Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy (IUPAC recommended name: Gibbs energy or Gibbs function; also known as free enthalpy[1] to distinguish it from Helmholtz free energy) is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum of reversible work that may be performed by a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure. The Gibbs free energy (, measured in joules in SI) is the maximum amount of non-expansion work that can be extracted from a thermodynamically closed system (can exchange heat and work with its surroundings, but not matter) in the standard state. This maximum can be attained only in a completely reversible process. When a system transforms reversibly from an initial state to a final state, the decrease in Gibbs free energy equals the work done by the system to its surroundings, minus the work of the pressure forces.[2]
| Thermodynamics | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
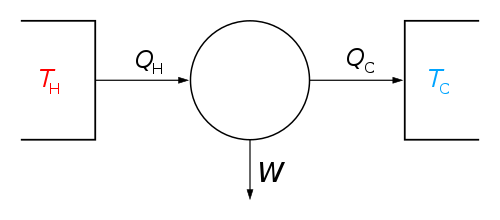 The classical Carnot heat engine | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
System properties Note: Conjugate variables in italics
|
||||||||||||
|
Material properties
|
||||||||||||
|
Equations
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
The Gibbs energy (symbol ) is also the thermodynamic potential that is minimized when a system reaches chemical equilibrium at constant pressure and temperature. Its derivative with respect to the reaction coordinate of the system vanishes at the equilibrium point. As such, a reduction in is necessary for a reaction to be spontaneous at constant pressure and temperature.
The Gibbs free energy, originally called available energy, was developed in the 1870s by the American scientist Josiah Willard Gibbs. In 1873, Gibbs described this "available energy" as[3]:400
the greatest amount of mechanical work which can be obtained from a given quantity of a certain substance in a given initial state, without increasing its total volume or allowing heat to pass to or from external bodies, except such as at the close of the processes are left in their initial condition.
The initial state of the body, according to Gibbs, is supposed to be such that "the body can be made to pass from it to states of dissipated energy by reversible processes". In his 1876 magnum opus On the Equilibrium of Heterogeneous Substances, a graphical analysis of multi-phase chemical systems, he engaged his thoughts on chemical free energy in full.
Overview

According to the second law of thermodynamics, for systems reacting at standard conditions for temperature and pressure (or any other fixed temperature and pressure), there is a general natural tendency to achieve a minimum of the Gibbs free energy.
A quantitative measure of the favorability of a given reaction at constant temperature and pressure is the change ΔG (sometimes written "delta G" or "dG") in Gibbs free energy that is (or would be) caused by the reaction. As a necessary condition for the reaction to occur at constant temperature and pressure, ΔG must be smaller than the non-pressure-volume (non-PV, e.g. electrical) work, which is often equal to zero (hence ΔG must be negative). ΔG equals the maximum amount of non-PV work that can be performed as a result of the chemical reaction for the case of reversible process. If analysis indicates a positive ΔG for a reaction, then energy — in the form of electrical or other non-PV work — would have to be added to the reacting system for ΔG to be smaller than the non-PV work and make it possible for the reaction to occur.[4]:298–299
One can think of ∆G as the amount of "free" or "useful" energy available to do work. The equation can be also seen from the perspective of the system taken together with its surroundings (the rest of the universe). First, one assumes that the given reaction at constant temperature and pressure is the only one that is occurring. Then the entropy released or absorbed by the system equals the entropy that the environment must absorb or release, respectively. The reaction will only be allowed if the total entropy change of the universe is zero or positive. This is reflected in a negative ΔG, and the reaction is called an exergonic process.
If two chemical reactions are coupled, then an otherwise endergonic reaction (one with positive ΔG) can be made to happen. The input of heat into an inherently endergonic reaction, such as the elimination of cyclohexanol to cyclohexene, can be seen as coupling an unfavourable reaction (elimination) to a favourable one (burning of coal or other provision of heat) such that the total entropy change of the universe is greater than or equal to zero, making the total Gibbs free energy difference of the coupled reactions negative.
In traditional use, the term "free" was included in "Gibbs free energy" to mean "available in the form of useful work".[2] The characterization becomes more precise if we add the qualification that it is the energy available for non-volume work.[5] (An analogous, but slightly different, meaning of "free" applies in conjunction with the Helmholtz free energy, for systems at constant temperature). However, an increasing number of books and journal articles do not include the attachment "free", referring to G as simply "Gibbs energy". This is the result of a 1988 IUPAC meeting to set unified terminologies for the international scientific community, in which the removal of the adjective "free" was recommended.[6][7][8] This standard, however, has not yet been universally adopted.
History
The quantity called "free energy" is a more advanced and accurate replacement for the outdated term affinity, which was used by chemists in the earlier years of physical chemistry to describe the force that caused chemical reactions.
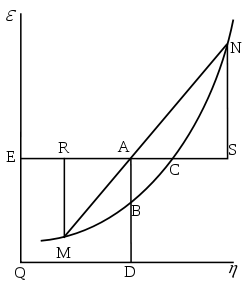
In 1873, Willard Gibbs published A Method of Geometrical Representation of the Thermodynamic Properties of Substances by Means of Surfaces, in which he sketched the principles of his new equation that was able to predict or estimate the tendencies of various natural processes to ensue when bodies or systems are brought into contact. By studying the interactions of homogeneous substances in contact, i.e., bodies composed of part solid, part liquid, and part vapor, and by using a three-dimensional volume-entropy-internal energy graph, Gibbs was able to determine three states of equilibrium, i.e., "necessarily stable", "neutral", and "unstable", and whether or not changes would ensue. Further, Gibbs stated:[3]
In this description, as used by Gibbs, ε refers to the internal energy of the body, η refers to the entropy of the body, and ν is the volume of the body.
Thereafter, in 1882, the German scientist Hermann von Helmholtz characterized the affinity as the largest quantity of work which can be gained when the reaction is carried out in a reversible manner, e.g., electrical work in a reversible cell. The maximum work is thus regarded as the diminution of the free, or available, energy of the system (Gibbs free energy G at T = constant, P = constant or Helmholtz free energy F at T = constant, V = constant), whilst the heat given out is usually a measure of the diminution of the total energy of the system (internal energy). Thus, G or F is the amount of energy "free" for work under the given conditions.
Until this point, the general view had been such that: "all chemical reactions drive the system to a state of equilibrium in which the affinities of the reactions vanish". Over the next 60 years, the term affinity came to be replaced with the term free energy. According to chemistry historian Henry Leicester, the influential 1923 textbook Thermodynamics and the Free Energy of Chemical Substances by Gilbert N. Lewis and Merle Randall led to the replacement of the term "affinity" by the term "free energy" in much of the English-speaking world.[9]:206
Graphical interpretation
Gibbs free energy was originally defined graphically. In 1873, American scientist Willard Gibbs published his first thermodynamics paper, "Graphical Methods in the Thermodynamics of Fluids", in which Gibbs used the two coordinates of the entropy and volume to represent the state of the body. In his second follow-up paper, "A Method of Geometrical Representation of the Thermodynamic Properties of Substances by Means of Surfaces", published later that year, Gibbs added in the third coordinate of the energy of the body, defined on three figures. In 1874, Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell used Gibbs' figures to make a 3D energy-entropy-volume thermodynamic surface of a fictitious water-like substance.[10] Thus, in order to understand the very difficult concept of Gibbs free energy one must be able to understand its interpretation as Gibbs defined originally by section AB on his figure 3 and as Maxwell sculpted that section on his 3D surface figure.
Definitions
The Gibbs free energy is defined as
which is the same as
where:
- U is the internal energy (SI unit: joule),
- p is pressure (SI unit: pascal),
- V is volume (SI unit: m3),
- T is the temperature (SI unit: kelvin),
- S is the entropy (SI unit: joule per kelvin),
- H is the enthalpy (SI unit: joule).
The expression for the infinitesimal reversible change in the Gibbs free energy as a function of its "natural variables" p and T, for an open system, subjected to the operation of external forces (for instance, electrical or magnetic) Xi, which cause the external parameters of the system ai to change by an amount dai, can be derived as follows from the first law for reversible processes:
where:
- μi is the chemical potential of the i-th chemical component. (SI unit: joules per particle[11] or joules per mole[2])
- Ni is the number of particles (or number of moles) composing the i-th chemical component.
This is one form of Gibbs fundamental equation.[12] In the infinitesimal expression, the term involving the chemical potential accounts for changes in Gibbs free energy resulting from an influx or outflux of particles. In other words, it holds for an open system or for a closed, chemically reacting system where the Ni are changing. For a closed, non-reacting system, this term may be dropped.
Any number of extra terms may be added, depending on the particular system being considered. Aside from mechanical work, a system may, in addition, perform numerous other types of work. For example, in the infinitesimal expression, the contractile work energy associated with a thermodynamic system that is a contractile fiber that shortens by an amount −dl under a force f would result in a term f dl being added. If a quantity of charge −de is acquired by a system at an electrical potential Ψ, the electrical work associated with this is −Ψ de, which would be included in the infinitesimal expression. Other work terms are added on per system requirements.[13]
Each quantity in the equations above can be divided by the amount of substance, measured in moles, to form molar Gibbs free energy. The Gibbs free energy is one of the most important thermodynamic functions for the characterization of a system. It is a factor in determining outcomes such as the voltage of an electrochemical cell, and the equilibrium constant for a reversible reaction. In isothermal, isobaric systems, Gibbs free energy can be thought of as a "dynamic" quantity, in that it is a representative measure of the competing effects of the enthalpic and entropic driving forces involved in a thermodynamic process.
The temperature dependence of the Gibbs energy for an ideal gas is given by the Gibbs–Helmholtz equation, and its pressure dependence is given by
If the volume is known rather than pressure, then it becomes
or more conveniently as its chemical potential:
In non-ideal systems, fugacity comes into play.
Derivation
The Gibbs free energy total differential natural variables may be derived by Legendre transforms of the internal energy.
The definition of G from above is
- .
Taking the total differential, we have
Replacing dU with the result from the first law gives[14]
The natural variables of G are then p, T, and {Ni}.
Homogeneous systems
Because S, V, and Ni are extensive variables, an Euler integral allows easy integration of dU:[14]
Because some of the natural variables of G are intensive, dG may not be integrated using Euler integrals as is the case with internal energy. However, simply substituting the above integrated result for U into the definition of G gives a standard expression for G:[14]
This result applies to homogeneous, macroscopic systems, but not to all thermodynamic systems.[15]
Gibbs free energy of reactions
The system under consideration is held at constant temperature and pressure, and is closed (no matter can come in or out). The Gibbs energy of any system is and an infinitesimal change in G, at constant temperature and pressure yields:
By the first law of thermodynamics, a change in the internal energy U is given by
where δQ is energy added as heat, and δW is energy added as work. The work done on the system may be written as δW = −PdV + δWx, where −PdV is the mechanical work of compression/expansion done on the system and δWx is all other forms of work, which may include electrical, magnetic, etc. Assuming that only mechanical work is done,
and the infinitesimal change in G is:
The second law of thermodynamics states that for a closed system, , and so it follows that:
This means that for a system which is not in equilibrium, its Gibbs energy will always be decreasing, and when it is in equilibrium (i.e. no longer changing), the infinitesimal change dG will be zero. In particular, this will be true if the system is experiencing any number of internal chemical reactions on its path to equilibrium.
In electrochemical thermodynamics
When electric charged dQ is passed in an electrochemical cell the emf ℰ yields a thermodynamic work term that appears in the expression for the change in Gibbs energy:
where G is the Gibb's free energy, S is the entropy, V is the system volume, P is its pressure and T is its absolute temperature.
The combination ( ℰ, Q ) is an example of a conjugate pair of variables. At constant pressure the above relationship produces a Maxwell relation that links the change in open cell voltage with temperature T (a measurable quantity) to the change in entropy S when charge is passed isothermally and isobarically. The latter is closely related to the reaction entropy of the electrochemical reaction that lends the battery its power. This Maxwell relation is:[16]
If a mole of ions goes into solution (for example, in a Daniell cell, as discussed below) the charge through the external circuit is:
where n0 is the number of electrons/ion, and F0 is the Faraday constant and the minus sign indicates discharge of the cell. Assuming constant pressure and volume, the thermodynamic properties of the cell are related strictly to the behavior of its emf by:
where ΔH is the enthalpy of reaction. The quantities on the right are all directly measurable.
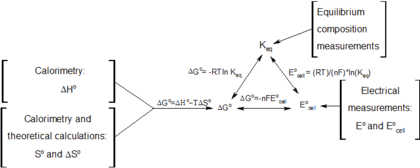
Useful identities to derive the Nernst equation
During a reversible electrochemical reaction at constant temperature and pressure, the following equations involving the Gibbs free energy hold:
- (see chemical equilibrium),
- (for a system at chemical equilibrium),
- (for a reversible electrochemical process at constant temperature and pressure),
- (definition of E°),
and rearranging gives
which relates the cell potential resulting from the reaction to the equilibrium constant and reaction quotient for that reaction (Nernst equation),
where
- ΔrG = Gibbs free energy change per mole of reaction,
- ΔrG° = Gibbs free energy change per mole of reaction for unmixed reactants and products at standard conditions (i.e. 298K, 100kPa, 1M of each reactant and product),
- R = gas constant,
- T = absolute temperature,
- ln = natural logarithm,
- Qr = reaction quotient (unitless),
- Keq = equilibrium constant (unitless),
- welec,rev = electrical work in a reversible process (chemistry sign convention),
- n = number of moles of electrons transferred in the reaction,
- F = Faraday constant = 96485 C/mol (charge per mole of electrons),
- E = cell potential,
- E° = standard cell potential.
Moreover, we also have:
which relates the equilibrium constant with Gibbs free energy. This implies that at equilibrium
- and
Standard energy change of formation
| Substance
(State) |
ΔfG°
(kJ/mol) |
ΔfG°
(kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| NO(g) | 87.6 | 20.9 |
| NO2(g) | 51.3 | 12.3 |
| N2O(g) | 103.7 | 24.78 |
| H2O(g) | −228.6 | −54.64 |
| H2O(l) | −237.1 | −56.67 |
| CO2(g) | −394.4 | −94.26 |
| CO(g) | −137.2 | −32.79 |
| CH4(g) | −50.5 | −12.1 |
| C2H6(g) | −32.0 | −7.65 |
| C3H8(g) | −23.4 | −5.59 |
| C6H6(g) | 129.7 | 29.76 |
| C6H6(l) | 124.5 | 31.00 |
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation of a compound is the change of Gibbs free energy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of that substance from its component elements, at their standard states (the most stable form of the element at 25 °C and 100 kPa). Its symbol is ΔfG˚.
All elements in their standard states (diatomic oxygen gas, graphite, etc.) have standard Gibbs free energy change of formation equal to zero, as there is no change involved.
- ΔfG = ΔfG˚ + RT ln Qf,
where Qf is the reaction quotient.
At equilibrium, ΔfG = 0, and Qf = K, so the equation becomes
- ΔfG˚ = −RT ln K,
where K is the equilibrium constant.
See also
- Calphad (CALculation of PHAse Diagrams)
- Critical point (thermodynamics)
- Electron equivalent
- Enthalpy-entropy compensation
- Free entropy
- Gibbs–Helmholtz equation
- Grand potential
- Non-random two-liquid model (NRTL model) – Gibbs energy of excess and mixing calculation and activity coeffients
- Spinodal – Spinodal Curves (Hessian matrix)
- Standard molar entropy
- Thermodynamic free energy
- UNIQUAC model – Gibbs energy of excess and mixing calculation and activity coeffients
Notes and references
- Greiner, Walter; Neise, Ludwig; Stöcker, Horst (1995). Thermodynamics and statistical mechanics. Springer-Verlag. p. 101.
- Perrot, Pierre (1998). A to Z of Thermodynamics. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-856552-6.
- J. W. Gibbs, "A Method of Geometrical Representation of the Thermodynamic Properties of Substances by Means of Surfaces", Transactions of the Connecticut Academy of Arts and Sciences 2, Dec. 1873, pp. 382–404.
- Peter Atkins; Loretta Jones (1 August 2007). Chemical Principles: The Quest for Insight. W. H. Freeman. ISBN 978-1-4292-0965-6.
- Reiss, Howard (1965). Methods of Thermodynamics. Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-69445-3.
- Calvert, J. G. (1 January 1990). "Glossary of atmospheric chemistry terms (Recommendations 1990)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 62 (11): 2167–2219. doi:10.1351/pac199062112167.
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry Commission on Physicochemical Symbols Terminology and Units (1993). Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry (2nd ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications. pp. 251. ISBN 0-632-03583-8. Retrieved 2013-12-20.
- Lehmann, H. P.; Fuentes-Arderiu, X.; Bertello, L. F. (1 January 1996). "Glossary of terms in quantities and units in Clinical Chemistry (IUPAC-IFCC Recommendations 1996)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 68 (4): 957–1000. doi:10.1351/pac199668040957.
- Henry Marshall Leicester (1971). The Historical Background of Chemistry. Courier Corporation. ISBN 978-0-486-61053-5.
- James Clerk Maxwell, Elizabeth Garber, Stephen G. Brush, and C. W. Francis Everitt (1995), Maxwell on heat and statistical mechanics: on "avoiding all personal enquiries" of molecules, Lehigh University Press, ISBN 0-934223-34-3, p. 248.
- Chemical Potential, IUPAC Gold Book.
- Müller, Ingo (2007). A History of Thermodynamics – the Doctrine of Energy and Entropy. Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-46226-2.
- Katchalsky, A.; Curran, Peter F. (1965). Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics in Biophysics. Harvard University Press. CCN 65-22045.
- Salzman, William R. (2001-08-21). "Open Systems". Chemical Thermodynamics. University of Arizona. Archived from the original on 2007-07-07. Retrieved 2007-10-11.
- Brachman, M. K. (1954). "Fermi Level, Chemical Potential, and Gibbs Free Energy". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 22 (6): 1152. Bibcode:1954JChPh..22.1152B. doi:10.1063/1.1740312.
- H. S. Harned, B. B. Owen, The Physical Chemistry of Electrolytic Solutions, third edition, Reinhold Publishing Corporation, N.Y.,1958, p. 2-6
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 2009, pp. 5-4–5-42, 90th ed., Lide.
External links
- IUPAC definition (Gibbs energy)
- Gibbs free energy calculator
- Gibbs energy – Florida State University
- Gibbs Free Energy – Eric Weissteins World of Physics
- Entropy and Gibbs Free Energy – www.2ndlaw.oxy.edu
- Gibbs Free Energy – Georgia State University
- Gibbs Free Energy Java Applet – University of California, Berkeley
- Using Gibbs Free Energy for prediction of chemical driven material ageing
- Topological Analysis of the Gibbs Energy Function (Liquid-Liquid Equilibrium Correlation Data). Including a Thermodinamic Review and a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for Surfaces/Tie-lines/Hessian matrix analysis – University of Alicante (Reyes-Labarta et al. 2015–18)