Kimono
The kimono (きもの/着物) (lit., "thing to wear" – from the verb ki (着), "to wear (on the shoulders)" and the noun mono (物), "thing")[1] is a traditional Japanese garment, and the national dress of Japan. It is a T-shaped, wrapped-front garment and is worn left over right (unless the wearer is deceased).[2] It is usually worn with an obi belt, alongside a number of other accessories, such as zōri shoes and tabi socks.

| Kimono | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
"Kimono" in kanji | |||||
| Japanese name | |||||
| Kanji | 着物 | ||||
| |||||


The kimono is constructed of mostly rectangular pieces of fabric, cut from a specific bolt of fabric known as a tanmono, which is 38–42 cm (15–17 in) in width and 12.5 m (41 ft) in length.[3] Various types of kimono indicate the wearer's age, gender, the formality of the occasion, and less commonly, marital status, when worn; decoration, style of wear, and accessories also denote these. Types of kimono can range in formality from the extremely informal to the most formal of occasions.
In modern day, the kimono is worn uncommonly within Japan as everyday dress and over time, has fallen out of fashion as the main article of clothing worn by Japanese people. Kimono are now most often seen at summer festivals—where the easy-to-wear yukata is most appropriate—or at formal events, such as weddings and funerals. The people who wear kimono most often (in some cases daily) are likely to be older men and women (who may have grown up wearing it), geisha, maiko, and sumo wrestlers, who are required to wear traditional dress whenever appearing in public.[4]
Though the kimono has garnered a reputation as uncomfortable and difficult to wear, it has experienced a number of revivals in popularity over the decades and is still worn as fashionable clothing within Japan.
History


.jpg)
The first prototypes of what would become the kimono were introduced to Japan via Chinese envoys during the Kofun period, with immigration between the two countries and Japanese envoys to the Tang dynasty court leading to a centuries-long fascination by the former of the cultured nature of the arts, architecture and clothing of the latter. The Imperial Japanese court quickly adopted Chinese styles of dress and clothing,[7] with evidence of the oldest samples of shibori fabric stored at the Shosoin Temple being Chinese in origin, due to the technical capacities of Japan's ability to produce the fabrics stored there at the time.
During Japan's Heian period (794-1192 CE) some centuries later, this style of dress became increasingly stylised, with some elements - such as the round-necked and tube-like sleeves of the chun ju jacket worn by both female and male courtiers in early seventh century Japan[1]:27 - being abandoned, and others, most importantly the lapped-front robes worn by both men and women, being kept. Some elements, such as the mo skirt worn by women, were kept in a vestigial sense, worn only to formal occasions as more of a train than a skirt proper.[1]
During the later Heian period, various clothing edicts reduced the number of layers a woman could wear, leading to the kosode - lit., "small sleeve" - garment, previously considered underwear, becoming outerwear within the Muromachi period (1336-1573 CE). Originally worn with hakama trousers over the top (another item of clothing previously underwear-only), the kosode began to be held closed with a small belt known as an obi.[1] The kosode at this time mostly had the same proportions as modern kimono, though the sleeves were sewn shut at the back, and were smaller in width in comparison to the much wider body of the kosode.
During the Edo period (1603-1867 CE), the sleeves of the kosode began to grow in length, especially amongst unmarried women, and the obi became much longer and wider, with various styles of knots coming into fashion, alongside stiffer weaves of material supporting them.[1] During the later Edo period, dress edicts intended to clamp down on the wealthy merchant classes drove the previously elaborate fashions of the era underground, where aesthetic ideals such as iki flourished, continuing to affect kimono aesthetics even in the present day. From this point onwards, the basic shape of both men's and women's kimono has remained largely unchanged.[1]
During the Meiji era, the opening of Japan to Western trade after the enclosure of the Edo period led to a drive towards Western dress as a sign of "modernity". After an edict by Emperor Meiji, for instance, policemen, railroad workers and teachers moved to wearing Western clothing within their job roles, with the adoption of Western clothing by men in Japan happening at a much greater pace than by women. Initiatives such as the Tokyo Women's & Children's Wear Manufacturers' Association (東京婦人子供服組合) promoted Western clothing as everyday dress.
Western clothing quickly became standard issue as army uniform for men[8] and school uniform for boys, and between 1920 and 1930, the sailor outfit replaced the kimono and undivided hakama as school uniform for girls.[1]:140
Today, the vast majority of people in Japan wear Western clothing in the everyday, and are most likely to wear kimono either to formal occasions such as wedding ceremonies and funerals, or to summer events, where the standard kimono is the easy-to-wear, single-layer cotton yukata.
In the Western world, kimono-style women's jackets, similar to a casual cardigan,[9] gained public attention as a popular fashion item in 2014.[10]
In 2019, the mayor of Kyoto announced that his staff were working to register “Kimono Culture” on UNESCO's intangible cultural heritage list.[11]
Textiles and construction of kimono

Though the basic shape and construction of the kimono has not changed in centuries, proportions have varied wildly throughout different eras.
Beginning in the later Heian period, the hitoe - an unlined robe worn directly against the skin as underwear - increasingly began to be worn as outerwear, as the heavily-layered styles of women's dress in previous decades fell out of fashion.
Though courtiers continued to layer their clothing, the beginning of the Kamakura period marked the point at which the kimono began its rise as the predominant item of dress for everyday people. The hitoe worn in the Kamakura period were pulled up to be ankle-length, bloused over the hip with no belt on top, and had small, rounded sleeves that were sewn to the body of the hitoe.
In the following centuries, the hitoe mostly retained its small, narrow and round-sleeved nature, with the length of women's sleeves increasing gradually over time and becoming occasionally detached from the body. The collar retained its relatively long and wide (in modern comparison) measurements, with the okumi front panel having a longer and shallower angle towards the hem.
During the Edo period, the kosode - lit., "small sleeve", as it had come to be known - developed further into proportions similar to modern kimono today.
Changes in women's fashion led to longer and more dramatic sleeves gaining popularity, with the sleeves themselves definitively becoming unattached from the body to emphasise this and permit the increasingly wider and stiffer obi - with men's sleeves staying, for the most part, sewn shut to the body along much of their length.
The sleeves grew in proportion to be roughly the same width as the panels used on the body, and the collar on both men's and women's kimono narrowed in width and length.
In the present day, both men's and women's kimono retain some key differences held over from these previous proportions. Men's kimono should fall to the ankle, as they have roughly always done, where as a woman's kimono - historically worn trailing along the floor, then hiked up for convenience - should be as tall as the person wearing it, owing to the hip fold known as the ohashori worn underneath the obi. Though the collars on both men's and women's kimono are narrower, on formal women's kimono, the collar retains its historically wider width, being folded inwards before wear. This style of collar is known as hiro-eri, "wide collar", whereas a regular-sized collar is known as bachi-eri. On either type of kimono, the sleeves should fall to the wrist, though the constrictions of the fabric used may prevent this.
Historically, kimono were often taken apart to wash in separate panels, as the cutting layout for a kimono is little more than a series of rectangles - two long panels for the body (one for children) and two smaller panels for the sleeves, with smaller strips forming the narrow front panels and the collar. The kimono, once cleaned, would then be resewn by hand, with the standardised method of its construction allowing for it to be easily retailored to fit a changing body, or indeed another person.[1] Though kimono are often machine-sewn in the present-day - with the exception of silk kimono - even a machine-made kimono will require hand-stitching to some degree.
Fabrics
Both kimono and obi are made from a wide variety of fibre types, including hemp, linen, silk, crepe (known as chirimen), and figured satin weaves such as rinzu. Fibres such as rayon became widespread during WW2, and modern kimono are widely available in fabrics considered easier to care for, such as polyester. However, formal kimono are always made entirely from silk.
Kimono textiles can to be classified into two categories: gofuku(呉服), which indicates silk textiles in general, and cotton/hemp futomono(太物) for everyday wear. Gofuku was named after 呉 (Wú) in ancient China, where the technology of silk fabrics originated from. Cotton clothing is called momenfuku(木綿服) whereas hemp clothing is called asafuku(麻服) in Japanese. Cotton/hemp fabrics are generally called as futomono (太物, Thick materials) as the fiber of these materials are thicker compared to that of silk. Till the end of the Edo period, tailoring of these fabrics were handled respectively at gofuku stores (Gofuku Dana) and futomono stores (Futomono Dana), however, after the Meiji period, kimono was not worn as daily wear very often and futomono stores eventually went out of business.

Kimono are traditionally made from a single bolt of fabric known as a tanmono, which are roughly 11.5m long and 36cm wide for women,[1] and 12.5m long and 42cm wide for men. The entire bolt is used to make one kimono, and some men's tanmono are woven to be long enough to create a matching haori jacket and juban as well. Some custom bolts of fabric are produced for especially tall or heavy people, such as sumo wrestlers, who must have kimono custom-made by either joining multiple bolts, weaving custom-width fabric, or using non-standard size fabric.[12]
Kimono fabrics are frequently hand-made and -decorated. Techniques such as yūzen dye resist are used for applying decoration and patterns to the base cloth. Repeating patterns that cover a large area of a kimono are traditionally done with the yūzen resist technique and a stencil. Over time there have been many variations in color, fabric, and style, as well as accessories such as the obi. Customarily, woven patterns and dyed repeat patterns are considered informal. Formal kimono have free-style designs dyed over the whole surface or along the hem.[13]
The pattern of the kimono can determine in which season it should be worn. For example, a pattern with butterflies or cherry blossoms would be worn in spring. Watery designs are common during the summer. A popular autumn motif is the russet leaf of the Japanese maple; for winter, designs may include bamboo, pine trees and plum blossoms (three friends of winter).
A popular form of textile art in Japan is shibori (intricate tie dye), found on some of the more expensive kimono and haori kimono jackets. Patterns are created by minutely binding the fabric and masking off areas, then dying it, usually by hand. When the bindings are removed, an undyed pattern is revealed. Shibori work can be further enhanced with yuzen (hand applied) drawing or painting with textile dyes or with embroidery; it is then known as tsujigahana. Shibori textiles are very time-consuming to produce and require great skill, so the textiles and garments created from them are very expensive and highly prized.
Old kimono have historically been recycled in various ways, depending on the type of kimono and its original use. Kimono were shortened, with the okumi taken off and the collar re-sewn, to make haori, or would simply be cut at the waist to create a side-tying jacket. After marriage or a certain age, young women would shorten the sleeves of their kimono, and extra material taken from kimono could be used to lengthen it at the waist, create an obi, or was used to patch similar kimono.
Kimono were also used to create dounuki, underkimono worn on top of the juban, and the material would show at the sleeve, hem and collar. Kimono were also used to create juban themselves, and after wearing layered kimono fell out of fashion, create a false underlayer – a hiyoku – was another use for old kimono. They could also be resewn into kimono for children.
Historically, skilled craftsmen would laboriously cut old silk kimono into strips roughly 1 cm wide to weave into obi, called saki-ori obi. The technique was a kind of rag-weaving, creating a mostly one-sided obi that was relatively narrow and informal. Saki-ori obi are prized for their craftsmanship and rustic quality today, as they would have taken many hours to create, and saki-ori obi often feature patterns of stripes, checks and arrows. The technique is kept alive to this day by craftspeople interested in rustic arts.
Parts
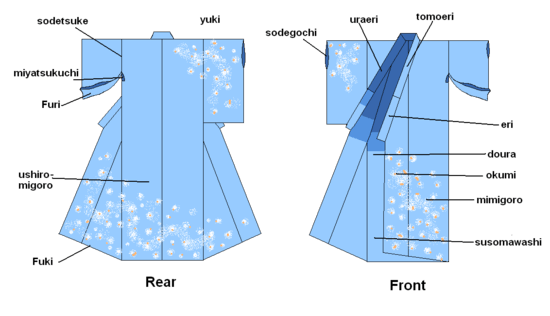
These terms refer to parts of a kimono:
- Dōura (胴裏): upper lining on a woman's kimono.
- Eri (衿): collar.
- Fuki (袘): hem guard.
- Furi (振り): sleeve below the armhole.
- Obi (帯): a belt used to tuck excess cloth away from the seeing public.
- Maemigoro (前身頃): front main panel, excluding sleeves. The covering portion of the other side of the back, maemigoro is divided into "right maemigoro" and "left maemigoro".
- Miyatsukuchi (身八つ口): opening under the sleeve.
- Okumi (衽): front inside panel on the front edge of the left and right, excluding the sleeve of a kimono. Until the collar, down to the bottom of the dress goes, up and down part of the strip of cloth. Have sewn the front body. It is also called "袵".
- Sode (袖): sleeve.
- Sodeguchi (袖口): sleeve opening.
- Sodetsuke (袖付): kimono armhole.
- Susomawashi (裾回し): lower lining.
- Tamoto (袂): sleeve pouch.
- Tomoeri (共衿): over-collar (collar protector).
- Uraeri (裏襟): inner collar.
- Ushiromigoro (後身頃): back main panel, excluding sleeves, covering the back portion. They are basically sewn back-centered and consist of "right ushiromigoro" and "left ushiromigoro", but for wool fabric, the ushiromigoro consists of one piece.
Cost

Both men's and women's brand-new kimono can range in expense, from the relatively cheap nature of second-hand garments, to high-end artisan pieces costing as much as US$50,000[14] (not allowing for the cost of accessories).
The high expense of some hand-crafted brand-new kimono reflects the traditional kimono making industry, where the most skilled artisans practice specific, expensive and time-consuming techniques, known to and mastered only by a few. These techniques, such as hand-plied bashofu fabrics and hand-tied kanoko shibori dotwork dyeing, may take over a year to finish. Kimono artisans may be made National Living Treasures in recognition of their work, with the pieces they produce being considered culturally important.
Even kimono that have not been hand-crafted will constitute a relatively high expense when bought new, as even for one outfit, a number of accessories of the right formality and appearance must be bought. Not all brand-new kimono originate from artisans, and mass-production of kimono - mainly of casual or semi-formal kimono - does exist, with mass-produced pieces being mostly cheaper than those purchased through a gofukuya (kimono shop, see below).
Though artisan-made kimono are some of the most accomplished works of textile art on the market, many pieces are not bought solely for appreciation of the craft. Unwritten social obligations to wear kimono to certain events - weddings, funerals - often leads consumers to purchase artisan pieces for reasons other than personal choice, fashion sense or love of kimono:
[Third-generation yuzen dyer Jotaro Saito] believes we are in a strange age where people who know nothing about kimono are the ones who spend a lot of money on a genuine handcrafted kimono for a wedding that is worn once by someone who suffers wearing it, and then is never used again.[15]
The high cost of most brand-new kimono reflects in part the pricing techniques within the industry.
Most brand-new kimono are purchased through gofukuya, where kimono are sold as fabric rolls only - known as tanmono - the price of which is often left to the shop's discretion. The shop will charge a fee separate to the cost of the fabric for it to be sewn to the customer's measurements, and fees for washing the fabric or weatherproofing it may be added as another separate cost.
If the customer is unfamiliar with wearing kimono, they may hire a service to help dress them; the end cost of a new kimono, therefore, remains uncertain until the kimono itself has been finished and worn.[16]
Gofukuya are also regarded as notorious for sales practices seen as unscrupulous and pressuring:
Many [Japanese kimono consumers] feared a tactic known as kakoikomi: being surrounded by staff and essentially pressured into purchasing an expensive kimono...Shops are also renowned for lying about the origins of their products and who made them...[My kimono dressing (kitsuke) teacher] gave me careful instructions before we entered the [gofukuya]: 'do not touch anything. And even if you don’t buy a kimono today, you have to buy something, no matter how small it is.’[16]
In contrast, kimono bought by hobbyists are likely to be less expensive, purchased from second-hand stores with no such sales practices or obligation to buy. Hobbyists may also buy cheaper synthetic kimono (marketed as 'washable') brand-new. Some enthusiasts also make their own kimono; this may be due to difficulty finding kimono of the right size, or simply for personal choice and fashion.
Second-hand items are seen as highly affordable; costs can be as little as ¥100 (about US$0.90) at thrift stores within Japan, and certain historic kimono production areas around the country - such as the Nishijin district of Kyoto - are well-known for their second-hand kimono markets. Kimono themselves do not go out of fashion, making even vintage or antique pieces viable for wear, depending on condition.[17]
However, even second-hand women's obi are likely to remain somewhat pricey; a used, well-kept and high-quality second-hand obi can cost upwards of US$300, as they are often intricately woven, or decorated with embroidery, goldwork and may be hand-painted. Men's obi, in contrast, retail much cheaper, as they are narrower, shorter, and have either very little or no decoration.
Types of kimono
Kimono range in variation from extremely formal to very casual. The formality of a woman's kimono is determined mostly by pattern placement, decoration style, fabric choice and colour. The formality of men's kimono differs, in that it is determined more by fabric choice and coordination elements (hakama, haori, etc.) than decoration, as men's kimono tend to be one colour with motifs only visible when looked at closely.
In both cases, formality is also determined by the number and type of kamon (crests). Five mon (itsutsu mon) are the most formal, three mon (mitsu mon) are mid-formality, and one mon (hitotsu mon) is the least formal, used for occasions such as tea ceremony. The type of mon adds formality as well, with a "full sun" (hinata) mon being the most formal, a "mid-shadow" (nakakage) mon being mid-formality, and a "shadow" (kage) mon being the least formal. Embroidered mon, called nui mon, are also seen.[18]
Formality can also be determined by the type and colour of accessories, such as weave of obijime and the style of obiage.
Women's kimono
The typical woman's kimono outfit may consist of up to twelve or more separate pieces; some outfits, such as formal wedding kimono, may require the assistance of licensed kimono dressers, though usually this is due to the wearer's inexperience with kimono and the difficult-to-tie nature of formal obi musubi. Most professional kimono dressers are found in Japan, where they work out of hair salons, as specialist businesses, or freelance.
Choosing an appropriate type of kimono requires knowledge of the wearer's age, occasionally marital status (though less so in modern times), the formality of the occasion at hand, and the season. Choice of fabric is also dependent on these factors, though some fabrics - such as crepe and rinzū - are never seen in certain varieties of kimono, and some fabrics such as shusu (satin) silk are barely ever seen in kimono altogether, instead being worn on the obi.
Though length of kimono, collar style and the way the sleeves are sewn on varies for susohiki kimono, in all other types of women's kimono, the construction generally does not change; the collar is set back slightly into the nape of the neck, the sleeves are only attached at the shoulder, not all the way down the sleeve length, and the kimono's length from shoulder to hem should generally equal the entire height of the woman wearing it, to allow for the ohashori hip fold.
Sleeve length increases for furisode - young women's formal dress - but young women are not limited to wearing only furisode, as outside of formal occasions that warrant it, can wear all other types of women's kimono such as irotomesode and komon.
Yukata
Yukata (浴衣) are casual cotton summer kimono. Yukata were originally very simple indigo and white cotton kimono, little more than a bathrobe never worn outside the house. However, from roughly the mid-1980s onwards, they began to be produced in a wide variety of bright colours, large motifs and loud patterns, responding to a demand for a more casual modern kimono that could be worn to a summer festival.
In the present day, yukata are worn with hanhaba (half-width) or heko obi, and for women, often accessorised with colour hair accessories. Yukata are always unlined, and it is possible to dress up a high-end, more subdued yukata with a relatively casual nagoya obi - one with a simple dyed design in an informal fabric such as ro or tsumugi.
Furisode

Furisode (振袖) (lit., "swinging sleeve") kimono are the most formal kimono for a young, often unmarried, woman. They are decorated with colourful patterns across the entirety of the garment, and usually worn to seijin shiki (Coming of Age Day) or weddings, either by the bride herself or an unmarried younger female relative.
The sleeves of the furisode average at between 100–110 cm in length. Chu-furisode (mid-size furisode) have shorter sleeves at roughly 80 cm in length; most chu-furisode are vintage kimono, as in the modern day furisode are not worn often enough to warrant buying a more casual form of the dress.
Hōmongi
Hōmongi (訪問着) literally translates as visiting wear. Hōmongi are distinguished in their motif placement - the motifs flow across the back right shoulder and back right sleeve, the front left shoulder and front left sleeve, and across the hem, higher at the left than the right. They are always made of silk, and are more formal than tsukesage.
Hōmongi are first roughly sewn up, the design sketched onto the fabric, before it is taken apart to be dyed again. The hōmongi's close relative, the tsukesage, has its patterns dyed on the bolt before sewing up. This method of production can usually distinguish the two, as the motifs on a hōmongi are likely to cross fluidly over seams in a way a tsukesage generally will not.[19]
Hōmongi may be worn by both married and unmarried women; often friends of the bride will wear hōmongi at weddings (except relatives) and receptions. They may also be worn to formal parties.
Iromuji
Iromuji (色無地) (lit. "solid colour") are monochromatic, undecorated kimono mainly worn to tea ceremonies. The dyed silk may have a flat woven pattern - iromuji suitable for autumn are often made of rinzu silk. Some edo komon with incredibly fine patterns may be suitable for tea ceremony, as from a distance they are visually similar to iromuji. Iromuji may occasionally have one kamon, though likely no more than this, and are always made of silk. Shibori accessories such as obiage are never worn with iromuji if the purpose of wear is a tea ceremony; instead, flat and untextured silks are chosen for accessories.
Edo komon
Edo komon (江戸小紋) is a type of komon characterised by an extremely small repeating pattern, usually done in white on a coloured background. The edo komon dyeing technique originated within the samurai classes during the Edo period. Edo komon are of a similar formality to iromuji, and edo komon with one kamon can be worn as low-formality visiting wear; because of this, they are always made of silk, unlike regular komon.
Mofuku
Mofuku (喪服) describes general formal mourning dress, and both men and women wear mofuku. Mofuku kimono are plain black silk with five kamon, worn with white undergarments and white tabi. Men wear a kimono of the same kind, with a subdued obi and a black-and-white or black-and-grey striped hakama, worn with black or white zōri.
A completely black mourning ensemble for women - a plain black obi, black obijime and black obiage - is usually reserved for those closest to the deceased. Those further away will wear kimono in dark and subdued colours, rather than a plain black kimono with a reduced number of crests. In time periods when kimono were worn more often, those closest to the deceased would slowly begin dressing in coloured kimono over a period of weeks after the death, with the obijime being the last thing to be changed over to colour.
Kurotomesode
Kurotomesode (黒留袖) (black short-sleeve kimono) are formal kimono with a black background and a design along the hem only, worn to formal events such as weddings and wedding parties. The design is seen along the hem only; the further up the body this design reaches, the younger the wearer is considered to be, though for a very young woman an irotomesode may be chosen instead, kurotomesode being considered somewhat more mature. The design is either symmetrically placed on the fuki and okumi portions of the kimono, or asymmetrically placed along the entirety of the hem, with the design being larger and higher-placed at the left side than the right. Vintage kimono are more likely to have the former pattern placement than the latter, though is not a hard rule.
Kurotomesode are always made of silk, and may have a hiyoku - a false lining layer - attached, occasionally with a slightly padded hem. A kurotomesode usually has between 3 and 5 crests; a kurotomesode of any number of crests outranks an irotomesode with less than five. Kurotomesode, though formalwear, are not allowed at the royal court, as black is the colour of mourning, despite the colour designs decorating the kimono itself; outside of the royal court, this distinction for kurotomesode does not exist. Kurotomesode are never made of flashy silks like rinzū, but are instead likely to be a matte fabric with little texture.
Irotomesode
Irotomesode (色留袖) (colour short-sleeve kimono) are slightly lower-ranking formal kimono with roughly the same pattern placement as kurotomesode on a coloured background. Irotomesode, though worn to formal events, may be chosen when a kurotomesode would make the wearer appear to be overdressed for the situation. The pattern placement for irotomesode is roughly identical to kurotomesode, though patterns seen along the fuki and okumi may drift slightly into the back hem itself. Irotomesode with five kamon are of the same formality as any kurotomesode. Irotomesode may be made of figured silk such as rinzū.
Tsukesage
Tsukesage (付け下げ) are lower-ranking formalwear, a step below hōmongi, wherein the motifs generally do not cross over the seams of each kimono panel, but have the same placement as a hōmongi. Similarities between the two often lead to confusion, and indeed, sometimes the two are so visually similar that the distinction is difficult to make. Tsukesage can have between one and three kamon, and can be worn to parties, but not ceremonies or highly formal events.
Uchikake

Uchikake (打ち掛け) are highly formal kimono worn only in bridalwear or on stage. The name uchikake comes from the verb uchikake-ru, "to drape upon", originating in roughly the 16th century from a fashion of the ruling classes of the time to wear kimono (then called kosode, "small sleeve") unbelted over the shoulders of one's other garments.[1]:34
Uchikake are worn in the same manner in the present day, though unlike their 16th-century counterparts, could never be worn as an everyday kimono as well; they are heavily-decorated, highly-formal garments with thickly-padded hems, designed to trail along the floor as a sort of coat. Bridal uchikake are either red or white, and often decorated heavily with auspicious motifs. Because they are not designed to be worn with an obi, the designs cover the entirety of the back.
Shiromuku
Shiromuku (白無垢, lit. "white pure-innocence") are the pure-white wedding kimono worn by the bride for a traditional Japanese Shinto wedding ceremony. Comparable to a uchikake and sometimes described as just a white uchikake, a shiromuku is worn for the part of the wedding ceremony, symbolising the purity of the bride coming into the marriage. The bride may later change into a red uchikake after the ceremony to symbolise good luck.
A shiromuku will form part of a bridal ensemble with matching or coordinating accessories, such as a bridal katsura, a set of matching kanzashi (usually mock-tortoiseshell), and a sensu fan tucked into the kimono. Due to the expensive nature of traditional bridal clothing, few are likely to buy brand-new shiromuku; it is not unusual to rent kimono for special occasions, and Shinto shrines are known to keep and rent out shiromuku for traditional weddings. Those who do possess shiromuku already are likely to have inherited them from close family members.
Susohiki / Hikizuri
Susohiki (lit. "trailing skirt") kimono are extremely long kimono worn by geisha, actors in kabuki and people performing traditional Japanese dance. A susohiki can be up to 230 cm long, and are generally no shorter than 200 cm from shoulder to hem; this is to allow the kimono to literally trail along the floor.
Susohiki, apart from their extreme length, are also sewn slightly differently to normal kimono, due to the way they are worn.[20] The collar on a susohiki is sewn further and deeper back into the nape of the neck, so that it can be pulled down much lower without causing the front of the kimono to ride up. The sleeves are set unevenly onto the body, shorter at the back than at the front, so that the underarm does not show when the collar is set this low.
Susohiki are also tied differently when they are put on - whereas regular kimono are tied with a visible ohashori, and the side seams kept straight, susohiki are pulled up somewhat diagonally, to emphasise the hips and ensure the kimono trails nicely on the floor. A small ohashori is tied, larger at the back than the front, but it wrapped against the body with a red momi wrap, which is then covered by the obi, rendering it not visible.[note 1]
Jūnihitoe

Jūnihitoe (十二単) (lit. "twelve layers") describes the layered garments worn by court ladies during the Heian period. The jūnihitoe consisted of up to twelve layered garments, with the innermost garment being the kosode - the small-sleeved kimono prototype which would eventually go on to become the outermost garment worn.
The total weight of the jūnihitoe could be up to 20 kg. The garments were decorated in relatively large motifs, with a more important aspect being the numerous recorded colour combinations an outfit could have.
An important accessory of this outfit was an elaborate hand fan, which could be tied together by tassels tied onto the end fan bones. These fans were made of cypress wood entirely, with the design painted onto the wide, flat bones themselves, and were known as hiōugi.
No garments from the Heian period survive, and today the jūnihitoe can only be seen as a reproduction in museums, movies, festivals and demonstrations. The Imperial Household still officially uses them at some important functions, such as the coronation of the new Empress.
Men's kimono

In contrast to women's kimono, men's kimono outfits are far simpler, typically consisting of five pieces, not including footwear.
Men's kimono sleeves are attached to the body of the kimono with no more than a few inches unattached at the bottom, unlike the women's style of very deep sleeves mostly unattached from the body of the kimono. Men's sleeves are less deep than women's kimono sleeves to accommodate the obi around the waist beneath them, whereas on a woman's kimono, the long, unattached bottom of the sleeve can hang over the obi without getting in the way.

In the modern era, the principal distinctions between men's kimono are in the fabric. The typical men's kimono is a subdued, dark color; black, dark blues, greens, and browns are common. Fabrics are usually matte. Some have a subtle pattern, and textured fabrics are common in more casual kimono. More casual kimono may be made in slightly brighter colors, such as lighter purples, greens and blues. Sumo wrestlers have occasionally been known to wear quite bright colors such as fuchsia.
The most formal style of kimono is plain black silk with five kamon on the chest, shoulders and back. Slightly less formal is the three-kamon kimono.
Accessories and related garments
Though the kimono is the national dress of Japan, it has never been the sole item of clothing worn throughout Japan; even before the Meiji Period and the introduction of Western dress to Japan, many variations of or cousins to the kimono existed as a separate style of dress, often as rural or (in the case of the Ainu people) cultural dress.
Some variations on the kimono were the contemporary clothing of previous decades and centuries, and have survived on in an official or ceremonial capacity, worn only by certain people for certain occasions. There are also a number of accessories that can be worn with the kimono, and these vary by occasion and use.
Related garments
Religious garments
Some related garments are specific to certain religious roles. The chihaya (ちはや/襅) is worn only by Kannushi and Miko in some Shinto shrine ceremonies, and the samue (作務衣) is the everyday clothing for a male Zen Buddhist lay-monk, and the favoured garment for Komusō monks playing the shakuhachi.
Ceremonial and professional garments
Jittoku (十徳) are a style of haori worn only by some high-ranking male practitioners of tea ceremony. Jittoku are made of unlined silk gauze, fall to the hip, and have sewn himo ties at the front made of the same fabric as the main garment. The jittoku has a wrist opening that is entirely open along the sleeve's vertical length. The garment originated in the Kamakura Period (1185-1333 CE), and are worn without hakama.
Both geisha and maiko wear various types of kimono, and variations on common accessories, that are not found in everyday dress. As an extension of this, many practitioners of Japanese traditional dance wear similar kimono and accessories to geisha and maiko.
For certain traditional holidays and occasions, kimono are more likely to be worn, and on some occasions specific types of kimono, and accessories, are worn. For instance, okobo, also known as pokkuri, are worn by girls for shichi-go-san, alongside brightly-coloured furisode. Okobo are also worn by young women on seijin no hi.
For formal ceremonies, members of Japanese nobility will wear certain types of antiquated kimono such as the suikan (水干) and the jūnihitoe (十二単). Outside of nobility, jūnihitoe are only found in dress-up (henshin) studios, or in museums as recreations; no examples of Heian period clothing exist, and only small and fragile samples of the fabrics used in those times survive.
Bridalwear
Brides in Japan who opt for a traditional ceremony will wear specific accessories and types of kimono, which may be changed and switched out for certain parts of the ceremony; for instance, the wata bōshi hood is removed during the ceremony, and uchikake are worn over the top of shiromuku bridal kimono once the ceremony has been completed, usually at the reception. Many bridalwear traditions, such as the addition of a small (fake) dagger, are amalgams and facsimiles of samurai dress from previous eras.

- Tsunokakushi (角隠し, lit. "horn-hiding")
- Tsunokakashi is a style of headwear worn by brides in traditional Shinto wedding ceremonies. Tsunokashi may be made of white silk and worn with the bride's white shiromuku wedding kimono, or they may be made of colored materials to match or coordinate when the bride opts for a non-shiromuku style. Tsunokakashi, unlike wata bōshi, do not cover the high topknot formed by the bride's takashimada-style wig.
- According to folk etymology, the headwear is worn to hide the bride's horns of jealousy and selfishness; however, this headdress was originally a simpler cap worn to keep the dirt and dust off a woman's hairstyle when travelling.[22] The custom spread from married women in samurai families in the Muromachi and Momoyama periods to younger women of lower classes during the Edo period.
- Wata bōshi (綿帽子, lit "cotton hat")
- Wata bōshi is a style of full-coverage hood also worn by the bride in traditional Shinto weddings. The wata bōshi is always white and worn with shiromuku. Wata bōshi entirely cover the bride's hairstyle.[23]
- Takashimada (高島田)
- takashimada katsura are the style of shimada wig worn by brides. This wig resembles the style worn by geisha, with a few key differences; namely that the wig appears to be shorter and fuller, with the mage (bun) at the back placed much higher on the head. The takashimada is worn with a matching set of tortoiseshell or faux-tortoiseshell kanzashi hair accessories
- Kanzashi (簪)
- Kanzashi hair ornaments, made of tortoiseshell or faux-tortoiseshell, are worn with the takashimada wig. These hair accessories will come in a matching set, including a highly-decorated kushi comb and kogai hair stick, and a number of bira-bira-style kanzashi, often decorated with flowers in either tortoiseshell or metal and coral or coral-substitute.
- Sensu (扇子)
- Sensu folding hand fans, in either entirely gold or silver leaf, are worn tucked into the obi.
- Futokorogatana (懐刀)
- Futokorogatana, lit. "chest sword", are small daggers tucked into the collar, often held inside a small, decorative purse made of brocade fabric.
- Hakoseko (箱迫)
- Hakoseko are small, highly-decorative purses worn with wedding kimono. These are also made out of decorative brocade fabric, often with tassels on the ends of the purse, and usually contain some combination of a small mirror and a comb.
Related accessories

- Datejime (伊達締め) or datemaki (伊達巻き)
- A wide undersash used to flatten and keep in place the kimono and/or the nagajuban when tied. Datejime can be made of a variety of fabrics, including silk, linen and elastic.[24]
- Fā (ファー)
- A fur collar, boa or stole worn by women over a kimono; white fur stoles are usually worn by young women on their Coming of Age Day (成人の日, Seijin no Hi), whereas other colours are likely to be worn by older women to help keep themselves warm.
- Geta (下駄)
- Wooden sandals worn by men and women with yukata and other casual kimono. They are usually made of a lightweight wood such as paulownia, and come in a variety of styles, such as ama geta ("rain geta", covered over the feet) and tengu geta (with just one prong on the sole instead of two).
- Hachimaki (鉢巻)
- Traditional Japanese stylized headband, worn to keep sweat off of one's face. In Japanese media, it is used as a trope to show the courage of the wearer, symbolising the effort put into their strife, and in kabuki, it can symbolise a character sick with love.

- Hakama (袴)
- A divided (umanori-bakama) or undivided skirt (andon-bakama) which resembles a wide pair of trousers. Hakama were historically worn by both men and women, and in modern day can be worn to a variety of formal or informal events. A hakama is typically pleated at the waist and fastened by waist ties over the obi. For women, shorter kimono may be worn underneath the hakama for ease of movement.
- Hakama are worn in several budo arts such as aikido, kendo, iaidō and naginata. They are also worn by Miko in Shintō shrines.
- Hakama Boots (袴ブーツ)
- A pair of boots (leather or faux leather), with low-to-mid heels, worn with a pair of hakama (a pair of traditional Japanese trousers); boots are a style of footwear that came in from the West during the Meiji Era; worn by women while wearing a hakama, optional footwear worn by young women, students and teachers at high-school and university graduation ceremonies, and by young women out celebrating their Coming of Age at shrines, etc., often with a hakama with furisode combination.
- Hakoseko (筥迫, lit. "boxy narrow thing")
- A small box-shaped billfold accessory; sometimes covered in materials to coordinate with the wearer's kimono or obi. Fastened closed with a cord, and carried tucked-within a person's futokoro, the space within the front of kimono collar and above the obi. Used for formal occasions that require traditional dress, such as a traditional Shinto wedding or a child's Shichi-Go-San ceremony. Originally used for practical uses, such as carrying around a woman's beni ita (lipstick), omamori (an amulet/talisman), kagami (mirror), tenugui (handkerchief), coins, and the like, it now has a more of a decorative role.
- Hanten (袢纏, lit. "half-wrap")
- The worker's version of the more formal haori. As winterwear, it is often padded for warmth, giving it insulating properties, as opposed to the somewhat lighter happi. It could be worn outside in the wintertime by fieldworkers out working in the fields, by people at home as a housecoat or a cardigan, and even slept-in over one's bedclothes.
_MET_DP330781.jpg)
- Haori (羽織)
- A hip- or thigh-length kimono-like overcoat with straight, rather than overlapping, lapels. Haori were originally worn by men until they were popularised as women's wear as well by geisha in the Meiji period. The jinbaori (陣羽織) was specifically made for armoured samurai to wear.
- Haori himo (羽織紐)
- A tasseled, woven string fastener for haori. The most formal color is white (see also fusa above).
- Happi (法被)
- A type of haori traditionally worn by shop keepers, sometimes uniform between the helpers of a shop (not unlike a propaganda kimono, but for advertising business), and is now associated mostly with festivals.
- Haramaki (腹巻, lit. "belly wrap")
- Are items of Japanese clothing that cover the stomach. They are worn for health, fashion and superstitious reasons.
- Hifu (被布)
- Originally a kind of padded over-kimono for warmth, this has evolved into a sleeveless over-kimono like a padded outer vest or pinafore (also similar to a sweater vest or gilet), worn primarily by girls on formal outings such as the Shichi-Go-San (literally "seven-five-three") ceremony for children aged seven, five, and three.
- Jika-tabi (地下足袋)
- A modification of the usual split-toe tabi sock design for use as a shoe, complete with rubber sole. Invented in the early 20th century.
- Jinbei (甚平)
- Traditional Japanese loose-woven two-piece clothing, consisting of a robe-like top and shorts below the waist. Worn by men, women, boys, girls, and even babies, during the hot, humid summer season, in lieu of kimono.
- Hadajuban (肌襦袢)
- A thin garment similar to a nagajuban; it is considered to be "kimono underwear", worn in direcr contact with the skin, and has tube-shaped sleeves. It is worn with a slip-like wrap tied around the waist, with the nagajuban worn on top.[25][26]
- Kappōgi (割烹着, lit. "cooking wear")
- A type of gown-like apron; first designed to protect kimono from food stains, it has baggy sleeves, is as long as the wearer's knees, and fastens with strips of cloth ties that are tied at the back of the neck and the waist. Particularly used when cooking and cleaning, it is worn by Japanese housewives, lunch ladies, cleaners, etc.
- Kasa (傘)
- A traditional Japanese oil-paper umbrella/parasol, these umbrellas as typically crafted from one length of bamboo split finely into spokes. See also Gifu umbrellas.
- Kinchaku (巾着)
- A traditional Japanese drawstring bag or pouch, worn like a purse or handbag (vaguely similar to the English reticule), for carrying around personal possessions (money, etc.). A kind of sagemono (see below).
- Kimono slip (着物スリップ, kimono surippu)
- A one-piece undergarment combining the hadajuban and the susoyoke.[27][28]
- Koshihimo (腰紐, lit. "hip cord")
- A narrow strip of fabric used to tie the kimono, nagajuban and ohashori in place while dressing oneself in kimono. They are often made of silk or wool.
- Michiyuki (道行き)
- A traditional Japanese overcoat (not to be confused with a haori or a hifu), characterised with a signature square neckline formed by the garment's front overlap. It is fastened at the front with snaps or buttons, and is often worn over the kimono for warmth, protection from the weather or as a casual housecoat. Some michiyuki will include a hidden pocket beneath the front panel, and they are typically thigh- or even knee-length.
- Nagajuban (長襦袢, lit. "long underwear")
- A long under-kimono worn by both men and women beneath the main outer garment.[29] Since silk kimono are delicate and difficult to clean, the nagajuban helps to keep the outer kimono clean by preventing contact with the wearer's skin. Only the collar edge of the nagajuban shows from beneath the outer kimono.[30] Many nagajuban have removable collars, to allow them to be changed to match the outer garment, and to be easily washed without washing the entire garment. They are often as beautifully ornate and patterned as the outer kimono. Since men's kimono are usually fairly subdued in pattern and color, the nagajuban allows for discreetly wearing very striking designs and colours.[31]
- Nemaki (寝間着)
- Japanese nightclothes.

- Netsuke (根付) or Netsuke (根付け)
- An ornament worn suspended from the men's obi, serving as a cordlock or a counterweight. (See also ojime, below).
- Obi-age (帯揚げ)
- A scarf-like sash worn tied above the obi, either knotted or tucked into the garment's collars. The obi-age has the duel purpose of hiding the obi-makura and providing a colour contrast against the obi. Obi-age are often silk, and are typically worn with more formal varieties of kimono. Obi-age can be plain-dyed silk, but are often decorated with shibori tie-dyeing; for maiko, obi-age are only ever red with a gold or silver foil design.
- Obi-dome (帯留め)
- A decorative fastening accessory piece, strung onto the obijime. For maiko, the obi-dome is commonly the most expensive part of the outfit, as it is carefully hand-crafted from many precious stones and metals.
- Obi-ita (帯板)
- A thin, stiff board, commonly inserted behind the obi at the front, helping to give a smooth, uniform appearance.
- Obijime (帯締め)
- A devorative woven or padded cord used to assist in tying more complex bows with the obi, also worn as simple decoration on the obi itself. It can be tied at the front, and the ends tucked into the band itself, or tied at the back, in the case of being worn with an obi-dome.
- An ojime (see below) can be used to fasten the obijime in place (similar to a netsuke), and also serves as a decoration.
- Obi-makura (帯枕)
- Padding used to put volume under the obi knot (musubi); to support the bows or ties at the back of the obi and keep them lifted. An essential part of the common taiko musubi ("drum knot").
- Ojime (緒締め)
- A type of bead which originated in Japan, used to fasten a obijime in place, like a cordlock. They are also worn between the inrō and netsuke and are typically under an inch in length. Each is carved into a particular shape and image, similar to the netsuke cordlock, though smaller.
- Sensu (扇子)
- A handheld fan (either an ōgi (扇) or an uchiwa (団扇)), generally made of thick paper coated in paint, lacquer or gold leaf, with bamboo spines. As well as being used for cooling-off, sensu fans are used as dancing props, and are often worn tucked into the obi.
- Setta (雪駄)
- A flat, thick-bottomed sandal made of bamboo and straw with leather soles, and with metal spikes protruding from the heel of the sole to prevent slipping on ice.
- Susoyoke (裾除け)
- A thin half-slip-like piece of underwear, like a petticoat, worn by women under their nagajuban.[25][32]
- Suzu (鈴)
- A round, hollow Japanese Shinto bell or chime, that contains pellets that sound when agitated. They are somewhat like a jingle bell in form, though the materials produce a coarse, rolling sound. Suzu come in many sizes, ranging from tiny ones on good luck charms (called omamori (お守り)) to large ones at shrine entrances. As an accessory to kimono wear, suzu are often part of kanzashi.
- Tabi (足袋)
- Ankle-high, divided-toe socks usually worn with zōri or geta. There also exist sturdier, boot-like jikatabi, which are used for example to fieldwork.
- Tasuki (襷)
- A pair sashes made from either cloth or cord that loops over each shoulder and crosses over the wearer's back, used for holding up the long sleeves of the Japanese kimono; the bottom of the kimono sleeves can then be tucked into the loop, so that they don't hang so low.
- Tenugui (手拭い, lit. "hand wiper")
- A handy piece of fabric, usually cotton or linen, they can come in a wide variety of colours and patterns, and with a myriad amount of uses—but mostly as a handkerchief, a hand towel, and larger ones can even serve as a napkin, bib, headscarf/kerchief/bandana (or to ad-lib as a hachimaki), and can double as a furoshiki (a traditional Japanese wrapping cloth), and even a shawl or a baby sling.
- Waraji (草鞋)
- Traditional sandals made of straw rope and bamboo bark and designed to wrap securely around the wearer's foot and up around the ankle; mostly worn by monks, and others who often travelled long-distance by foot (traders and merchants, etc.).
- Yumoji (湯文字)
- The traditional Japanese undergarment (like a loincloth or perizoma) for adult females; it may also be worn as a kimono underskirt, and as a single-layer absorbent bathrobe (worn during or after a bath).

- Zōri (草履)
- Traditional sandals worn by both men and women, similar in design to flip-flops. Their formality ranges from strictly informal to fully formal. They are made of many materials, including cloth, leather, vinyl and woven grass, and can be highly decorated or very simple.
Layering
Pre-WW2, kimono were commonly worn layered, with three being the standard number of layers worn over the top of undergarments. The layered kimono underneath were known as dōnuki, and were often a patchwork of older or unwearable kimono taken apart for their fabric.
In modern-day Japan, layered kimono are only seen on the stage, whether for classical dances or in kabuki. A false second layer called a hiyoku ("second wing", 比翼) may be attached instead of an entirely separate kimono to achieve this look; it is a type of floating lining, sewn to the kimono only along the centre back and underneath the collar.
This effect allows it to show at the collar and the hem, and in some kabuki performances such as Fuji Musume, the kimono will be worn with the okumi flipped back slightly underneath the obi to expose the design on the hiyoku. The hiyoku can also be seen on some bridal kimono.
Care
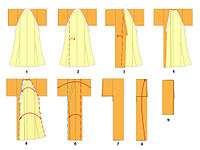
In the past, a kimono would often be entirely taken apart for washing, and then re-sewn for wearing.[13] This traditional washing method is called arai hari. Because the stitches must be taken out for washing, traditional kimono need to be hand sewn. Arai hari is very expensive and difficult and is one of the causes of the declining popularity of kimono. Modern fabrics and cleaning methods have been developed that eliminate this need, although the traditional washing of kimono is still practiced, especially for high-end garments.
New, custom-made kimono are generally delivered to a customer with long, loose basting stitches placed around the outside edges. These stitches are called shitsuke ito. They are sometimes replaced for storage. They help to prevent bunching, folding and wrinkling, and keep the kimono's layers in alignment.
Like many other traditional Japanese garments, there are specific ways to fold kimono. These methods help to preserve the garment and to keep it from creasing when stored. Kimono are often stored wrapped in paper called tatōshi.
Kimono need to be aired out at least seasonally and before and after each time they are worn. Many people prefer to have their kimono dry cleaned. Although this can be extremely expensive, it is generally less expensive than arai hari but may be impossible for certain fabrics or dyes.
Notes
- Video reference showing Atami geisha Kyouma being dressed in hikizuri – the second video shows the difference between ohashori length at the front and back, and how it is tied into the obi so as to be not visible.[21]
References
- Dalby, Liza (1993). Kimono: Fashioning Culture (1st ed.). Seattle: University of Washington Press. ISBN 9780099428992.
- Spacey, John. "5 Embarrassing Kimono Mistakes". japan-talk.com. Japan Talk. Retrieved 27 January 2020.
- "About the size of tanmono (a roll of kimono cloth)". hirotatsumugi.jp. Hirota Tsumugi. Retrieved 27 January 2020.
- Sharnoff, Lora (1993). Grand Sumo: The Living Sport and Tradition. Weatherhill. ISBN 0-8348-0283-X.
- Liddell, Jill (1989). The Story of the Kimono. E.P. Dutton. p. 28. ISBN 978-0525245742.
- Fassbender, Bardo; Peters, Anne; Peter, Simone; Högger, Daniel (2012). The Oxford Handbook of the History of International Law. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 477. ISBN 978-0198725220.
- Elizabeth LaCouture, Journal of Design History, Vol. 30, Issue 3, 1 September 2017, Pages 300–314.
- 更新日:2010年11月25日. "戦時衣生活簡素化実施要綱". Ndl.go.jp. Archived from the original on 2008-06-16. Retrieved 2012-07-22.
- Ruddick, Graham (12 August 2014). "Rise of the kimono, the Japanese fashion taking Britain by storm". The Telegraph. Retrieved 12 August 2014.
- Butler, Sarah; Moulds, Josephine; Cochrane, Lauren (12 August 2014). "Kimonos on a roll as high street sees broad appeal of Japanese garment". Retrieved 12 August 2014.
- Ho, Vivian (2019-07-01). "#KimOhNo: Kim Kardashian West renames Kimono brand amid outcry". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2019-07-02.
- "男のきもの大全". Kimono-taizen.com. 1999-02-22. Retrieved 2012-08-13.
- Dalby, Liza (2000). Geisha (3rd ed.). London: Vintage Random House. ISBN 978-0099286387.
- Hindell, Juliet (22 May 1999). "Saving the kimono". BBC News. BBC News World. Retrieved 8 January 2020.
- Cliffe, Sheila (23 March 2017). The Social Life of Kimono (1st ed.). New York: Bloomsbury Academic. p. 134. ISBN 978-1-4725-8553-0.
- Valk, Julie (2018). "Survival or Success? The Kimono Retail Industry in Contemporary Japan" (D.Phil thesis). University of Oxford. pp. 115–117. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- Tsuruoka, Hiroyuki. "The unspoiled market found by the lost office workers". Japan Business Press (in Japanese). Retrieved 14 May 2019.
- "Mon and Kamon". wafuku.co.uk. Wafuku.co.uk. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- Coline, Youandi. "Formality Series: Tsukesage". chayatsujikimono.wordpress.com. Chayatsuji Kimono. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- Coline, Youandi. "Are kimono and hikizuri the same?". Chayatsuji Kimono. Retrieved 14 May 2019.
- "[Video from Atami Geigi Kenban on Instagram]" (in Japanese). 11 December 2018. Retrieved 14 May 2019.
- Kimino, Rinko; Somegoro, Ichikawa (2016). Photographic Kabuki Kaleidoscope (1st ed.). Tokyo: Shogakukan. p. 34. ISBN 978-4-09-310843-0.
- Yoshie, Fuami (26 March 2008). "Japanese Traditional Wedding Style: Shiromuku for Brides". Japanese Mind ―日本の心―. fyoshie060861.blogspot.com. Retrieved 4 January 2020.
- Coline, Youandi (5 December 2018). "Datejime". Chayatsuji Kimono. chayatsujikimono.wordpress.com. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- Yamanaka, Norio (1982). The Book of Kimono. Tokyo; New York: Kodansha International, p. 60. ISBN 0-87011-500-6 (USA), ISBN 4-7700-0986-0 (Japan).
- Underwear (Hadagi): Hada-Juban. KIDORAKU Japan. Accessed 22 October 2009.
- Yamanaka, Norio (1982). The Book of Kimono. Tokyo; New York: Kodansha International, p. 76. ISBN 0-87011-500-6 (USA), ISBN 4-7700-0986-0 (Japan).
- Underwear (Hadagi): Kimono Slip. KIDORAKU Japan. Accessed 22 October 2009.
- Yamanaka, Norio (1982). The Book of Kimono. Tokyo; New York: Kodansha International, p. 61. ISBN 0-87011-500-6 (USA), ISBN 4-7700-0986-0 (Japan).
- Nagajuban Archived 2008-08-30 at the Wayback Machine undergarment for Japanese kimono
- Imperatore, Cheryl, & MacLardy, Paul (2001). Kimono Vanishing Tradition: Japanese Textiles of the 20th Century. Atglen, Penn.: Schiffer Publishing. Chap. 3 "Nagajuban—Undergarments", pp. 32–46. ISBN 0-7643-1228-6. OCLC 44868854.
- Underwear (Hadagi): Susoyoke. KIDORAKU Japan. Accessed 22 October 2009.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to kimono. |
| Look up kimono in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Kimono buying guide. |
- - The Canadian Museum of Civilization - Archive of the exhibition "The Landscape Kimonos of Itchiku Kubota"
- - The Kyoto Costume Museum - Costume History in Japan
- - Archived link to the Immortal Geisha Forums; comprehensive resource on kimono knowledge and culture
- - Articles on kimono from the V&A Collection
