Microsoft Store (digital)
Microsoft Store (formerly known as Windows Store) is a digital distribution platform owned by Microsoft. It started as an app store for Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 as the primary means of distributing Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps. With Windows 10, Microsoft merged its other distribution platforms (Windows Marketplace, Windows Phone Store, Xbox Music, Xbox Video, Xbox Store, and a web storefront also known as "Microsoft Store") into Microsoft Store, making it a unified distribution point for apps, console games, digital music, and digital videos. E-books were included until 2019.[1] Some content is available free of charge from the store.
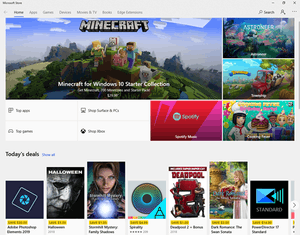 Microsoft Store on Windows 10 | |
| Other names | Windows Store |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Initial release | October 26, 2012 |
| Operating system | Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows 10, Windows 10 Mobile, Xbox One |
| Predecessor | Windows Marketplace, Windows Phone Store, Xbox Video, Xbox Music, Xbox Store |
| Service name | Windows Store Service (WSService) |
| Type | App store, online music store |
| Website | www |
| Part of a series on |
| Windows 10 |
|---|
|
| Related |
|
In 2015, over 669,000 apps were available on the store. Categories containing the largest number of apps are "Books and Reference", "Education", "Entertainment", and "Games". The majority of the app developers have one app.
As with other similar platforms, such as the Google Play and Mac App Store, Microsoft Store is curated, and apps must be certified for compatibility and content. In addition to the user-facing Microsoft Store client, the store has a developer portal with which developers can interact. Microsoft takes 30% of the sale price for apps. Prior to January 1, 2015, this cut was reduced to 20% after the developer's profits reached $25,000.
History
The Web-based storefront
Microsoft previously maintained a similar digital distribution system for software known as Windows Marketplace, which allowed customers to purchase software online. The marketplace tracked product keys and licenses, allowing users to retrieve their purchases when switching computers.[2] Windows Marketplace was discontinued in November 2008.[3] At this point, Microsoft opened a Web-based storefront called "Microsoft Store".[4]
Windows 8
Microsoft first announced Windows Store, a digital distribution service for Windows at its presentation during the Build developer conference on September 13, 2011.[5] Further details announced during the conference revealed that the store would be able to hold listings for both certified traditional Windows apps, as well as what were called "Metro-style apps" at the time: tightly-sandboxed software based on Microsoft design guidelines that are constantly monitored for quality and compliance. For consumers, Windows Store is intended to be the only way to obtain Metro-style apps.[6][7] While announced alongside the "Developer Preview" release of Windows 8, Windows Store itself did not become available until the "Consumer Preview", released in February 2012.[8][9]
Updates to apps published on the Store after July 1, 2019 will not be available to Windows 8 RTM users. Per Microsoft lifecycle policies, Windows 8 had been unsupported since 2016.[10]
Windows 8.1
An updated version of Windows Store was introduced in Windows 8.1. Its home page was remodeled to display apps in focused categories (such as popular, recommended, top free and paid, and special offers) with expanded details, while the ability for apps to automatically update was also added.[11] Windows 8.1 Update also introduced other notable presentation changes, including increasing the top app lists to return 1000 apps instead of 100 apps, a 'picks for you' section, and changing the default sorting for reviews to be by 'most popular'.
Updates to apps published on the Store after July 1, 2023 will not be available to Windows 8.1.[10]
Windows 10
Windows 10 was released with an updated version of the Windows Store which merged Microsoft's other distribution platforms (Windows Marketplace, Windows Phone Store, Xbox Video and Xbox Music) into a unified store front for Windows 10 on all platforms, offering apps, games, music, film, TV series,[12][13] themes,[14] and ebooks.[15]

In September 2017, Microsoft began to re-brand Windows Store as Microsoft Store, with a new icon carrying the Microsoft logo.[16] Xbox Store was merged into this new version of the platform.[17]
Web apps and traditional desktop software can be packaged for distribution on Windows Store. Desktop software distributed through Windows Store are packaged using the App-V system to allow sandboxing.[18][19]
In February 2018, Microsoft announced that Progressive Web Apps would begin to be available in the Microsoft Store, and Microsoft would automatically add selected quality progressive web apps through the Bing crawler or allow developers to submit Progressive Web Apps to the Microsoft Store.[20][21]
Windows Server
Windows Store is available in Windows Server 2012 but is not installed by default.[22] It is unavailable in Windows Server 2016. However, UWP apps can be acquired from Microsoft Store for Business (formerly Windows Store for Business) and installed through sideloading.[23][24]
Details
Microsoft Store is the primary means of distributing Windows Store apps to users. Although sideloading apps from outside the store is supported, out-of-box sideloading support on Windows 8 is only available on the Enterprise edition of Windows 8 running on computers that have joined a Windows domain. Sideloading on Windows RT and Windows 8 Pro, and on Windows 8 Enterprise computers without a domain affiliation, requires purchase of additional licenses through volume licensing.[25] Windows 10 removes this requirement, allowing users to freely enable or disable sideloading.[26]
Initially, Microsoft took a 30% cut of app sales until it reached US$25,000 in revenue, after which the cut dropped to 20%. On January 1, 2015, the reduction in cut at $25,000 was removed, and Microsoft takes a 30% cut of all app purchases, regardless of overall sales.[27] Third-party transactions are also allowed, of which Microsoft does not take a cut.[28] In early 2019, Microsoft lets app developers get 95% of app revenues, while Microsoft will only take 5% but only if user will download the app through a direct URL.[29] Individual developers are able to register for US$19 and companies for US$99.[30]
In 2015 over 669,000 apps were available on the store, including apps for Windows NT, Windows Phone, and UWP apps, which work on both platforms.[31] Categories containing the largest number of apps are "Games", "Entertainment", "Books and Reference", and "Education". The majority of the app developers have one app.[32] Both free and paid apps can be distributed through Microsoft Store, with paid apps ranging in cost from US$0.99 to $999.99. Developers from 120 countries can submit apps to Microsoft Store.[33] Apps may support any of 109 languages, as long as they support one of 12 app certification languages.[34][35][36]
On April 2, 2019, Microsoft announced that the sale of e-books on Microsoft Store had ceased. Due to DRM licenses that will not be renewed, all books will become inaccessible by July 2019, and Microsoft will automatically refund all users that had purchased books via the service.[37][1]
Guidelines
Similar to Windows Phone Store, Microsoft Store is regulated by Microsoft. Applicants must obtain Microsoft's approval before their app becomes available on the store. These apps may not contain, support or approve, gratuitous profanity, obscenity, pornography, discrimination, defamation, or politically offensive content. They may also not contain contents that are forbidden by or offensive to the jurisdiction, religion or norms of the target market. They may also not encourage, facilitate or glamorize violence, drugs, tobacco, alcohol and weapons.[38][39]
The following types of app are forbidden:
- Video game console emulators that are "primarily gaming experiences or target Xbox One"[39]
- Third-party web browsers that use their own layout engines[40]
Microsoft has indicated that it can remotely disable or remove apps from end-user systems for security or legal reasons; in the case of paid apps, refunds may be issued when this is done.[41]
Microsoft initially banned PEGI "18"-rated content from the store in Europe. However, critics noted that this made the content policies stricter than intended, as some PEGI 18-rated games are rated "Mature" on the U.S. ESRB system, which is the next lowest before its highest rating, "Adults Only". The guidelines were amended in December 2012 to remove the discrepancy.[42]
Developer portal
In addition to the user facing Microsoft Store client, the store also has a developer portal with which developers can interact. The Windows developer portal has the following sections for each app:
- App Summary - An overview page of a given app, including a downloads chart, quality chart, finance summary, and a sales chart.
- App Adoption - A page which shows adoption of the app, including conversions, referrers, and downloads.
- App Ratings - A ratings breakdown, as well as the ability to filter reviews by a region.
- App Quality - An overview page showcasing exceptions which have occurred in the app.
- App Finance - A page where a developer can download all transactions related to their app.
Developer tools
Microsoft Store provides developer tools for tracking apps in the store. One can track downloads, financials, crashes, adoption and ratings.[43]
The dashboard also presents a detailed breakdown on users by market, age, and region, as well as charts on number of downloads, purchases, and average time spent in an app. The dashboard also allows a developer to claim an app name for up to one year before the name is returned to the available pool.
See also
- List of Microsoft software
References
- Lee, Dave (April 4, 2019). "When this eBook store closes, your books disappear too". BBC. Retrieved April 4, 2019.
- "Microsoft Adds Digital Locker To Windows Marketplace". CRN. The Channel Company. August 28, 2006. Retrieved October 26, 2012.
- Leonhard, Woody. "What do we really know about Windows 8?". InfoWorld. IDG. Retrieved October 26, 2012.
- Chandran, Chakkaradeep (December 12, 2008). "Microsoft: Closing your digital locker account". Neowin. Retrieved October 23, 2019.
- "Keynote #1 | BUILD2011 | Channel 9". Channel 9. September 13, 2011. Retrieved October 14, 2012.
- "Microsoft talks Windows Store features, Metro app sandboxing for Windows 8 developers". The Verge. Vox Media. Retrieved September 8, 2012.
- Rosoff, Matt. "Here's Everything You Wanted To Know About Microsoft's Upcoming iPad Killers". Business Insider. Archived from the original on January 22, 2013. Retrieved February 10, 2012.
- "Windows 8 Developer Preview Available Tonight". PC Magazine. Retrieved May 29, 2013.
- "13 New Features in Windows 9 Consumer Preview". PC World. Retrieved August 21, 2013.
- Popa, Bogdan. "Microsoft Kills Off Windows 8 App Updates Earlier than Anticipated". softpedia. Retrieved April 19, 2019.
- Thurrott, Paul (June 17, 2013). "In Blue: Windows Store 2.0". Paul Thurrott's SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on June 20, 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- LeBlanc, Brandon (April 9, 2015). "Delivering a single unified Store experience in Windows 10". Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- LeBlanc, Brandon (July 6, 2015). "Updates to Entertainment in Windows 10". Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- Sarkar, Dona (January 12, 2017). "Announcing Windows 10 Insider Preview Build 15007 for PC and Mobile". Windows Experience Bog. Microsoft.
- Sarkar, Dona (January 19, 2017). "Announcing Windows 10 Insider Preview Build 15014 for PC and Mobile". Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- Warren, Tom (September 22, 2017). "Windows Store rebranded to Microsoft Store in Windows 10". The Verge. Vox Media.
- "Xbox Store rebranding to 'Microsoft Store' on Xbox One". Windows Central. Retrieved August 28, 2018.
- Peter, Bright (March 3, 2015). "Microsoft's next attempt to fill the Windows 10 app gap: Web app apps". Ars Technica. Condé Nast.
- Foley, Mary Jo (April 29, 2015). "Here's how Microsoft hopes to get Android and iOS phone apps into its Windows 10 Store". ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- "Microsoft is turning Progressive Web Apps into Windows apps". The Verge. Retrieved April 17, 2018.
- "Welcoming Progressive Web Apps to Microsoft Edge and Windows 10 - Microsoft Edge Dev BlogMicrosoft Edge Dev Blog". blogs.windows.com. Retrieved April 17, 2018.
- "Managing Privacy: Windows Store and Resulting Internet Communication". TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved January 30, 2014.
- Benisch, Derk (October 4, 2016). "Appreciating the Windows Server 2016 Desktop Experience". Nano Server blog. Microsoft.
- Savill, John (October 5, 2016). "Get Universal Applications on Windows Server 2016". Windows IT Pro. Penton. Archived from the original on October 6, 2017. Retrieved June 6, 2017.
- "How to Add and Remove Apps". TechNet. Microsoft. May 31, 2012. Retrieved October 4, 2012.
To enable sideloading on a Windows 8 Enterprise computer that is not domain-joined or on any Windows® 8 Pro computer, you must use a sideloading product activation key. To enable sideloading on a Windows® RT device, you must use a sideloading product activation key. For more information about sideloading product activation keys, see Microsoft Volume Licensing.
- "How to sideload apps in Windows 10". CNET. Retrieved April 6, 2017.
- "Microsoft Changes Windows Phone Developer Agreement, Takes Bigger Cut". UberGizmo. Retrieved November 21, 2014.
- "Making money with your apps through the Windows Store". Windows Store for developers. Microsoft. July 20, 2012. Retrieved October 14, 2012.
- "Microsoft Store Revenue Now Gives Developers A 95% Cut, On One Condition". Retrieved March 8, 2019.
- Brix, Todd (November 6, 2013). "Unifying Developer Registration". Windows App Builder Blog. Microsoft.
- "Microsoft by the numbers". Archived from the original on May 5, 2018.
- "AppFeds - Windows Store Stats".
- Wilhelm, Alex (September 11, 2012). "The Windows Store is now accepting open app submissions from developers in 120 countries". The Next Web. The Next Web Inc. Retrieved January 9, 2013.
- O'Brien, Terrence (April 18, 2012). "Windows Store slowly going global, 26 country specific markets launching with next update". Engadget. AOL. Retrieved July 9, 2012.
- Leblond, Antoine (April 18, 2012). "Windows Store expanding to new markets". Windows Store for developers. Microsoft. Retrieved July 9, 2012.
- Kerr, Dara (April 18, 2012). "Microsoft's Windows Store goes global with 33 more countries". CNET News. CBS Interactive. Retrieved July 9, 2012.
- Etienne, Stefan (April 2, 2019). "Microsoft stops selling ebooks and will refund customers for previous purchases". The Verge. Retrieved June 1, 2019.
- "Windows Store Policies". MSDN. Microsoft. March 29, 2017. Retrieved April 6, 2017.
- "Microsoft formally bans emulators on Xbox, Windows 10 download shops". Ars Technica. Retrieved April 6, 2017.
- Bott, Ed (March 10, 2017). "Google Chrome won't be allowed on Windows 10 S". ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- Keizer, Gregg. "Microsoft: We can remotely delete Windows 8 apps". Computerworld. IDG. Retrieved October 8, 2013.
- Kerr, Dara (October 25, 2012). "Microsoft reverses 'Mature' games ban in Euro Windows Store". CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved October 26, 2012.
- "Using the Windows Store Dashboard apps". May 17, 2013.
External links
- Microsoft Store Online
- "App page". Microsoft Store.