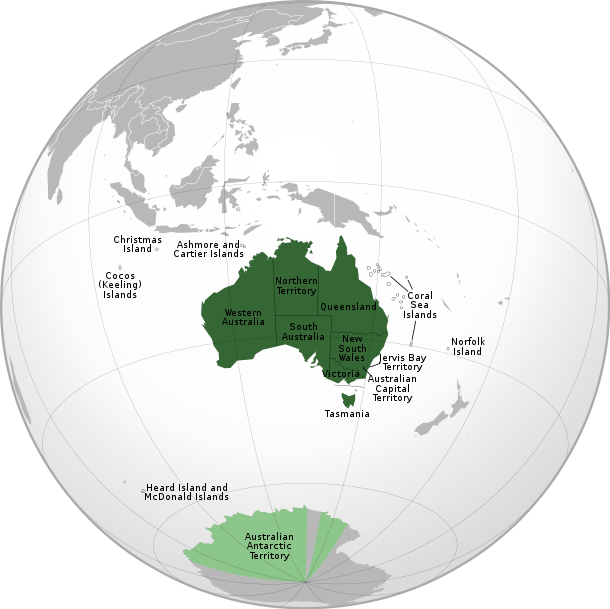
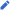
States and territories of Australia
Government in the Commonwealth of Australia is exercised on three levels: federal, states and territories, and local government.
| Australian states and territories | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Federation:
|
| Location | Commonwealth of Australia |
| Populations | Two territories are uninhabited: Ashmore & Cartier Islands and Heard & McDonald Islands. The most populous state/territory is New South Wales, with 7,955,900 people (2016). |
| Areas | The smallest territory is the Cocos (Keeling) Islands with an area of 14 km2 (5.4 sq mi). The largest state/territory is the Australian Antarctic Territory, which is 5,896,500 km2 (2,276,700 sq mi). |
| Subdivisions | Local government areas Cadastral divisions |
There are six states: New South Wales, Victoria, Queensland, Western Australia, South Australia and Tasmania. Historically, each is a successor to one of the previous Australian colonies. Each state has its own constitution, with its own legislature (parliament), judiciary and executive. The state parliaments have plenary legislative power, except that some areas of legislative power are exclusive to the Federal Parliament, many others are exercised concurrently with it and, in case of conflict between federal and state legislation, the federal legislation prevails. A decision of a state judiciary is subject to appeal to the High Court.
There are also ten territories, whose existence and governmental structure (if any) depend on federal legislation. The territories are distinguished for federal administrative purposes between internal territories, i.e. those within the Australian mainland, and external territories, although the differences among all the territories relate to population rather than location.
Two of the three internal territories—the Australian Capital Territory (ACT), which was established to be a neutral site of the federal capital, and the Northern Territory—function almost as states. Each has self-government, through its legislative assembly, but the assembly's legislation can be federally overridden. Each has its own judiciary, with appeal to a federal court. The third internal territory, the Jervis Bay Territory, is the product of Australia's complex relationship with its capital city; rather than having the same level of autonomy as the other internal territories, it has services provided by the ACT.
There are also seven external territories, not part of the Australian mainland or of any state. Three of them have a small permanent population, two have tiny and transient populations, and two are uninhabited. All are directly administered by the federal Department of Infrastructure, Regional Development and Cities (or the Department of the Environment and Energy in the case of the Australian Antarctic Territory). Norfolk Island, which is permanently populated, was partially self-governing until 2015.
The term "interstate" is used within Australia to refer to any cross-border events, transactions, or travel.
Geographic Australia
The term geographic Australia is used by the Australian government to describe the area covered by demographic statistics such as national population figures. This area comprises Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands in addition to the six states and three mainland territories; Norfolk Island is the only territory with a permanent population that is not part of geographic Australia.[1]
States and territories
| Administrative divisions of Australia |
|---|
| First level |
|
|
| Second level |
|
 |
| Flag | State | Postal | ISO[2] | Capital | Population (Jun 2019)[3] |
Area (km²)[4] | Seats in House of Representatives[5] | Seats in The Senate[6] | Governor | Premier | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | New South Wales | NSW | AU-NSW | Sydney | 8,089,526 | 809,952 | 47 | 12 | Margaret Beazley | Gladys Berejiklian (Liberal) | |
.svg.png) | Victoria | VIC | AU-VIC | Melbourne | 6,594,804 | 237,657 | 38 | 12 | Linda Dessau | Daniel Andrews (Labor) | |
 | Queensland | QLD | AU-QLD | Brisbane | 5,095,100 | 1,851,736 | 30 | 12 | Paul de Jersey | Annastacia Palaszczuk (Labor) | |
 | Western Australia | WA | AU-WA | Perth[n 2] | 2,621,680 | 2,642,753 | 16 | 12 | Kim Beazley | Mark McGowan (Labor) | |
 | South Australia | SA | AU-SA | Adelaide | 1,751,693 | 1,044,353 | 10 | 12 | Hieu Van Le | Steven Marshall (Liberal) | |
 | Tasmania | TAS | AU-TAS | Hobart | 534,281 | 90,758 | 5 | 12 | Kate Warner | Peter Gutwein (Liberal) | |
| Flag | Territory | Postal | ISO[2] | Capital | Population (Jun 2019)[3] |
Area (km²)[4] | Seats in House of Representatives[7] | Seats in The Senate[8] | Administrator | Chief Minister | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Australian Capital Territory | ACT | AU-ACT | Canberra | 426,709 | 2,358 | 3 | 2 | none[9] | Andrew Barr (Labor) | |
 | Northern Territory | NT | AU-NT | Darwin | 245,869 | 1,419,630 | 2 | 2 | Vicki O'Halloran | Michael Gunner (Labor) | |
| Jervis Bay Territory | ACT | none (Jervis Bay Village) | 405 | 67 | (part of Division of Fenner) | (votes in ACT Senate elections) | none[10] | none | |||
| Flag | Territory | Postal | ISO[2] | Capital (or largest settlement) |
Population (Jun 2018)[3] |
Area (km²)[4] | Seats in House of Representatives | Seats in the Senate | Administrator | Shire President |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ashmore and Cartier Islands | (Offshore anchorage) | 0 | 199 | - | - | none | none | |||
| Australian Antarctic Territory | AQ[n 5] | Davis Station | 60[n 6] | 5,896,500 | - | - | none | none | ||
 | Christmas Island | WA | CX | Flying Fish Cove | 1,938 | 135 | (part of Division of Lingiari) | (Votes in NT Senate elections) | Natasha Griggs | Gordon Thompson |
_Islands.svg.png) | Cocos (Keeling) Islands | WA | CC | West Island | 547 | 14 | (part of Division of Lingiari) | (Votes in NT Senate elections) | Seri Wati Iku | |
| Coral Sea Islands | (Willis Island) | 0 | 780,000 | - | - | none | none | |||
| Heard Island and McDonald Islands | HM | (Atlas Cove) | 0 | 372 | - | - | none | none | ||
 | Norfolk Island | NSW | NF | Kingston | 1,758 | 35 | (part of Division of Bean) | (Votes in ACT Senate elections) | Eric Hutchinson | none |

At Federation in 1901, what is now the Northern Territory was within South Australia, what are now the Australian Capital Territory and the Jervis Bay Territory were within New South Wales, and Coral Sea Islands was part of Queensland. Ashmore and Cartier Islands was accepted by Australia in 1934[11] and was annexed to the Northern Territory prior to adoption of the Statute of Westminster in 1942, deemed effective from 1939; it has thus become part of Australia.
Cocos (Keeling) Islands voted for integration in 1984. Together with Christmas Island, Commonwealth laws apply automatically to the territory unless expressly stated otherwise[12] and residents of both external territories are associated with Northern Territory for federal elections. They are, thus, constitutionally part of Australia.
Uninhabited Heard and McDonald Island is treated as constitutionally part of Australia by the central government.[13]
The constitutional status of the Australian Antarctic Territory is unclear, with successive governments treating it either as a separate territory (as in the United Kingdom and Norway) or an integral part of the country (as in New Zealand and France). As of 2018, the present government appears to take the view that it is not constitutionally part of Australia.[14]
Norfolk Island's status is controversial, with the present (as of 2018) government taking measures to integrate the territory into Australia proper (including representation in parliament and compulsory voting). The Norfolk Islanders have not formally consented to this change in constitutional status and assert that they are not Australian.[15]
Former territories
Internal territories
Three territories established by the federal government under section 122 of the Constitution of Australia no longer exist:
External territories
Two present-day countries, Papua New Guinea (PNG) and Nauru, were administered by the federal government of Australia as de facto and/or de jure external territories, for differing periods, between 1902 and 1975. Nauru and parts of PNG were previously part of the German colonial empire.
Papua & New Guinea, 1883–1949
- Territory of Papua:
- 1883–1902: A de facto part of Queensland (de jure British territory in 1888–1900)
- 1902–1949: An external territory of Australia
- Territory of New Guinea: 1920–1949, under a League of Nations mandate. (The territory was previously known as German New Guinea, between 1884 and 1914; it was formally under Australian military occupation, in 1914–1920.)
In 1949, the combined Territory of Papua and New Guinea was created, although both the two territories remained technically distinct, for some administrative and legal purposes, until 1975, when the combined entity became independent.
Nauru, 1920–1968
The Australian government received a League of Nations mandate for Nauru, following World War I.
Following World War II, Papua, New Guinea and Nauru were controlled by the Australian government as United Nations trust territories. The Papua and New Guinea Act 1949 placed the Territory of New Guinea in an "administrative union" with the Territory of Papua. The Territory of Papua and New Guinea was eventually given independence as Papua New Guinea in 1975. Nauru was granted independence in 1968.
Background and overview

The states originated as separate British colonies prior to Federation in 1901. The Colony of New South Wales was founded in 1788 and originally comprised much of the Australian mainland, as well as Lord Howe Island, New Zealand, Norfolk Island, and Van Diemen's Land, in addition to the area currently referred to as the state of New South Wales. During the 19th century, large areas were successively separated to form the Colony of Tasmania (initially established as a separate colony named Van Diemen's Land in 1825), the Colony of Western Australia (initially established as the smaller Swan River Colony in 1829), the Province of South Australia (1836), the Colony of New Zealand (1840),[17] the Victoria Colony (1851) and the Colony of Queensland (1859). Upon Federation, the six colonies of New South Wales, Victoria, Queensland, South Australia, Western Australia, and Tasmania became the founding states of the new Commonwealth of Australia.
Legislative powers of the states are protected by the Australian constitution, section 107, and under the principle of federalism, Commonwealth legislation only applies to the states where permitted by the constitution. The territories, by contrast, are from a constitutional perspective directly subject to the Commonwealth Government; laws for territories are determined by the Australian Parliament.[18]
Most of the territories are directly administered by the Commonwealth Government, while two (the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory) have some degree of self-government although less than that of the states. In the self-governing territories, the Australian Parliament retains the full power to legislate, and can override laws made by the territorial institutions, which it has done on rare occasions. For the purposes of Australian (and joint Australia-New Zealand) intergovernmental bodies, the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory are treated as if they were states.
Each state has a governor, appointed by the monarch (currently Queen Elizabeth II), which by convention she does on the advice of the state premier. The Administrator of the Northern Territory, by contrast, is appointed by the Governor-General. The Australian Capital Territory has neither a Governor nor an Administrator, but the Governor-General exercises some powers that in other jurisdictions are exercised by the Governor of a state or Administrator of a territory, such as the power to dissolve the Legislative Assembly.
Jervis Bay Territory is the only non-self-governing internal territory. Until 1989, it was administered as if it were a part of the ACT, although it has always been a separate territory. Under the terms of the Jervis Bay Territory Acceptance Act 1915,[19] the laws of the ACT apply to the Jervis Bay Territory insofar as they are applicable and providing they are not inconsistent with an Ordinance.[20] Although residents of the Jervis Bay Territory are generally subject to laws made by the ACT Legislative Assembly, they are not represented in the Assembly. They are represented in the Parliament of Australia as part of the Electoral Division of Fraser in the ACT and by the ACT's two Senators. In other respects, the territory is administered directly by the Federal Government through the Territories portfolio.
The external territory of Norfolk Island possessed a degree of self-government from 1979 until 2015.
Each state has a bicameral parliament except Queensland, which abolished its upper house in 1922. The lower house is called the Legislative Assembly, except in South Australia and Tasmania, where it is called the House of Assembly. Tasmania is the only state to use proportional representation for elections to its lower house; all others elect members from single member constituencies, using preferential voting. The upper house is called the Legislative Council and is generally elected from multi-member constituencies using proportional representation. The three self-governing territories, the ACT, the Northern Territory, and Norfolk Island, each have unicameral Legislative Assemblies.
The head of government of each state is called the premier, appointed by the state's Governor. In normal circumstances, the Governor will appoint as premier whoever leads the party or coalition which exercises control of the lower house (in the case of Queensland, the only house) of the state Parliament. However, in times of constitutional crisis, the Governor can appoint someone else as Premier. The head of government of the self-governing internal territories is called the chief minister. The Northern Territory's chief minister, in normal circumstances whoever controls the Legislative Assembly, is appointed by the administrator.
The term "interstate" is used within Australia to refer to a number of events, transactions, registrations, travel, etc. which occurs across borders or outside of the particular state or territory of the user of the term. Examples of use include motor vehicle registration,[21] travel,[22] applications to educational institutions out of one's home state.[23]
There are very few urban areas bifurcated by state/territory borders. The Queensland/New South Wales border runs through Coolangatta (Queensland) and Tweed Heads (New South Wales) and splits Gold Coast Airport. Oaks Estate, a contiguous residential of Queanbeyan, was excised out of New South Wales when the Australian Capital Territory was established in 1909. Some Urban Centres and Localities reported by the Australian Bureau of Statistics include some agglomerations of cities spreading across state lines, including Gold Coast–Tweed Heads, Canberra–Queanbeyan, Albury–Wodonga (New South Wales-Victoria) and Mildura–Wentworth (Victoria-New South Wales)
Timeline
- 1788 – British Empire establishes Colony of New South Wales across central and eastern mainland Australia, the island of Tasmania, both islands of New Zealand and Norfolk Island.
- 1803 – The Coral Sea Islands are claimed by New South Wales
- 1825 – The island of Tasmania becomes the independent colony of Van Diemen's Land. New South Wales extends its borders further west in mainland Australia.
- 1829 – British Empire establishes Swan River Colony in western mainland Australia
- 1832 – Swan River Colony is renamed the colony of Western Australia
- 1836 - The Colony of South Australia is established
- 1841 – The islands of New Zealand become the independent colony of New Zealand. Much of eastern Antarctica is annexed by Britain as Victoria Land.
- 1844 – New South Wales transfers Norfolk Island to Van Diemen's Land
- 1846 – Northern central and eastern Australia briefly become the independent Colony of North Australia, then are returned to New South Wales.
- 1851 – Southeastern mainland Australia becomes the independent colony of Victoria
- 1856 – Van Diemen's Land is renamed the colony of Tasmania. Norfolk Island becomes the independent colony of Norfolk Island, however it is to be administered by the same Governor as New South Wales.
- 1857 – Much of southern central mainland Australia becomes the independent colony of South Australia. The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are annexed by Britain.
- 1859 – Northeastern mainland Australia and Coral Sea Islands become the independent colony of Queensland
- 1860 – A pocket of New South Wales territory remaining in southern central mainland Australia is transferred to South Australia
- 1862 – Some of New South Wales' northern central mainland Australian territory is transferred to Queensland
- 1863 – New South Wales' remaining northern central mainland Australian territory is transferred to South Australia
- 1878 – Britain annexes Ashmore Island
- 1883 – Queensland annexes southeastern New Guinea
- 1884 – Southeastern New Guinea becomes the independent Territory of Papua
- 1886 – The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are to be administered by the same Governor as the Straits Settlements
- 1888 – Christmas Island is annexed by Britain and incorporated into the Straits Settlements
- 1897 – Norfolk Island is officially reintegrated into New South Wales
- 1901 – New South Wales, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria and South Australia federate into the Commonwealth of Australia. Queensland transfers the Coral Sea Islands to the federal government, creating a federal external territory.
- 1902 – Britain transfers Papua to Australia as an external territory
- 1903 – The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are incorporated into the Straits Settlements
- 1909 – Britain annexes Cartier Island
- 1910 – Britain claims Heard Island and the McDonald Islands
- 1911 – The state of South Australia transfers control of northern central mainland Australia to the federal government, creating the Northern Territory. A small pocket of New South Wales around the city of Canberra is transferred to the federal government (who are seated within it), creating the Federal Capital Territory.
- 1913 – New South Wales transfers Norfolk Island to the federal government, making it a federal external territory
- 1915 – A small pocket of New South Wales around Jervis Bay is transferred to the federal government and incorporated into the Federal Capital Territory
- 1920 – Following the defeat of the German Empire in World War I, the League of Nations establishes an Australian mandate in northeastern New Guinea, it becomes the external Territory of New Guinea
- 1923 – Another conquered German territory, the island of Nauru, is established as an Australian mandate and external territory by the League of Nations, this time as a co-mandate with Britain and New Zealand
- 1927 – The Northern Territory is split into two territories – North Australia and Central Australia
- 1930 – Remaining territory in eastern Antarctica is annexed by Britain as Enderby Land
- 1931 – North Australia and Central Australia are reincorporated as the Northern Territory. Britain recognises Australia as possessors of the uninhabited Ashmore and Cartier Islands, making them an external federal territory.
- 1933 – Britain transfers Victoria Land and Enderby Land to Australia, creating the Australian Antarctic Territory, with ongoing limited international recognition
- 1938 – The Federal Capital Territory is renamed the Australian Capital Territory
- 1942 – The Japanese Empire conquers Nauru from Australia, Britain and New Zealand as part of World War II. Japan also conquers much of the Straits Settlements, including Christmas Island. The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are not conquered and are transferred to the Colony of Ceylon.
- 1946 – The United Nations, the successor to the League of Nations, renews its mandate of New Guinea to Australia
- 1947 – Following the defeat of Japan in World War II, the United Nations returns Nauru to Australia, Britain and New Zealand as a joint mandate. Christmas Island returns to Britain and is incorporated into the Colony of Singapore. The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are also transferred to Singapore.
- 1949 – Papua and New Guinea are incorporated into the singular Territory of Papua and New Guinea. Britain transfers Heard Island and the McDonald Islands to Australia, creating a federal external territory.
- 1955 – Britain transfers the Cocos (Keeling) Islands to Australia, they become an external territory
- 1958 – Britain transfers Christmas Island to Australia, it becomes an external territory
- 1966 – The Republic of Nauru is established, ending Australian/British/New Zealander control of the island
- 1975 – Papua and New Guinea becomes the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, ending British/Australian control
- 1978 – Northern Territory gains self-government with certain Commonwealth control.
- 1989 – Jervis Bay becomes independent of the ACT, becoming the Jervis Bay Territory
- 1993 – Australian Capital Territory gains self-government with certain Commonwealth control.
- 2015 – Norfolk Island loses self-government with full Commonwealth control.
Comparative terminology
| Entity | Type of entity | Tie to the monarch | Domestic administrator | Head of government | Upper House of Parliament | Lower House of Parliament | Member of Parliament | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper house | Lower house[note 1] | |||||||
| Commonwealth of Australia | Federal government | Direct | Governor-General | Prime Minister | Senate | House of Representatives | Senator | MP |
| South Australia | Federated state | Direct (established by the Australia Act 1986) | Governor | Premier | Legislative Council | House of Assembly | MLC | MHA |
| Tasmania | ||||||||
| New South Wales | Legislative Assembly | MP | ||||||
| Victoria | MLA | |||||||
| Western Australia | ||||||||
| Queensland | N/A (abolished 1922) | N/A | MP | |||||
| Australian Capital Territory | Self-governing territory | Indirect (through Governor-General acting as "administrator") | Assembly and Chief minister | Chief minister | N/A | MLA | ||
| Northern Territory | Indirect (through Governor-General) | Administrator | ||||||
| Christmas Island | External territory | Shire president | Shire Council | Councillor | ||||
| Cocos (Keeling) Islands | ||||||||
| Norfolk Island | Mayor | Regional Council[note 2] | ||||||
Note:
| ||||||||
Governors and administrators of states and territories
| Post | Incumbent | Appointed |
|---|---|---|
| Governor of Queensland | His Excellency Paul de Jersey | 29 July 2014 |
| Governor of South Australia | His Excellency Hieu Van Le | 1 September 2014 |
| Governor of Tasmania | Her Excellency Kate Warner | 10 December 2014 |
| Governor of Victoria | Her Excellency Linda Dessau | 1 July 2015 |
| Governor of Western Australia | His Excellency Kim Beazley | 1 May 2018 |
| Governor of New South Wales | Her Excellency Margaret Beazley | 2 May 2019 |
| Administrator of the Northern Territory | Her Honour Vicki O'Halloran | 31 October 2017 |
| Administrator of Norfolk Island | His Honour Eric Hutchinson | 1 April 2017 |
| Administrator of Australian Indian Ocean Territories (Christmas Island and Cocos (Keeling) Islands) |
Her Honour Natasha Griggs | 5 October 2017 |
Premiers and chief ministers of states and territories
| Post | Incumbent | Political party | Appointed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Premier of New South Wales | Gladys Berejiklian MP | Liberal | 23 January 2017 |
| Premier of Queensland | Annastacia Palaszczuk MP | Labor | 14 February 2015 |
| Premier of South Australia | Steven Marshall MHA | Liberal | 19 March 2018 |
| Premier of Tasmania | Peter Gutwein MP | Liberal | 20 January 2020 |
| Premier of Victoria | Daniel Andrews MP | Labor | 4 December 2014 |
| Premier of Western Australia | Mark McGowan MLA | Labor | 17 March 2017 |
| Chief Minister of the Australian Capital Territory | Andrew Barr MLA | Labor | 11 December 2014 |
| Chief Minister of the Northern Territory | Michael Gunner MLA | Labor | 31 August 2016 |
| Mayor of Norfolk Island Council | Councillor Robin Adams | 6 July 2016 | |
Presidents of Australian Indian Ocean Territories:
|
Councillor Foo Kee Heng |
18 October 2011 |
State and territorial parliaments
- Parliament of New South Wales
- Parliament of Queensland
- Parliament of South Australia
- Parliament of Tasmania
- Parliament of Victoria
- Parliament of Western Australia
- Northern Territory Legislative Assembly
- Australian Capital Territory Legislative Assembly
State and territory supreme courts
- Supreme Court of the Australian Capital Territory
- Supreme Court of New South Wales
- Supreme Court of the Northern Territory
- Supreme Court of Queensland
- Supreme Court of South Australia
- Supreme Court of Tasmania
- Supreme Court of Victoria
- Supreme Court of Western Australia
- Supreme Court of Norfolk Island
State and territory police forces
- Australian Capital Territory Police (performed by Australian Federal Police)
- New South Wales Police
- Northern Territory Police
- Queensland Police
- South Australia Police
- Tasmania Police
- Victoria Police
- Western Australia Police
State and territory borders
- Australian Capital Territory border
- New South Wales borders
- Northern Territory borders
- Queensland borders
- South Australian borders
- Tasmanian borders
- Victorian borders
- Western Australia border
Statistics
| State / territory | Abbreviation | Land area[4][24] |
|
Population density |
|
Notes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | sq mi | Rank | Number | Rank | /km2 | /sq mi | Rank | % | Rank | |||
| ACT | 2,358 | 910 | 8 | 395,200 | 7 | 167.6 | 434 | 1 | 99.6% | 1 | [25] | |
| NSW | 801,150 | 309,330 | 5 | 7,704,300 | 1 | 9.62 | 24.9 | 3 | 63.0% | 5 | [26] | |
| NT | 1,347,791 | 520,385 | 3 | 244,000 | 8 | 0.18 | 0.47 | 8 | 54.0% | 6 | [27] | |
| QLD | 1,729,742 | 667,857 | 2 | 4,827,000 | 3 | 2.79 | 7.2 | 5 | 46.0% | 7 | [28] | |
| SA | 984,321 | 380,048 | 4 | 1,706,500 | 5 | 1.74 | 4.5 | 6 | 73.5% | 2 | [29] | |
| TAS | 68,401 | 26,410 | 7 | 518,500 | 6 | 7.58 | 19.6 | 4 | 41.0% | 8 | [30] | |
| VIC | 227,444 | 87,817 | 6 | 6,039,100 | 2 | 26.56 | 68.8 | 2 | 71.0% | 4 | [31] | |
| WA | 2,527,013 | 975,685 | 1 | 2,613,700 | 4 | 1.03 | 2.7 | 7 | 73.4% | 3 | [32] | |
State and territory codes
| State/territory | Abbrev. | Call signs | Postal | Telephone numbers in Australia | Time zone | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AM/FM | TV | Amateur | Abbrev. | Postcode | Std | Summer | |||
| Australian Capital Territory | ACT | 1xx(x)[nb 1] | xx(x)Cn[nb 1] | VK1xx[nb 1] | ACT | 02nn,[nb 2] 26nn, 29nn | +61 2 62xx xxxx +61 2 61xx xxxx | +10 | +11 |
| New South Wales | NSW | 2xx(x) | xx(x)Nn | VK2xx | NSW | 1nnn,[nb 2] 2nnn | +61 2 xxxx xxxx[nb 3] | +10 (+9 1⁄2)[nb 4] | +11 |
| Victoria | Vic | 3xx(x) | xx(x)Vn | VK3xx | VIC | 3nnn, 8nnn[nb 2] | +61 3 xxxx xxxx[nb 3] | +10 | +11 |
| Queensland | Qld | 4xx(x) | xx(x)Qn | VK4xx | QLD | 4nnn, 9nnn[nb 2] | +61 7 xxxx xxxx | +10 | |
| South Australia | SA | 5xx(x) | xx(x)Sn | VK5xx | SA | 5nnn | +61 8 8xxx xxxx +61 8 7xxx xxxx | +9 1⁄2 | +10 1⁄2 |
| Western Australia | WA | 6xx(x) | xx(x)Wn | VK6xx | WA | 6nnn | +61 8 9xxx xxxx +61 8 6xxx xxxx | +8 | |
| Tasmania | Tas | 7xx(x) | xx(x)Tn | VK7xx | TAS | 7nnn | +61 3 6xxx xxxx | +10 | +11 |
| Northern Territory | NT | 8xx(x) | xx(x)Dn | VK8xx | NT | 08nn | +61 8 89xx xxxx | +9 1⁄2 | |
| External territories | |||||||||
| Norfolk Island | 2xx(x) | xx(x)Nn | VK2xx | NSW | 2899 | +672 3 xx xxx | +11 | ||
| Christmas Island | 6xx(x) | xx(x)Wn | VK9xx | WA | 6798 | +61 8 9164 xxxx | +7 | ||
| Cocos Island | 6xx(x) | xx(x)Wn | VK9xx | WA | 6799 | +61 8 9162 xxxx | +6 1⁄2 | ||
| Australian Antarctic Territory | AAT | none | VK0xx | TAS | +672 1 | +6 to +8 | |||
| |||||||||
See also
- Australian regional rivalries
- ISO 3166-2:AU, the ISO codes for the states and territories of Australia.
- List of Australian demonyms
- List of Australian states by Human Development Index
- List of proposed states of Australia
Notes
- Unless provided, references and details on data provided in the table can be found within the individual state and territory articles.
- Perth was defined as the capital by statute in 2016: City of Perth Act 2016 (WA) in AustLII.
- Unless provided, references and details on data provided in the table can be found within the individual state and territory articles.
- Unless provided, references and details on data provided in the table can be found within the individual state and territory articles.
- Under the definitions in ISO 3166-1, the AAT is covered by the Antarctican ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code "AQ".
- No permanent population, research station with fluctuating staff numbers.
References
- Pink, Brian (2010). "Definition of Australia". Australian Standard Geographical Classification (ASGC) (Report). Australian Bureau of Statistics. p. 5.
- ISO 3166-2:AU (ISO 3166-2 codes for the states and territories of Australia)
- "3101.0 – Australian Demographic Statistics, Jun 2019". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 19 December 2019. Retrieved 20 January 2020.
- "Area of Australia – States and Territories". Geoscience Australia: National Location Information. Geoscience Australia. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
- corporateName=Commonwealth Parliament; address=Parliament House, Canberra. "Number of Members". www.aph.gov.au. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- corporateName=Commonwealth Parliament; address=Parliament House, Canberra. "Senators and Members". www.aph.gov.au. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- corporateName=Commonwealth Parliament; address=Parliament House, Canberra. "Number of Members". www.aph.gov.au. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- corporateName=Commonwealth Parliament; address=Parliament House, Canberra. "Senators and Members". www.aph.gov.au. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- Crown represented by Governor-General of Australia.
- Administered by the Commonwealth.
- "Ashmore and Cartier Islands Acceptance Act 1933". Federal Register of Legislation.
- "10. External territories". www.alrc.gov.au. 15 July 2010.
- "Frequently asked questions". heardisland.antarctica.gov.au.
- "Australian Antarctic Territory". www.antarctica.gov.au.
- Davey, Melissa (21 May 2015). "'We're not Australian': Norfolk Islanders adjust to shock of takeover by mainland". The Guardian.
- Ling, Ted. "Dividing the Territory, 1926–31". Commonwealth Government Records about the Northern Territory. National Archives of Australia. Retrieved 28 September 2018.
- A.H. McLintock (ed), An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand, 3 vols, Wellington, NZ:R.E. Owen, Government Printer, 1966, vol 3 p. 526.'
- Constitution of Australia, section 122
- Jervis Bay Territory Acceptance Act 1915 (Cth).
- "Jervis Bay Territory Governance and Administration". The Department of Regional Australia, Local Government, Arts and Sport. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
Although the Jervis Bay Territory is not part of the Australian Capital Territory, the laws of the ACT apply, insofar as they are applicable and, providing they are not inconsistent with an Ordinance, in the Territory by virtue of the 'Jervis Bay Acceptance Act 1915'
- "Interstate-registered vehicles". sa.gov.au. Government of South Australia. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- "Interstate travel". Public Transport Victoria. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- "Applying interstate". VTAC. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- "Area of Australia - States and Territories". www.ga.gov.au. 15 May 2014.
- Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "Australian Capital Territory". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 2 July 2017.
- Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "New South Wales". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 2 July 2017.

- Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "Northern Territory". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 2 July 2017.

- Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "Queensland". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 2 July 2017.

- Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "South Australia". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 2 July 2017.

- Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "Tasmania". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 2 July 2017.

- Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "Victoria". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 2 July 2017.

- Australian Bureau of Statistics (31 October 2012). "Western Australia". 2011 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 12 February 2013.

