Arabic script
The Arabic script is a writing system used for writing Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa, such as Persian, Kurdish, Azerbaijani, Sindhi, Balochi, Pashto, Lurish, Urdu and Mandinka, among others.[1] Until the 16th century, it was also used to write some texts in Spanish. Additionally, prior to the language reform in 1928, it was the writing system of Turkish.[2] It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by the number of countries using it and the third by the number of users, after Latin and Chinese characters.[3]
| Arabic script | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Languages | See below |
Time period | 400 CE to the present |
Parent systems | Proto-Sinaitic
|
Child systems | Inspired the N'Ko alphabet and the Hanifi script |
| Direction | Right-to-left |
| ISO 15924 | Arab, 160 |
Unicode alias | Arabic |
Unicode range |
|
The Arabic script is written from right to left in a cursive style. In most cases, the letters transcribe consonants or consonants and a few vowels, so most Arabic alphabets are abjads.
The script was first used to write texts in Arabic, most notably the Qurʼān, the holy book of Islam. With the spread of Islam, it came to be used as the primary script for many language families, leading to the addition of new letters and other symbols, with some versions, such as Kurdish, Uyghur and old Bosnian being abugidas or true alphabets. It is also the basis for the tradition of Arabic calligraphy.
History
Languages written with the Arabic script
| خ | ح | ج | ث | ت | ب | ا |
| ḫāʾ / khāʾ | ḥāʾ | jīm | ṯāʾ / thaʾ | tāʾ | bāʾ | ʾalif |
| ص | ش | س | ز | ر | ذ | د |
| ṣād | šīn / shīn | sīn | zāy/zayn | rāʾ | ḏāl / dhāl | dāl |
| ق | ف | غ | ع | ظ | ط | ض |
| qāf | fāʾ | ġayn / ghayn | ʿayn | ẓāʾ | ṭāʾ | ḍād |
| ي | و | ه | ن | م | ل | ك |
| yāʾ | wāw | hāʾ | nūn | mīm | lām | kāf |
| Worldwide use of the Arabic script | ||
|---|---|---|
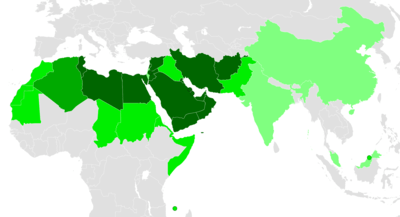 Arabic alphabet world distribution | ||
| Countries where the Arabic script: | ||
| → | is the only official script | |
| → | is the only official script, but other scripts are recognized for national or regional languages | |
| → | is official alongside other scripts | |
| → | is official at a sub-national level (China, India) or is a recognized alternative script (Malaysia) | |
The Arabic script has been adapted for use in a wide variety of languages besides Arabic, including Persian, Malay and Urdu, which are not Semitic. Such adaptations may feature altered or new characters to represent phonemes that do not appear in Arabic phonology. For example, the Arabic language lacks a voiceless bilabial plosive (the [p] sound), therefore many languages add their own letter to represent [p] in the script, though the specific letter used varies from language to language. These modifications tend to fall into groups: Indian and Turkic languages written in the Arabic script tend to use the Persian modified letters, whereas the languages of Indonesia tend to imitate those of Jawi. The modified version of the Arabic script originally devised for use with Persian is known as the Perso-Arabic script by scholars.
In the cases of Bosnian, Kurdish, Kashmiri and Uyghur writing systems, vowels are mandatory. The Arabic script can therefore be used in both abugida and abjad forms, although it is often strongly if erroneously connected to the latter.
Use of the Arabic script in West African languages, especially in the Sahel, developed with the spread of Islam. To a certain degree the style and usage tends to follow those of the Maghreb (for instance the position of the dots in the letters fāʼ and qāf). Additional diacritics have come into use to facilitate the writing of sounds not represented in the Arabic language. The term ʻAjamī, which comes from the Arabic root for "foreign," has been applied to Arabic-based orthographies of African languages.
Current use
Today Afghanistan, Iran, India, Pakistan and China are the main non-Arabic speaking states using the Arabic alphabet to write one or more official national languages, including Azerbaijani, Baluchi, Brahui, Persian, Pashto, Central Kurdish, Urdu, Sindhi, Kashmiri, Punjabi and Uyghur.
An Arabic alphabet is currently used for the following languages:
Middle East and Central Asia
 |
| Calligraphy |
|---|
|
- Arabic
- Garshuni (or Karshuni) originated in the 7th century, when Arabic became the dominant spoken language in the Fertile Crescent, but Arabic script was not yet fully developed or widely read, and so the Syriac alphabet was used. There is evidence that writing Arabic in this other set of letters (known as Garshuni) influenced the style of modern Arabic script. After this initial period, Garshuni writing has continued to the present day among some Syriac Christian communities in the Arabic-speaking regions of the Levant and Mesopotamia.
- Kazakh in Kazakhstan, China, Iran and Afghanistan
- Kurdish in Northern Iraq and Northwest Iran. (In Turkey and Syria the Latin script is used for Kurdish)
- Kyrgyz by its 150,000 speakers in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in northwestern China, Pakistan, Kyrgyzstan and Afghanistan
- Turkmen in Turkmenistan, Afghanistan and Iran
- Uzbek in Uzbekistan and Afghanistan
- Official Persian in Iran and its dialects, like Dari in Afghanistan and Tajiki in Tajikistan
- Baluchi in Iran, in Pakistan's Balochistan region, Afghanistan and Oman[4] An academy for the protection of the Baluchi Language was established in Iran in 2009[5]
- Southwestern Iranian languages as Lori dialects and Bakhtiari language[6][7]
- Pashto in Afghanistan and Pakistan
- Uyghur changed to Latin script in 1969 and back to a simplified, fully voweled Arabic script in 1983
- Judeo-Arabic languages
- Judeo-Tunisian Arabic[8]
- Azerbaijani language in Iran
- Talysh language in Iran
East Asia
- The Chinese language is written by some Hui in the Arabic-derived Xiao'erjing alphabet (see also Sini (script))
- The Turkic Salar language is written by some Salar in the Arabic alphabet
- Uyghur alphabet
South Asia
- Balochi in Pakistan and Iran
- Dari in Afghanistan
- Kashmiri in India and (also written in Sharada and Devanagari )
- Pashto in Afghanistan and Pakistan
- Khowar in Northern Pakistan, which also uses the Latin script
- Punjabi (where the script is known as Shahmukhi) in Pakistan, Punjabi is written with the Brahmic Gurmukhi script in India
- Saraiki is written with a modified Arabic script that has 45 letters
- Sindhi in Arabic script; British commissioner in Sindh on August 29, 1857 ordered to change Arabic script,[9] Sindhi is often written with the Devanagari script in India
- Aer language[10]
- Bhadrawahi language[11]
- Ladakhi language ( India) although it is more commonly written using the Tibetan script
- Balti[12] (a Sino-Tibetan language), which is more rarely written in the Tibetan script
- Brahui language of Brahui people of Pakistan and Afghanistan[13]
- Burushaski or Burusho language, a language isolated to Pakistan[14]
- Urdu (and historically several other Hindustani languages). Urdu is one of several official languages in the states of Jammu and Kashmir, Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal and Telangana; Kashmiri also uses Devanagari script, and more rarely the Sharada script
- Dogri language (डोगरी or ڈوگرى) spoken by about five million people in India and Pakistan, chiefly in the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir and in Himachal Pradesh, but also in northern Punjab, although Dogri is more commonly written in Devanagari
- The Arwi language (a mixture of Arabic and Tamil) uses the Arabic script together with the addition of 13 letters. It is mainly used in Sri Lanka and the South Indian state of Tamil Nadu for religious purposes. Arwi language is the language of Tamil Muslims
- Malayalam language represented by Arabic script variant is known as Arabi Malayalam. The script has particular letters to represent the peculiar sounds of Malayalam. This script is mainly used in madrasas of the South Indian state of Kerala and of Lakshadweep to teach Malayalam. In everyday life, Malayalam is written with the Malayalam script
- Chittagonian language, spoken by the people of Chittagong, in Bangladesh,[15] although it is far more commonly written in Bengali script
- Rohingya language (Ruáingga) is a language spoken by the Rohingya people of Rakhine State, formerly known as Arakan (Rakhine), Burma (Myanmar). It is similar to Chittagonian language in neighboring Bangladesh[16] and sometimes written using the Roman script, or an Arabic-derived script known as Hanifi
Southeast Asia
- Malay in the Arabic script known as Jawi. In some cases it can be seen in the signboards of shops and market stalls. Particularly in Brunei, Jawi is used in terms of writing or reading for Islamic religious educational programs in primary school, secondary school, college, or even higher educational institutes such as universities. In addition, some television programming uses Jawi, such as announcements, advertisements, news, social programs or Islamic programs
- co-official in Brunei
- Malaysia but co-official in Kelantan, an Islamic state in Malaysia
- Indonesia, Jawi script is co-used with Latin in provinces of Riau and Riau Islands. The Javanese, Madurese and Sundanese also use another Arabic variant, the Pegon in Islamic writings and pesantren community.
- Southern Thailand
- Singapore
- Predominantly Muslim areas of the Philippines (especially Tausug language)
- Ida'an language (also Idahan) a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken by the Ida'an people of Sabah, Malaysia[17]
- Cham language in Cambodia[18] besides Western Cham script.
Africa
- North Africa
- Arabic
- Maghrebi Arabic uses a modified Arabic script, with additional letters, in order to support /g/ (ڨ/ڭ), /v/ (ڥ) and /p/ (پ) along with the older /f/ (ڢ) and /q/ (ڧ)[19][20]
- Berber languages have often been written in an adaptation of the Arabic alphabet. The use of the Arabic alphabet, as well as the competing Latin and Tifinagh scripts, has political connotations
- Tuareg language, (sometimes called Tamasheq) which is also a Berber lamguage
- Coptic language of Egyptian Coptics as Coptic text written in Arabic letters[21]
- Northeast Africa
- Bedawi or Beja, mainly in northeastern Sudan
- Wadaad writing, used in Somalia
- Nubian languages
- Dongolawi language or Andaandi language of Nubia, in the Nile Vale of northern Sudan
- Nobiin language, the largest Nubian language (previously known by the geographic terms Mahas and Fadicca/Fiadicca) is not yet standardized, being written variously in both Latinized and Arabic scripts; also, there have been recent efforts to revive the Old Nubian alphabet.[22][23]
- Fur language of Darfur, Sudan
- Southeast Africa
- Comorian, in the Comoros, currently side by side with the Latin alphabet (neither is official)
- Swahili, was originally written in Arabic alphabet, Swahili orthography is now based on the Latin alphabet that was introduced by Christian missionaries and colonial administrators
- West Africa
- Zarma language of the Songhay family. It is the language of the southwestern lobe of the West African nation of Niger, and it is the second leading language of Niger, after Hausa, which is spoken in south central Niger[24]
- Tadaksahak is a Songhay language spoken by the pastoralist Idaksahak of the Ménaka area of Mali[25]
- Hausa language uses an adaptation of the Arabic script known as Ajami, for many purposes, especially religious, but including newspapers, mass mobilization posters and public information[26]
- Dyula language is a Mandé language spoken in Burkina Faso, Côte d'Ivoire and Mali.[27]
- Jola-Fonyi language of the Casamance region of Senegal[28]
- Balanta language a Bak language of west Africa spoken by the Balanta people and Balanta-Ganja dialect in Senegal
- Mandinka, widely but unofficially (known as Ajami), (another non-Latin script used is the N'Ko script)
- Fula, especially the Pular of Guinea (known as Ajami)
- Wolof (at zaouia schools), known as Wolofal.
- Arabic script outside Africa
- In writings of African American slaves
- Writings of by Omar Ibn Said (1770–1864) of Senegal[29]
- The Bilali Document also known as Bilali Muhammad Document is a handwritten, Arabic manuscript[30] on West African Islamic law. It was written by Bilali Mohammet in the 19th century. The document is currently housed in the library at the University of Georgia
- Letter written by Ayuba Suleiman Diallo (1701–1773)
- Arabic Text From 1768[31]
- Letter written by Abdulrahman Ibrahim Ibn Sori (1762–1829)
- In writings of African American slaves
Former use
In the 20th century, the Arabic script was generally replaced by the Latin alphabet in the Balkans, parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, and Southeast Asia, while in the Soviet Union, after a brief period of Latinisation,[32] use of Cyrillic was mandated. Turkey changed to the Latin alphabet in 1928 as part of an internal Westernizing revolution. After the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, many of the Turkic languages of the ex-USSR attempted to follow Turkey's lead and convert to a Turkish-style Latin alphabet. However, renewed use of the Arabic alphabet has occurred to a limited extent in Tajikistan, whose language's close resemblance to Persian allows direct use of publications from Afghanistan and Iran.[33]
Most languages of the Iranian languages family continue to use Arabic script, as well as the Indo-Aryan languages of Pakistan and of Muslim populations in India. However, the Bengali language of India and Bangladesh was never written in Arabic script, which has been written in the Bengali alphabet since inception.[34]
Africa
- Afrikaans (as it was first written among the "Cape Malays", see Arabic Afrikaans)
- Berber in North Africa, particularly Shilha in Morocco (still being considered, along with Tifinagh and Latin, for Central Atlas Tamazight)
- French by the Arabs and Berbers in Algeria and other parts of North Africa during the French colonial period
- Harari, by the Harari people of the Harari Region in Ethiopia. Now uses the Geʻez and Latin alphabets
- For the West African languages—Hausa, Fula, Mandinka, Wolof and some more—the Latin alphabet has officially replaced Arabic transcriptions for use in literacy and education
- Kinyarwanda in Rwanda
- Kirundi in Burundi
- Malagasy in Madagascar (script known as Sorabe)
- Nubian
- Shona in Zimbabwe
- Somali (see wadaad Arabic) has mostly used the Latin alphabet since 1972
- Songhay in West Africa, particularly in Timbuktu
- Swahili (has used the Latin alphabet since the 19th century)
- Yoruba in West Africa (this was probably limited, but still notable)
Europe
- Albanian called Elifbaja shqip
- Aljamiado (Mozarabic, Berber, Aragonese, Portuguese, Ladino, and Spanish, during and residually after the Muslim rule in the Iberian peninsula
- Belarusian (among ethnic Tatars; see Belarusian Arabic alphabet)
- Bosnian (only for literary purposes; currently written in the Latin alphabet; Text example: مۉلٖىمۉ سه تهبٖى بۉژه = Molimo se tebi, Bože (We pray to you, O God); see Arebica)
- Crimean Tatar
- Greek in certain areas in Greece and Anatolia. In particular, Cappadocian Greek written in Perso-Arabic
- Polish (among ethnic Lipka Tatars)
Central Asia and Caucasus
- Adyghe language also known as West Circassian, is an official languages of the Republic of Adygea in the Russian Federation. It used Arabic alphabet before 1927
- Avar as well as other languages of Daghestan: Nogai, Kumyk, Lezgian, Lak and Dargwa
- Azeri in Azerbaijan (now written in the Latin alphabet and Cyrillic script in Azerbaijan)
- Bashkir (officially for some years from the October Revolution of 1917 until 1928, changed to Latin, now uses the Cyrillic script)
- Chaghatay across Central Asia
- Chechen (sporadically from the adoption of Islam; officially from 1917 until 1928)[35]
- Circassian and some other members of the Abkhaz–Adyghe family in the western Caucasus and sporadically – in the countries of Middle East, like Syria
- Ingush
- Karachay-Balkar in the central Caucasus
- Karakalpak
- Kazakh in Kazakhstan (until the 1930s, changed to Latin, currently using Cyrillic, phasing in Latin)
- Kyrgyz in Kyrgyzstan (until the 1930s, changed to Latin, now uses the Cyrillic script)
- Mandarin Chinese and Dungan, among the Hui people (script known as Xiao'erjing)
- Ottoman Turkish
- Tat in South-Eastern Caucasus
- Tatar before 1928 (changed to Latin Yañalif), reformed in the 1880s (İske imlâ), 1918 (Yaña imlâ – with the omission of some letters)
- Turkmen in Turkmenistan (changed to Latin in 1929, then to the Cyrillic script, then back to Latin in 1991)
- Uzbek in Uzbekistan (changed to Latin, then to the Cyrillic script, then back to Latin in 1991)
- Some Northeast Caucasian languages of the Muslim peoples of the USSR between 1918 and 1928 (many also earlier), including Chechen, Lak, etc. After 1928, their script became Latin, then later Cyrillic
Southeast Asia
- Acehnese in Sumatra, Indonesia
- Banjarese in Kalimantan, Indonesia
- Maguindanaon in the Philippines
- Malay in Malaysia, Singapore and Indonesia. Although Malay speakers in Brunei and Southern Thailand still use the script on a daily basis
- Minangkabau in Sumatra, Indonesia
- Pegon script of Javanese, Madurese and Sundanese in Indonesia, used only in Islamic schools and institutions
- Tausug in the Philippines
- Maranao in the Philippines
Middle East
- Hebrew was written in Arabic letters in a number of places in the past[36][37]
- Northern Kurdish in Turkey and Syria was written in Arabic script until 1932, when a modified Kurdish Latin alphabet was introduced by Jaladat Ali Badirkhan in Syria
- Turkish in the Ottoman Empire was written in Arabic script until Mustafa Kemal Atatürk declared the change to Latin script in 1928. This form of Turkish is now known as Ottoman Turkish and is held by many to be a different language, due to its much higher percentage of Persian and Arabic loanwords (Ottoman Turkish alphabet)
Special letters
| Language Family | Austron. | Dravid | Turkic | Indic (Indo-European) | Iranian (Indo-European) | Arabic (Semitic) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language/Script | Jawi | Pegon | Arwi | Uyghur | Sindhi | Punjabi | Urdu | Persian | Balochi | Kurdish | Pashto | Moroccan | Tunisian | Algerian | Hejazi | Najdi | Egyptian | Palestinian | Iraqi | Gulf | |
| /p/ | ڤ | ڣ | پ | پ / ب | |||||||||||||||||
| /g/ | ݢ | ࢴ | گ | ګ | ڭ / گ | ڨ / ڧـ ـڧـ ـٯ / ق | ق | ج | چ / ج | گ / ك | ق / گ | ||||||||||
| /t͡ʃ/ | چ | Ø | چ | ڜ | تش | چ | |||||||||||||||
| /v/ | ۏ | ف | و | ۋ | و | Ø | ڤ | Ø | ڥ / ڢ / ف | ڤ / ف | |||||||||||
| /ʒ/ | Ø | ژ | Ø | ژ | its usage depends on the dialect | ||||||||||||||||
| /ŋ/ | ڠ | ࢳ | ڭ | ڱ | نگ | Ø | Ø | ||||||||||||||
| /ɳ/ | Ø | Ø | ڹ | Ø | ڻ | ݨ | ن | Ø | ڼ | Ø | |||||||||||
| /ɲ/ | ڽ | ۑ | ݧ | Ø | نج | Ø | Ø | ||||||||||||||
- ٻ – B̤ē, used to represent a voiced bilabial implosive /ɓ/ in Hausa, Sindhi and Saraiki.
- پ – Pe, used to represent the phoneme /p/ in Persian, Pashto, Punjabi, Khowar, Sindhi, Urdu, Kurdish; it is not used in most Arabic varieties (except Mesopotamian and Gulf) and it is normalized as /b/; e.g., pepsi > bibsi.
- ݐ – used to represent the equivalent of the Latin letter Ƴ (palatalized glottal stop /ʔʲ/) in some African languages such as Fulfulde.
- ڀ – represents an aspirated voiced bilabial plosive /bʱ/ in Sindhi.
- ٺ – Ṭhē, represents the aspirated voiceless retroflex plosive /ʈʰ/ in Sindhi.
- ټ – ṭē, used to represent the phoneme /ʈ/ in Pashto.
- ٽ – Ṭe, used to represent the phoneme (a voiceless retroflex plosive /ʈ/) in Sindhi
- ﭦ – Ṭe, used to represent Ṭ (a voiceless retroflex plosive /ʈ/) in Punjabi, Urdu.
- ٿ – Teheh, used in Sindhi and Rajasthani (when written in Sindhi alphabet); used to represent the phoneme /t͡ɕʰ/ (pinyin q) in Chinese Xiao'erjing.
- ڄ – represents the "ц" voiceless dental affricate /t͡s/ phoneme in Bosnian.
- ڃ – represents the "ћ" voiceless alveolo-palatal affricate /t͡ɕ/ phoneme in Bosnian.
- چ – Che, used to represent /t͡ʃ/ ("ch"). It is used in Persian, Pashto, Punjabi, Urdu and Kurdish. /ʒ/ in Egypt.
- څ – Ce, used to represent the phoneme /t͡s/ in Pashto.
- ݗ – represents the "ђ" voiced alveolo-palatal affricate /d͡ʑ/ phoneme in Bosnian.
- ځ – źim, used to represent the phoneme /d͡z/ in Pashto.
- ݙ – used in Saraiki to represent a Voiced alveolar implosive /ɗ̢/.
- ڊ – used in Saraiki to represent a voiced retroflex implosive /ᶑ/.
- ڈ – Ḍal, used to represent a Ḍ (a voiced retroflex plosive /ɖ/) in Punjabi and Urdu.
- ڌ – Dhal used to represent the phoneme /d̪ʱ/ in Sindhi
- ډ – Ḍal, used to represent the phoneme /ɖ/ in Pashto.
- ڑ – Ṛe, represents a retroflex flap /ɽ/ in Punjabi and Urdu.
- ړ – "ṛe" represents a retroflex lateral flap in Pashto.
- ݫ – used in Ormuri to represent a voiced alveolo-palatal fricative /ʑ/, as well as in Torwali.
- ژ – Že/zhe, used to represent the voiced postalveolar fricative /ʒ/ in, Persian, Pashto, Kurdish, Urdu, Punjabi and Uyghur.
- ږ – ǵe / ẓ̌e, used to represent the phoneme /ʐ/ /ɡ/ /ʝ/ in Pashto.
- ڕ – used in Kurdish to represent rr /r/ in Soranî dialect.
- ݭ – used in Kalami to represent a voiceless retroflex fricative /ʂ/, and in Ormuri to represent a voiceless alveolo-palatal fricative /ɕ/.
- ݜ – used in Shina to represent a voiceless retroflex fricative /ʂ/.
- ښ – x̌īn /ṣ̌īn, used to represent the phoneme /x/ /ʂ/ /ç/ in Pashto.
- ڜ — used to represent Spanish words with /t͡ʃ/ in Morocco.
- ڨ – Ga, used to represent the voiced velar plosive /ɡ/ in Algerian and Tunisian.
- گ – Gaf, represents a voiced velar plosive /ɡ/ in Persian, Pashto, Punjabi, Kyrgyz, Kazakh, Kurdish, Uyghur, Mesopotamian, Urdu and Ottoman Turkish.
- ګ – Gaf, used to represent the phoneme /ɡ/ in Pashto.
- ݢ or ڬ – Gaf, represents a voiced velar plosive /ɡ/ in the Jawi script of Malay.
- ࢴ – Gaf, represents a voiced velar plosive /ɡ/ in the Pegon script of Indonesian.
- ڭ – Ng, used to represent the /ŋ/ phone in Ottoman Turkish, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, and Uyghur, and to represent the /ɡ/ in Morocco and in many dialects of Algerian.
- أي – Ee, used to represent the phoneme /eː/ in Somali.
- ﺉ – E, used to represent the phoneme /e/ in Somali.
- ىٓ – Ii, used to represent the phoneme /iː/ in Somali and Saraiki.
- ؤ – O, used to represent the phoneme /o/ in Somali.
- ې – Pasta Ye, used to represent the phoneme /e/ in Pashto and Uyghur.
- ی – Nārīna Ye, used to represent the phoneme [ɑj] and phoneme /j/ in Pashto.
- ۍ – x̌əźīna ye Ye, used to represent the phoneme [əi] in Pashto.
- ئ – FāiliyaYe, used to represent the phoneme [əi] and /j/ in Pashto, Punjabi, Saraiki and Urdu
- أو – Oo, used to represent the phoneme /oː/ in Somali.
- ﻭٓ – Uu, used to represent the phoneme /uː/ in Somali.
- ڳ – represents a voiced velar implosive /ɠ/ in Sindhi and Saraiki
- ڱ – represents the Velar nasal /ŋ/ phoneme in Sindhi.
- ﮎ – Khē, represents /kʰ/ in Sindhi.
- ݣ – used to represent the phoneme /ŋ/ (pinyin ng) in Chinese.
- ڼ – represents the retroflex nasal /ɳ/ phoneme in Pashto.
- ڻ – represents the retroflex nasal /ɳ/ phoneme in Sindhi.
- ݨ – used in Punjabi to represent /ɳ/ and Saraiki to represent /ɲ/.
- ڽ – Nya /ɲ/ in the Jawi script.
- ۑ – Nya /ɲ/ in the Pegon script.
- ڠ – Nga /ŋ/ in the Jawi script and Pegon script and Gain /g/ in Khowar alphabet.
- ڵ – used in Kurdish to represent ll /ɫ/ in Soranî dialect.
- ݪ – used in Marwari to represent a retroflex lateral flap /ɺ̢/, and in Kalami to represent a voiceless lateral fricative /ɬ/.
- ࣇ – used in Punjabi to represent voiced retroflex lateral approximant /ɭ/
- ڥ – Vi, used in Algerian and Tunisian when written in Arabic script to represent the sound /v/.
- ڤ – Ve, used in by some Arabic speakers to represent the phoneme /v/ in loanwords, and in the Kurdish language when written in Arabic script to represent the sound /v/. Also used as pa /p/ in the Jawi script and Pegon script.
- ۏ – Va in the Jawi script.
- ۋ – represents a voiced labiodental fricative /v/ in Kyrgyz, Uyghur, and Old Tatar; and /w, ʊw, ʉw/ in Kazakh; also formerly used in Nogai.
- ۆ – represents "O" /o/ in Kurdish, and in Uyghur it represents the sound similar to the French eu andœu /ø/ sound. It represents the "у" close back rounded vowel /u/ phoneme in Bosnian.
- ێ – represents Ê or É /e/ in Kurdish.
- ھ – Do-chashmi he (two-eyed hāʼ), used in digraphs for aspiration /ʰ/ and breathy voice /ʱ/ in Punjabi and Urdu.
- ے – Baṛī ye ('big yāʼ'), represents "ai" or "e" in Urdu /ɛː/, /eː/ and Punjabi.
- ڞ – used to represent the phoneme /tsʰ/ (pinyin c) in Chinese.
- ط – used to represent the phoneme /t͡s/ (pinyin z) in Chinese.
- ۉ – represents the "o" open-mid back rounded vowel /ɔ/ phoneme in Bosnian.
- ݩ – represents the "њ" palatal nasal /ɲ/ phoneme in Bosnian.
- ڵ – represents the "љ" palatal lateral approximant /ʎ/ phoneme in Bosnian.
- اٖى – represents the "и" close front unrounded vowel /i/ phoneme in Bosnian.
Writing systems
| Alphabet | #Chars | Languages | Region | Derived from | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabic alphabet | 28 | Arabic | North Africa, West Asia | Aramaic alphabet, Syriac alphabet, Nabataean alphabet | |
| Ajami script | 33 | Hausa language, Swahili | West Africa | Arabic | Abjad |
| Arebica | 30 | Bosnian | Southeastern Europe | Perso-Arabic | latest stage with full vowel marking |
| Arwi alphabet | 41 | Tamil | Southern India, Sri Lanka | Perso-Arabic | |
| Belarusian Arabic alphabet | 32 | Belarusian | Eastern Europe | Perso-Arabic | 15th/16th century |
| Berber Arabic alphabet(s) | various Berber languages | North Africa | Arabic | ||
| Chagatai alphabet(s) | 32 | Chagatai | Central Asia | Perso-Arabic | |
| Galal alphabet | 32 | Somali | Horn of Africa | Arabic | |
| Jawi script | 36 | Malay | Peninsular Malay | Perso-Arabic | Since 1303 AD (Trengganu Stone) |
| Kashmiri alphabet | 44 | Kashmiri | South Asia | Perso-Arabic | |
| Kazakh Arabic alphabet | 35 | Kazakh | Central Asia, China | Perso-Arabic/Chagatai | since 11th century, now official only in China |
| Khowar alphabet | 60 | Khowar | South Asia | Perso-Arabic | |
| Kyrgyz Arabic alphabet | 33 | Kyrgyz | Perso-Arabic | now official only in China | |
| Kuryan alphabet | 44 | Korean language | East Asia, South Korea | Perso-Arabic | invented by Korean Muslim in the 2000s |
| Nasta'liq script | Urdu and others | Perso-Arabic | |||
| Pashto alphabet | 45 | Pashto | Afghanistan and Pakistan | Perso-Arabic | |
| Pegon alphabet | 35 | Javanese, Sundanese | Indonesia | Perso-Arabic | |
| Persian alphabet | 32 | Persian | Iran | Arabic | |
| Saraiki alphabet | 45 | Saraiki | Pakistan | Perso-Arabic | |
| Shahmukhi script | 41 (58 with aspirated letters) | Punjabi | Pakistan | Perso-Arabic | Similar to Urdu, has aspirated letters |
| Sindhi alphabet | 64 | Sindhi | Pakistan | Perso-Arabic | |
| Sorabe alphabet | 33 | Malagasy | Madagascar | Arabic | |
| Soranî alphabet | 33 | Central Kurdish | Perso-Arabic | Vowels are mandatory, i.e. abugida | |
| Swahili | |||||
| İske imlâ alphabet | 35 | Tatar | Perso-Arabic/Chagatai | before 1920 | |
| Ottoman Turkish alphabet | 32 | Ottoman Turkish | Ottoman Empire | Perso-Arabic | Official until 1928 |
| Urdu alphabet | 39 (58 with aspirated letters) | Urdu | South Asia | Perso-Arabic | Aspirated letters |
| Uyghur Arabic alphabet | 32 | Uyghur | China, Central Asia | Perso-Arabic/Chagatai | Vowels are mandatory, i.e. abugida |
| Wolofal script | 28 | Wolof | West Africa | Arabic | |
| Xiao'erjing | 36 | Sinitic languages | China, Central Asia | Perso-Arabic | |
| Yaña imlâ alphabet | 29 | Tatar | Perso-Arabic/Chagatai | 1920–1927 |
Unicode
As of Unicode 13.0, the following ranges encode Arabic characters:
- Arabic (0600–06FF)
- Arabic Supplement (0750–077F)
- Arabic Extended-A (08A0–08FF)
- Arabic Presentation Forms-A (FB50–FDFF)
- Arabic Presentation Forms-B (FE70–FEFF)
- Arabic Mathematical Alphabetic Symbols (1EE00–1EEFF)
- Rumi Numeral Symbols (10E60–10E7F)
- Indic Siyaq Numbers (1EC70–1ECBF)
- Ottoman Siyaq Numbers (1ED00–1ED4F)
See also
- History of the Arabic alphabet
- Eastern Arabic numerals (digit shapes commonly used with Arabic script)
- Arabic (Unicode block)
- Transliteration of Arabic
- Xiao'erjing
References
- Mahinnaz Mirdehghan. 2010. Persian, Urdu, and Pashto: A comparative orthographic analysis. Writing Systems Research Vol. 2, No. 1, 9–23.
- "Exposición Virtual. Biblioteca Nacional de España". Bne.es. Retrieved 2012-04-06.
- "Arabic Alphabet". Encyclopædia Britannica online. Archived from the original on 26 April 2015. Retrieved 2015-05-16.
- "Sayad Zahoor Shah Hashmii". baask.com.
- Language Protection Academy
- Sarlak, Riz̤ā (2002). "Dictionary of the Bakhtiari dialect of Chahar-lang". google.com.eg.
- Iran, Mojdeh (5 February 2011). "Bakhtiari Language Video (bak) بختياري ها! خبری مهم" – via Vimeo.
- "Ethnologue". Retrieved Feb 1, 2020.
- "Pakistan should mind all of its languages!". tribune.com.pk.
- "Ethnologue". Retrieved Feb 1, 2020.
- "Ethnologue". Retrieved Feb 1, 2020.
- Khadim. "Balti to English". khadimskardu1.blogspot.com.
- "The Bible in Brahui". Worldscriptures.org. Retrieved August 5, 2013.
- "HUNZA DEVELOPMENT FORUM". hisamullahbeg.blogspot.com.
- "Chittagonian". scriptsource.org.
- "Rohingya Language Book A-Z". Scribd.
- "Ida'an". scriptsource.org.
- urangCam. "Bông Sứ". naipaleikaohkabuak.blogspot.com.
- "Zribi, I., Boujelbane, R., Masmoudi, A., Ellouze, M., Belguith, L., & Habash, N. (2014). A Conventional Orthography for Tunisian Arabic. In Proceedings of the Language Resources and Evaluation Conference (LREC), Reykjavík, Iceland".
- Brustad, K. (2000). The syntax of spoken Arabic: A comparative study of Moroccan, Egyptian, Syrian, and Kuwaiti dialects. Georgetown University Press.
- "The Coptic Studies' Corner". stshenouda.com. Archived from the original on 2012-04-19. Retrieved 2012-04-17.
- "--The Cradle of Nubian Civilisation--". thenubian.net.
- "2 » AlNuba egypt". 19 July 2012. Archived from the original on 19 July 2012.
- "Zarma". scriptsource.org.
- "Tadaksahak". scriptsource.org.
- "Lost Language — Bostonia Summer 2009". bu.edu.
- "Dyula". scriptsource.org.
- "Jola-Fonyi". scriptsource.org.
- "Ibn Sayyid manuscript". Archived from the original on 2015-09-08. Retrieved 2018-09-27.
- "Muhammad Arabic letter". Archived from the original on 2015-09-08. Retrieved 2018-09-27.
- "Charno Letter". Muslims In America. Archived from the original on May 20, 2013. Retrieved August 5, 2013.
- Alphabet Transitions – The Latin Script: A New Chronology – Symbol of a New Azerbaijan, by Tamam Bayatly
- Sukhail Siddikzoda. "Tajik Language: Farsi or Not Farsi?" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 13, 2006.
- Escudero Pascual Alberto (23 October 2005). "Writing Systems/ Scripts" (PDF). Primer to Localization of Software. it46.se. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 March 2009. Retrieved 20 November 2006.
- "Brief history of writing in Chechen". Archived from the original on December 23, 2008.
- p. 20, Samuel Noel Kramer. 1986. In the World of Sumer: An Autobiography. Detroit: Wayne State University Press.
- J. Blau. 2000. Hebrew written in Arabic characters: An instance of radical change in tradition. (In Hebrew, with English summary). In Heritage and Innovation in Judaeo-Arabic Culture: Proceedings of the Sixth Conference of the Society For Judaeo-Arabic Studies, p. 27-31. Ramat Gan.
External links
![]()
- Unicode collation charts—including Arabic letters, sorted by shape
- Why the right side of your brain doesn't like Arabic
- Arabic fonts by SIL's Non-Roman Script Initiative
- Alexis Neme and Sébastien Paumier (2019), Restoring Arabic vowels through omission-tolerant dictionary lookup, Lang Resources & Evaluation, Vol 53, 1–65 pages
