Melilla
Melilla (US: /məˈliːjə/ mə-LEE-yə, UK: /mɛˈ-/ meh-,[2][3] Spanish: [meˈliʎa]; Tarifit: Mlilt[4]) is a Spanish autonomous city located on the northwest coast of Africa, sharing a border with Morocco. It has an area of 12.3 km2 (4.7 sq mi). Melilla is one of two permanently inhabited Spanish cities in mainland Africa, the other being nearby Ceuta. It was part of the Province of Málaga until 14 March 1995, when the city's Statute of Autonomy was passed.
Melilla Mlilt (Tarifit) | |
|---|---|
 Port of Melilla | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
| Motto(s): «Praeferre Patriam Liberis Parentem Decet» (Latin) ("It is seemly for a parent to put his fatherland before his children") «Non Plus Ultra» (Latin) ("Nothing more beyond") | |
.svg.png) Location of Melilla | |
| Coordinates: 35°18′N 2°57′W | |
| Country | Spain |
| Government | |
| • Mayor-President | Eduardo de Castro (Cs) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 12.3 km2 (4.7 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 19th |
| Population (2018)[1] | |
| • Total | 86,384 |
| • Rank | 19th |
| • Density | 7,000/km2 (18,000/sq mi) |
| • % of Spain | 0.16% |
| Demonyms | Melillan melillense (es) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | ES-ML |
| Official languages | Spanish |
| Statute of Autonomy | 14 March 1995 |
| Parliament | Assembly of Melilla |
| Congress | 1 deputy (of 350) |
| Senate | 2 senators (of 264) |
| Website | www.melilla.es |
Melilla, like Ceuta, was a free port before Spain joined the European Union in 1986. As of 2011, Melilla had a population of 78,476, made up of ethnic Iberian Catholics (primarily from Andalusia and Catalonia), ethnic Riffian Berbers, and a small number of Sephardic Jews and Sindhi Hindus. Spanish and Riffian-Berber are the two most widely spoken languages, the former being the official language.
Melilla, like Ceuta, is officially claimed by Morocco.[5][6]
History
The current Berber name of Melilla is Mřič or Mlilt, which means the "white one". Melilla was an ancient Berber village. It was a Phoenician and later Punic trade establishment under the name of Rusadir (Rusaddir for the Romans and Russadeiron (Ancient Greek: Ῥυσσάδειρον) for the Greeks). Later Rome absorbed it as part of the Roman province of Mauretania Tingitana. Rusaddir is mentioned by Ptolemy (IV, 1) and Pliny (V, 18) who called it "oppidum et portus" (a fortified town and port). It was also cited by Mela (I, 33) as Rusicada, and by the Itinerarium Antonini.[7] Rusaddir was said to have once been the seat of a bishop, but there is no record of any bishop of the purported see,[7] which is not included in the Catholic Church's list of titular sees.[8] As centuries passed, it was ruled by Vandal, Byzantine and Hispano-Visigothic bands. The political history is similar to that of towns in the region of the Moroccan Rif and southern Spain. Local rule passed through a succession of Amazigh, Phoenician, Punic, Roman, Umayyad, Idrisid, Almoravid, Almohad, Marinid, and then Wattasid rulers. During the Middle Ages, it was known as the Berber city of Mlila. It was part of the Kingdom of Fez when the Catholic Monarchs, Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, asked Juan Alfonso Pérez de Guzmán, 3rd Duke of Medina Sidonia, to take the city.
In the Conquest of Melilla, the duke sent Pedro Estopiñán, who conquered the city in 1497 virtually without any violence,[9] a few years after Castile had taken control of the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada in 1492, which was the last remnant of Al-Andalus, the Muslim state in Iberia. Some Spaniards envisioned continuing the southward conquest of Muslim lands, deeper into Morocco, but such action was not seriously attempted. Spain's imperial energy was directed elsewhere, to the newly discovered continent across the Atlantic. The Muslims tried to take back control of Melilla in later centuries: they besieged it during 1694–1696 and 1774–1775. One Spanish officer reflected, "an hour in Melilla, from the point of view of merit, was worth more than thirty years of service to Spain."[10]

The current limits of the Spanish territory around the Melilla fortress were fixed by treaties with Morocco in 1859, 1860, 1861, and 1894. In the late 19th century, as Spanish influence expanded in this area, the Crown authorized Melilla as the only centre of trade on the Rif coast between Tetuan and the Algerian frontier. The value of trade increased, with goat skins, eggs and beeswax being the principal exports, and cotton goods, tea, sugar and candles being the chief imports.
In 1893, the Rif Berbers launched the First Melillan campaign to take back this area; Spain sent 25,000 Spanish soldiers to defend against them. The conflict was also known as the Margallo War, after Spanish General Juan García y Margallo, who was killed in the battle, and was the Governor of Melilla.
In 1908 two companies under the protection of Bou Hmara, a chieftain then ruling the Rif region, started mining lead and iron some 20 kilometers (12.4 miles) from Melilla. They started to construct a railway between the port and the mines. In October of that year the Bou Hmara's vassals revolted against him and raided the mines, which remained closed until June 1909. By July the workmen were again attacked and several were killed. Severe fighting between the Spaniards and the tribesmen followed, in the Second Melillan campaign.
In 1910, with the Rif having submitted, the Spaniards restarted the mines and undertook harbor works at Mar Chica, but hostilities broke out again in 1911. On 22 July 1921, the Berbers under the leadership of Abd el Krim inflicted a grave defeat on the Spanish (see Battle of Annual). The Berbers controlled the area until 1926, when the Spanish Protectorate finally managed to regain the area.

The city was used as one of the staging grounds for the July 1936 military coup d'état that started the Spanish Civil War. A statue of Francisco Franco, the putschist general assuming the control of the Army of Africa in 1936, is still prominently featured, the last statue of Franco in Spain.
On 6 November 2007, King Juan Carlos I and Queen Sofia visited the city, which caused a massive demonstration of support. The visit also sparked protests from the Moroccan government.[11] It was the first time a Spanish monarch had visited Melilla in 80 years.
Melilla (and Ceuta) have declared the Muslim holiday of Eid al-Adha or Feast of the Sacrifice, as an official public holiday from 2010 onward. This is the first time a non-Christian religious festival has been officially celebrated in Spain since the Reconquista.[12][13]
Geography
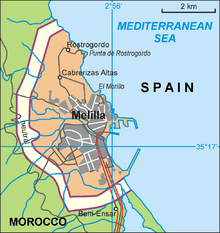
Melilla is located in the northwest of the African continent, next to the Alboran Sea and across the sea from the Spanish provinces of Granada and Almería. The city layout is arranged in a wide semicircle around the beach and the Port of Melilla, on the eastern side of the peninsula of Cape Tres Forcas, at the foot of Mount Gurugú and the mouth of the Río de Oro, 1 meter (3 ft 3 in) above sea level. The urban nucleus was originally a fortress, Melilla la Vieja, built on a peninsular mound about 30 meters (98 ft) in height.
The Moroccan settlement of Beni Ansar lies immediately south of Melilla. The nearest Moroccan city is Nador, and the ports of Melilla and Nador are both within the same bay; nearby is the Bou Areg Lagoon[14]
Political status
Local administration
Melilla has held local elections for its 25-seat legislature every four years since 1979. Since its Statute of Autonomy in 1995, the legislature has been called the Assembly and its leader the Mayor-President. In the most recent election in 2019, the People's Party (PP) won the most seats (10 seats), but could not maintain the role of Mayor-President for Juan José Imbroda, who had held office since 2000. The regionalist and leftist party Coalition for Melilla (CPM, 8 seats), the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE, 4 seats) and Citizens–Party of the Citizenry (Cs, 1 seat) voted in favour of the candidate of Cs, Eduardo de Castro.[15][16]
Subdivisions
Melilla is subdivided into eight districts (distritos), which are further subdivided into neighbourhoods (barrios):
- 1st
- Barrio de Medina Sidonia.
- Barrio del General Larrea.
- Barrio de Ataque Seco.
- 2nd
- Barrio Héroes de España.
- Barrio del General Gómez Jordana.
- Barrio Príncipe de Asturias.
- 3rd
- Barrio del Carmen.
- 4th
- Barrio Polígono Residencial La Paz.
- Barrio Hebreo-Tiro Nacional.
- 5th
- Barrio de Cristóbal Colón.
- Barrio de Cabrerizas.
- Barrio de Batería Jota.
- Barrio de Hernán Cortes y Las Palmeras.
- Barrio de Reina Regente.
- 6th
- Barrio de Concepción Arenal.
- Barrio Isaac Peral (Tesorillo).
- 7th
- Barrio del General Real.
- Polígono Industrial SEPES.
- Polígono Industrial Las Margaritas.
- Parque Empresarial La Frontera.
- 8th
- Barrio de la Libertad.
- Barrio del Hipódromo.
- Barrio de Alfonso XIII.
- Barrio Industrial.
- Barrio Virgen de la Victoria.
- Barrio de la Constitución.
- Barrio de los Pinares.
- Barrio de la Cañada de Hidum
Dispute with Morocco
The government of Morocco has repeatedly called for Spain to transfer the sovereignty of Ceuta and Melilla, along with uninhabited islets such as the islands of Alhucemas, Velez and the Perejil island, drawing comparisons with Spain's territorial claim to Gibraltar. In both cases, the national governments and local populations of the disputed territories reject these claims by a large majority.[17] The Spanish position states that both Ceuta and Melilla are integral parts of Spain, and have been since the 16th century, centuries prior to Morocco's independence from France in 1956, whereas Gibraltar, being a British Overseas Territory, is not and never has been part of the United Kingdom.[18] Both cities also have the same semi-autonomous status as the mainland region in Spain. Melilla has been under Spanish rule for longer than cities in northern Spain such as Pamplona or Tudela, and was conquered roughly in the same period as the last Muslim cities of Southern Spain such as Granada, Málaga, Ronda or Almería: Spain claims that the enclaves were established before the creation of the Kingdom of Morocco. Morocco denies these claims and maintains that the Spanish presence on or near its coast is a remnant of the colonial past which should be ended. The United Nations list of Non-Self-Governing Territories does not include these Spanish territories and the dispute remains bilaterally debated between Spain and Morocco.[19][20]
Climate
Melilla has a warm Mediterranean climate influenced by its proximity to the sea, rendering much cooler summers and more precipitation than inland areas deeper into Africa. The climate, in general, has a lot in common with the type found in southern coastal Spain on the European mainland, with relatively small temperature differences between seasons.
| Climate data for Melilla 47 m (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 25.6 (78.1) |
34.2 (93.6) |
29.6 (85.3) |
30.6 (87.1) |
33.0 (91.4) |
37.0 (98.6) |
41.8 (107.2) |
39.2 (102.6) |
36.0 (96.8) |
35.0 (95.0) |
32.6 (90.7) |
30.6 (87.1) |
41.8 (107.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 16.7 (62.1) |
17.0 (62.6) |
18.5 (65.3) |
20.1 (68.2) |
22.5 (72.5) |
25.8 (78.4) |
28.9 (84.0) |
29.4 (84.9) |
27.1 (80.8) |
23.7 (74.7) |
20.3 (68.5) |
17.8 (64.0) |
22.3 (72.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 13.3 (55.9) |
13.8 (56.8) |
15.2 (59.4) |
16.6 (61.9) |
19.1 (66.4) |
22.4 (72.3) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.9 (78.6) |
23.8 (74.8) |
20.4 (68.7) |
17.0 (62.6) |
14.6 (58.3) |
18.9 (66.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 9.9 (49.8) |
10.6 (51.1) |
11.9 (53.4) |
13.2 (55.8) |
15.7 (60.3) |
19.0 (66.2) |
21.7 (71.1) |
22.4 (72.3) |
20.5 (68.9) |
17.2 (63.0) |
13.7 (56.7) |
11.2 (52.2) |
15.6 (60.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 0.4 (32.7) |
2.8 (37.0) |
3.4 (38.1) |
6.0 (42.8) |
9.4 (48.9) |
12.4 (54.3) |
16.0 (60.8) |
14.6 (58.3) |
13.6 (56.5) |
9.4 (48.9) |
5.0 (41.0) |
4.0 (39.2) |
0.4 (32.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 58 (2.3) |
57 (2.2) |
44 (1.7) |
36 (1.4) |
20 (0.8) |
7 (0.3) |
1 (0.0) |
4 (0.2) |
16 (0.6) |
40 (1.6) |
57 (2.2) |
50 (2.0) |
391 (15.4) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 6 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 44 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 72 | 74 | 73 | 69 | 67 | 67 | 66 | 69 | 72 | 75 | 74 | 73 | 71 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 184 | 170 | 192 | 220 | 258 | 279 | 289 | 268 | 210 | 194 | 176 | 168 | 2,607 |
| Source: Agencia Estatal de Meteorología[21] | |||||||||||||
Economy
The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the autonomous community was 1.6 billion euros in 2018, accounting for 0.1% of Spanish economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 19,900 euros or 66% of the EU27 average in the same year. Melilla was the community with the lowest GDP per capita in Spain.[22]
The principal industry is fishing. Cross-border commerce (legal or smuggled) and Spanish and European grants and wages are the other income sources.
Melilla is regularly connected to the Iberian peninsula by air and sea traffic and is also economically connected to Morocco: most of its fruit and vegetables are imported across the border. Moroccans in the city's hinterland are attracted to it: 36,000 Moroccans cross the border daily to work, shop or trade goods.[23] The port of Melilla offers several daily connections to Almería and Málaga. Melilla Airport offers daily flights to Almería, Málaga and Madrid. Spanish operators Air Europa and Iberia operate in Melilla's airport.
Many people travelling between Europe and Morocco use the ferry links to Melilla, both for passengers and for freight. Because of this, the port and related companies form an important economic driver for the city.[23]
City culture and society

Melilla's Capilla de Santiago, or James's Chapel, by the city walls, is the only authentic Gothic structure in Africa.
In the first quarter of the 20th century, Melilla became a thriving port benefitting from the recently established Protectorate of Spanish Morocco in the contiguous Rif. The new architectural style of Modernisme was expressed by a new bourgeois class. This style, frequently referred to as the Catalan version of Art Nouveau, was extremely popular in the early part of the 20th century in Spain.
The workshops inspired by the Catalan architect Enrique Nieto continued in the modernist style, even after Modernisme went out of fashion elsewhere. Accordingly, Melilla has the second most important concentration of Modernist works in Spain after Barcelona. Nieto was in charge of designing the main Synagogue, the Central Mosque and various Catholic Churches.[24]
.jpg)
Melilla has been praised as an example of multiculturalism, being a small city in which one can find four major religions represented. However, the Christian majority of the past, constituting around 65% of the population at one point, has been shrinking, while the number of native Muslim inhabitants has steadily increased to its present 45% of the population. The Jewish and Hindu communities have also been shrinking due to economic emigration to mainland Spain (notably Malaga and Madrid).
Jews, who had lived in Melilla for centuries, have been leaving the city in recent years (from 20% of the population before World War II to less than 5% today). Most of the Jewish population has left for Israel and Venezuela. There is a small, autonomous, and commercially important Hindu community present in Melilla, which numbers about 100 members today.[25]
The amateur radio call sign used for both cities is EA9.[26]
Immigration

Melilla has been a popular destination for refugees and economic migrants in order to enter the European Union. The border is secured by the Melilla border fence, a six-metre-tall double fence with watch towers; yet refugees frequently manage to cross it.[27] Detection wires, radar, and day/night vision cameras are planned to increase security and prevent illegal immigration. In February 2014, over 200 migrants from sub-Saharan Africa scaled a security fence to get into the Melilla migrant reception centre. The reception centre, built for 480 migrants, was already overcrowded with 1,300 people.[28]
In recent years, the Spanish government has urged Moroccan security forces to stem the flow of migrants traveling towards Melilla. In 2015, Moroccan police dispersed migrant camps in the forests surrounding Melilla by torching makeshift homes and arresting migrants. Since the 2014 incident, Spain has installed additional security measures, including increased fencing, camera surveillance systems, and a more salient troop presence.[29] Attempted border crossings by migrants has decreased at both Melilla and Ceuta since its peak in 2015–2016; arrivals are down twenty-five percent since 2018. However, attempts by migrants to swarm the security fences at Melilla have been widely broadcast by Spanish media sources, creating a sense of urgency in mainland Spain. This fear over African migrants is seen by many as the main factor leading to the rise of Vox, Spain's populist party. Vox officials have frequently pointed to the immigration situation at Melilla and Ceuta proof of a crisis at Spain's border.[30]
Transportation
_ATR_ATR-72-500_(ATR-72-212A).jpg)

Melilla Airport is serviced by Air Nostrum, flying to the Spanish cities of Málaga, Madrid, Barcelona, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Palma de Mallorca, Granada, Badajoz, Sevilla and Almería. In April 2013, a local enterprise set up Melilla Airlines, flying from the city to Málaga.[31] The city is linked to Málaga, Almería and Motril by ferry.
Three roads connect Melilla and Morocco but require clearance through border checkpoints.
Sport

Melilla is a surfing destination.[32] The city's football club, UD Melilla, plays in the third tier of Spanish football, the Segunda División B. The club was founded in 1943 and since 1945 have played at the 12,000-seater Estadio Municipal Álvarez Claro. Until the other club was dissolved in 2012, UD Melilla played the Ceuta-Melilla derby against AD Ceuta. The clubs travelled to each other via the Spanish mainland to avoid entering Morocco.[33] The second-highest ranked club in the city are Casino del Real CF of the fourth-tier Tercera División. Football in the exclave is administered by the Melilla Football Federation.
Twin towns and sister cities
Melilla is twinned with:
- Caracas (Venezuela).
- Cavite City (Philippines).
- Ceuta (Spain).
- Toledo (Spain).
- Málaga (Spain).
- Montevideo (Uruguay).
- Motril (Spain); since January 2008.[34]
- Almería (Spain).[35]
- Mantua (Italy); since September 2013.[36]
- Vélez-Málaga (Spain); since January 2014.[37]
- Antequera (Spain); as of 2016, in process.[38]
Notable people
- Joaquín García-Morato y Castaño, 1st Count of Jarama (1904 in Melilla – 1939 in Griñón) was the leading Nationalist fighter ace of the Spanish Civil War.[39][40][41]
- Luis Prendes (1913 in Melilla – 1998 in Madrid) was a Spanish film actor. He appeared in 75 films between 1936 and 1998.
- Anselmo Pardo Alcaide (1913 in Melilla – 1977) was a Spanish entomologist, a world authority on Melyridae Meloidae- Malachiinae.[42]
- Mustafa Arruf (born 1958 in Melilla) is a Spanish sculptor.
- Mercedes Vecino (1916 in Melilla– 2004 in Alicante) was a Spanish film actress.[43]
- Emilio el Moro (1924 in Melilla – 1987) was a Spanish guitarist, singer and comedian.
- Lucinda Urrusti (born 1929 in Melilla) is a Mexican artist, born to a Spanish family which came to Mexico in 1939 to escape the Spanish Civil War and has remained in Mexico since
- Fernando Arrabal Terán (born 1932 in Melilla) is a Spanish playwright, film director, novelist and poet, settled in France in 1955
- Juan José Imbroda Ortiz (born 1944 in Melilla) is a politician who was the mayor-president of the Spanish enclave of Melilla from 2000 to 2019.
- Ignacio Velázquez Rivera (born 1953 in Ceuta) is a Spanish politician who served as mayor of Melilla from 1991 and the first Mayor-President in 1995
- Paloma McLardy (born 1955 in Melilla), known as Palmolive, is a Spanish-born songwriter and drummer for influential punk groups
- Mustafa Aberchán (born 1959 in Melilla) is a Spanish politician from Melilla, leader of Coalition for Melilla and was the Mayor-President of the city 1999/2000.[44][45]
- Arly Jover (born 1971 in Melilla) is a Spanish actress, now lives in Paris
- Farid Bang (born 1986 in Melilla) is a German rapper of Moroccan descent.
Sport
- Ramón Martínez Pérez (1929 in Melilla – 2017) also known as Ramoní, was a Spanish footballer.
- Enrique González (born 1933 in Melilla) is a Spanish fencer, he competed in the individual foil event at the 1960 Summer Olympics
- Al-Lal Mohamed Amar (born 1957 in Melilla) known as Álex, is a Spanish retired footballer who played as a defender.
- Chota (born 1975 in Melilla) is a Spanish retired footballer who played as a striker, mostly for UD Melilla
- Mohamed Hamed Al-lal (born 1979 in Melilla) known as Aloisio, is a Spanish retired footballer who played as a central defender.
- Munir Mohand Mohamedi (born 1989 in Melilla) is a Moroccan professional footballer who plays for CD Numancia as a goalkeeper.
- Ezequiel Calvente Criado (born 1991 in Melilla) is a Spanish footballer who plays for Hungarian club Békéscsaba 1912 Előre
- David Sánchez (born 1994 in Melilla) is a Spanish weightlifter, competed in the 2016 Summer Olympics
- Yusef Abdeselam Kaddur (born 1985 in Melilla). Grappling world champion
See also
- European enclaves in North Africa before 1830
- List of Mayor-Presidents of Melilla
- List of Spanish Colonial Wars in Morocco
- Melilla (Spanish Congress Electoral District)
- Porteadoras – mule ladies, bale workers
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Málaga
- Spanish Morocco
References

- Municipal Register of Spain 2018. National Statistics Institute.
- "Melilla" (US) and "Melilla". Oxford Dictionaries UK Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 19 May 2019.
- "Melilla". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved 19 May 2019.
- Yahia, Jahfar Hassan (2014). Curso de lengua tamazight, nivel elemental. Caminando en la didáctica de la lengua rifeña (in Spanish and Riffian). Melilla: GEEPP Ed.
- "Morocco Restates Claim to Ceuta and Melilla". Expatica. 1 February 2006. Retrieved 18 May 2018.
- "Gibraltar in Reverse". The Economist. 21 February 2002. Retrieved 18 May 2018.
- Sophrone Pétridès, "Rusaddir" in Catholic Encyclopedia (New York 1912)
- Annuario Pontificio 2013 (Libreria Editrice Vaticana, 2013, ISBN 978-88-209-9070-1), p. 960
- Ayuntamientos de España, Ayuntamiento.es, archived from the original on 1 March 2012, retrieved 7 March 2012
- Rezette, p. 41
- Mohamed VI "condena" y "denuncia" la visita "lamentable" de los Reyes de España a Ceuta y Melilla, Elpais.com, 6 November 2007, retrieved 7 March 2012
- Muslim Holiday in Ceuta and Melilla, Spainforvisitors.com, archived from the original on 29 September 2011, retrieved 7 March 2012
- Public Holidays and Bank Holidays for Spain, Qppstudio.net, archived from the original on 30 September 2011, retrieved 7 March 2012
- World Port Source about Port Nador, retrieved 10 June 2012
- "Resultados Electorales en Melilla: Elecciones Municipales 2019 en EL PAÍS". El País. Resultados.elpais.com. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- Alba, Nicolás (15 June 2019). "El único diputado de Ciudadanos consigue la presidencia de Melilla tras 19 años de Gobierno del PP". El Mundo. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
-
- François Papet-Périn, "La mer d'Alboran ou Le contentieux territorial hispano-marocain sur les deux bornes européennes de Ceuta et Melilla". Tome 1, 794 p., tome 2, 308 p., thèse de doctorat d'histoire contemporaine soutenue en 2012 à Paris 1-Sorbonne sous la direction de Pierre Vermeren.
- Tremlett, Giles (12 June 2003). "A rocky relationship | World news | guardian.co.uk". London: Guardian. Retrieved 17 June 2009.
-
- François Papet-Périn, "La mer d'Alboran ou Le contentieux territorial hispano-marocain sur les deux bornes européennes de Ceuta et Melilla". Tome 1, 794 p., tome 2, 308 p., thèse de doctorat d'histoire contemporaine soutenue en 2012 à Paris 1-Sorbonne sous la direction de Pierre Vermeren.
- Govan, Fiona (10 August 2013). "The battle over Ceuta, Spain's African Gibraltar". Telegraph. Ceuta. Retrieved 12 July 2018.
- "Valores climatológicos normales (1981–2010). Melilla". Agencia Estatal de Meteorología. Retrieved 1 May 2017.
- "Regional GDP per capita ranged from 30% to 263% of the EU average in 2018". Eurostat.
- English translation of Volkskrant article: Melilla North-Africa's European dream, 5 August 2010, visited 3 June 2012
- "Melilla Modernista". Melilla Turismo. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013. Retrieved 25 March 2013.
Nieto was in charge of designing the main Synagogue, the Central Mosque and various Catholic churches
- "Melilla: Where Catalan "Modernisme" Meets North Africa". Huffington Post. Retrieved 19 September 2013.
- Amateur Radio Prefixes, Ac6v.com, archived from the original on 27 June 2017, retrieved 7 March 2012
- "BBC News - Hundreds breach Spain enclave border". Bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
- "African migrants storm into Spanish enclave of Melilla". BBC. 28 February 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
- "Morocco destroys migrant camps near border with Spanish enclave". The Guardian. 11 February 2015. Retrieved 21 November 2019.
- "Border games: Has Spain found an answer to the populist challenge on migration?". European Council on Foreign Relations. 3 September 2019. Retrieved 21 November 2019.
- "Una nueva compañía aérea comunica Melilla con Málaga tras la marcha de Helitt – Transporte aéreo – Noticias, última hora, vídeos y fotos de Transporte aéreo en lainformacion.com". Noticias.lainformacion.com. 28 April 2013. Archived from the original on 16 December 2013. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
- "Melilla - Weather Stations". Magicseaweed.com. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
- Hawkey, Ian (2009). Feet of the chameleon : the story of African football. London: Portico. ISBN 978-1-906032-71-5.
- Rubio Cano, Begoña (18 January 2008). "El presidente de Melilla y el alcalde de Motril hermanan a las dos ciudades y firman un convenio". Diario Sur.
- Revilla, María Victoria (19 October 2010). "Almería se hermana con los Emiratos Árabes y abre nuevas vías de negocio". Diario de Almería.
- "Mantua, hermana e invitada de honor". El Faro de Melilla. 17 September 2013.
- "Vélez y Melilla, dos ciudades hermanadas". Diario Sur. 10 January 2013.
- "Melilla y Antequera comienzan los trámites de hermanamiento el próximo septiembre". El Faro de Melilla. 1 July 2016.
- Beevor, Antony (1983). The Spanish Civil War. New York: Cassell. p. 461. ISBN 0-911745-11-4.
- Logoluso, Alfredo (2010). Fiat CR.32 Aces of the Spanish Civil War. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. p. 96. ISBN 978-1-84603-983-6.
- Shores, Christopher (1983). Air Aces. Greenwich, CT: Presidio Press. pp. 192. ISBN 0-86124-104-5.
- López-Colón, José Ignacio; Baena, Manuel (2005). Anselmo Pardo Alcaide. Una vida dedicada a la entomología: (biografía y obra científica). Ciudad Autónoma de Melilla: Consejería de Cultura. p. 196.
- Goble, Alan (1 January 1999). The Complete Index to Literary Sources in Film. Walter de Gruyter. p. 34. ISBN 9783110951943.
- Ramos, Toñy; Cué E., Carlos (6 July 1999). "Coalición por Melilla, un partido de mayoría musulmana y moderado en sus reivindicaciones". El País (in Spanish). Melilla: Edicíones El País. Retrieved 11 August 2010.
- Ramos, Toñy (4 July 1999). "Un musulmán gobernará la ciudad autónoma de Melilla con apoyo socialista y del GIL". El País (in Spanish). Melilla: Edicíones El País. Retrieved 11 August 2010.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Melilla. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Melilla. |
- (in Spanish) Official website
- Postal Codes Melilla