New Hampshire
New Hampshire (/ˈhæmpʃər/) is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the north. New Hampshire is the 5th smallest by area and the 10th least populous U.S. state.
New Hampshire | |
|---|---|
| State of New Hampshire | |
 Flag  Seal | |
| Nickname(s): | |
| Motto(s): "Live Free or Die" | |
| Anthem: "Old New Hampshire"[3] | |
 Map of the United States with New Hampshire highlighted | |
| Country | United States |
| Before statehood | Province of New Hampshire |
| Admitted to the Union | June 21, 1788 (9th) |
| Capital | Concord 44°N 71.5°W |
| Largest city | Manchester |
| Largest metro | Manchester–Nashua |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Chris Sununu (R) |
| • Senate President | Donna Soucy (D)[4] |
| Legislature | General Court |
| • Upper house | Senate |
| • Lower house | House of Representatives |
| U.S. senators | Jeanne Shaheen (D) Maggie Hassan (D) |
| U.S. House delegation | 1: Chris Pappas (D) 2: Ann McLane Kuster (D) (list) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 9,349 sq mi (24,214[5] km2) |
| Area rank | 46th |
| Dimensions | |
| • Length | 190 mi (305 km) |
| • Width | 68 mi (110 km) |
| Elevation | 1,000 ft (300 m) |
| Highest elevation | 6,288 ft (1,916.66 m) |
| Lowest elevation (Atlantic Ocean[7]) | 0 ft (0 m) |
| Population (2019) | |
| • Total | 1,359,711 |
| • Rank | 41st |
| • Density | 147/sq mi (56.8/km2) |
| • Density rank | 21st |
| • Median household income | $73,381[8] |
| • Income rank | 7th |
| Demonym(s) | Granite Stater, New Hampshirite |
| Language | |
| • Official language | English[9] (French allowed for official business with Quebec)[10] |
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (EDT) |
| USPS abbreviation | NH |
| ISO 3166 code | US-NH |
| Trad. abbreviation | N.H. |
| Latitude | 42° 42′ N to 45° 18′ N |
| Longitude | 70° 36′ W to 72° 33′ W |
| Website | www |
| New Hampshire state symbols | |
|---|---|
 The Flag of New Hampshire | |
 The Seal of New Hampshire | |
| Living insignia | |
| Amphibian | Red-spotted newt Notophthalmus viridescens |
| Bird | Purple finch Haemorhous purpureus |
| Butterfly | Karner Blue Lycaeides melissa samuelis |
| Dog breed | Chinook |
| Fish | Freshwater: Brook trout Salvelinus fontinalis Saltwater: Striped bass Morone saxatilis |
| Flower | Purple lilac Syringa vulgaris |
| Insect | Ladybug Coccinellidae |
| Mammal | White-tailed deer Odocoileus virginianus |
| Tree | White birch Betula papyrifera |
| Inanimate insignia | |
| Food | Fruit: Pumpkin Vegetable: White Potato Berry: Blackberry[11] |
| Gemstone | Smoky quartz |
| Mineral | Beryl |
| Rock | Granite |
| Sport | Skiing |
| Tartan | New Hampshire state tartan |
| State route marker | |
 | |
| State quarter | |
 Released in 2000 | |
| Lists of United States state symbols | |
Concord is the state capital, while Manchester is the largest city. New Hampshire has no general sales tax, nor income tax other than on interest and dividends. The New Hampshire primary is the first primary in the U.S. presidential election cycle. Its license plates carry the state motto, "Live Free or Die". The state's nickname, "The Granite State", refers to its extensive granite formations and quarries.[12]
In January 1776, it became the first of the British North American colonies to establish a government independent of the Kingdom of Great Britain's authority, and it was the first to establish its own state constitution. Six months later, it became one of the original 13 colonies that signed the United States Declaration of Independence, and in June 1788 it was the ninth state to ratify the United States Constitution, bringing that document into effect.
Historically, New Hampshire was a major center for textile manufacturing, shoemaking, and papermaking, with Amoskeag Manufacturing Company in Manchester at one time being the largest cotton textile plant in the world. Numerous mills were located along various rivers in the state, especially the Merrimack and Connecticut rivers. Many French Canadians migrated to New Hampshire to work the mills in the late 19th and early 20th century; New Hampshire still ranks second among states by percentage of people claiming French American ancestry, with 24.5% of the state identifying as such.
Manufacturing centers such as Manchester, Nashua, and Berlin were hit hard in the 1930s–1940s, as major manufacturing industries left New England and moved to the southern United States or overseas, reflecting nationwide trends. In the 1950s and 1960s, defense contractors moved into many of the former mills, such as Sanders Associates in Nashua, and the population of southern New Hampshire surged beginning in the 1980s as major highways connected the region to Greater Boston and established several bedroom communities in the state.
With some of the highest ski mountains on the East Coast, New Hampshire's major recreational attractions include skiing, snowmobiling, and other winter sports, hiking and mountaineering (Mount Monadnock in the state's southwestern corner is among the most climbed mountains in the U.S.), observing the fall foliage, summer cottages along many lakes and the seacoast, motor sports at the New Hampshire Motor Speedway, and Motorcycle Week, a popular motorcycle rally held in Weirs Beach in Laconia in June. The White Mountain National Forest links the Vermont and Maine portions of the Appalachian Trail, and has the Mount Washington Auto Road, where visitors may drive to the top of 6,288-foot (1,917 m) Mount Washington.
Among prominent individuals from New Hampshire are founding father Nicholas Gilman, Senator Daniel Webster, Revolutionary War hero John Stark, editor Horace Greeley, founder of the Christian Science religion Mary Baker Eddy, poet Robert Frost, astronaut Alan Shepard, rock musician Ronnie James Dio, author Dan Brown, actor Adam Sandler, inventor Dean Kamen, comedians Sarah Silverman and Seth Meyers, restaurateurs Richard and Maurice McDonald, and President of the United States Franklin Pierce.
Etymology
The state was named after the southern English county of Hampshire by Captain John Mason.[13]
Geography
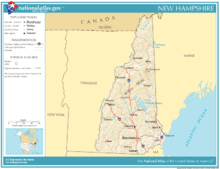
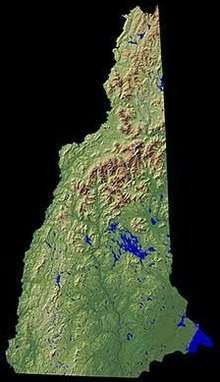


New Hampshire is part of the six-state New England region. It is bounded by Quebec, Canada, to the north and northwest; Maine and the Atlantic Ocean to the east; Massachusetts to the south; and Vermont to the west. New Hampshire's major regions are the Great North Woods, the White Mountains, the Lakes Region, the Seacoast, the Merrimack Valley, the Monadnock Region, and the Dartmouth-Lake Sunapee area. New Hampshire has the shortest ocean coastline of any U.S. coastal state, with a length of 18 miles (29 km),[14] sometimes measured as only 13 miles (21 km).[15] New Hampshire was home to the rock formation called the Old Man of the Mountain, a face-like profile in Franconia Notch, until the formation disintegrated in May 2003.
The White Mountains range in New Hampshire spans the north-central portion of the state. The range includes Mount Washington, the tallest in the northeastern U.S.—site of the second-highest wind speed ever recorded—[16]as well as Mount Adams and Mount Jefferson. With hurricane-force winds every third day on average, more than a hundred recorded deaths among visitors, and conspicuous krumholtz (dwarf, matted trees much like a carpet of bonsai trees), the climate on the upper reaches of Mount Washington has inspired the weather observatory on the peak to claim that the area has the "World's Worst Weather".[17]
In the flatter southwest corner of New Hampshire, the landmark Mount Monadnock has given its name to a class of earth-forms—a monadnock—signifying, in geomorphology, any isolated resistant peak rising from a less resistant eroded plain.
Major rivers include the 110-mile (177 km) Merrimack River, which bisects the lower half of the state north–south and ends up in Newburyport, Massachusetts. Its tributaries include the Contoocook River, Pemigewasset River, and Winnipesaukee River. The 410-mile (660 km) Connecticut River, which starts at New Hampshire's Connecticut Lakes and flows south to Connecticut, defines the western border with Vermont. The state border is not in the center of that river, as is usually the case, but at the low-water mark on the Vermont side; meaning that the entire river along the Vermont border (save for areas where the water level has been raised by a dam) lies within New Hampshire.[18] Only one town—Pittsburg—shares a land border with the state of Vermont. The "northwesternmost headwaters" of the Connecticut also define the Canada–U.S. border.
The Piscataqua River and its several tributaries form the state's only significant ocean port where they flow into the Atlantic at Portsmouth. The Salmon Falls River and the Piscataqua define the southern portion of the border with Maine. The Piscataqua River boundary was the subject of a border dispute between New Hampshire and Maine in 2001, with New Hampshire claiming dominion over several islands (primarily Seavey's Island) that include the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard. The U.S. Supreme Court dismissed the case in 2002, leaving ownership of the island with Maine. New Hampshire still claims sovereignty of the base, however.[19]
The largest of New Hampshire's lakes is Lake Winnipesaukee, which covers 71 square miles (184 km2) in the east-central part of New Hampshire. Umbagog Lake along the Maine border, approximately 12.3 square miles (31.9 km2), is a distant second. Squam Lake is the second largest lake entirely in New Hampshire.
New Hampshire has the shortest ocean coastline of any state in the United States, approximately 18 miles (29 km) long.[20] Hampton Beach is a popular local summer destination. About 7 miles (11 km) offshore are the Isles of Shoals, nine small islands (four of which are in New Hampshire) known as the site of a 19th-century art colony founded by poet Celia Thaxter, and the alleged location of one of the buried treasures of the pirate Blackbeard.
It is the state with the highest percentage of timberland area in the country.[21] New Hampshire is in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome. Much of the state, in particular the White Mountains, is covered by the conifers and northern hardwoods of the New England-Acadian forests. The southeast corner of the state and parts of the Connecticut River along the Vermont border are covered by the mixed oaks of the Northeastern coastal forests.[22]
The northern third of the state is locally referred to as the "north country" or "north of the notches", in reference to White Mountain passes that channel traffic. It contains less than 5% of the state's population, suffers relatively high poverty, and is steadily losing population as the logging and paper industries decline. However, the tourist industry, in particular visitors who go to northern New Hampshire to ski, snowboard, hike and mountain bike, has helped offset economic losses from mill closures.
Winter season lengths are projected to decline at ski areas across New Hampshire due to the effects of global warming, which is likely to continue the historic contraction and consolidation of the ski industry and threaten individual ski businesses and communities that rely on ski tourism.[23]
Climate

New Hampshire experiences a humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dfa in some southern areas, Dfb in most of the state, and Dfc subarctic in some northern highland areas), with warm, humid summers, and long, cold, and snowy winters. Precipitation is fairly evenly distributed all year. The climate of the southeastern portion is moderated by the Atlantic Ocean and averages relatively milder winters (for New Hampshire), while the northern and interior portions experience colder temperatures and lower humidity. Winters are cold and snowy throughout the state, and especially severe in the northern and mountainous areas. Average annual snowfall ranges from 60 inches (150 cm) to over 100 inches (250 cm) across the state.[24]
Average daytime highs are in the mid 70s°F to low 80s°F (24–28°C) throughout the state in July, with overnight lows in the mid 50s°F to low 60s°F (13–15°C). January temperatures range from an average high of 34 °F (1 °C) on the coast to overnight lows below 0 °F (−18 °C) in the far north and at high elevations. Average annual precipitation statewide is roughly 40 inches (100 cm) with some variation occurring in the White Mountains due to differences in elevation and annual snowfall. New Hampshire's highest recorded temperature was 106 °F (41 °C) in Nashua on July 4, 1911, while the lowest recorded temperature was −47 °F (−44 °C) atop Mount Washington on January 29, 1934. Mount Washington also saw an unofficial −50 °F (−46 °C) reading on January 22, 1885, which, if made official, would tie the all-time record low for New England (also −50 °F (−46 °C) at Big Black River, Maine, on January 16, 2009, and Bloomfield, Vermont on December 30, 1933).
Extreme snow is often associated with a nor'easter, such as the Blizzard of '78 and the Blizzard of 1993, when several feet accumulated across portions of the state over 24 to 48 hours. Lighter snowfalls of several inches occur frequently throughout winter, often associated with an Alberta Clipper.
New Hampshire, on occasion, is affected by hurricanes and tropical storms although by the time they reach the state they are often extratropical, with most storms striking the southern New England coastline and moving inland or passing by offshore in the Gulf of Maine. Most of New Hampshire averages fewer than 20 days of thunderstorms per year and an average of two tornadoes occur annually statewide.[25]
The National Arbor Day Foundation plant hardiness zone map depicts zones 3, 4, 5, and 6 occurring throughout the state[26] and indicates the transition from a relatively cooler to warmer climate as one travels southward across New Hampshire. The 1990 USDA plant hardiness zones for New Hampshire range from zone 3b in the north to zone 5b in the south.[27]
| Location | July (°F) | July (°C) | January (°F) | January (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manchester | 82/64 | 28/17 | 33/15 | 0/−9 |
| Nashua | 82/59 | 28/15 | 33/12 | 0/−11 |
| Concord | 82/57 | 28/14 | 30/10 | −1/−12 |
| Portsmouth | 79/61 | 26/16 | 32/16 | 0/−9 |
| Keene | 82/56 | 28/13 | 31/9 | −1/−12 |
| Laconia | 81/60 | 27/16 | 30/11 | −1/−11 |
| Lebanon | 82/58 | 28/14 | 30/8 | −1/−13 |
Metropolitan areas

Metropolitan areas in the New England region are defined by the U.S. Census Bureau as New England City and Town Areas (NECTAs). The following is a list of NECTAs fully or partially in New Hampshire:[29][30]
- Berlin
- Boston–Cambridge–Nashua
- Claremont
- Concord
- Dover–Durham
- Franklin
- Keene
- Laconia
- Lebanon
- Manchester
- Portsmouth
History
.jpg)
.jpg)
Various Algonquian-speaking Abenaki tribes, largely divided between the Androscoggin and Pennacook nations, inhabited the area before European settlement.[31] Despite the similar language, they had a very different culture and religion from other Algonquian peoples. English and French explorers visited New Hampshire in 1600–1605, and David Thompson settled at Odiorne's Point in present-day Rye in 1623. The first permanent settlement was at Hilton's Point (present-day Dover). By 1631, the Upper Plantation comprised modern-day Dover, Durham and Stratham; in 1679, it became the "Royal Province". Father Rale's War was fought between the colonists and the Wabanaki Confederacy throughout New Hampshire.
New Hampshire was one of the thirteen colonies that rebelled against British rule during the American Revolution. By the time of the American Revolution, New Hampshire was a divided province. The economic and social life of the Seacoast region revolved around sawmills, shipyards, merchants' warehouses, and established village and town centers. Wealthy merchants built substantial homes, furnished them with the finest luxuries, and invested their capital in trade and land speculation. At the other end of the social scale, there developed a permanent class of day laborers, mariners, indentured servants and even slaves.
The only battle fought in New Hampshire was the raid on Fort William and Mary, December 14, 1774, in Portsmouth Harbor, which netted the rebellion sizable quantities of gunpowder, small arms and cannon. (General Sullivan, leader of the raid, described it as, "remainder of the powder, the small arms, bayonets, and cartouche-boxes, together with the cannon and ordnance stores") over the course of two nights. This raid was preceded by a warning to local patriots the previous day, by Paul Revere on December 13, 1774, that the fort was to be reinforced by troops sailing from Boston. According to unverified accounts, the gunpowder was later used at the Battle of Bunker Hill, transported there by Major Demerit, who was one of several New Hampshire patriots who stored the powder in their homes until it was transported elsewhere for use in revolutionary activities. During the raid, the British soldiers fired upon the rebels with cannon and muskets. Although there were apparently no casualties, these were among the first shots in the American Revolutionary period, occurring approximately five months before the Battles of Lexington and Concord.
The United States Constitution was ratified by New Hampshire on June 21, 1788, when New Hampshire became the ninth state to do so.[32]
New Hampshire was a Jacksonian stronghold; the state sent Franklin Pierce to the White House in the election of 1852. Industrialization took the form of numerous textile mills, which in turn attracted large flows of immigrants from Quebec (the "French Canadians") and Ireland. The northern parts of the state produced lumber, and the mountains provided tourist attractions. After 1960, the textile industry collapsed, but the economy rebounded as a center of high technology and as a service provider.
Starting in 1952, New Hampshire gained national and international attention for its presidential primary held early in every presidential election year. It immediately became the most important testing grounds for candidates for the Republican and Democratic nominations. The media gave New Hampshire and Iowa about half of all the attention paid to all states in the primary process, magnifying the state's decision powers and spurring repeated efforts by out-of-state politicians to change the rules.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 141,885 | — | |
| 1800 | 183,858 | 29.6% | |
| 1810 | 214,460 | 16.6% | |
| 1820 | 244,155 | 13.8% | |
| 1830 | 269,328 | 10.3% | |
| 1840 | 284,574 | 5.7% | |
| 1850 | 317,976 | 11.7% | |
| 1860 | 326,073 | 2.5% | |
| 1870 | 318,300 | −2.4% | |
| 1880 | 346,991 | 9.0% | |
| 1890 | 376,530 | 8.5% | |
| 1900 | 411,588 | 9.3% | |
| 1910 | 430,572 | 4.6% | |
| 1920 | 443,083 | 2.9% | |
| 1930 | 465,293 | 5.0% | |
| 1940 | 491,524 | 5.6% | |
| 1950 | 533,242 | 8.5% | |
| 1960 | 606,921 | 13.8% | |
| 1970 | 737,681 | 21.5% | |
| 1980 | 920,610 | 24.8% | |
| 1990 | 1,109,252 | 20.5% | |
| 2000 | 1,235,786 | 11.4% | |
| 2010 | 1,316,470 | 6.5% | |
| Est. 2019 | 1,359,711 | 3.3% | |
| Source: 1910–2010[33] 2018 estimate[34] | |||
Population
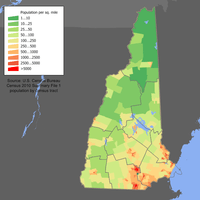
The United States Census Bureau estimates the population of New Hampshire was 1,359,711 on July 1, 2019, a 3.28% increase since the 2010 United States Census.[34] The center of population of New Hampshire is in Merrimack County, in the town of Pembroke.[35] The center of population has moved south 12 miles (19 km) since 1950,[36] a reflection of the fact the state's fastest growth has been along its southern border, which is within commuting range of Boston and other Massachusetts cities.
The most densely populated areas generally lie within 50 miles (80 km) of the Massachusetts border, and are concentrated in two areas: along the Merrimack River Valley running from Concord to Nashua, and in the Seacoast Region along an axis stretching from Rochester to Portsmouth. Outside of those two regions, only one community, the city of Keene, has a population over 20,000. The four counties covering these two areas account for 72% of the state population, and one (Hillsborough) has nearly 30% of the state population, as well as the two most populous communities, Manchester and Nashua. The northern portion of the state is very sparsely populated: the largest county by area, Coos, covers the northern one-fourth of the state and has only around 31,000 people, about a third of whom live in a single community (Berlin). The trends over the past several decades have been for the population to shift southward, as many northern communities lack the economic base to maintain their populations, while southern communities have been absorbed by the Greater Boston metropolis.
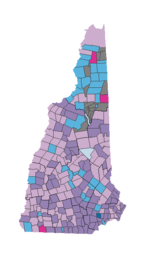
As of the 2010 Census, the population of New Hampshire was 1,316,470. The gender makeup of the state was 49.3% male and 50.7% female. 21.8% of the population were under the age of 18; 64.6% were between the ages of 18 and 64; and 13.5% were 65 years of age or older.[37]
The racial makeup of New Hampshire as of the 2010 Census was:[37]
- White: 93.9% (92.3% non-Hispanic)
- Black or African American: 1.1%
- American Indian and Alaska Native: 0.2%
- Asian: 2.2%
- Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander: approx. 0.0%
- Other race: 0.9%
- Two or more races: 1.6%
| Racial composition | 1990[38] | 2000[39] | 2010[37] |
|---|---|---|---|
| White | 98.0% | 96.0% | 93.9% |
| Black or African American | 0.6% | 0.7% | 1.1% |
| American Indian and Alaska Native | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% |
| Asian | 0.8% | 1.3% | 2.2% |
| Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander | – | – | 0.0% |
| Other race | 0.3% | 0.6% | 0.9% |
| Two or more races | – | 1.1% | 1.6% |
Hispanic or Latino of any race were 2.8% of the population in 2010: 0.6% were of Mexican, 0.9% Puerto Rican, 0.1% Cuban, and 1.2% other Hispanic or Latino origin.
According to the 2012–2017 American Community Survey, the largest ancestry groups in the state were Irish (20.6%), English (16.5%), French (14.0%), Italian (10.4%), German (9.1%), French Canadian (8.9%), and American (4.8%).[40]
New Hampshire has the highest percentage (22.9%) of residents with French/French-Canadian/Acadian ancestry of any U.S. state.[41]
According to the Census Bureau's American Community Survey estimates from 2017, 2.1% of the population aged 5 and older speak Spanish at home, while 1.8% speak French.[42] In Coos County, 9.6% of the population speaks French at home,[43] down from 16% in 2000.[44]
Birth data
Note: Percentages in table do not add up to 100, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.
| Race | 2013[45] | 2014[46] | 2015[47] | 2016[48] | 2017[49] | 2018[50] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White: | 11,570 (93.3%) | 11,494 (93.4%) | 11,600 (93.3%) | ... | ... | ... |
| > Non-Hispanic White | 11,064 (89.2%) | 10,917 (88.7%) | 10,928 (87.9%) | 10,641 (86.7%) | 10,524 (86.9%) | 10,317 (86.0%) |
| Asian | 485 (3.9%) | 528 (4.3%) | 527 (4.2%) | 504 (4.1%) | 479 (4.0%) | 472 (3.9%) |
| Black | 316 (2.5%) | 259 (2.1%) | 280 (2.3%) | 208 (1.7%) | 234 (1.9%) | 241 (2.0%) |
| American Indian | 25 (0.2%) | 21 (0.2%) | 26 (0.2%) | 8 (0.0%) | 26 (0.2%) | 13 (0.1%) |
| Hispanic (of any race) | 513 (4.1%) | 591 (4.8%) | 638 (5.1%) | 697 (5.7%) | 673 (5.6%) | 745 (6.2%) |
| Total New Hampshire | 12,396 (100%) | 12,302 (100%) | 12,433 (100%) | 12,267 (100%) | 12,116 (100%) | 11,995 (100%) |
- Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic origin are not collected, but included in one Hispanic group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
Religion
A Pew survey showed that the religious affiliations of the people of New Hampshire was as follows: Protestant 30%, Catholic 26%, LDS (Mormon) 1%, Jewish 1%, Jehovah's Witness 2% and non-religious at 36%.[51]
A survey suggests people in New Hampshire and Vermont[note 3] are less likely than other Americans to attend weekly services and only 54% say that they are "absolutely certain there is a God" compared to 71% in the rest of the nation.[note 4][52] New Hampshire and Vermont are also at the lowest levels among states in religious commitment. In 2012, 23% of New Hampshire residents in a Gallup poll considered themselves "very religious", while 52% considered themselves "non-religious".[53] According to the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) the largest denominations are the Catholic Church with 311,028 members; The United Church of Christ with 26,321 members; and the United Methodist Church with 18,029 members.[54]
In 2016, a Gallup Poll found that New Hampshire was the least religious state in the United States. Only 20% of respondents in New Hampshire categorized themselves as "very religious", while the nationwide average was 40%.[55]
Economy
- Total employment (2016): 594,243
- Number of employer establishments: 37,868[56]
The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that New Hampshire's total state product in 2018 was $86 billion, ranking 40th in the United States.[57] Median household income in 2017 was $74,801, the fourth highest in the country (including Washington, DC).[58] Its agricultural outputs are dairy products, nursery stock, cattle, apples and eggs. Its industrial outputs are machinery, electric equipment, rubber and plastic products, and tourism is a major component of the economy.[59]
New Hampshire experienced a major shift in its economic base during the 20th century. Historically, the base was composed of traditional New England textiles, shoe making, and small machine shops, drawing upon low-wage labor from nearby small farms and from parts of Quebec. Today, of the state's total manufacturing dollar value, these sectors contribute only two percent for textiles, two percent for leather goods, and nine percent for machining.[60] They experienced a sharp decline due to obsolete plants and the lure of cheaper wages in the Southern United States.
New Hampshire today has a broad-based and growing economy, with a state GDP growth rate of 2.2% in 2018.[57] The state's largest economic sectors in 2018, based on contribution to GDP, are: 15% real estate and rental and leasing; 13% professional business services; 12% manufacturing; 10% government and government services; and 9% health care and social services.[61]
The state's budget in FY2018 was $5.97 billion, including $1.79 billion in federal funds.[62] The issue of taxation is controversial in New Hampshire, which has a property tax (subject to municipal control) but no broad sales tax or income tax. The state does have narrower taxes on meals, lodging, vehicles, business and investment income, and tolls on state roads.
According to the Energy Information Administration, New Hampshire's energy consumption and per capita energy consumption are among the lowest in the country. The Seabrook Station Nuclear Power Plant, near Portsmouth, is the largest nuclear reactor in New England and provided 57% of New Hampshire's electricity generation and 27% of its electricity consumption in 2017. In 2016 and 2017, New Hampshire obtained more of its electricity generation from wind power than coal-fired power plants. Approximately 32% of New Hampshire's electricity consumption came from renewable resources (including nuclear, hydroelectric, wind, and other renewable resources). New Hampshire was a net exporter of electricity, exporting 63 trillion British thermal units (18 TWh).[63]
New Hampshire's residential electricity use is low compared with the national average, in part because demand for air conditioning is low during the generally mild summer months and because few households use electricity as their primary energy source for home heating. Nearly half of New Hampshire households use fuel oil for winter heating, which is one of the largest shares in the United States. New Hampshire has potential for renewable energies like wind power, hydroelectricity, and wood fuel.[63]
The state has no general sales tax and no personal state income tax (the state does tax, at a 5 percent rate, income from dividends and interest), and the legislature has exercised fiscal restraint. Efforts to diversify the state's general economy have been ongoing.
New Hampshire's lack of a broad-based tax system has resulted in the state's local communities having some of the nation's highest property taxes. However, the state's overall tax burden is relatively low; in 2010 New Hampshire ranked 44th highest among states in combined average state and local tax burden.[64]
As of February 2010, the state's unemployment rate was 7.1%.[65] By October 2010, the unemployment rate had dropped to 5.4%.[66] The (preliminary) seasonally unemployment rate in April 2019 was 2.4% based on a 767,500 person civilian workforce with 749,000 people in employment. New Hampshire's workforce is 90% in nonfarm employment, with 18% employed in trade, transportation, and utilities; 17% in education and health care; 12% in government; 11% in professional and business services; and 10% in leisure and hospitality.[67]
According to a 2013 study by Phoenix Marketing International, New Hampshire had the eighth-highest percentage of millionaire households in the United States, at 6.48% of all households.[68] In 2013, New Hampshire also had the nation's lowest poverty rate at just 8.7% of all residents, according to the Census Bureau.[69]
Largest employers
In March 2018, 86% of New Hampshire's workforce were employed by the private sector, with 53% of those workers being employed by firms with less than 100 employees. About 14% of private sector employees are employed by firms with more than 1,000 employees.[70]
According to community surveys by the Economic & Labor Market Information Bureau of NH Employment Security, the following are the largest private employers in the state:[71]
| Employer | Location (base) | Employees |
|---|---|---|
| Dartmouth–Hitchcock Medical Center | Lebanon | 7,000 |
| Fidelity Investments | Merrimack | 6,000 |
| BAE Systems North America | Nashua | 4,700 |
| Liberty Mutual | Dover | 3,800 |
| Elliot Hospital | Manchester | 3,800 |
| Dartmouth College | Hanover | 3,500 |
| Southern New Hampshire University | Manchester | 3,200 |
| Capital Regional Health Care | Concord | 3,000 |
| Catholic Medical Center | Manchester | 2,300 |
| Southern New Hampshire Health System | Nashua | 2,200 |
New Hampshire's state government employs approximately 6,100 people. Additionally, the U.S. Department of State employs approximately 1,600 people at the National Visa Center in Portsmouth, which processes United States immigrant visa petitions.[71]
Law and government

The governor of New Hampshire, since January 5, 2017, is Chris Sununu (Republican). New Hampshire's two U.S. senators are Jeanne Shaheen and Maggie Hassan (both Democrats), both of whom are former governors. New Hampshire's two U.S. representatives as of January 2019 are Chris Pappas and Ann McLane Kuster (both Democrats).
New Hampshire is an alcoholic beverage control state, and through the State Liquor Commission it takes in $100 million from the sale and distribution of liquor.[72]
New Hampshire is the only state in the U.S. that does not require adults to wear seat belts in their vehicles.
Governing documents
The New Hampshire State Constitution of 1783 is the supreme law of the state, followed by the New Hampshire Revised Statutes Annotated and the New Hampshire Code of Administrative Rules. These are roughly analogous to the federal United States Constitution, United States Code and Code of Federal Regulations respectively.
Branches of government
New Hampshire has a bifurcated executive branch, consisting of the governor and a five-member executive council which votes on state contracts worth more than $5,000 and "advises and consents" to the governor's nominations to major state positions such as department heads and all judgeships and pardon requests. New Hampshire does not have a lieutenant governor; the Senate president serves as "acting governor" whenever the governor is unable to perform the duties.
The legislature is called the General Court. It consists of the House of Representatives and the Senate. There are 400 representatives, making it one of the largest elected bodies in the English-speaking world,[73] and 24 senators. Legislators are paid a nominal salary of $200 per year, the lowest in the U.S. by far, thus most are effectively volunteers, nearly half of which are retirees. (For details, see the article on Government of New Hampshire.)
The state's sole appellate court is the New Hampshire Supreme Court. The Superior Court is the court of general jurisdiction and the only court which provides for jury trials in civil or criminal cases. The other state courts are the Probate Court, District Court, and the Family Division.
Local government
New Hampshire has 10 counties and 234 cities and towns.
New Hampshire is a "Dillon Rule" state, meaning the state retains all powers not specifically granted to municipalities. Even so, the legislature strongly favors local control, particularly with regard to land use regulations. New Hampshire municipalities are classified as towns or cities, which differ primarily by the form of government. Most towns generally operate on the town meeting form of government, where the registered voters in the town act as the town legislature, and a board of selectmen acts as the executive of the town. Larger towns and the state's thirteen cities operate either on a council–manager or council–mayor form of government. There is no difference, from the state government's point of view, between towns and cities besides the form of government. All state-level statutes treat all municipalities identically.
New Hampshire has a small number of unincorporated areas that are titled as grants, locations, purchases, or townships. These locations have limited to no self-government, and services are generally provided for them by neighboring towns or the county or state where needed. As of the 2000 census, there were 25 of these left in New Hampshire, accounting for a total population of 173 people (as of 2000); several were entirely depopulated. All but two of these unincorporated areas are in Coos County.
Politics
The Republican Party and the Democratic Party are the two largest parties in the state. A plurality of voters are registered as undeclared, and can choose either ballot in the primary and then regain their undeclared status after voting.[74] The Libertarian Party had official party status from 1990 to 1996. There is also a program known as the Free State Project with the goal of turning New Hampshire into a libertarian stronghold by suggesting that libertarians move there so they can concentrate their power. The Libertarian Party regained ballot access after the 2016 election because the gubernatorial candidate received more than four percent of the vote.[75]
As of February 5, 2016, there were 882,959 registered voters, of whom 389,472 (44.1%) did not declare a political party affiliation, 262,111 (29.7%) were Republican, and 231,376 (26.2%) were Democratic.[76]
New Hampshire primary

New Hampshire is internationally known for the New Hampshire primary, the first primary in the quadrennial American presidential election cycle. State law requires that the Secretary of State schedule this election at least one week before any "similar event". However, the Iowa caucus has preceded the New Hampshire primary. This primary, as the nation's first contest that uses the same procedure as the general election, draws more attention than those in other states, and it has been decisive in shaping the national contest.
State law permits a town with fewer than 100 residents to open its polls at midnight, and close when all registered citizens have cast their ballots. As such, the communities of Dixville Notch in Coos County and Hart's Location in Carroll County, among others, have chosen to implement these provisions. Dixville Notch and Hart's Location are traditionally the first places in both New Hampshire and the U.S. to vote in presidential primaries and elections.
Nominations for all other partisan offices are decided in a separate primary election. In Presidential election cycles, this is the second primary election held in New Hampshire.
Saint Anselm College in Goffstown has become a popular campaign spot for politicians as well as several national presidential debates because of its proximity to Manchester-Boston Regional Airport.[77][78][79]
Elections

In the past, New Hampshire has often voted Republican. Between 1856 and 1988, New Hampshire cast its electoral votes for the Democratic presidential ticket six times: Woodrow Wilson (twice), Franklin D. Roosevelt (three times), and Lyndon B. Johnson (once).
Beginning in 1992, New Hampshire became a swing state in both national and local elections. The state supported Democrats Bill Clinton in 1992 and 1996, John Kerry in 2004, Barack Obama in 2008 and 2012, and Hillary Clinton in 2016. It was the only state in the country to switch from supporting Republican George W. Bush in the 2000 election to supporting his Democratic challenger in the 2004 election, when John Kerry, a senator from neighboring Massachusetts, won the state. Donald Trump very narrowly lost the state in 2016.
The Democrats dominated elections in New Hampshire in 2006 and 2008. In 2006, Democrats won both congressional seats (electing Carol Shea-Porter in the first district and Paul Hodes in the second), re-elected Governor John Lynch, and gained a majority on the Executive Council and in both houses for the first time since 1911. Democrats had not held both the legislature and the governorship since 1874.[80] Neither U.S. Senate seat was up for a vote in 2006. In 2008, Democrats retained their majorities, governorship, and Congressional seats; and former governor Jeanne Shaheen defeated incumbent Republican John E. Sununu for the U.S. Senate in a rematch of the 2002 contest.
The 2008 elections resulted in women holding a majority, 13 of the 24 seats, in the New Hampshire Senate, a first for any legislative body in the United States.[81]
In the 2010 midterm elections, Republicans made historic gains in New Hampshire, capturing veto-proof majorities in the state legislature, taking all five seats in the Executive Council, electing a new U.S. senator, Kelly Ayotte, winning both U.S. House seats, and reducing the margin of victory of incumbent Governor John Lynch compared to his 2006 and 2008 landslide wins.
In the 2012 state legislative elections, Democrats took back the New Hampshire House of Representatives and narrowed the Republican majority in the New Hampshire Senate to 13–11.[82] In 2012, New Hampshire became the first state in U.S. history to elect an all-female federal delegation: Democratic Congresswomen Carol Shea-Porter of Congressional District 1 and Ann McLane Kuster of Congressional District 2 accompanied U.S. Senators Jeanne Shaheen and Kelly Ayotte in 2013. Further, the state elected its second female governor: Democrat Maggie Hassan.
In the 2014 elections, Republicans retook the New Hampshire House of Representatives with a 239–160 majority and expanded their majority in the New Hampshire Senate to 14 of the Senate's 24 seats. On the national level, incumbent Democratic Senator Jeanne Shaheen defeated her Republican challenger, former Massachusetts senator Scott Brown. New Hampshire also elected Frank Guinta (R) for its First Congressional District representative and Ann Kuster (D) for its Second Congressional District representative.
In the 2016 elections, Republicans held the New Hampshire House of Representatives with a majority of 220–175, and held onto their 14 seats in the New Hampshire Senate. In the gubernatorial race, retiring Governor Maggie Hassan was succeeded by Republican Chris Sununu, who defeated Democratic nominee Colin Van Ostern. Sununu became the state's first Republican governor since Craig Benson, who left office in 2005 following defeat by John Lynch. Republicans control the governor's office and both chambers of the state legislature, a governing trifecta in which the Republicans have full governing power.[83] In the presidential race, the state voted for the Democratic nominee, former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton over the Republican nominee, Donald Trump, by a margin of 2,736 votes, or 0.3%, one of the closest results the state has ever seen in a presidential race, while Libertarian nominee Gary Johnson received 4.12% of the vote. The Democrats also won a competitive race in the Second Congressional District, as well as a competitive senate race. New Hampshire's congressional delegation currently consists of exclusively Democrats. It is one of only eight states with an entirely Democratic delegation, five of which are in New England (the others are Delaware, Hawaii, and New Mexico).
Transportation
Highways
New Hampshire has a well-maintained, well-signed network of Interstate highways, U.S. highways, and state highways. State highway markers still depict the Old Man of the Mountain despite that rock formation's demise in 2003. Several route numbers align with the same route numbers in neighboring states. State highway numbering is arbitrary, with no overall system as with U.S. and Interstate systems. Major routes include:








Air
New Hampshire has 25 public-use airports, three with some scheduled commercial passenger service. The busiest airport by number of passengers handled is Manchester-Boston Regional Airport in Manchester and Londonderry, which serves the Greater Boston metropolitan area.
Public transportation
Long-distance intercity passenger rail service is provided by Amtrak's Vermonter and Downeaster lines.
Greyhound, Concord Coach, Vermont Translines and Dartmouth Coach all provide intercity bus connections to and from points in New Hampshire and to long-distance points beyond and in between.
As of 2013, Boston-centered MBTA Commuter Rail services reach only as far as northern Massachusetts. The New Hampshire Rail Transit Authority is working to extend "Capital Corridor" service from Lowell, Massachusetts, to Nashua, Concord, and Manchester, including Manchester-Boston Regional Airport; and "Coastal Corridor" service from Haverhill, Massachusetts, to Plaistow, New Hampshire.[84][85] Legislation in 2007 created the New Hampshire Rail Transit Authority (NHRTA) with the goal of overseeing the development of commuter rail in the state of New Hampshire. In 2011, Governor John Lynch vetoed HB 218, a bill passed by Republican lawmakers, which would have drastically curtailed the powers and responsibilities of NHRTA.[86][87] The I-93 Corridor transit study suggested a rail alternative along the Manchester and Lawrence branch line which could provide freight and passenger service.[88] This rail corridor would also have access to Manchester-Boston Regional Airport.
Eleven public transit authorities operate local and regional bus services around the state, and eight private carriers operate express bus services which link with the national intercity bus network.[89] The New Hampshire Department of Transportation operates a statewide ride-sharing match service, in addition to independent ride matching and guaranteed ride home programs.[89]
Tourist railroads include the Conway Scenic Railroad, Hobo-Winnipesaukee Railroad, and the Mount Washington Cog Railway.
Freight railways
Freight railways in New Hampshire include Claremont & Concord Railroad (CCRR), Pan Am Railways via subsidiary Springfield Terminal Railway (ST), the New England Central Railroad (NHCR), the St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad (SLR), and New Hampshire Northcoast Corporation (NHN).
Education


High schools
The first public high schools in the state were the Boys' High School and the Girls' High School of Portsmouth, established either in 1827 or 1830 depending on the source.[90][91][92]
New Hampshire has more than 80 public high schools, many of which serve more than one town. The largest is Pinkerton Academy in Derry, which is owned by a private non-profit organization and serves as the public high school of a number of neighboring towns. There are at least 30 private high schools in the state.
New Hampshire is also the home of several prestigious university-preparatory schools, such as Phillips Exeter Academy, St. Paul's School, Proctor Academy, Brewster Academy, and Kimball Union Academy.
In 2008 the state tied with Massachusetts as having the highest scores on the SAT and ACT standardized tests given to high school students.[93]
Colleges and universities
- Antioch University New England
- Colby-Sawyer College
- Community College System of New Hampshire:
- Great Bay Community College
- Lakes Region Community College
- Manchester Community College
- Nashua Community College
- NHTI, Concord's Community College
- River Valley Community College
- White Mountains Community College
- Dartmouth College
- Tuck School of Business
- Geisel School of Medicine
- Thayer School of Engineering
- Franklin Pierce University
- Hellenic American University
- Magdalen College of the Liberal Arts
- MCPHS University
- New England College
- New Hampshire Institute of Art
- Rivier University
- Saint Anselm College
- Southern New Hampshire University
- Thomas More College of Liberal Arts
- University System of New Hampshire:
- University of New Hampshire
- University of New Hampshire School of Law
- University of New Hampshire at Manchester
- Granite State College
- Keene State College
- Plymouth State University
- University of New Hampshire
Media
Daily newspapers
- Berlin Daily Sun
- Concord Monitor
- Conway Daily Sun
- The Dartmouth of Dartmouth College/Hanover
- Eagle Times of Claremont
- Eagle Tribune (Lawrence, Massachusetts area, including parts of southern New Hampshire)
- Foster's Daily Democrat of Dover
- Keene Sentinel
- Laconia Citizen
- Laconia Daily Sun
- New Hampshire Union Leader of Manchester, formerly known as the Manchester Union-Leader
- The Portsmouth Herald
- The Telegraph of Nashua
- The Sun (Lowell, Massachusetts area, including parts of southern New Hampshire)
- Valley News of Lebanon
Other publications
- Area News Group
- Business New Hampshire Magazine
- The Cabinet Press
- Milford Cabinet
- Bedford Journal
- Hollis/Brookline Journal
- Merrimack Journal
- Carriage Towne News (covering Kingston and surrounding towns)
- The Exeter News-Letter
- The Hampton Union
- Hippo Press (covering Manchester, Nashua and Concord)
- Manchester Express
- Manchester Ink Link[94]
- The New Hampshire (University of New Hampshire student newspaper)
- New Hampshire Business Review
- New Hampshire Free Press
- The New Hampshire Gazette (Portsmouth alternative biweekly)
- NH Living Magazine[95]
- Salmon Press Newspapers (family of weekly newspapers covering Lakes Region & North Country)
Radio stations
Television stations
Sports
The following professional and professional development sports teams are in New Hampshire:
| Club | Sport / League | Level |
|---|---|---|
| New Hampshire Fisher Cats | Eastern League (class AA baseball) | Professional |
| Seacoast United Phantoms | USL League Two (soccer) | Professional development (adult) |
| Manchester Freedom | Independent Women's Football League | Professional |
| NH Olympic Development Program (soccer) | US Soccer Region 1 | Professional development (youth: ages 11–17) |
The New Hampshire Motor Speedway in Loudon is an oval track and road course which has been visited by national motorsport championship series such as the NASCAR Monster Energy Cup Series, the NASCAR Xfinity Series, the NASCAR Camping World Truck Series, NASCAR Whelen Modified Tour, American Canadian Tour (ACT), the Champ Car and the IndyCar Series. Other motor racing venues include Star Speedway and New England Dragway in Epping, Lee Speedway in Lee, Twin State Speedway in Claremont, Monadnock Speedway in Winchester and Canaan Fair Speedway in Canaan.
New Hampshire has two NCAA Division I teams: the Dartmouth Big Green (Ivy League) and the New Hampshire Wildcats (America East Conference), as well as three Division II teams: Franklin Pierce Ravens, Saint Anselm Hawks and Southern New Hampshire Penmen (Northeast-10 Conference).
The Seacoast United Phantoms are a soccer team based in Hampton, New Hampshire. Founded in 1996, the team plays in the USL League Two, the fourth tier of the American Soccer Pyramid, in the Northeast Division of the Eastern Conference. The team plays its home games at Amesbury Sports Park, where they have played since 2017.
Annually since 2002, high-school statewide all-stars compete against Vermont in ten sports during "Twin State" playoffs.[96]
Culture
In the spring, New Hampshire's many sap houses hold sugaring-off open houses. In summer and early autumn, New Hampshire is home to many county fairs, the largest being the Hopkinton State Fair, in Contoocook. New Hampshire's Lakes Region is home to many summer camps, especially around Lake Winnipesaukee, and is a popular tourist destination. The Peterborough Players have performed every summer in Peterborough, New Hampshire since 1933. The Barnstormers Theatre in Tamworth, New Hampshire, founded in 1931, is one of the longest-running professional summer theaters in the United States.[97]
In September, New Hampshire is host to the New Hampshire Highland Games. New Hampshire has also registered an official tartan with the proper authorities in Scotland, used to make kilts worn by the Lincoln Police Department while its officers serve during the games. The fall foliage peaks in mid-October. In the winter, New Hampshire's ski areas and snowmobile trails attract visitors from a wide area.[98] After the lakes freeze over they become dotted with ice fishing ice houses, known locally as bobhouses.
Funspot, the world's largest video arcade[99] (now termed a museum), is in Laconia.
In fiction
Comics
- Al Capp, creator of the comic strip Li'l Abner, used to joke that Dogpatch, the setting for the strip, was based on Seabrook, where he would vacation with his wife.[100]
Television
- In the cable television series Breaking Bad, the character Walter White escapes to a cabin in a fictional county in northern New Hampshire, and two of the show's episodes are titled "Live Free or Die" and "Granite State".[101]
- In the show The West Wing, President Bartlet is from New Hampshire, and the state features prominently in several episodes.
Notable residents or natives
New Hampshire firsts
- On January 5, 1776 at Exeter, the Provincial Congress of New Hampshire ratified the first independent constitution in the Americas, free of British rule.[102]
- On June 12, 1800, Fernald's Island in the Piscataqua River became the first government-sanctioned U.S. Navy shipyard.
- Started in 1822, Dublin's Juvenile Library was the first free public library.
- In 1828, the first women's strike in the nation took place at Dover's Cocheco Mills.
- Founded in 1833, the Peterborough Town Library was the first public library, supported with public funds, in the world.[103]
- On August 3, 1852, Center Harbor was the site of the first intercollegiate athletic event. Harvard defeated Yale in a 2-mile (3.2 km) rowing race on Lake Winnipesaukee, the first meeting in a rivalry that continues to this day.
- Finished on June 27, 1874, the first trans-Atlantic telecommunications cable between Europe and America stretched from Balinskelligs Bay, Ireland, to Rye, New Hampshire.
- On February 6, 1901, a group of nine conservationists founded the Society for the Protection of New Hampshire Forests, the first forest-conservation advocacy group in the U.S.
- In 1908, Monsignor Pierre Hevey organized the nation's first credit union, "La Caisse Populaire, Ste-Marie" (The People's Bank) in Manchester, to help mill workers save and borrow money, which is now St. Mary's Bank.[104]
- In 1933, the League of New Hampshire Craftsmen held the first crafts fair in the nation.[105]
- In July 1944, the Bretton Woods Agreement, the first fully negotiated system intended to govern monetary relations among independent nation-states, was signed at the Mount Washington Hotel.
- On May 5, 1961, Alan Shepard of Derry rode a Mercury spacecraft and became the first American in space.
- In 1963, New Hampshire's legislature approved the nation's first modern state lottery, which began play in 1964.
- In 1966, Ralph Baer of Sanders Associates, Inc., Nashua, recruited engineers to develop the first home video game.
- Christa McAuliffe of Concord became the first private citizen selected to venture into space. She perished with her six Challenger crewmates on January 28, 1986.
- On May 17, 1996, New Hampshire became the first state in the country to install a green LED traffic light. New Hampshire was selected because it was the first state to install the red and yellow variety statewide.[106]
- On May 31, 2007, New Hampshire became the first state to recognize same-sex unions "without a court order or the threat of one".[107]
Notes
- Elevation adjusted to North American Vertical Datum of 1988.
- The summit of Mount Washington is the highest point in northeastern North America.
- which were polled jointly
- 86% in Alabama and South Carolina
References
- "New Hampshire Almanac: Fast New Hampshire Facts". NH.gov. New Hampshire State Library. 2011. Archived from the original on July 31, 2012. Retrieved December 22, 2014.
- For use in a reference publication see Mencken, H. L. (1990). American Language Supplement 2. Knopf-Doubleday.
The adjoining New Hampshire is usually called the Granite State, which the DAE traces to 1830. It has also been called the White Mountain State, the Mother of Rivers, and the Switzerland of America
- For official use see "Fast New Hampshire Facts". New Hampshire Almanac. State of New Hampshire. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved February 12, 2018.
- For contemporary use see "'Live Free or Die' – The Story of the New Hampshire Motto". New England Today. Yankee Publishing, Inc. August 10, 2017. Archived from the original on February 12, 2018. Retrieved February 12, 2018.
For tourism purposes, however, New Hampshire typically tones it down a bit, presenting itself as the Granite State or the White Mountain State...
- "New Hampshire Almanac: State Official and Honorary State Song". NH.gov. New Hampshire State Library. 2012. Archived from the original on October 17, 2014. Retrieved December 22, 2014.
- In the event of a vacancy in the office of Governor, the President of the State Senate is first in line to assume the gubernatorial powers and duties as Acting Governor.
- "Geographic Identifiers: New Hampshire". American Factfinder. U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved June 10, 2016.
- "Mt Wash". NGS data sheet. U.S. National Geodetic Survey.
- "Elevations and Distances in the United States". United States Geological Survey. 2001. Archived from the original on October 15, 2011. Retrieved October 24, 2011.
- "Income in the Past 12 Months (in 2017 Inflation-Adjusted Dollars) (S1901): 2017 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates: New Hampshire". American Factfinder. U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2019.
- "New Hampshire Revised Statutes, Title 1, Chapter 3-C:1—Official State Language". State of New Hampshire. 1995. Archived from the original on October 4, 2018. Retrieved December 9, 2016.
- "New Hampshire Revised Statutes, Title 1, Chapter 3-C:2—Exceptions". State of New Hampshire. 1995. Archived from the original on November 17, 2004. Retrieved December 9, 2016.
- Fehlau, Erin (June 16, 2017). "Blackberry now the state berry of NH". WMUR News. Retrieved December 30, 2019.
- "Visit NH: State Facts". NH Department of Resources and Economic Development. Archived from the original on October 14, 2010. Retrieved August 30, 2010.
- "Origin of 'New Hampshire'". State Symbols USA. Archived from the original on September 4, 2015. Retrieved August 30, 2015.
- New Hampshire Coastal Access Map (PDF) (Map). New Hampshire Coastal Program. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved February 3, 2016.
- Beaver, Janice Cheryl (November 9, 2006). "U.S. International Borders: Brief Facts" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 1, 2019. Retrieved February 3, 2016.
- Filipov, David (January 31, 2010). "Record blown away, but pride stays put: N.H. summit's claim to nasty weather intact". The Boston Globe. Archived from the original on February 3, 2010. Retrieved February 9, 2010.
- "Mount Washington...Home of the World's Worst Weather". Mt. Washington Observatory. Archived from the original on January 18, 2010. Retrieved March 22, 2010.
- Vermont v. New Hampshire 289 U.S. 593 (1933)
- "HJR 1—Final Version". New Hampshire General Court. Archived from the original on October 16, 2015. Retrieved September 22, 2015.
- "New Hampshire Water Resources Primer, Chapter 6: Coastal and Estuarine Waters" (PDF). NH Dept. of Environmental Services. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 5, 2011. Retrieved April 11, 2011.
- Nowak, David J.; Greenfield, Eric J. (May 9, 2012). "Tree and impervious cover in the United States (2012)" (PDF). Landscape and Urban Planning. 107: 21–30. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2012.04.005. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 12, 2014. Retrieved February 3, 2016.
- Olson, D. M.; Dinerstein, E.; et al. (2001). "Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World: A New Map of Life on Earth". BioScience. 51 (11): 933–938. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[0933:TEOTWA]2.0.CO;2. Archived from the original on October 14, 2011.
- "Climate Change Vulnerability of the Northeast US Winter Tourism Sector" (PDF). University of Ottawa Department of Geography and Institute of Science. Retrieved February 3, 2019.
- Dellinger, Dan (June 23, 2004). "Snowfall — Average Total in Inches". NOAA. Archived from the original on June 19, 2011. Retrieved May 25, 2007.
- "Annual average number of tornadoes 1953–2004". NOAA. Archived from the original on October 16, 2011. Retrieved May 25, 2007.
- "2006 arborday.org Hardiness Zone Map". National Arbor Day Foundation. Archived from the original on February 17, 2011. Retrieved May 25, 2007.
- "New Hampshire USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map". PlantMaps. Archived from the original on December 8, 2010. Retrieved November 15, 2010.
- "New Hampshire climate averages". Weatherbase. Archived from the original on November 22, 2015. Retrieved November 21, 2015.
- "Metropolitan New England City and Town Areas—Current/ACS18—Data as of January 1, 2018". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 7, 2019. Retrieved February 5, 2019.
- "Metropolitan and NECTA Divisions published by CES". Bureau of Labor Statistics. Archived from the original on February 7, 2019. Retrieved February 5, 2019.
- "Abenaki". tolatsga.org. Archived from the original on April 11, 2010. Retrieved September 4, 2017.
- "Observing Constitution Day". Archives.gov. Archived from the original on August 17, 2019. Retrieved April 7, 2016.
- "Resident Population Data—2010 Census". 2010.census.gov. US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on December 20, 2012. Retrieved December 24, 2012.
- "QuickFacts New Hampshire; UNITED STATES". 2018 Population Estimates. United States Census Bureau, Population Division. March 10, 2019. Archived from the original on February 2, 2019. Retrieved March 10, 2019.
- "Population and Population Centers by State: 2000". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on September 18, 2008. Retrieved December 5, 2008.
- "Population Center of New Hampshire, 1950–2000" (PDF). NH Office of Energy and Planning. October 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 24, 2008. Retrieved September 10, 2008.
- "2010 Demographic Profile Data". U.S. Census Bureau.
- "Historical Census Statistics on Population Totals By Race, 1790 to 1990, and By Hispanic Origin, 1970 to 1990, For The United States, Regions, Divisions, and States". Census.gov. July 25, 2008. Archived from the original on July 25, 2008. Retrieved September 4, 2017.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
- "Census Viewer". Censusviewer.com. January 8, 2014. Archived from the original on January 8, 2014. Retrieved September 4, 2017.
- "2017 American Community Survey". U.S. Census Bureau.
- "Selected Social Characteristics in the United States: 2017 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates (DP02): All States within United States and Puerto Rico". United States Census Bureau. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved March 25, 2020.
- "Language Spoken at Home by Ability to Speak English for the Population 5 Years and Over: 2015 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates (B16001): New Hampshire". American Factfinder. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved April 6, 2017.
- "Language Spoken at Home by Ability to Speak English for the Population 5 Years and Over: 2015 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates (B16001): Coos County, New Hampshire". American Factfinder. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved April 6, 2017.
- "MLA Language Map Data Center". Modern Language Association. July 17, 2007. Archived from the original on December 5, 2010. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- "Births: Final Data for 2013" (PDF). Cdc.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 11, 2017. Retrieved September 4, 2017.
- "Births: Final Data for 2014" (PDF). Cdc.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 14, 2017. Retrieved September 4, 2017.
- "Births: Final Data for 2015" (PDF). Cdc.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 31, 2017. Retrieved September 4, 2017.
- "National Vital Statistics Reports" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on June 3, 2018. Retrieved September 26, 2018.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on February 1, 2019. Retrieved February 21, 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Data" (PDF). www.cdc.gov. Retrieved December 21, 2019.
- "Adults in New Hampshire". Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. May 11, 2015. Archived from the original on September 25, 2017. Retrieved September 19, 2017.
- Allen, Mike (June 23, 2008). "Pew survey finds believers flexible". Politico.com. Politico. Archived from the original on September 18, 2010. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- Frank Newport (March 27, 2012). "Mississippi Is the Most Religious U.S. State". Gallup. Archived from the original on March 28, 2012. Retrieved March 28, 2012.
- "The Association of Religion Data Archives | State Membership Report". Thearda.com. The Association of Religion Data Archives. Archived from the original on December 2, 2013. Retrieved November 22, 2013.
- Inc, Gallup (February 4, 2016). "New Hampshire Now Least Religious State in U.S." Gallup.com. Archived from the original on November 6, 2019. Retrieved November 6, 2019.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on November 16, 2019. Retrieved November 11, 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Gross Domestic Product by State, Fourth Quarter and Annual 2018" (PDF). Bea.gov. US Bureau of Economic Analysis. May 1, 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 1, 2019. Retrieved June 13, 2019.
- "U.S. Census Bureau—Historical Income Tables: Table H-8. Median Household Income by State". census.gov. September 12, 2018. Archived from the original on April 10, 2019. Retrieved June 20, 2019.
- "State at a Glance — New Hampshire". U.S. Department of Labor. October 12, 2007. Archived from the original on October 23, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- U.S. Economic Census for 1997, Manufacturing, New Hampshire
- "Bureau of Economic Analysis—Gross Domestic Product by State". May 1, 2019. Archived from the original on October 23, 2018. Retrieved June 18, 2019.
- "FY 2017 and FY2018 Budget" (PDF). New Hampshire General Court. June 22, 2017. Retrieved June 13, 2019.
- "New Hampshire—State Energy Profile Overview—U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)". www.eia.gov. Archived from the original on June 15, 2019. Retrieved June 18, 2019.
- "New Hampshire's State and Local Tax Burden, 1970–2006". The Tax Foundation. August 7, 2008. Archived from the original on May 12, 2012. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- "Local Area Unemployment Statistics". Bureau of Labor Statistics. Archived from the original on July 25, 2018. Retrieved March 26, 2010.
- "NH unemployment rate drops to 5.4 percent in Oct". BusinessWeek. November 16, 2010. Archived from the original on September 12, 2012. Retrieved December 8, 2010.
- "New Hampshire Economy at a Glance". www.bls.gov. Archived from the original on April 18, 2019. Retrieved June 18, 2019.
- Frank, Robert. "Top states for millionaires per capita". CNBC. Archived from the original on January 22, 2014. Retrieved January 25, 2014.
- Hess, Alexander E.M. (October 6, 2014). "The 10 states with the best quality of life". Yahoo Finance. Archived from the original on November 26, 2018. Retrieved November 12, 2014.
- "Firms by Size | Data & Statistics | Data and Analysis | Economic & Labor Market Information Bureau (ELMI) | NH Employment Security". www.nhes.nh.gov. Archived from the original on May 3, 2017. Retrieved June 18, 2019.
- "New Hampshire Community Profiles | Data and Analysis | Economic & Labor Market Information Bureau (ELMI) | NH Employment Security". www.nhes.nh.gov. Archived from the original on November 10, 2018. Retrieved June 18, 2019.
- "State of New Hampshire Monthly Revenue Focus (FY 2005)" (PDF). NH Department of Administrative Services. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 11, 2011. Retrieved February 3, 2016.
- ""House Fast Fact", New Hampshire House of Representatives". Gencourt.state.nh.us. New Hampshire General Court. Archived from the original on August 15, 2007. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- "Independents Become Largest Voting Bloc in New Hampshire". Archived from the original on September 8, 2008. Retrieved December 29, 2008.
- Brooks, David (November 11, 2016). "Libertarian Party likely on N.H. ballots by 2018". Concord Monitor. Archived from the original on December 3, 2016. Retrieved December 9, 2016.
- "2016 Election Information". NH Secretary of State. February 5, 2016. Archived from the original on February 8, 2016. Retrieved February 8, 2016.
- "CBS's Face the Nation : Saint Anselm College". November 13, 2008. Archived from the original on November 13, 2008. Retrieved September 4, 2017.
- "Saint Anselm College—Saint Anselm to Host ABC Debates in Dana Center". May 11, 2008. Archived from the original on May 11, 2008. Retrieved September 4, 2017.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
- William Schpero (January 7, 2008). "Candidates Face Off at St. Anselm's College". CBS News. Archived from the original on November 1, 2010. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- Kocher, Fred (December 22, 2006). "Storm of change sweeps through N.H. Legislature". Mass High Tech: The Journal of New England Technology. Archived from the original on January 12, 2008. Retrieved April 28, 2008.
- Senate President Sylvia Larsen, quoted in "Women make up majority in state Senate," New Hampshire Union Leader, November 6, 2008.
- Sullivan, Sean (November 9, 2012). "New Hampshire's Democratic wave, explained". The Washington Post. Washington, DC. Archived from the original on May 14, 2015. Retrieved September 2, 2017.
- Lee, K. k Rebecca Lai, Jasmine C.; Russell, Karl (November 11, 2016). "In a Further Blow to Democrats, Republicans Increase Their Hold on State Governments". Nytimes.com. Archived from the original on August 27, 2017. Retrieved September 4, 2017.
- "Draft NHRTA Prioritized Goals" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 2, 2010. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- "NH Rail Transit Authority Meeting". Nashua Regional Planning Commission. Archived from the original on June 5, 2009. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- "Business groups unite to support NH Rail Transit Authority". New Hampshire Journal. Archived from the original on August 23, 2011.
- "Governor Lynch's Veto Message Regarding HB 218". Press Releases. Governor John Lynch. Archived from the original on June 19, 2011.
- "New Hampshire State Rail Plan" (PDF). Nh.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved September 4, 2017.
- "NH Rideshare—Your Source for Transportation Alternatives". NH Dept. of Transportation. Archived from the original on April 25, 2011. Retrieved February 3, 2016.
- Grizzell, Emit Duncan (1923). Origin and Development of the High School in New England Before 1865. New York: Macmillan Company. p. 181. ISBN 978-1-4067-4258-9. OCLC 1921554.
- Bush, George Gary (1898). № 22, History of Education in New Hampshire. United States Bureau of Education Circular of Information, № 3, 1898. Washington, D. C.: GPO. p. 134. OCLC 817663.
- Wallace, R. Stuart; Hall, Douglas E. "A New Hampshire Education Timeline" (PDF). New Hampshire Historical Society. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 25, 2009. Retrieved January 28, 2009.
- "The IQ-Trapper". V-weiss.de. Volkmar Weiss. May 30, 2009. Archived from the original on April 17, 2010. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- "ManchesterInkLink.com". Manchester Ink Link. Archived from the original on December 1, 2016. Retrieved December 9, 2016.
- "NHLiving.com". New Hampshire Living. Archived from the original on January 24, 2016. Retrieved February 3, 2016.
- Fantino, John A. (July 20, 2008). "Vermont breaks through". Burlington Free Press.
- "The New England Summer Theater—Six of the Oldest". May 27, 2017. Archived from the original on February 21, 2019. Retrieved February 20, 2019.
- "Bureau of Trails". nhstateparks.org. NH Division of Parks and Recreation. Archived from the original on February 5, 2016. Retrieved February 3, 2016.
- "2017 Business Excellence Winner: Robert Lawton of Funspot". www.nhbr.com. November 1, 2017. Archived from the original on December 23, 2017. Retrieved December 22, 2017.
- Morse, Susan (July 4, 2004). "Last of the Yankees". Portsmouth Herald. Archived from the original on September 26, 2005. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- Goodman, Tim (September 22, 2013). "'Breaking Bad' Deconstruction, Ep. 15: 'Granite State'". The Hollywood Reporter. Archived from the original on February 19, 2014. Retrieved March 10, 2014.
- "NH Firsts & Bests". Nh.gov. State of New Hampshire. Archived from the original on November 28, 2011. Retrieved December 13, 2011.
- "The Peterborough Town Library". Libraryhistorybuff.org. The Library History Buff. Archived from the original on July 14, 2010. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- "History". St. Mary's Bank. Archived from the original on February 8, 2016. Retrieved February 3, 2016.
- Nowers, E. (August 25, 2007). "League of New Hampshire Craftsmen's Fair". nhcrafts.org. League of N.H. Craftsmen. Archived from the original on October 13, 2007. Retrieved November 9, 2007.
- "Sending a bright signal", Concord Monitor pg B-6, May 18, 1996
- Wang, Beverley (April 26, 2007). "State Senate approves civil unions for same-sex couples". Concord Monitor. Archived from the original on November 3, 2007. Retrieved April 26, 2007.
Further reading
- Sletcher, Michael (2004). New England. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press. ISBN 978-0-313-32753-7.
- Land Use in Cornish, N.H., a 2006 documentary presentation by James M. Patterson of the Valley News, depicts various aspects of the societal and cultural environment of northern New Hampshire.
External links
- State government
- Official website
- New Hampshire Almanac
- Visitnh.gov, New Hampshire Office of Travel and Tourism Development
- U.S. Government
- New Hampshire State Guide from the Library of Congress
- Energy Facts for New Hampshire
- New Hampshire State Facts, USDA Economic Research Service
- USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of New Hampshire
- Other
- Internet Movie Database listing of films shot in the state
- New Hampshire Historical Society
- New Hampshire at Curlie
| Preceded by South Carolina |
List of U.S. states by date of admission to the Union Ratified Constitution on June 21, 1788 (9th) |
Succeeded by Virginia |