Nottingham Forest F.C.
Nottingham Forest Football Club, often referred to as Forest, is a professional football club based in West Bridgford, Nottinghamshire, England. Founded in 1865, Forest are now considered the oldest football league club in England after the relegation of Notts County to the National League in 2019.[3] Since 1898 Forest have played their home matches at the City Ground. They currently compete in the EFL Championship, the second tier of the English football league system.
 | |||
| Full name | Nottingham Forest Football Club | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nickname(s) | Forest, The Reds, Tricky Trees | ||
| Founded | 1865[1] | ||
| Ground | City Ground | ||
| Capacity | 30,446 | ||
| Owner | Evangelos Marinakis, Sokratis Kominakis[2] | ||
| Chairman | Nicholas Randall QC[2] | ||
| Head coach | Sabri Lamouchi | ||
| League | Championship | ||
| 2018–19 | Championship, 9th of 24 | ||
| Website | Club website | ||
|
| |||
Forest have won one League title, two FA Cups, four League Cups, one FA Charity Shield, two European Cups, and one UEFA Super Cup. The club has competed in the top two tiers of English football since their admission to the Football League, except for five seasons spent in the third tier. Their most successful period was under the management of Brian Clough and Peter Taylor in the late 1970s and early 1980s.
In Clough's last decade at the club, Forest won the 1989 and 1990 League Cups and were losing finalists in the 1991 FA Cup Final, before relegation from the Premier League in 1993. Upon an immediate return Forest finished third in the Premier League in 1995, before the club suffered relegation again in 1997 and, after a brief return, once more in 1999. Forest have not been back in the Premier League since.
Forest contest the Nottingham derby with city rivals Notts County, however as Forest have predominantly played in higher leagues than their neighbours fixtures between the two clubs have been rare in recent history. As such their main rivalry is with Derby County, and matches between the two clubs are known as the East Midlands derby.
History
19th century
In 1865 a group of shinty players met at the Clinton Arms on Nottingham's Shakespeare Street. J. S. Scrimshaw's proposal to play association football instead was agreed and Nottingham Forest Football Club was formed. It was agreed at the same meeting that the club would purchase twelve tasselled caps coloured 'Garibaldi Red' (named after the leader of the Italian 'Redshirts' fighters). Thus the club's official colours were established. Forest's first ever official game was played against Notts County taking place on 22 March 1866.[4]
In their early years Forest were a multi-sports club. As well as their roots in bandy and shinty, Forest's baseball club were British champions in 1899.[5] Forest's charitable approach helped clubs like Liverpool, Arsenal and Brighton & Hove Albion to form. In 1886, Forest donated a set of football kits to help Arsenal establish themselves – the North London team still wear red. Forest also donated shirts to Everton and helped secure a site to play on for Brighton.
In 1878–79 season Forest entered the FA Cup for the first time. Forest beat Notts County 3–1 in the first round at Beeston Cricket Ground before eventually losing 2–1 to Old Etonians in the semi-final.[4]
Forest's application was rejected to join the Football League at its formation in 1888.[4] Forest instead joined the Football Alliance in 1889.
They won the competition in 1892 before then entering the Football League.[4] That season they reached and lost in an FA Cup semi-final for the fourth time to date. This time it was to West Bromwich Albion after a replay.

Forest's first FA Cup semi-final win was at the fifth attempt, the 1897–98 FA Cup 2–0 replay win against Southampton. The first game was drawn 1–1. Derby County beat Forest 5–0 five days before the final. Six of the cup final side were rested in that league game.[4] In that 1898 FA Cup Final at Crystal Palace before 62,000 fans, Willie Wragg passed a 19th minute free kick to Arthur Capes. Capes shot through the defensive wall to score. Derby equalised with a free kick headed home by Steve Bloomer off the underside of the cross bar after 31 minutes. In the 42nd minute Jack Fryer was unable to hold a Charlie Richards shot giving Capes a tap in for his second goal. Wragg's injury meant Forest had to change their line up with Capes dropping back to midfield. In the 86th minute John Boag headed away a corner by Forest. John McPherson moved in to collect shooting low into the goal to win 3–1.[6]
First half of 20th century
Forest lost FA Cup semi-finals in 1900 and 1902. They finished fourth in the 1900–01 Football League followed with fifth place the season after. The club then started to slide down the table. Forest were relegated for the first time in 1905–06. Grenville Morris had his first of five seasons as the club's highest scorer en route to becoming the all-time club highest goalscorer with 213 goals.
Promotion as champions was immediate in 1906–07. They were relegated a second time to the Second Division in 1911 and had to seek re-election in 1914 after finishing bottom of that tier. As World War One approached they were in serious financial trouble. The outbreak of The Great War along with the benevolence of the committee members mitigated the club going under.[4]
In 1919, the Football League First Division was to be expanded from twenty clubs to twenty-two in time for the 1919–20 Football League: Forest were one of eight clubs to campaign for entry but received only three votes. Arsenal and Chelsea gained the two additional top tier slots.[7]
In a turnaround from the first six seasons struggling back in the Second Division, Forest were promoted as champions in 1921–22. They survived each of the first two seasons back in the top flight by one position. In the third season after promotion they were relegated as the division's bottom club in 1924–25. They remained in the second tier until relegation in 1949 to the Football League Third Division.
Re-emergence then decline (1950–74)
They were quickly promoted back two years later as champions having scored a record 110 goals in the 1950–51 season. They regained First Division status in 1957.[4]
Johnny Quigley's solitary 1958–59 FA Cup semi-final goal beat Aston Villa. Billy Walker's Forest beat Luton Town 2–1 in the 1959 FA Cup Final. Like in 1898 Forest had lost heavily to their opponents only weeks earlier in the league.[4] Stewart Imlach crossed for a 10th-minute opener by Roy Dwight (the cousin of Reg Dwight better known as Elton John). Tommy Wilson had Forest 2–0 up after 14 minutes. The game had an unusually large number of stoppages due to injury, particularly to Forest players. This was put down to the lush nature of the Wembley turf. The most notable of these stoppages was Dwight breaking his leg in a 33rd minute tackle with Brendan McNally. Forest had been on top until that point. Luton though gradually took control of the match with Dave Pacey scoring midway through the second half. Forest were reduced to nine fit men with ten minutes remaining when Bill Whare crippled with cramp became little more than a spectator. Despite late Allan Brown and Billy Bingham chances Chick Thomson conceded no further goals for Forest to beat the Wembley 1950s 'hoodoo' (where one team was hampered by losing a player through injury).[8] Club record appearance holder Bobby McKinlay played in the final winning team captained by Jack Burkitt.
By this time Forest had replaced Notts County as the biggest club in Nottingham. Johnny Carey assembled a team including Joe Baker and Ian Storey-Moore that for a long spell went largely unchanged in challenging for the 1966–67 Football League title. They beat title rivals Manchester United 4–1 at the City Ground on 1 October.[9] The 3–0 win against Aston Villa on 15 April had Forest second in the table a point behind United.[10] Injuries eventually took effect meaning Forest had to settle for being League Runners-up and losing in the FA Cup semi-final to Dave Mackay's Tottenham Hotspur.[4]
The 1966/67 season's success seemed an opportunity to build upon with crowds of 40,000 virtually guaranteed at the time. Instead a mixture at the club of poor football management, the unique committee structure and proud amateurism meant decline after the 66/67 peak. Despite Peter Cormack being in the team Forest were relegated from the top flight in 1972. Matt Gillies' October 1972 managerial departure was followed by short managerial reigns by Dave Mackay and Allan Brown.[4] A 0–2 Boxing Day home defeat by Notts County prompted the committee (Forest had no board of directors then) to sack Brown.
Brian Clough and Peter Taylor (1975–82)

Brian Clough became manager of Nottingham Forest on 6 January 1975 twelve weeks after the end of his 44-day tenure as manager of Leeds United.[11] Clough brought Jimmy Gordon to be his club trainer as Gordon had been for him at Derby County and Leeds United.[12] Scottish centre-forward Neil Martin scored the only goal beating Tottenham Hotspur in Clough's FA Cup third round replay first game in charge.[13]
Ian Bowyer was already at Forest and had won domestic and European trophies with Manchester City. Clough signed Scots duo John McGovern and John O'Hare in February who both were part of Clough's Derby County 1971–72 Football League title win. He signed Colin Barrett in March initially on loan. Clough brought John Robertson and Martin O'Neill back into the fold after they had requested transfers under Brown.[4] Viv Anderson had previously debuted for the first team and became a regular under Clough.[14] The young Tony Woodcock was at Forest but was then unrated by Clough and was to be loaned to Lincoln City.[15] Forest were 13th in English football's second tier when Clough joined. They finished that season 16th. Forest signed Frank Clark in July of that close season on a free transfer.[16] The season after Forest finished eighth in Clough's 1975–76 Football League first full season in charge.[11] It was in this season McGovern became long standing club captain taking over from a game in which Bob 'Sammy' Chapman and Liam O'Kane were both injured.[17]
Peter Taylor on 16 July 1976 rejoined Clough becoming his Assistant Manager as he had been when winning the league at Derby.[11] Taylor included being the club's talent spotter in his role. After assessing the players Taylor told Clough "that was a feat by you to finish eighth in the Second Division because some of them are only Third Division players".[18] Taylor berated John Robertson for allowing himself to become overweight and disillusioned. He got Robertson on a diet and training regime that would help him become a European Cup winner.[19] Taylor turned Woodcock from a reserve midfielder into a 42 cap England striker.[20] In September 1976 he bought striker Peter Withe to Forest for £43,000, selling him to Newcastle United for £250,000 two years later.[21] Withe was replaced in the starting team by Garry Birtles who Taylor had scouted playing for non-league Long Eaton United. Birtles also went on to represent England.[22] In October 1976 Brian Clough acting on Peter Taylor's advice signed Larry Lloyd for £60,000 after an initial loan period.
Together Clough and Taylor took Forest to new heights. The first trophy of the Clough and Taylor reign was the 1976–77 Anglo-Scottish Cup. Forest beat Orient 5–1 on aggregate in the two-legged final played in December 1976.[11] Clough valued winning a derided trophy as the club's first silverware since 1959. He said, "Those who said it was a nothing trophy were absolutely crackers. We'd won something, and it made all the difference."[23]
On 7 May 1977, Alan Moore's own goal meant Forest in their last league game of the season beat Millwall 1–0 at the City Ground.[24] This kept Forest in the third promotion spot in the league table and dependent on Bolton Wanderers dropping points in three games in hand in the fight for third place.[25] On 14 May Kenny Hibbitt's goal from his rehearsed free kick routine with Willie Carr gave Wolves a 1–0 win at Bolton.[17][26] Bolton's defeat reached the Forest team mid-air en route to an end of season break in Mallorca.[17] Forest's third place promotion from the 1976–77 Football League Second Division was the fifth-lowest points tally of any promoted team in history, 52[4][11] (two points for a win in England until 1981).
Taylor secretly followed Kenny Burns concluding Burns's reputation as a hard drinker and gambler was exaggerated. Taylor sanctioned his £150,000 July signing. Burns become FWA Footballer of the Year in 1977–78 after being moved from centre-forward to centre-back.[27][28] Forest started their return to the top league campaign with a 3–1 win at Everton. Three further wins in league and cup followed without conceding a goal. Then came five early September goals conceded in losing 3–0 at Arsenal and beating Wolves 3–2 at home.[29] Peter Shilton then signed for a record fee for a goalkeeper of £325,000. Taylor reasoned: "Shilton wins you matches."[30] 20-year-old John Middleton was first team goalkeeper pre-Shilton. Middleton later in the month went in part exchange with £25,000 to Derby County for Archie Gemmill transferring to Forest.[31] Gemmill was another Scottish former 1972 Derby title winner.[27][32]
Forest lost only three of their first 16 league games the last of which was at Leeds United on 19 November 1977. They lost only one further game all season, the 11 March FA Cup sixth round defeat at West Bromwich Albion.[29] Forest won the 1977–78 Football League seven-points ahead of runners-up Liverpool. Forest became one of the few teams (and the most recent team to date) to win the First Division title the season after winning promotion from the Second Division.[nb 1][33][34] This made Clough the third of four managers to win the English league championship with two different clubs.[nb 2] Forest conceded just 24 goals in 42 league games.[30] They beat Liverpool 1–0 in the 1978 Football League Cup Final replay despite cup-tied Shilton, Gemmill and December signing David Needham missing out.[35] Chris Woods chalked up two clean sheets in the final covering Shilton's League Cup absence. McGovern missed the replay through injury, meaning Burns lifted the trophy as deputising captain. Robertson's penalty was the only goal of the game.[23][36]
Forest started season 1978–79 by beating Ipswich Town 5–0 for an FA Charity Shield record winning margin.[11] In the 1978–79 European Cup they were drawn to play the trophy winners of the past two seasons, Liverpool. Home goals by Birtles and Barrett put Forest through 2–0 on aggregate.[37] 26-year-old Barrett suffered a serious leg injury ten days later against Middlesbrough that ultimately ended his professional career two years later. On 9 December 1978, Liverpool ended Forest's 42 match unbeaten league run dating back to November the year before.[11] The unbeaten run was the equivalent of a whole season surpassing the previous record of 35 games held by Burnley in 1920/21.[38] The record stood until surpassed by Arsenal in August 2004, a month before Clough's death. Arsenal played 49 league games without defeat.[39]
In February 1979, Taylor authorised the English game's first £1 million transfer signing Trevor Francis from Birmingham City.[40] In the European Cup semi-final first leg at home against 1. FC Köln, Forest were two goals behind after 20 minutes, then scored three to edge ahead before Köln equalised to start the German second leg ahead on the away goals rule. Ian Bowyer's goal in Germany put Forest through. Günter Netzer asked afterwards, "Who is this McGovern? I have never heard of him, yet he ran the game." Forest beat Malmö 1–0 in Munich's Olympiastadion in the 1979 European Cup Final; Francis, on his European debut, scored with a back post header from Robertson's cross. Forest beat Southampton in the final 3–2 to retain the League Cup; Birtles scored twice as did Woodcock once. Forest finished second in the 1978–79 Football League, eight points behind Liverpool.
_-_Francis%2C_Clough%2C_Robertson.jpg)
Forest declined to play in the home and away 1979 Intercontinental Cup against Paraguay's Club Olimpia. Forest beat F.C. Barcelona 2–1 on aggregate in the 1979 European Super Cup in January and February 1980, Charlie George scoring the only goal in the home first leg, while Burns scored an equaliser in the return in Spain.[41] In the 1979-80 Football League Cup Forest reached a third successive final. A defensive mix up between Needham and Shilton let Wolves' Andy Gray tap in to an empty net. Forest passed up numerous chances, losing 1–0.[42] In the 1979–80 European Cup quarter-final, Forest won 3–1 at Dinamo Berlin to overturn a 1–0 home defeat. In the semi-final they beat Ajax 2–1 on aggregate. They beat Hamburg 1–0 in the 1980 European Cup Final at Madrid's Santiago Bernabéu Stadium to retain the trophy; Robertson scored after exchanging passes with Birtles.[43] Forest finished fifth in the 1979-80 Football League.
In the 1980–81 European Cup first round, Forest lost 2–0 on aggregate to 1–0 defeats home and away by CSKA Sofia.[44] McGovern subsequently said the double defeat by CSKA affected the team's self-confidence, in that they had lost out to modestly talented opponents.[17] Forest lost the 1980 European Super Cup on away goals after a 2–2 aggregate draw against Valencia; Bowyer scored both Forest goals in the home first leg.[45] On 11 February 1981, Forest lost 1–0 in the 1980 Intercontinental Cup against Uruguayan side, Club Nacional de Football. The match was played for the first time at the neutral venue National Stadium in Tokyo before 62,000 fans.[46]
The league and European Cup winning squad was broken up to capitalise on player sale value. Clough and Taylor both later said this was a mistake.[12] The rebuilt side comprising youngsters and signings such as Ian Wallace, Raimondo Ponte and Justin Fashanu did not challenge for trophies. Taylor said in 1982,[47]
For many weeks now I don't believe I've been doing justice to the partnership and I certainly haven't been doing justice to Nottingham Forest the way I felt. And consequently after a great deal of thought, there was no option. I wanted to take an early retirement. That's exactly what I've done.
John McGovern and Peter Shilton transferred and Jimmy Gordon retired in the same close season.[12]
Clough without Taylor (1982–93)
Anderlecht beat Forest in the 1983–84 UEFA Cup semi-finals in controversial circumstances. Several contentious refereeing decisions went against Forest. Over a decade later it emerged that before the match the referee Guruceta Muro received a £27,000 "loan" from Anderlecht's chairman Constant Vanden Stock.[48] UEFA subsequently in 1997 banned Anderlecht for one year from European competition for this misdemeanour. Muro died in a car crash in 1987.[49]
Forest beat Sheffield Wednesday on penalties in the Football League Centenary Tournament final in April 1988 after drawing 0–0.[50] Forest finished third in the league in 1988 and made the 1987-88 FA Cup semi-finals. Stuart Pearce won the first of his five successive selections for the PFA Team of the Year.
On 18 January 1989 Clough joined the fray of a City Ground pitch invasion by hitting two of his own team's fans when on the pitch. The football authorities responded with a fine and touchline ban for Clough.[51] Forest beat QPR 5–2 in that 1988-89 Football League Cup tie.[52]
Forest beat Everton 4–3 after extra time in the 1989 Full Members Cup final. They came back to beat Luton Town 3–1 in the 1989 Football League Cup Final. Nigel Clough scored two and Neil Webb one. Forest chased a unique cup treble but tragedy struck a week after the League Cup win. Forest and Liverpool met for the second season in a row in the FA Cup semi-finals. The Hillsborough disaster claimed the lives of 96 Liverpool fans. The match was abandoned after six minutes. When the emotion laden rescheduled game took place Forest struggled as Liverpool won 3–1. Forest finished third in the First Division for a second successive year. However they were unable to compete in the UEFA Cup. The 1985 post Heysel Stadium Disaster UEFA competition ban on English clubs still had one season to run. Des Walker won the first of his four successive selections for the PFA Team of the Year.
Nigel Jemson scored as Forest beat Oldham Athletic 1–0 to retain the League Cup in 1990.
Brian Clough reached his only FA Cup final in 1991 after countless replays and postponements in the 3rd, 4th and 5th rounds. Pearce put Forest ahead after 16 minutes direct from a free kick against Tottenham Hotspur at Wembley. Spurs won 2–1 after an extra time own goal by Walker. Roy Keane declared himself fit to play in the final and was selected in preference to Steve Hodge. Keane later admitted he was not fit to play and that was why he had such an insignificant role in the final.[53] English clubs were re-admitted to Europe for the 1990–91 season. English places in the competition were initially limited. 1990 League Cup winners Forest were not included. The only UEFA Cup place that season went to league runners-up Aston Villa.
In the summer of 1991 Millwall's league top scorer Teddy Sheringham set Forest's record signing fee at £2.1 million. In that 1991–92 season Forest beat Southampton 3–2 after extra time in the Full Members Cup Final. Brian McClair's solitary Manchester United goal beat Forest in the 1992 Football League Cup Final. Forest had played in seven domestic cup finals at Wembley in five seasons winning five of the finals. Forest finished eighth in the league that season to earn a place in the new FA Premier League.
Walker transferred in summer 1992 to Sampdoria. On 16 August 1992 Forest beat Liverpool 1–0 at home in the first ever televised live premier league game. Sheringham scored the only goal against Liverpool. Sheringham transferred a week later to Tottenham. Forest's form slumped meaning Brian Clough's 18-year managerial reign ended in May 1993 with Forest relegated from the inaugural Premier League.[54] The final game of that season was away at Ipswich. Forest lost 2–1 with his son, Nigel, scoring the last goal of Clough's era.[4] Relegation was followed by Keane's £3.75 million British record fee transfer to Manchester United.
Frank Clark (1993–1996)
Frank Clark from Forest's 1979 European Cup winning team returned to the club in May 1993 succeeding Brian Clough as manager. Clark's previous greatest management success was promotion from the Fourth Division with Leyton Orient in 1989. Clark convinced Stuart Pearce to remain at the club and also signed Stan Collymore, Lars Bohinen and Colin Cooper. Clark brought immediate return to the Premier League when the club finished Division One runners-up at the end of the 1993–94 season.[55]
Forest finished third in 1994–95[56] and qualified for the UEFA Cup – their first entry to European competition in the post-Heysel era. Collymore then transferred in the 1995–96 close season to Liverpool for a national record fee of £8.5million. Forest reached the 1995-96 UEFA Cup quarter-finals, the furthest an English team reached in UEFA competition that season. They finished ninth in the league.
The 1996–97 season quickly became a relegation battle. Clark left the club in December.[57]
Stuart Pearce and Dave Bassett (1997–1999)
34-year-old captain Stuart Pearce was installed as player-manager on a temporary basis just before Christmas in 1996 and he inspired a brief upturn in the club's fortunes. However, in March 1997 he was replaced on a permanent basis by Dave Bassett and left the club that summer after 12 years.[58] Forest were unable to avoid relegation and finished the season in bottom place.[59] They won promotion back to the Premier League at the first attempt, being crowned Division One champions in 1997–98.[60] Bassett was sacked in January 1999, with Ron Atkinson replacing him.[61][62]
Into the 21st century below the top-flight (1999–2012)
Ron Atkinson was unable to prevent Forest from once again slipping back into Division One, and announced his retirement from football management when Forest's relegation was confirmed on 24 April 1999, with three weeks of the Premier League seasons still to play.
Former England captain David Platt succeeded Atkinson and spent approximately £12 million on players in the space of two seasons, including the Italian veterans Moreno Mannini, Salvatore Matrecano and Gianluca Petrachi.[63] However, Forest could only finish 14th in Platt's first season and 11th in his second. He departed in July 2001 to manage the England U21 side and was succeeded by youth team manager Paul Hart.[64]
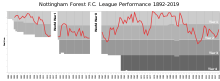
Now faced with huge debts, which reduced Forest's ability to sign new players, they finished 16th in Hart's first season in charge.[65] By December 2001, Forest were reported as losing over £100,000 every week,[66] and their financial outlook was worsened by the collapse of ITV Digital, which left Forest and many other Football League clubs in severe financial difficulties.[67] Despite the off-field difficulties, Forest finished 2002–03 in sixth place[68] and qualified for the play-offs, where they lost to Sheffield United in the semi-finals. A poor league run the following season, following the loss of several key players, led to the sacking of Hart in February 2004 with Forest in danger of relegation.[69] The decision was unpopular with certain quarters of the fanbase and Hart was described as a 'scapegoat'.[70]
Joe Kinnear was subsequently appointed and led the club to a secure 14th place in the final league table.[71] The 2004–05 season saw Forest drop into the relegation zone once more, leading to Kinnear's resignation in December 2004.[72] Mick Harford took temporary charge of Forest over Christmas, before Gary Megson was appointed in the new year. Megson had already won two promotions to the Premier League with his previous club West Bromwich Albion, having arrived at the club when they were in danger of going down to Division Two, but failed to stave off relegation as the club ended the season second from bottom in 23rd place,[73] becoming the first European Cup-winners ever to fall into their domestic third division.[74]
In Forest's first season in the English third tier in 54 years, a 3–0 defeat at Oldham Athletic[75] in February 2006 led to the departure of Megson by "mutual consent" leaving the club mid-table only four points above the relegation zone.[76] Frank Barlow and Ian McParland took temporary charge for the remainder of the 2005–06 season, engineering a six-match winning run and remaining unbeaten in ten games, the most notable result a 7–1 win over Swindon Town.[77] Forest took 28 points from a possible 39 under the two, narrowly missing out on a play-off place, as they finished in 7th place.[78]
Colin Calderwood, previously of Northampton Town, was appointed as Forest's new manager in May 2006. He was their 12th new manager to be appointed since the retirement of Brian Clough 13 years earlier, and went on to become Forest's longest-serving manager since Frank Clark. The Calderwood era was ultimately one of rebuilding, and included the club's first promotion in a decade. In his first season, he led the club to the play-offs, having squandered a 7-point lead at the top of League One which had been amassed by November 2006. Forest eventually succumbed to a shock 5–4 aggregate defeat in the semi-finals against Yeovil Town; they had taken a 2–0 lead in the first leg at Huish Park, but were then beaten 5–2 on their own soil by the Somerset club.[79] Calderwood achieved automatic promotion in his second year at the club, following an impressive run which saw Forest win six out of their last seven games of the season, culminating in a dramatic final 3–2 win against Yeovil at the City Ground. Forest kept a league record of 24 clean sheets out of 46 games, proving to be the foundation for their return to the second tier of English football and leaving them just one more promotion away from a return to the Premier League.
However, Calderwood's side struggled to adapt to life in the Championship in the 2008–09 campaign and having been unable to steer Forest out of the relegation zone, Calderwood was sacked following a Boxing Day 4–2 defeat to the Championship's bottom club Doncaster Rovers.[80]
Under the temporary stewardship of John Pemberton, Forest finally climbed out of the relegation zone, having beaten Norwich City 3–2.[81] Billy Davies, who had taken Forest's local rivals Derby County into the Premier League two seasons earlier, was confirmed as the new manager on 1 January 2009[82] and watched Pemberton's side beat Manchester City 3–0 away in the FA Cup,[83] prior to taking official charge. Under Davies, Forest stretched their unbeaten record in all competitions following Calderwood's sacking to six matches, including five wins. He also helped them avoid relegation as they finished 19th in the Championship,[84] securing survival with one game to go.
Forest spent most of the 2009–10 campaign in a top-three position, putting together an unbeaten run of 19 league games, winning 12 home league games in a row (a club record for successive home wins in a single season), going unbeaten away from home from the beginning of the season until 30 January 2010 (a run spanning 13 games) whilst also claiming memorable home victories over local rivals Derby County and Leicester City. The club finished third, missing out on automatic promotion, and in the two-legged play-off semi-final were beaten by Blackpool, 2–1 away and 4–3 in the home leg, the club's first defeat at home since losing to the same opposition in September 2009.
The 2010–11 season saw Forest finish in sixth place in the Championship table with 75 points,[85] putting them into a play-off campaign for the fourth time in the space of eight years. Promotion was yet again to elude Forest, as they were beaten over two legs by eventual play-off final winners Swansea City. Having drawn the first leg 0–0 at the City Ground,[86] they were eventually beaten 3–1 in the second leg.[87]
In June 2011, Billy Davies had his contract terminated,[88][89] and was replaced as manager by Steve McClaren, who signed a three-year contract.[90][91] Forest started the 2011–12 season with several poor results and after a 5–1 defeat away to Burnley, David Pleat and Bill Beswick left the club's coaching setup.[92] Less than a week later, following a home defeat to Birmingham City, McClaren resigned, and chairman Nigel Doughty announced that he intended to resign at the end of the season.[92] In October 2011, Nottingham Forest underwent several changes. These changes included the appointment of Frank Clark as new chairman of the club and also that of Steve Cotterill, replacing the recently departed Steve McClaren.[93]

Nigel Doughty, owner and previous chairman of the club, died on 4 February 2012, having been involved with the club since the late 1990s, with many estimating his total contribution as being in the region of £100 million.
The Al-Hasawi era (2012–2017)
The Al-Hasawi family, from Kuwait, purchased the club and became the new owners in July 2012. The Al-Hasawi family told press that they had a long-term vision for the club based around a 3–5-year plan, and after interviewing several potential new managers, appointed Sean O'Driscoll, formerly the manager at Doncaster Rovers and Crawley Town, as the manager on 19 July 2012 after a second round of talks with the then Crawley man. He was known for playing an attractive brand of passing football (which had taken Doncaster Rovers into the league's second tier for the first time since the 1950s) and what football fans would consider the Forest way.[94] O'Driscoll had spent five months at the City Ground as Coach under Steve Cotterill in the 2011–12 season before taking over at Crawley. After taking over at Crawley, O'Driscoll never took charge of a single competitive game.
By 15 December 2012, after the team's 0–0 draw away to Brighton, Forest sat in ninth position with 33 points, just three points off the play-off positions. The Al-Hasawi's 3–5-year plan had turned into a push for the play-offs in their first season as the owners. On the same weekend, the club announced that Omar Al-Hasawi had stepped down due to personal reasons and Fawaz Al-Hasawi, the majority shareholder with 75% had taken the position,[95] with his brother Abdulaziz Al-Hasawi holding a 20% share and his cousin Omar Al-Hasawi holding a 5% share.
On Boxing Day 2012, manager Sean O'Driscoll was sacked following a 4–2 victory over Leeds United with the club stating their intentions of a change ahead of the January transfer window and hopes of appointing a manager with Premiership experience.[96] The man to replace O'Driscoll was Alex McLeish.[97] The move was criticised by some members of the Forest fan base. Chief executive Mark Arthur as well as scout Keith Burt and club ambassador Frank Clark were dismissed in January 2013.[98] On 5 February 2013, Forest and Alex McLeish had parted company by mutual agreement, just 40 days after McLeish took charge of the club.[99] Forest supporters and pundits alike registered their concern for the state of the club,[94] with journalist Pat Murphy describing the situation as a "shambles".[100]
Two days after McLeish's departure, the club re-appointed Billy Davies as manager, having been sacked as the team's manager twenty months previously.[101] His first match in charge was a draw,[102] followed by a run of 10 undefeated games. In March 2014, the club terminated Davies's employment, following a 5–0 defeat by Derby County.[103] Neil Warnock turned down the job as Forest manager on the day Davies was sacked. After initially rejecting the job in March 2014,[104] fans favourite Stuart Pearce was named the man to replace Billy Davies, taking over from caretaker manager Gary Brazil. He signed a two-year contract commencing on 1 July 2014. Pearce led Forest to an unbeaten start to the season but failed to keep up the form. He was sacked in February 2015 and replaced by another former Forest player, Dougie Freedman.
Another mid-table finish meant that Forest began the 2015–16 season still in the Championship and now in their 17th season away from the Premier League. On 13 March 2016, Freedman was sacked, following a 3–0 defeat at home to Sheffield Wednesday.[105] Paul Williams was then appointed as temporary manager as Nottingham Forest searched for their new manager. Finally, following months of speculation the former US Boulogne, Valenciennes FC, Real Sociedad, and Stade Rennais head coach Philippe Montanier was appointed on a two-year contract on 27 June 2016, but was sacked after fewer than seven months in charge. Mark Warburton was named as the club's new manager on 14 March 2017. Forest narrowly avoided relegation on the final day of the 2016–17 season, where a 3–0 home victory against Ipswich ensured their safety at the expense of Blackburn.[106]
Evangelos Marinakis (2017– )
On 18 May 2017 it was confirmed that Evangelos Marinakis had completed his takeover of Nottingham Forest,[107] bringing an end to Al-Hasawi's reign as Forest owner. Incumbent manager Mark Warburton was sacked on 31 December 2017 following a 1–0 home defeat to struggling Sunderland, with a record of one win in seven.[108] He was replaced by Spaniard Aitor Karanka, who arrived on 8 January 2018, immediately after caretaker manager Gary Brazil had masterminded a 4–2 home win over FA Cup holders Arsenal in the third round of the FA Cup.[109] Karanka made 10 new signings during the January transfer window.[110] Following a 17th-place finish in the Championship for the 2017–18 season, Karanka made 14 new signings during the summer transfer window and the following season results improved.[111] However, despite a strong league position, Karanka left his position on 11 January 2019 after having been asked to be released from his contract.[112] He was replaced with former Republic of Ireland boss Martin O'Neill four days later.[113] However, O'Neill was sacked in June after reportedly falling out with some of the senior first team players. He was replaced with Sabri Lamouchi on the same day.[114]
Club identity
Crest and colours
Nottingham Forest have worn red since the club's foundation in 1865. At the meeting in the Clinton Arms which established Nottingham Forest as a football club, the committee also passed a resolution that the team colours should be 'Garibaldi red'.[115] This decision was made in honour of Giuseppe Garibaldi, the Italian patriot who was the leader of the redshirts volunteers. At this time, clubs identified themselves more by their headgear than their shirts and a dozen red caps with tassels were duly purchased, making Forest the first club to 'officially' wear red, a colour that has since been adopted by a significant number of others. Forest is the reason behind Arsenal's choice of red, having donated a full set of red kits following Arsenal's foundation in 1886. Forest's tour of South America in 1905 inspired Argentine club Independiente to adopt red as their club colour, after club's President Arístides Langone described the tourists as looking like diablos rojos ("red devils"), which would become Independiente's nickname.[116]
The first club crest used by Forest was the city arms of Nottingham, which was first used on kits in 1947.[117] The current club badge was introduced in 1974.[117] The logo has been reported as being the brainchild of manager Brian Clough.[118] However, he did not arrive at the club until the year after. Forest have two stars above the club badge to commemorate the European Cup victories in 1979 and 1980.[119] There was a competition, announced in March 1973,[120] to design a new Forest badge, and the winning design was by Trent Polytechnic graphic design lecturer David Lewis. To maintain anonymity, David Lewis entered his design using his mother's maiden name. The reason being that one of the five judges was his head of department, Mr. W. Payne, the Associate Head of the Graphics Department.[121] David Lewis also designed the Nottinghamshire County Council logo.
| Period | Kit manufacturer | Shirt sponsor |
|---|---|---|
| 1973–76 | Umbro | None |
| 1976–77 | U-Win[122] | |
| 1977–80 | Adidas | |
| 1980–82 | Panasonic | |
| 1982–84 | Wrangler | |
| 1984–86 | Skol | |
| 1986–87 | Umbro | Home Ales |
| 1987–93 | Shipstones | |
| 1993–97 | Labatt's | |
| 1997–2003 | Pinnacle | |
| 2003–09 | Capital One | |
| 2009–12 | Victor Chandler | |
| 2012–13 | John Pye Auctions[123] | |
| 2013–16 | Adidas | Fawaz International Refrigeration & Air Conditioning Company |
| 2016–18 | 888sport | |
| 2018–2019 | Macron[124] | BetBright[125] |
| 2019– | Football Index[126] |
Nomenclature
The club has garnered many nicknames over time. Historically, the nickname of "Foresters" was used,[127] as was "Garibaldis".[128] "The Forest"[129] or the simpler "Forest" – as used on the club crest – is commonly used, as is "the Reds". Another, lesser-used, nickname referring to the club is the "Tricky Trees".[130][131] Nottingham Forest is sometimes referred to as Notts Forest, which is not correct, as 'Notts' is an abbreviation of the word 'Nottinghamshire'.
Stadium
City Ground
Since 1898 Nottingham Forest have played their home games at the City Ground in West Bridgford, on the banks of the River Trent. Prior to moving to the City Ground, Forest played their home games at Forest Recreation Ground, then Trent Bridge, and finally the purpose-built Town Ground. Since 1994 the City Ground has been all-seater, a preparation that was made in time for the ground to be a venue for Euro 96, and currently has a capacity of 30,445.
The City Ground is 300 yards away from Notts County's Meadow Lane stadium on the opposite side of the Trent, meaning the two grounds are the closest professional football stadia geographically in England. In 1898 the City Ground was within the boundaries of Nottingham, which had been given city status the year before and gave rise to the name of the stadium, however a boundary change in the 1950s means that the City Ground now stands just outside of the city's boundaries in the town of West Bridgford.
On 28 February 2019 Nottingham Forest announced plans to redevelop the City Ground and surrounding area, including the "creation of a new, world-class Peter Taylor Stand". It is expected this will increase the capacity of the stadium to 38,000, making it the largest football stadium in the East Midlands. The club are hopeful that building work can begin at the end of the 2019-20 season.[132]
Ground history
| Period | Ground | Location |
|---|---|---|
| 1865 – 1878 | Forest Recreation Ground | Forest Fields |
| 1879 – 1880 | Castle Ground | The Meadows |
| 1880 – 1882 | Trent Bridge Cricket Ground | West Bridgford |
| 1882 – 1885 | Parkside Ground | Lenton |
| 1885 – 1890 | Gregory Ground | Lenton |
| 1890 – 1898 | Town Ground | The Meadows |
| 1898 – | City Ground | West Bridgford |
Local rivals, derbies and supporters
Whilst Notts County is the closest professional football club geographically, Forest have remained at least one division higher since the 1994–95 season and the club's fiercest rivalry is with Derby County, located 14 miles away.[133] The two clubs contest the East Midlands derby, a fixture which has taken on even greater significance since the inception of the Brian Clough Trophy in 2007. Leicester City are Forest's other East Midlands rival due to the close proximity of the two cities.
Forest's other regional rival is Sheffield United, based in the neighbouring county of South Yorkshire, a rivalry which has roots in the UK miners' strike of 1984–85 when the miners of South Yorkshire walked out on long strikes but some Nottinghamshire miners, who insisted on holding a ballot, continued to work. The exciting 2003 Football League Championship Play-off semi-final between the two clubs, in which Sheffield United finished as 5–4 aggregate winners, also fueled the rivalry.
Honours
Domestic
League
- Champions (1): 1977–78
- Runners-up (2): 1966–67, 1978–79
- Second Division/Championship[nb 4]
- Champions (3): 1906–07, 1921–22, 1997–98
- Runners-up (2): 1956–57, 1993–94
- Promoted (1): 1976–77
- Third Division/League One
- Champions (1): 1950–51 (South)
- Runners-up (1): 2007–08
- Football Alliance
- Champions (1): 1891–92
Cups
- Winners (2): 1897–98, 1958–59
- Runners-up (1): 1990–91
- Winners (4): 1977–78, 1978–79, 1988–89, 1989–90
- Runners-up (2): 1979–80, 1991–92
- FA Charity Shield
- Winners (1): 1978
- Runners-up (1): 1959
- Full Members Cup
- Winners (2): 1988–89, 1991–92
European
- European Cup/UEFA Champions League
- Winners (2): 1978–79, 1979–80
- UEFA Super Cup
- Winners (1): 1979
- Runners-up (1): 1980
Worldwide
- Intercontinental Cup[135]
- Runners-up (1): 1980
Minor
- Anglo-Scottish Cup
- Winners (1): 1977
Managers
Information correct as of match played 1 January 2020. Only competitive matches are counted.
- Caretaker managers are in italics
| Number | Manager | From | To | Played | Won | Drawn | Lost | Won % | Drawn % | Lost % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Harry Radford | 1 Aug 1889 | 31 May 1897 | 176 | 69 | 34 | 73 | 39.2% | 19.3% | 41.5% |
| 2 | Harry Hallam | 1 Aug 1897 | 31 May 1909 | 462 | 188 | 104 | 170 | 40.7% | 22.5% | 36.8% |
| 3 | 1 Aug 1909 | 31 May 1912 | 120 | 35 | 26 | 59 | 29.2% | 21.7% | 49.2% | |
| 4 | Bob Masters | 1 Aug 1912 | 31 May 1925 | 385 | 108 | 97 | 180 | 28.1% | 25.2% | 46.8% |
| 5 | John Baynes | 1 Aug 1925 | 31 May 1929 | 182 | 69 | 47 | 66 | 37.9% | 25.8% | 36.3% |
| 6 | 1 Aug 1930 | 31 May 1931 | 43 | 14 | 9 | 20 | 32.6% | 20.9% | 46.5% | |
| 7 | Noel Watson | 1 Aug 1931 | 31 May 1936 | 223 | 79 | 57 | 87 | 35.4% | 25.6% | 39.0% |
| 8 | 1 Aug 1936 | 31 May 1939 | 119 | 33 | 27 | 59 | 27.7% | 22.7% | 49.6% | |
| 9 | 1 May 1939 | 1 Jun 1960 | 650 | 272 | 147 | 231 | 41.8% | 22.6% | 35.5% | |
| 10 | 1 Sep 1960 | 1 Jul 1963 | 140 | 52 | 30 | 58 | 37.1% | 21.4% | 41.4% | |
| 11 | 1 Jul 1963 | 31 Dec 1968 | 267 | 99 | 65 | 93 | 38.5% | 25.3% | 36.2% | |
| 12 | 1 Jan 1969 | 20 Oct 1972 | 177 | 49 | 48 | 80 | 27.7% | 27.1% | 45.2% | |
| 13 | 2 Nov 1972 | 23 Oct 1973 | 44 | 13 | 14 | 17 | 29.5% | 31.8% | 38.6% | |
| 14 | 19 Nov 1973 | 3 Jan 1975 | 57 | 20 | 17 | 20 | 35.1% | 29.8% | 35.1% | |
| 15 | 3 Jan 1975 | 8 May 1993 | 968 | 447 | 258 | 263 | 46.2% | 26.7% | 27.2% | |
| 16 | 13 May 1993 | 19 Dec 1996 | 178 | 73 | 58 | 47 | 41.0% | 32.6% | 26.4% | |
| 17 | 20 Dec 1996 | 8 May 1997 | 23 | 7 | 9 | 7 | 30.4% | 39.1% | 30.4% | |
| 18 | 8 May 1997 | 5 Jan 1999 | 77 | 30 | 20 | 24 | 42.9% | 26.0% | 31.2% | |
| 19 | 5 Jan 1999 | 11 Jan 1999 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.0% | 0.0% | 100.0% | |
| 20 | 11 Jan 1999 | 16 May 1999 | 17 | 5 | 2 | 10 | 29.4% | 11.8% | 58.8% | |
| 21 | 1 Jul 1999 | 12 Jul 2001 | 103 | 37 | 25 | 41 | 35.9% | 24.3% | 39.8% | |
| 22 | 12 Jul 2001 | 7 Feb 2004 | 135 | 42 | 44 | 49 | 31.1% | 32.6% | 36.3% | |
| 23 | 10 Feb 2004 | 16 Dec 2004 | 44 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 34.1% | 34.1% | 31.8% | |
| 24 | 16 Dec 2004 | 10 Jan 2005 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 33.3% | 16.7% | 50.0% | |
| 25 | 10 Jan 2005 | 16 Feb 2006 | 59 | 17 | 18 | 24 | 28.8% | 30.5% | 40.7% | |
| 26 | 17 Feb 2006 | 30 May 2006 | 13 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 61.5% | 30.8% | 7.7% | |
| 27 | 30 May 2006 | 26 Dec 2008 | 136 | 57 | 42 | 37 | 41.9% | 30.9% | 27.2% | |
| 28 | 27 Dec 2008 | 4 Jan 2009 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 100.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | |
| 29 | 4 Jan 2009 | 12 Jun 2011 | 126 | 53 | 36 | 37 | 42.1% | 28.6% | 29.4% | |
| 30 | 13 Jun 2011 | 2 Oct 2011 | 13 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 23.1% | 23.1% | 53.8% | |
| 31 | 2 Oct 2011 | 15 Oct 2011 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0% | 0% | 100% | |
| 32 | 14 Oct 2011 | 12 Jul 2012 | 37 | 12 | 7 | 18 | 32.4% | 18.9% | 48/6% | |
| 33 | 20 Jul 2012 | 26 Dec 2012 | 26 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 38.5% | 34.6% | 26.9% | |
| 34 | 27 Dec 2012 | 5 Feb 2013 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 14.3% | 28.6% | 57.1% | |
| 35 | 5 Feb 2013 | 9 Feb 2013 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0% | 0% | 100% | |
| 36 | 7 Feb 2013 | 24 Mar 2014 | 59 | 25 | 21 | 13 | 42.3% | 35.6% | 22.0% | |
| 37 | 24 Mar 2014 | 3 May 2014 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 22.2% | 22.2% | 55.6% | |
| 38 | 1 Jul 2014 | 1 Feb 2015 | 32 | 10 | 10 | 12 | 31.25% | 31.25% | 37.5% | |
| 39 | 1 Feb 2015 | 13 Mar 2016 | 57 | 19 | 16 | 22 | 33.3% | 28.1% | 38.6% | |
| 40 | 13 Mar 2016 | 12 May 2016 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 20.0% | 40.0% | 40.0% | |
| 41 | 27 June 2016 | 14 Jan 2017 | 30 | 9 | 6 | 15 | 30.0% | 20.0% | 50.0% | |
| 42 | 14 Jan 2017 | 14 March 2017 | 11 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 36.4% | 9.1% | 54.5% | |
| 43 | 14 March 2017 | 31 December 2017 | 37 | 15 | 3 | 19 | 40.5% | 8.1% | 51.4% | |
| 44 | 31 December 2017 | 8 January 2018 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 50.0% | 50.0% | 0.0% | |
| 45 | 8 January 2018 | 11 January 2019 | 51 | 16 | 19 | 16 | 31.4% | 37.2% | 31.4% | |
| 46 | 11 January 2019 | 15 January 2019 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.0% | 0.0% | 100.0% | |
| 47 | 15 January 2019 | 28 June 2019 | 19 | 8 | 3 | 8 | 42.1% | 15.8% | 42.1% | |
| 48 | 28 June 2019 | Present | 28 | 14 | 7 | 7 | 50% | 25% | 25% |
Records
- Most appearances for the club (in all competitions): 692 – Bob McKinlay (1951–1970)[137]
- Most goals for the club (in all competitions): 217 – Grenville Morris (1898–1913)
- Highest attendance: 49,946 Vs. Manchester United in Division 1, 28 October 1967
- Lowest attendance: 4,030 Vs. Morecambe F.C. in the Football League Cup, 13 August 2008
- Record receipts: £499,099 Vs. FC Bayern Munich in UEFA Cup quarter final 2nd leg, 19 March 1996
- Longest sequence of league wins: 7, wins from 9 May 1922 to 1 September 1922
- Longest sequence of league defeats: 14, losses from 21 March 1913 to 27 September 1913
- Longest sequence of unbeaten league matches: 42, from 26 November 1977 to 25 November 1978
- Longest sequence of league games without a win: 19, from 8 September 1998 to 16 January 1999
- Longest sequence of league games without a goal: 7, 13 December 2003 to 7 February 2004 and 26 November 2011 to 31 December 2011
- Quickest goal:
- League: 14 seconds,[138] Jack Lester vs Norwich City, 8 March 2000
- League Cup: 23 seconds,[139] Paul Smith vs Leicester City, 18 September 2007 in the League Cup.¹
- Record win (in all competitions): 14–0, Vs. Clapton (away), 1st round FA Cup, 17 January 1891
- Record defeat (in all competitions): 1–9, Vs. Blackburn Rovers, Division 2, 10 April 1937
- Most league points in one season
- 2 points for a win (46 games): 70, Division 3 South, 1950–51
- 2 points for a win (42 Games): 64, Division 1. 1977-78
- 3 points for a win: 94, Division 1, 1997–98
- Most league goals in one season: 110, Division 3, 1950–51
- Highest league scorer in one season: Wally Ardron, 36, Division 3 (South), 1950–51
- Most internationally capped player: Stuart Pearce, 76 for England (78 total)
- Youngest league player: Craig Westcarr, 16 years, Vs. Burnley 13 October 2001
- Oldest league player: Dave Beasant, 42 years 47 days, Vs. Tranmere Rovers 6 May 2001
- Largest transfer fee paid: £13,200,000 to Benfica for João Carvalho[140]
- Largest transfer fee received: £15,000,000 from Middlesbrough for Britt Assombalonga.[141]
¹ By agreement with Leicester City, the game was a replay as the original match three weeks previous was abandoned at half time, due to the collapse of Leicester player Clive Clarke, with Forest leading 1–0.[142]
European record
| Competition[143] | P | W | D | L | GF | GA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| European Cup | 20 | 12 | 4 | 4 | 32 | 14 |
| UEFA Cup | 20 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 18 | 16 |
| Inter-Cities Fairs Cup | 6 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 9 |
| UEFA Super Cup | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| Intercontinental Cup | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Total | 51 | 27 | 10 | 14 | 62 | 43 |
| Season | Competition | Round | Opponent | Home | Away | Aggregate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1961–62 | Inter-Cities Fairs Cup | First round | 1–5 | 0–2 | 1–7 | |
| 1967–68 | Inter-Cities Fairs Cup | First round | 4–0 | 1–0 | 5–0 | |
| Second round | 2–1 | 0–1 | 2–2 (A) | |||
| 1978–79 | European Cup | First round | 2–0 | 0–0 | 2–0 | |
| Second round | 5–1 | 2–1 | 7–2 | |||
| Quarter-final | 4–1 | 1–1 | 5–2 | |||
| Semi-final | 3–3 | 1–0 | 4–3 | |||
| Final | 1–0 | |||||
| 1979 | European Super Cup | 1–0 | 1–1 | 2–1 | ||
| 1979–80 | European Cup | First round | 2–0 | 1–1 | 3–1 | |
| Second round | 2–0 | 2–1 | 4–1 | |||
| Quarter-final | 0–1 | 3–1 | 3–2 | |||
| Semi-final | 2–0 | 0–1 | 2–1 | |||
| Final | 1–0 | |||||
| 1980 | European Super Cup | 2–1 | 0–1 | 2–2 (A) | ||
| 1980 | Intercontinental Cup | 0–1 | ||||
| 1980–81 | European Cup | First round | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–2 | |
| 1983–84 | UEFA Cup | First round | 2–0 | 1–0 | 3–0 | |
| Second round | 1–0 | 2–1 | 3–1 | |||
| Third round | 0–0 | 2–1 | 2–1 | |||
| Quarter-final | 1–0 | 1–1 | 2–1 | |||
| Semi-final | 2–0 | 0–3 | 2–3 | |||
| 1984–85 | UEFA Cup | First round | 0–0 | 0–1 | 0–1 | |
| 1995–96 | UEFA Cup | First round | 1–0 | 1–2 | 2–2 (A) | |
| Second round | 0–0 | 1–0 | 1–0 | |||
| Third round | 1–0 | 0–0 | 1–0 | |||
| Quarter-final | 1–5 | 1–2 | 2–7 | |||
Players
Current squad
- As of 31 January 2020[144]
Note: Flags indicate national team as defined under FIFA eligibility rules. Players may hold more than one non-FIFA nationality.
|
|
First-team out on loan
Note: Flags indicate national team as defined under FIFA eligibility rules. Players may hold more than one non-FIFA nationality.
|
|
Under 23s squad
- As of 31 January 2020[145]
Note: Flags indicate national team as defined under FIFA eligibility rules. Players may hold more than one non-FIFA nationality.
|
|
Under 23s out on loan
Note: Flags indicate national team as defined under FIFA eligibility rules. Players may hold more than one non-FIFA nationality.
|
|
Under 18s squad
- As of 5 January 2020[146]
Note: Flags indicate national team as defined under FIFA eligibility rules. Players may hold more than one non-FIFA nationality.
|
|
Notable former players
Player of the Season

Kenny Burns, Nigel Clough, Andy Reid and Chris Cohen are the only players to win the award twice.
Andy Reid holds the record for longest gap between Player of the Year awards with a gap of ten years
|
|
|
All-time XI
In 1997 and 1998, as part of the release of the book The Official History of Nottingham Forest, a vote was carried out to decide on the club's official All Time XI.[169]
| Position | Player | Years at club |
|---|---|---|
| GK | 1977–82 | |
| RB | 1974–84 | |
| RCB | 1984–92; 2002–04 | |
| LCB | 1977–81 | |
| LB | 1985–97 | |
| RCM | 1971–81 | |
| ACM | 1990–93 | |
| LCM | 1977–79 | |
| RW | 1962–72 | |
| CF | 1979–81 | |
| LW | 1970–83; 1985–86 |
International players
- See List of Nottingham Forest F.C. international footballers
Club staff
| Executive & Front Office | |
|---|---|
| Majority owner | |
| Minority owner | |
| Chairman | |
| Director | |
| Director of football | |
| Technical director | |
| Head of international recruitment | |
| Head of football operations | |
| Chief executive officer | |
| Chief commercial officer | |
| First team | |
| Head coach | |
| Assistant coach | |
| Assistant coach | |
| Assistant coach | |
| Goalkeeping coach | |
| Head of performance | |
| Head Sport scientist | |
| Sport scientist | |
| Head physio | |
| Physio | |
| Physio | |
| Soft-tissue therapist | |
| Soft-tissue therapist | |
| Head video analyst | |
| Video analyst | |
| Video analyst | |
| Nutritionist | |
| Academy | |
| Academy manager | |
| Head of coaching | |
| Assistant academy manager | |
| Under 23s lead coach | |
| Academy technical coach | |
| Under 18s lead coach | |
| Under 18s assistant coach | |
Notes
- The others were Liverpool in 1906, Everton in 1932, Tottenham Hotspur in 1951 and Ipswich Town in 1962. Forest remain the only club to achieve this feat having not been promoted as champions.
- The others are Tom Watson, Herbert Chapman and Kenny Dalglish.
- From 1888 to 1992 the Football League First Division was the top tier of English football. It was superseded by the Premier League in 1992.
- Upon its formation in 1992, the Premier League became the top tier of English football; the First and Second Divisions then became the second and third tiers, respectively. The First Division is now known as the Football League Championship and the Second Division is now known as Football League One.
References
- "History of NFFC". Nottingham Forest Football Club. Retrieved 25 August 2019.
- "Who's Who". Nottingham Forest Football Club. Retrieved 25 August 2019.
- Leach, Tom (9 May 2019). "Forest are now League's oldest club, not Stoke". nottinghampost. Retrieved 23 December 2019.
- "History of NFFC". Nottingham Forest F.C.
- "Weirdest football team suffixes". The Guardian. 5 August 2015. Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- "F A Cup Final 1898". 28 September 2011. Archived from the original on 28 September 2011.
- Smyth, Rob; Burnton, Simon (30 October 2009). "The Joy of Six: Classic Arsenal v Tottenham matches". The Guardian. Retrieved 5 March 2016.
- Lacey, David (4 February 2006). "Wembley hoodoo rises from the rubble". The Guardian. Retrieved 12 August 2015.
- "Nottingham Forest Results Fixtures 1966/1967". stats.football.co.uk.
- "Nottingham Forest Historical Standings 15th Apr 1967" stats.football.co.uk
- Taylor, Daniel (10 October 2015). "Brian Clough and the miracle of Nottingham Forest". The Guardian.
- Miller, Nick (17 September 2014). "The forgotten story of … Brian Clough's other right-hand man". The Guardian.
- "QosFC: Queens Legends". qosfc.com.
- Bandini, Paolo (5 March 2010). "Viv Anderson – Small Talk". The Guardian.
- "Lincoln Spell Turned Me Around... says Woodcock". New Straits Times. Kuala Lumpur. 19 February 1984. p. 16. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- Gibson, John (10 September 2016). "How Newcastle United legend Frank Clark celebrated his birthday – with a host of Geordie fans".
- "My Forest story: John McGovern". 1 June 2015 – via YouTube.
- Taylor 1980, p. 87
- Taylor 1980, p. 88
- Taylor 1980, p. 90
- Taylor 1980, p. 91
- Taylor 1980, p. 104
- ""Old Big 'Ead ignites Forest fire" ESPN 22 March 2012".
- ""Game Details – Millwall (H) – Sat May 07, 1977 (League Tier 2)" thecityground.com". Archived from the original on 25 September 2018. Retrieved 6 December 2017.
- "Nottingham Forest Results Fixtures 1976/1977" stats.football.co.uk
- "Bolton Wanderers Results Fixtures 1976/1977"
- Taylor, Daniel (11 November 2015). "Signing 'a hooligan' and a Shankly team talk: how Clough set up Forest for title". The Guardian.
- Taylor 1980, p. 96
- "footballsite – Nottingham Forest results 1977/78". footballsite.co.uk. Archived from the original on 6 December 2017. Retrieved 5 December 2017.
- Stevenson, Jonathan (21 September 2004). "Forest's unforgettable fairytale". BBC Sport. Retrieved 18 May 2009.
- "Derby County – Leeds United 2:2 (Premier League 1977/1978, 6. Round)". worldfootball.net.
- "Archie GEMMILL – League appearances for Forest. – Nottingham Forest FC". Sporting Heroes.
- Scott Murray (21 January 2011). "The Joy of Six: Newly promoted success stories". The Guardian. Retrieved 3 October 2018.
- Karel Stokkermans (17 June 2018). "English Energy and Nordic Nonsense". RSSSF. Retrieved 3 October 2018.
- Taylor 1980, p. 113
- "English League Cup Betting – 1977/78 – Soccer Base". soccerbase.com.
- "UEFA Champions League – Nottm Forest-Liverpool". UEFA.
- Stevenson, Jonathan (23 August 2004). "Wenger repeats Clough feat". BBC News. Retrieved 11 July 2009.
- "49 Unbeaten". Arsenal F.C.
- Taylor 1980, p. 124
- "UEFA Super Cup – 1979: Burns' night for Forest". UEFA.
- "15/03/1980 Wolverhampton W v Nottingham Forest". 21 December 2013 – via YouTube.
- ""Nottingham Forest 1979/80" uefa.com".
- "Nottingham Forest FC 1980/81 uefa.com".
- UEFA.com. "UEFA Super Cup – 1980: Valencia profit from Felman's fortune". UEFA.
- Gorgazzi, Osvaldo (13 February 2005). "Intercontinental Club Cup 1980". Rec.Sport.Soccer Statistics Foundation. Retrieved 5 December 2017.
- "Peter Taylor Leaves Nottingham Forest 1982". 31 December 2016 – via YouTube.
- "Forest sues Anderlecht over '84 bribery scandal". BBC News. 24 December 1997. Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- Catherine Riley: Football: After 13 years Anderlecht are punished by Uefa, The Independent, 23 September 1997 (per 7 June 2013).
- "The Mercantile Credit Football Festival". 24 January 2013.
- "Seven deadly sins of football: Lust – from Antonio Cassano to a Dutch pool party". The Guardian. 21 May 2009.
- "footballsite – Nottingham Forest results 1988/89". footballsite.co.uk. Archived from the original on 22 December 2017. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- "Keane; The Autobiography". Roy Keane, Penguin Publishing Group, ISBN 9780718193997
- "On this day: Teddy Sheringham nets first televised Premier League goal – Sports Mole". amp.sportsmole.co.uk.
- "Football League First Division 1993/94". Soccerbase. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- "Premiership 1994/95". Soccerbase. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- "Winless Forest lose manager Clark". The Nation. Bangkok: Nation Multimedia Group. Agence France-Presse. 20 December 1996. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- "Bassett quits Palace and joins Forest". The Nation. Bangkok: Nation Multimedia Group. Reuters. 1 March 1997. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- "Premiership 1996/97". Soccerbase. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- "Football League First Division 1997/98". Soccerbase. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- Barnes, Alan (12 January 1999). "Forest hire Atkinson the troubleshooter". The Independent. London. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- "AFC Wimbledon: Dave Bassett involved in manager search". BBC Sport. 25 September 2012.
- "Platt hires Italians as Goldbaek balks". The Independent. London. 3 August 1999.
- "Hart named new Forest boss". BBC Sport. 12 July 2001. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- "Football League First Division 2001/02". Soccerbase. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- Perry, Dwight (5 December 2001). "Sideline Chatter: Gesture gives soccer peace a chance". The Seattle Times. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- Boltanski, Christophe (29 March 2002). "Des clubs anglais privés de leur télé vache à lait" [English clubs deprived of their TV cash cow]. Libération (in French). Retrieved 16 November 2012.
- "Football League First Division 2002/03". Soccerbase. Retrieved 14 October 2011.
- "Forest finally lose patience with Hart". The Guardian. London. 7 February 2004. Retrieved 14 October 2011.
- Rawling, John (9 February 2004). "Hart a hapless scapegoat as Forest fire their fans' outrage". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 14 October 2011.
- "Football League First Division 2003/04". Soccerbase. Retrieved 14 October 2011.
- "Kinnear resigns as Forest manager". BBC Sport. 16 December 2004. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- "Championship 2004/05". Soccerbase. Retrieved 14 October 2011.
- Bailey, Ben; Whyte, Patrick (19 March 2009). "Premier League casualties – clubs that have struggled since relegation". London Evening Standard. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- "Oldham 3–0 Nottm Forest". BBC Sport. 15 February 2006. Retrieved 14 October 2011.
- "Manager Megson leaves Forest". The Daily Telegraph. London. 16 February 2006.
- "Nottingham Forest 7–1 Swindon". BBC Sport. 25 February 2006. Retrieved 14 October 2011.
- "League One 2005/06". Soccerbase. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- Sinnott, John (18 May 2007). "Nottm Forest 2–5 Yeovil". BBC Sport. Retrieved 10 April 2010.
- "Calderwood sacked as Forest boss". BBC Sport. 26 December 2008. Retrieved 10 April 2010.
- "Nottm Forest 2–4 Doncaster". BBC Sport. 26 December 2008. Retrieved 10 April 2010.
- Harvey, Chris (1 January 2009). "Forest appoint Davies". Sky Sports. British Sky Broadcasting. Archived from the original on 4 January 2009. Retrieved 1 January 2009.
- "Man City 0–3 Nottm Forest". BBC Sport. 3 January 2009. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- "Championship 2008/09". Soccerbase. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- "Championship 2010/11". Soccerbase. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- Rae, Richard (12 May 2011). "Ten-man Swansea have little trouble dousing Nottingham Forest's fire". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- Lovejoy, Joe (16 May 2011). "Darren Pratley finishes off Nottingham Forest to take Swansea to final". The Guardian. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- "Nottingham Forest talk to McClaren after sacking Davies". BBC Sport. 12 June 2011. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- "Billy Davies Contract Terminated". Nottingham Forest F.C. 12 June 2011. Archived from the original on 13 January 2012. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- "Steve McClaren confirmed as Nottingham Forest boss". BBC Sport. 13 June 2011. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- "New Manager Confirmed". Nottingham Forest F.C. 13 June 2011. Archived from the original on 13 January 2012. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- Ashdown, John (2 October 2011). "Birmingham fight-back seals exits of Steve McClaren and Nigel Doughty". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 3 October 2011.
- "Steve Cotterill takes over as Nottingham Forest manager". The Guardian. London. 14 October 2011.
- James, Stuart (5 February 2013). "Alex McLeish's sudden exit turns once-proud Forest into laughing stock". The Guardian. Retrieved 6 February 2013.
- "Fawaz Al Hasawi Statement". Nottingham Forest F.C. 16 December 2012. Retrieved 19 December 2012.
- "Nottingham Forest sack manager Sean O'Driscoll". BBC Sport. 26 December 2012.
- "Nottingham Forest name Alex McLeish as new manager". BBC Sport. 27 December 2012. Retrieved 27 December 2012.
- "Nottingham Forest: Mark Arthur, Keith Burt and Frank Clark leave". BBC Sport. 17 January 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- "Nottingham Forest part company with manager Alex McLeish by mutual agreement". Sky Sports. British Sky Broadcasting. 5 February 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- Phillips, Owen; Newsum, Matt (5 February 2013). "Nottingham Forest: Alex McLeish's exit leaves Reds in a mess". BBC Sport. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- "Billy Davies: Nottingham Forest re-appoint ex-manager". BBC Sport. 7 February 2013. Retrieved 7 February 2013.
- "Nottm Forest 1–1 Bolton". BBC Sport. 16 February 2013.
- "Club Statement". Nottingham Forest F.C. 24 March 2014.
- "Stuart Pearce refuses Notts Forest job". The Irish Independent. 27 March 2014. Retrieved 8 July 2014.
- "Dougie Freedman: Nottingham Forest manager sacked". BBC Sport. 13 March 2016.
- "Nottingham Forest 3–0 Ipswich Town". BBC Sport. 7 May 2017. Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- "Evangelos Marinakis completes Nottingham Forest takeover and denies match-fixing allegations". The Guardian. 18 May 2017.
- "Mark Warburton: Nottingham Forest sack manager after nine months in charge". BBC Sport. 31 December 2017.
- "Nottingham Forest sign new manager". nottinghamforest.co.uk. 8 January 2018.
- "Stefanos Kapino and Juan Fuentes join Nottingham Forest". BBC Sport. 8 February 2018.
- "Sam Byram: West Ham defender joins Nottingham Forest on loan". BBC Sport. 10 August 2018.
- "Aitor Karanka: Nottingham Forest manager leaves Championship club". BBC Sport. 11 January 2019. Retrieved 11 January 2019.
- "Martin O'Neill takes charge at Nottingham Forest". Sky Sports. 15 January 2019. Retrieved 15 January 2019.
- "Sabri Lamouchi: Nottingham Forest appoint Frenchman 18 minutes after sacking Martin O'Neill". BBC Sport. 28 June 2019. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 21 September 2012. Retrieved 7 September 2012.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) The Official History of Nottingham Forest
- "Década del '10" [The 1910s]. caindependiente.com (in Spanish). Club Atlético Independiente. Archived from the original on 6 March 2008.
- Moor, Dave. "Nottingham Forest". historicalkits.co.uk. Historical Football Kits. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- Murray, Scott (3 December 2010). "The Joy of Six: Brief trends in football". The Guardian. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- Doda, Zola (23 October 2013). "The star on Orlando Pirates badge explained". kickoff.com. South Africa. Retrieved 12 July 2014.
- Announced in the Programme of 06 March 1973 - NFFC v Hull City
- Nottingham Evening Post – Bygones - April 3rd 1999 – P.25
- Hurley, Denis (30 July 2017). "Nottingham Forest 1986–88 – not far off a grand slam of combinations". museumofjerseys.com. museumofjerseys.com. Retrieved 14 October 2018.
- Moor, Dave. "Nottingham Forest". Historical Football Kits. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
- "Nottingham Forest announce record-breaking long-term partnership with Macron". Nottingham Forest F.C. 1 March 2018. Retrieved 1 March 2018.
- "Nottingham Forest announce landmark deal with BetBright". Nottingham Forest. Retrieved 13 June 2018.
- "Football Index announced as official shirt partner". Nottingham Forest. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- "Footy Nicknames – Nottingham Forest". footynicknames.co.uk. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 8 July 2014.
- "Nottingham Forest". The Beautiful History. Retrieved 8 July 2014.
- "Notts Forest, 5; Liverpool, 1". Daily Mirror. 9 October 1908. p. 14.
- Gardner, Alan (24 November 2008). "Monday's football transfer rumours: Kazim-Richards to the Premier League?". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 8 July 2014.
- Mendes, Chris (7 November 2011). "Football's top 10 nicknames: The Pensioners, Tricky Trees, Smoggies, Monkey Hangers and more". talksport.com. UTV Radio. Retrieved 8 July 2014.
- "Major stadium redevelopment to go ahead at Nottingham Forest". Nottingham Forest Football Club. 28 February 2019.
- "Positions 11 – 15 | Football Rivalries Report 2008". Footballpools.com. Archived from the original on 27 April 2014. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 22 September 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2013.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Malmö FF". svenskfotboll.se (in Swedish). The Swedish Football Association. Retrieved 22 August 2012.
- "Fred William Earp". England's Oldest Football Clubs. Retrieved 14 March 2019.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 22 September 2012. Retrieved 23 September 2012.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- van Wijk, Jim. "Nottm For 1 Norwich 1". Sporting Life.
- "Nottingham Forest 2 v 3 Leicester City". Nottingham Forest F.C. 19 September 2007. Archived from the original on 22 July 2012. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- "Joao Carvalho and Diogo Goncalves complete Nottingham Forest moves..." BBC Sport. 14 June 2018. Retrieved 14 June 2018.
- "Britt Assombalonga completes £15m move from Nottingham Forest to Middlesbrough". Nottingham Post. 17 July 2017. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- Rae, Richard (19 September 2007). "Forest get a freebie but Clemence clinches it late for Leicester". The Guardian. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- "Nottingham Forest Football Club: Statistics". thefinalball.com.
- "Squad Numbers Confirmed". Nottingham Forest Football Club Official Website. Retrieved 2 August 2019.
- "Under 23s Team". Nottingham Forest Football Club Official Website. Retrieved 1 January 2018.
- "Under 18s Team". Nottingham Forest Football Club Official Website. Retrieved 1 January 2018.
- "Players of the Season 1970's". Nottingham Forest F.C. Archived from the original on 11 November 2013. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- "Players of the Season 1980's". Nottingham Forest F.C. Archived from the original on 30 March 2016. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- "Players of the Season 1990's". Nottingham Forest F.C. Archived from the original on 30 March 2016. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- "Players of the Season 2000's". Nottingham Forest F.C. Archived from the original on 11 November 2013. Retrieved 7 September 2012.
- "Gareth's Our Top Idol". Nottingham Forest F.C. 13 April 2002. Archived from the original on 5 August 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- "Player of the Year". Nottingham Forest F.C. 27 April 2003. Archived from the original on 5 August 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- "Player of the Year". Nottingham Forest F.C. 1 May 2004. Archived from the original on 5 August 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- "Paul Gerrard – Player of the Year". Nottingham Forest F.C. 8 May 2005. Archived from the original on 7 September 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- "Breckin Scoops Award". Nottingham Forest F.C. 29 April 2006. Archived from the original on 5 August 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- "Prize Guy Grant". Nottingham Forest F.C. 11 July 2007. Archived from the original on 9 May 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- "'Jules' Tops Poll". Nottingham Forest F.C. 4 May 2008. Archived from the original on 6 May 2008. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- "Chris Is Your Choice". Nottingham Forest F.C. 3 May 2009. Archived from the original on 6 May 2009. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- "Camp Fire Lands Award". Nottingham Forest F.C. 24 April 2010. Archived from the original on 29 April 2010. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- "Star Man Luke". Nottingham Forest F.C. 30 April 2011. Archived from the original on 29 January 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- "G-Mac And Adi Land Awards". Nottingham Forest F.C. 28 April 2012. Archived from the original on 4 July 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- Richardson, Nick (4 May 2013). "Cohen Wins Player of the Season". Nottingham Forest F.C. Retrieved 4 May 2013.
- "Andy Reid Named Player of the Season". Nottingham Forest F.C. 3 May 2014. Retrieved 4 May 2013.
- "Antonio scoops top prize". Nottingham Forest F.C. 4 May 2015. Retrieved 4 May 2015.
- "Dorus de Vries has been named Nottingham Forest's Player of the Season for 2015–16". Nottingham Forest F.C. via Facebook. 30 April 2016. Retrieved 30 April 2016.
- "Honour I will remember for rest of my life says Eric Lichaj as he wins top Nottingham Forest award". 10 May 2017. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Osborn crowned Player of the Season". Nottingham Forest F.C. 5 May 2018. Retrieved 5 May 2018.
- "Lolley crowned Player of the Season". Nottingham Forest F.C. 3 May 2018. Retrieved 3 May 2018.
- Soar, Philip (1998). The Official History of Nottingham Forest. Polar Publishing. p. 196. ISBN 1-899538-08-9.
