries as was shown in Gordon.[54][55]
In open-access resources like fish stocks, in the absence of a system like individual transferable quotas, the impossibility of excluding others provokes the fishermen who want to increase catch to do so effectively by taking someone else' share, intensifying competition. This tragedy of the commons provokes a capitalization process that leads them to increase their costs until they are equal to their revenue, dissipating their rent completely.
Resistance from fishermen
There is always disagreement between fishermen and government scientists... Imagine an overfished area of the sea in the shape of a hockey field with nets at either end. The few fish left therein would gather around the goals because of fish like structured habitats. Scientists would survey the entire field, make lots of unsuccessful hauls, and conclude that it contains few fish. The fishermen would make a beeline to the goals, catch the fish around them, and say the scientists do not know what they are talking about. The subjective impression the fishermen get is always that there's lots of fish - because they only go to places that still have them... fisheries scientists survey and compare entire areas, not only the productive fishing spots.[56] –Fisheries scientist Daniel Pauly
See also
- Biodiversity
- Bycatch
- Catch and release
- Environmental impact of fishing
- Factory ship
- Pacific bluefin tuna
- Shark finning
- Holocene extinction
- Human overpopulation
- Jellyfish blooms
- Life history theory
- List of harvested aquatic animals by weight
- Natural environment
- Maximum sustainable yield
- Oceanic carbon cycle
- Population dynamics of fisheries
- Sustainable fishing
- Tragedy of the commons
- World Oceans Day
- The United Nations Ocean Conference
References
Citations
- "Overfishing". National Geographic. 2010-04-27. Retrieved 2019-12-29.
- The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018; Meeting the sustainable development goals (PDF). Rome: FAO. 2018. p. 40. ISBN 978-92-5-130562-1. Retrieved 29 December 2019.
- Scales, Helen (29 March 2007). "Shark Declines Threaten Shellfish Stocks, Study Says". National Geographic News. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- fao.org. "SOFIA 2018 - State of Fisheries and Aquaculture in the world 2018". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- Bolster, W. Jeffery (2012). The Mortal Sea: Fishing the Atlantic in the Age of Sail. Belknap Press. ISBN 978-0-674-04765-5.
- In brief, The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture, 2018 (PDF). FAO. 2018.
- Pauly, Daniel. Fisheries on the brink (YouTube video). Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- Lu Hui, ed. (16 August 2006). "Pollution, overfishing destroy East China Sea fishery". Xinhua on GOV.cn. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- "Peruvian Anchovy Case: Anchovy Depletion and Trade". Trade and Environment Database. 1999. Retrieved 2012-01-05.
- Foreign Assistance Legislation for Fiscal Year 1982. Committee on Foreign Affairs. 1981.
- "Peru - Fishing". Federal Research Division of the U.S. Library of Congress. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- Kunzig, R (April 1995). "Twilight of the Cod". Discover: 52. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- Kurlansky 1997
- Fishing, Costa Rica Experts. "Fishing Costa Rica".
- Floyd, Mark (2007). "Long-lived deep-sea fishes imperilled by technology, overfishing". AAAS. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- .http://awsassets.wwf.org.au/downloads/mo038_living_blue_planet_report_16sep15.pdf
- Specia, Megan (5 January 2019). "Japan's 'King of Tuna' Pays Record $3 Million for Bluefin at New Tokyo Fish Market". New York Times. Retrieved 19 December 2019.
- Gaia Vince. "BBC - Future - How the world's oceans could be running out of fish". BBC.
- "Once Decimated U.S. Fish Stocks Enjoy Big Bounce Back". National Ggeographic. 2013-03-26.
- Black, Richard (8 October 2008). "Fisheries waste costs billions". BBC News. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- Owen, James. "Overfishing Is Emptying World's Rivers, Lakes, Experts Warn". National Geographic News. Retrieved 16 October 2013.
- Richardson, Anthony J.; Bakun, Andrew; Hays, Graeme C.; Gibbons, Mark J. (2009-06-01). "The jellyfish joyride: causes, consequences and management responses to a more gelatinous future". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 24 (6): 312–322. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2009.01.010. PMID 19324452.
- Lynam, C. P.; Lilley, M. K. S.; Bastian, T.; Doyle, T. K.; Beggs, S. E.; Hays, G. C. (2011-02-01). "Have jellyfish in the Irish Sea benefited from climate change and overfishing?". Global Change Biology. 17 (2): 767–782. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02352.x. ISSN 1365-2486.
- "Fish recruitment". The Scottish Government. 2009-12-08. Retrieved 16 October 2013.
- Pauly 1983
- "Growth overfishing". Archived from the original on 2012-04-25. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- Pauly, D.; G. Silvestre; I.R. Smith (1989). "On development, fisheries and dynamite: a brief review of tropical fisheries management" (PDF). Natural Resource Modeling. 3 (3): 307–329. doi:10.1111/j.1939-7445.1989.tb00084.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 August 2012. Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- Froese, Rainer; Branch, Trevor A; Proelß, Alexander; Quaas, Martin; Sainsbury, Keith; Zimmermann, Christopher (1 September 2011). "Generic harvest control rules for European fisheries" (PDF). Fish and Fisheries. 12 (3): 340–351. doi:10.1111/j.1467-2979.2010.00387.x.
- Coad, Brian W; McAllister, Don E (2008). "Dictionary of Ichthyology". Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- Kirkley, J.E; Squires, D (1999), "Capacity and Capacity Utilization in Fishing Industries, Discussion paper 99-16", Department of Economics, University of California, San Diego
- Vestergaard, N.; Squires, D.; Kirkley, J.E. (2003). "Measuring Capacity and Capacity Utilization in Fisheries. The Case of the Danish Gillnet Fleet". Fisheries Research. 60 (2–3): 357–68. doi:10.1016/S0165-7836(02)00141-8.
- "Text of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea: Part V". Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- Benjamin, Daniel K (2001). "Fisheries are Classic Example of the Tragedy of the Commons". PERC Reports. 19 (1). Archived from the original on 2005-02-19.
- "What do fishing and family planning have in common?". Deutsche Welle. 2016-12-20. Retrieved 2019-01-28.
- "Guide to Good Fish Guides". Overfishing. Retrieved 19 December 2019.
- Moustakas, Silvert & Dimitromanolakis 2006
- Pearson, Aria (6 January 2009). "Why storms are good news for fishermen". New Scientist (2689). Retrieved 2012-05-01.(subscription required)
- Costello, Gaines & Lynham 2008
- MacKenzie, Debora. "Guaranteed fish quotas halt commercial free-for-all". New Scientist. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- "A Rising Tide: Scientists find proof that privatising fishing stocks can avert a disaster". The Economist. 18 September 2008. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- "New study offers solution to global fisheries collapse". Eureka alert. 18 September 2008. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- Zhang Xiang, ed. (9 June 2009). "South China Sea fishing ban "indisputable": foreign ministry spokesman". Chinaview. Archived from the original on 4 November 2012. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- "The last wild hunt – Deep-sea fisheries scrape bottom of the sea" (PDF). AAAS. 2007. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- "The Top 10 Everything of 2009: Top 10 Scientific Discoveries: 5. Breeding Tuna on Land". Time. 8 December 2009. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- Monbiot, George (9 May 2019). "Stop eating fish. It's the only way to save the life in our seas" (Opinion). The Guardian. Retrieved 19 December 2019.
- "Monterey Bay Aquarium: Seafood Watch Program - Frequently Asked Questions". Archived from the original on 2009-02-15. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- "Seafood Choices - Promoting Sustainable Seafood". seafoodchoices.com. Archived from the original on 2006-03-23.
- Google Launches Global Fishing Watch—Digital Trends (September 16, 2016)
- Oceana Unveils Global Fishing Watch—Huffington Post (September 15, 2016)
- Illegal fishing targeted by crowdsourcing thanks to new Global Fishing Watch website—ABC News (Australia) (September 15, 2016)
- "Illegal fishing « World Ocean Review". worldoceanreview.com.
- Sumaila, U. R.; Alder, J.; Keith, H. (2006-11-01). "Global scope and economics of illegal fishing". Marine Policy. 30 (6): 696–703. doi:10.1016/j.marpol.2005.11.001.
- "INTERNATIONAL PLAN OF ACTION TO PREVENT, DETER AND ELIMINATE ILLEGAL, UNREPORTED AND UNREGULATED FISHING". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2016-11-17.
- Gordon, H. S. (1953). "An Economic Approach to the optimum utilization of Fishery Resources". Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada. 10 (7): 442–57. doi:10.1139/f53-026.
- Gordon, H.S. (1954). "The Economic Theory of a Common-Property Resource: The Fishery". Journal of Political Economy. 62 (2): 124–42. doi:10.1086/257497.
- Boyes, Margaret (March 2008). "An interview with Daniel Pauly" (PDF). Fisherman Life. Retrieved 2019-12-19.
Sources
- MN DNR. (2018). Improving fishing: Adjust regulations - Division of Fisheries - Minnesota DNR - MN Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved from https://www.dnr.state.mn.us/fisheries/management/regs.html
![]()
Bibliography
- Hilborn, Ray; Hilborn, Ulrike (2012). Overfishing: What Everyone Needs to Know. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0199798148.
- Allan, J David; Abell, Robin; Hogan, Zeb; Revenga, Carmen; Taylor, Brad W; Welcomme, Robin L; Winemiller, Kirk (2005) Overfishing of inland waters. BioScience, 5 December.
- Clover, Charles (2004) End of the Line: How overfishing is changing the world and what we eat. Ebury Press, London. ISBN 0-09-189780-7
- Costello, Christopher; Gaines, Steven D; Lynham, John (2008). "Can Catch Shares Prevent Fisheries Collapse?". Science. 321 (5896): 1678–1681. doi:10.1126/science.1159478. PMID 18801999. Retrieved 2012-05-01.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Kurlansky, Mark (1997). "11–12". Cod: A Biography of the Fish That Changed the World. New York: Walker. ISBN 978-0-8027-1326-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Loder, Natasha (July–September 2005). "Point of No Return". Conservation. 6 (3): 28–34. Archived from the original on 2008-12-01. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- Olden, Julian D.; Hogan, Zeb S.; Zanden, M. Jake Vander (2007). "Small fish, big fish, red fish, blue fish: size‐biased extinction risk of the world's freshwater and marine fishes" (PDF). Global Ecology and Biogeography. 16 (6): 694–701. doi:10.1111/j.1466-8238.2007.00337.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-24. Retrieved 2012-05-01.
- Moustakas, A; Silvert, W; Dimitromanolakis, A (2006). "A spatially explicit learning model of migratory fish and fishers for evaluating closed areas" (PDF). Ecological Modelling. 192 (1–2): 245–258. doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2005.07.007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-01. Retrieved 2012-05-01.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Myers, Ransom A. and Boris Worm (2003) "Rapid Worldwide Depletion of Predatory Fish Communities," Nature, 423, 280–283.(subscription required)
- Myers, Ransom A. and Boris Worm (2005) "Decline of Pacific tuna populations exaggerated," Nature 434:E1-E2.(subscription required)
- Pauly, Daniel (1983). Some simple methods for the assessment of tropical fish stocks. FAO Fisheries technical paper 234. ISBN 978-92-5-101333-5. Retrieved 2012-05-01.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Roberts, Callum (2007) The Unnatural History of the Sea Island Press. ISBN 978-1-59726-102-9
- Young, Margaret (2011). Trading Fish, Saving Fish: The Interaction between Regimes in International Law. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521765725.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Overfishing. |
- The World Is Running Out of Fish Faster Than We Thought (15 December 2016), Vice
- "Overfishing Factsheet". Waitt Institute. Retrieved 2016-04-08.
- Jackson, J. "Ocean Appocolypse Now". UCSB. Retrieved 2015-06-08.
- Microdocs: City vs. village fishing
- Bye bye bluefin: Managed to death, The Economist. 30 October 2008. Retrieved 6 February 2009.

