Giant Pacific octopus
The giant Pacific octopus (Enteroctopus dofleini, formerly also Octopus apollyon), also known as the North Pacific giant octopus, is a large marine cephalopod belonging to the genus Enteroctopus. Its spatial distribution includes the coastal North Pacific, along California, Oregon, Washington, British Columbia, Alaska, Russia, Japan, and Korean Peninsula.[1] It can be found from the intertidal zone down to 2,000 m (6,600 ft), and is best adapted to cold, oxygen-rich water. It is the largest octopus species, based on a scientific record of a 71-kg (156-lb) individual weighed live.[2]
| Giant Pacific octopus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| E. dofleini observed off Point Piños, California, at a depth of 65 m (213 ft) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Cephalopoda |
| Order: | Octopoda |
| Family: | Enteroctopodidae |
| Genus: | Enteroctopus |
| Species: | E. dofleini |
| Binomial name | |
| Enteroctopus dofleini (Wülker, 1910) | |
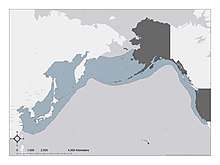 | |
| Distribution of E. dofleini | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Size and description


All cephalopods have bilateral symmetry, a shell gland, a mantle, and a well-developed head with sucker-covered arms. The octopus has eight arms, each of which has two rows of suckers. Many of the suckers are lined with papillae or hooks for adhesion.[3] The web between the arms can be expanded to form a parachute-like structure to capture prey.[3] In the center of the arms is a mouth, containing beak and radula (toothed-tongue).

Cephalopods have a paralytic and digestive toxin in two salivary glands to aid in opening prey.[3] Water is pulled into the mantle and over gills or lamellae for oxygen uptake, and can be ejected forcefully through the siphon for jet propulsion. They are able to reach speeds up to 40 km/h (25 mph) for short sprints. They tend to use their arms as legs, and slowly crawl along the bottom.[4] The siphon is also used to expel ink for escaping predators. The entire body of the octopus is compressible, so they are able to fit through any opening slightly bigger than the size of their beaks (the only hard part of their bodies). Their arms are muscular hydrostats, which lengthen, contract, and contort.[4] Octopuses are poikilothermic or cool-blooded, and have three hearts and blue, copper-based blood.[1]
The mantle of the octopus is spherical in shape and contains most of the animal's major organs. By contracting or expanding tiny pigment-containing sacs within cells known as chromatophores, an octopus can change the color of its skin, giving it the ability to blend into the environment. Subcategories of chromatophores include iridophores (reflective platelets) and leucophores (refractive platelets).[1] Octopuses are also able to alter their skin texture, providing even better camouflage. Dermal muscles in the octopus's skin can create a heavily textured look through papillation, or cause skin to appear smooth.[5] All of these abilities are under nervous system control.
E. dofleini is distinguished from other species by its large size. Adults usually weigh around 15 kg (33 lb), with an arm span up to 4.3 m (14 ft).[6] The larger individuals have been measured at 50 kg (110 lb) and have a radial span of 6 m (20 ft)[1] American zoologist G.H. Parker found that the largest suckers on a giant Pacific octopus are about 6.4 cm (2.5 in) and can support 16 kg (35 lb) each.[1] The alternative contender for the largest species of octopus is the seven-arm octopus (Haliphron atlanticus) based on a 61-kg (134-lb) incomplete carcass estimated to have a live mass of 75 kg (165 lb).[7][8] However, a number of questionable size records would suggest E. dofleini is the largest of all octopus species by a considerable margin,[9] including a report of one up to 272 kg (600 lb) in weight with a 9-m (30-ft) arm span.[10] Guinness World Records lists the biggest as 136 kg (300 lb) with an arm span of 9.8 m (32 ft).[1][11] A UN catalog of octopuses sizes E. dofleini at 180 kg (396 lb) with an arm length of 3 m (9.8 ft).[12]
Ecology
Diet
E. dofleini preys upon shrimp, crabs, scallop, abalone, cockles, snails, clams, lobsters, fish, and other octopuses.[13][14] Food is procured with its suckers and then bitten using its tough beak of chitin. It has also been observed to catch spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias) up to 1.2 m (4 ft) in length while in captivity.[15] Additionally, consumed carcasses of this same shark species have been found in giant Pacific octopus middens in the wild, providing strong evidence of these octopuses preying on small sharks in their natural habitat.[16] In May 2012, amateur photographer Ginger Morneau was widely reported to have photographed a wild giant Pacific octopus attacking and drowning a seagull, demonstrating that this species is not above eating any available source of food within its size range, even birds.[17]
Predators
Scavengers and other organisms often attempt to eat octopus eggs, even when the female is present to protect them. Giant Pacific octopus paralarvae are preyed upon by many other zooplankton and filter feeders. Marine mammals, such as harbor seals, sea otters, and sperm whales depend upon the giant Pacific octopus as a source of food. Pacific sleeper sharks are also confirmed predators of this species.[18] In addition, the octopus (along with cuttlefish and squid) are major sources of protein for human consumption. About 3.3 million tons are commercially fished, worth $6 billion annually.[1] Over thousands of years, humans have caught them using lures, spears, pot traps, nets, and bare hands.[4] The octopus is parasitized by Dicyemodeca anthinocephalum, which lives in their renal appendages.[19]

Lifespan and reproduction

The giant Pacific octopus is considered to be long-lived compared to other species, with lifespans typically 3–5 years in the wild. Many other octopuses go through a lifespan in one year, from egg to end of life.[1] To make up for its relatively short lifespan, the octopus is extremely prolific. It can lay between 120,000 and 400,000 eggs which are intensively cared for by the females. The female stops eating during this care and her life ends soon after the eggs hatch.[20] Eggs are coated in chorion, and the female attaches the eggs to a hard surface. She continuously blows water over the eggs, and grooms them to remove algae and other growths. Eggs hatch in about 6 months.[4] Hatchlings are about the size of a grain of rice,[21] and very few survive to adulthood. Their growth rate is incredibly high. Starting from 3⁄100ths of a gram and growing to 20–40 kg (44–88 lb) at adulthood, which is an increase of around 0.9% of growth a day.[1] Because they are cool-blooded, they are able to convert most of consumed energy into body mass, respiration, activity, and reproduction.[4]
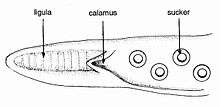
During reproduction, the male octopus deposits a spermatophore (or sperm packet) more than 1 m long using his hectocotylus (specialized arm) in the female's mantle. Large spermatophores are characteristic of octopuses in this genus.[9] The female stores the spermatophore in her spermatheca until she is ready to fertilize her eggs. One female at the Seattle Aquarium was observed to hold onto the spermatophore for seven months before laying fertilized eggs.[4]
Giant Pacific octopuses are semelparous; they breed once before death. After reproduction, they enter a stage called senescence, which involves obvious changes in behavior and appearance, including a reduced appetite, retraction of skin around the eyes giving them a more pronounced appearance, increased activity in uncoordinated patterns, and white lesions all over the body. While the duration of this stage is variable, it typically lasts about one to two months. Death is typically attributed to starvation, as the females stop hunting and instead protect their eggs; males often spend more time in the open, making them more likely to be preyed upon.[22]
Intelligence
_(7007259144).jpg)
Octopuses are ranked as the most intelligent invertebrates.[23] Giant Pacific Octopuses are commonly kept on display at aquariums due to their size and interesting physiology, and have demonstrated the ability to recognize humans that they frequently come in contact with. These responses include jetting water, changing body texture, and other behaviors that are consistently demonstrated to specific individuals.[24] They have the ability to solve simple puzzles, open childproof bottles and use tools.[4] The octopus brain has folded lobes (a distinct characteristic of complexity), visual and tactile memory centers. They have about 300 million neurons.[4] They have been known to open tank valves, disassemble expensive equipment, and generally wreak havoc in labs and aquaria.[4] Some researchers even claim that they are capable of motor play[25] and having personalities.[3]
Conservation and climate change
Giant Pacific octopuses are not currently under the protection of Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora or evaluated in the IUCN Red List.[26] The giant Pacific octopus has not been assessed by the Monterey Bay Aquarium Seafood Watch, although other octopus species are listed.[27] Combined with lack of assessment and mislabeling, tracking the species' abundance is nearly impossible. Scientists have relied on catch numbers to estimate stock abundance, but the animals are solitary and difficult to find.[4] DNA techniques have assisted in genetic and phylogenetic analysis of the species' evolutionary past. After DNA analysis, the giant Pacific octopus may actually be three subspecies (one in Japan, another in Alaska, and a third in Puget Sound).
In Puget Sound, the Washington Fish and Wildlife Commission adopted rules for protecting the harvest of giant Pacific octopuses at seven sites, after a legal harvest caused a public outcry.[28] Populations in Puget Sound are not considered threatened.
Regardless of these data gaps in abundance estimates, future climate change scenarios may affect these organisms in different ways. Climate change is complex, with predicted biotic and abiotic changes to multiple processes including oxygen limitation, reproduction ocean acidification, toxins, effects on other trophic levels, and RNA editing.
Oxygen limitation
Octopuses have been found to migrate for a variety of reasons. Using tag and recapture methods, scientists found they move from den to den in response to decreased food availability, change in water quality, increase in predation, or increased density (or decreased available habitat/den space)[29] Because their blue blood is copper-based (hemocyanin) and not an efficient oxygen carrier, octopuses favor and move toward cooler oxygen-rich water. This dependency limits octopus habitat, typically in temperate waters 8–12 °C (46–54 °F).[1] If sea water temperatures continue to rise, these organisms may be forced to move to deeper, cooler water.
Each fall in Washington's Hood Canal, a habitat for many octopuses, phytoplankton and macroalgae die and create a dead zone. As these micro-organisms decompose, oxygen is used up in the process and has been measured to be as low as 2 parts per million (ppm). This is a state of hypoxia. Normal levels are measured at 7–9 ppm.[30] Fish and octopuses move from the deep towards the shallow water for more oxygen. Females do not leave, and die with their eggs at nesting sites. Warming seawater temperatures promote phytoplankton growth, and annual dead zones have been found to be increasing in size.[4] To avoid these dead zones, octopuses must move to shallower waters which may be warmer in temperature and less oxygen-rich, trapping the organism between two low-oxygen zones.
Reproduction
Increased seawater temperatures also increase metabolic processes. The warmer the water, the faster octopus eggs develop and hatch.[1] After hatching, the paralarvae swim up to the surface to join other plankton, where they are often preyed upon by birds, fish, and other plankton feeders. Quicker hatching time may also affect critical timing with food availability.[31] One study found that higher water temperatures accelerated all aspects of reproduction and even shortened lifespan by up to 20%.[32] Other studies concur that warming climate scenarios result in higher embryo and paralarvae mortalites.[33]
Ocean acidification
The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, industrialization, and other land-use changes cause increased carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere. The ocean absorbs an estimated 30% of emitted anthropogenic CO2.[34] As the ocean absorbs CO2, it becomes more acidic and lowers in pH. Ocean acidification lowers available carbonate ions, which is a building block for calcium carbonate (CaCO3). Calcifying organisms use calcium carbonate to produce shells, skeletons, and tests.[35] The prey base that octopuses prefer (crab, clams, scallops, mussels, etc.) are negatively impacted by ocean acidification, and may decrease in abundance. Shifts in available prey may force a change upon octopus diets to other nonshelled organisms.
Because octopuses have hemocyanin as copper-based blood, a small change in pH can reduce oxygen-carrying capacity. A pH change from 8.0 to 7.7 or 7.5 will have life-or-death effects on cephalopods.[4]
Toxins
Dr. Roland Anderson, an octopus specialist, found high concentrations of heavy metals and PCBs in tissues and digestive glands. He suggests that these high concentrations were obtained from their preferred prey, red rock crab (Cancer productus).[36] These crabs bury themselves in contaminated sediments and eat prey that live nearby.[1] What effects these toxins have on octopuses are unknown, but other exposed animals have been known to show liver damage, changes in immune systems, and death.
Effects on other trophic levels
Potential changes in octopus populations will affect upper and lower trophic levels.[31] Lower trophic levels include all prey items, and may fluctuate inversely with octopus abundance. Higher trophic levels include all predators of octopuses, and may fluctuate inversely with octopus abundance, although many may prey upon a variety of organisms. Protection of other threatened species may affect octopus populations (the sea otter, for example), as they may rely on octopuses for food. Some research suggests that fishing other species have aided octopus populations, by taking out predators and competitors.
RNA editing
Some octopuses exhibit the ability to alter speeds of sodium and potassium ion movement across cell membranes, allowing them to live in very cold water. Joshua Rosenthal, at the University of Puerto Rico's Institute of Neurobiology has found that they have altered protein synthesis, and can speed up potassium channels in cold water, to keep up with sodium ion exchange. He is now looking into whether individuals can alter their protein synthesis in response to changing temperatures, or if it is done over long-term adaptations. If changes are possible by the individual, octopuses may be able to adapt quickly to changing climate scenarios.[4]
See also
- Octopus wrestling
- Cephalopod size
References
- Cosgrove, James (2009). Super Suckers, The Giant Pacific octopus. BC: Harbour Publishing. ISBN 978-1-55017-466-3.
- Cosgrove, J.A. 1987. Aspects of the Natural History of Octopus dofleini, the Giant Pacific Octopus. M.Sc. Thesis. Department of Biology, University of Victoria (Canada), 101 pp.
- Mather, J.A.; Kuba, M.J. (2013). "The cephalopod specialties: complex nervous system, learning and cognition". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 91 (6): 431–449. doi:10.1139/cjz-2013-0009.
- Courage, Katherine Harmon (2013). Octopus!. USA: The Penguin Group. ISBN 978-1-59184-527-0.
- Mather, J.A.; Kuba, M.J. (2013). "The cephalopod specialties: Complex nervous system, learning, and cognition". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 91 (6): 431–449. doi:10.1139/cjz-2013-0009.
- Smithsonian National Zoological Park: Giant Pacific Octopus Archived 23 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- O'Shea, S. (2004). "The giant octopus Haliphron atlanticus (Mollusca : Octopoda) in New Zealand waters". New Zealand Journal of Zoology. 31 (1): 7–13. doi:10.1080/03014223.2004.9518353.
- O'Shea, S. (2002). "Haliphron atlanticus – a giant gelatinous octopus" (PDF). Biodiversity Update. 5: 1.
- Norman, M. 2000. Cephalopods: A World Guide. Hackenheim, ConchBooks, p. 214. ISBN 978-3-925919-32-9
- High, W.L. (1976). "The Giant Pacific Octopus". U.S. National Marine Fisheries Service, Marine Fisheries Review. 38 (9): 17–22.
- McClain, Craig R.; Balk, Meghan A.; Benfield, Mark C.; Branch, Trevor A.; Chen, Catherine; Cosgrove, James; Dove, Alistair D.M.; Gaskins, Lindsay C.; Helm, Rebecca R. (13 January 2015). "Sizing ocean giants: patterns of intraspecific size variation in marine megafauna". PeerJ. 3: e715. doi:10.7717/peerj.715. ISSN 2167-8359. PMC 4304853. PMID 25649000.
- Jereb, Patrizia; Roper, Clyde; Norman, Mark; Finn, Julian (2016). Cephalopods of the World: An annotated and Illustrated Catalogue of cephalopod species known to date (PDF). Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. p. 124. ISBN 978-92-5-107989-8. Retrieved 23 February 2017.
- "Giant Pacific Octopus". Giant Pacific Octopus - Oceana.
- "Giant Pacific octopus facts". www.animalspot.net.
- "Octopus Eats Shark". Google Video. Retrieved 13 November 2012.
- Walla Walla University Marine Invertebrates Key: Giant Pacific Octopus Archived 14 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- McCulloch, S. (3 May 2012). "B.C. woman nets fame for photos of octopus eating seagull". National Post.
- Sigler, M. F.; L. B. Hulbert; C. R. Lunsford; N. H. Thompson; K. Burek; G. O'Corry-Crowe; A. C. Hirons (24 July 2006). "Diet of Pacific sleeper shark, a potential Steller sea lion predator, in the north-east Pacific Ocean" (PDF). Journal of Fish Biology. 69 (2): 392–405. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.330.8593. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2006.01096.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 May 2010.
- Furuya, Hidetaka; Tsuneki, Kazuhiko (2003). "Biology of Dicyemid Mesozoans". Zoological Science. 20 (5): 519–532. doi:10.2108/zsj.20.519. PMID 12777824.
- Scheel, David. "Giant Octopus: Fact Sheet". Alaska Pacific University. Archived from the original on 15 November 2012. Retrieved 13 November 2012.
- "Giant Pacific Octopus (Octopus dofleini)". NPCA. Archived from the original on 21 November 2008. Retrieved 13 November 2012.
- Anderson, R. C.; Wood, J. B.; Byrne, R. A. (2002). "Octopus Senescence: The Beginning of the End". Journal of Applied Animal Welfare Science. 5 (4): 275–283. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.567.3108. doi:10.1207/S15327604JAWS0504_02. PMID 16221078.
- Anderson, R. C. (2005). "How smart are octopuses?". Coral Magazine. 2: 44–48.
- Anderson, R. C.; Mather, J. A.; Monette, M. Q.; Zimsen, S. R. M. (2010). "Octopuses (Enteroctopus dofleini) Recognize Individual Humans". Journal of Applied Animal Welfare Science. 13 (3): 261–272. doi:10.1080/10888705.2010.483892. PMID 20563906.
- Tzar, Jennifer. "Through the Eye of an Octopus". Discover.
- "IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2". Archived from the original on 27 June 2014. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- "Monterey Bay Seafood Watch". Archived from the original on 13 May 2014.
- "Giant Pacific Octopus Rulemaking Process". Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- Mather, J.A.; Resler, S.; Cosgrove, J.A. (1985). "Activity and Movement patterns of Octopus dofleini". Journal of Marine Behavior and Physiology. 11 (4): 301–14. doi:10.1080/10236248509387055.
- Mather, J.A. (2010). Octopus: The Ocean's Intelligent Invertebrate. Portland. London.: J.B. Timber Press. ISBN 978-1-60469-067-5.
- Andre, J; Haddon, M.; Pecl, G.T. (2010). "Modeling climate-change induced nonlinear thresholds in cephalopod population dynamics". Global Change Biology. 16 (10): 2866–2875. Bibcode:2010GCBio..16.2866A. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02223.x.
- Forsythe, J.W.; Hanlon, R.T. (1988). "Effect of temperature on laboratory growth, reproduction, and life span of Octopus bimaculoides". Marine Biology. 98 (3): 369–379. doi:10.1007/bf00391113.
- Repolho, Tiago (2014). "Developmental and physiological challenges of octopus (Octopus vulgaris) early life stages under ocean warming". Journal of Comparative Physiology B. 184 (1): 55–64. doi:10.1007/s00360-013-0783-y. PMID 24100467.
- Guinotte, J.M.; Fabry, V.J. (2008). "Ocean acidification and its potential effects on marine ecosystems". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1134 (1): 320–342. Bibcode:2008NYASA1134..320G. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.316.7909. doi:10.1196/annals.1439.013. PMID 18566099.
- Gazeau, F.; Quiblier, C.; Jansen, J.M.; Gattuso, J.P.; Middelburg, J.J.; Heip, C.H. (2007). "Impact of elevated CO2 on shellfish calcification". Geophysical Research Letters. 34 (7): L07603. Bibcode:2007GeoRL..34.7603G. doi:10.1029/2006gl028554.
- Scheel, D.; Anderson, R. (2012). "Variability in the diet specialization of Enteroctopus dofleini (Cephalopoda: Octopodidae) in the eastern Pacific examined from midden contents". American Malacological Bulletin. 30 (2): 267–279. doi:10.4003/006.030.0206.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Enteroctopus dofleini. |
- "CephBase: Giant Pacific octopus". Archived from the original on 2005.
- The Cephalopod Page