Aaron Burr
Aaron Burr Jr. (February 6, 1756 – September 14, 1836) was an American politician and lawyer. He was the third vice president of the United States (1801–1805), serving during President Thomas Jefferson's first term.
Aaron Burr Jr. | |
|---|---|
 Portrait by John Vanderlyn, 1802 | |
| 3rd Vice President of the United States | |
| In office March 4, 1801 – March 4, 1805 | |
| President | Thomas Jefferson |
| Preceded by | Thomas Jefferson |
| Succeeded by | George Clinton |
| United States Senator from New York | |
| In office March 4, 1791 – March 3, 1797 | |
| Preceded by | Philip Schuyler |
| Succeeded by | Philip Schuyler |
| 3rd Attorney General of New York | |
| In office September 29, 1789 – November 8, 1791 | |
| Governor | George Clinton |
| Preceded by | Richard Varick |
| Succeeded by | Morgan Lewis |
| Personal details | |
| Born | Aaron Burr Jr. February 6, 1756 Newark, New Jersey, British America |
| Died | September 14, 1836 (aged 80) Staten Island, New York, U.S. |
| Resting place | Princeton Cemetery |
| Political party | Democratic-Republican |
| Spouse(s) | Theodosia Bartow Prevost (m. 1782; died 1794) Eliza Jumel (m. 1833) |
| Children | 7 or more including: Theodosia John Aaron |
| Relatives | Aaron Burr Sr. (Father) Esther Edwards (Mother) Theodore Burr (Cousin) |
| Education | Princeton University (BA) |
| Signature |  |
| Military service | |
| Allegiance | |
| Branch/service | Continental Army |
| Years of service | 1775–1779 |
| Rank | Lieutenant colonel |
| Battles/wars | American Revolutionary War • Battle of Quebec • Battle of Monmouth |
Burr served as a Continental Army officer in the American Revolutionary War, after which he became a successful lawyer and politician. He was elected twice to the New York State Assembly (1784–1785, 1798–1799),[1] was appointed New York State Attorney General (1789–1791), was chosen as a U.S. senator (1791–1797) from the State of New York, and reached the apex of his career as vice president. In the waning months of his tenure as president of the Senate, he oversaw the 1805 impeachment trial of Supreme Court Justice Samuel Chase.
As campaign manager for the Democratic-Republican Party during the presidential election of 1800, Burr (along with his unofficial campaign team, known as the Little Band)[2] was responsible for the first open, public political campaign.[3][4][5]
Burr shot his political rival Alexander Hamilton in an 1804 duel, during the last full year of his single term as vice president. He was never tried for the illegal duel and all charges against him were eventually dropped, but Hamilton's death ended Burr's political career.
Burr left Washington, D.C., and traveled west seeking new opportunities, both economic and political—as well as refuge from the controversy surrounding him in the rest of the country. His activities eventually led to his arrest on charges of treason in 1807. He was tried and acquitted multiple times, but the fallout left him with large debts and few influential friends. To avoid vigilante execution and further charges by the state, he left the United States for Europe. He remained overseas until 1812, when he returned to the United States to practice law in New York City. He spent the rest of his life there in relative obscurity.
Early life

Aaron Burr Jr. was born in Newark, New Jersey, in 1756 as the second child of the Reverend Aaron Burr Sr., a Presbyterian minister and second president of the College of New Jersey, which became Princeton University. His mother Esther Edwards Burr was the daughter of noted theologian Jonathan Edwards and his wife Sarah.[6] Burr had an older sister Sarah ("Sally") who was named for her maternal grandmother. She married Tapping Reeve, founder of the Litchfield Law School in Litchfield, Connecticut.[7]
Burr's father died in 1757, and his mother died the following year, leaving him and his sister orphans when he was two years old. He and his sister first lived with their maternal grandparents, but his grandmother also died in 1757, and his grandfather Jonathan Edwards died in 1758. Young Aaron and Sally were placed with the William Shippen family in Philadelphia. In 1759, the children's guardianship was assumed by their 21-year-old maternal uncle Timothy Edwards. The next year, Edwards married Rhoda Ogden and moved with the children to Elizabeth, New Jersey near her family. Burr had a very strained relationship with his uncle, who frequently employed physical punishment.[8] As a child, he made several attempts to run away from home.[9]
Burr was admitted to Princeton as a sophomore at age 13 where he joined the American Whig Society and the Cliosophic Society, the college's literary and debating societies.[10] He received his Bachelor of Arts degree in 1772 at age 16 but continued studying theology at Princeton for an additional year. He then undertook rigorous theological training with Joseph Bellamy, a Presbyterian, but changed his career path after two years. At age 19, he moved to Connecticut to study law with his brother-in-law Tapping Reeve, who had married Burr's sister in 1771.[11] News reached Litchfield in 1775 of the clashes with British troops at Lexington and Concord, and Burr put his studies on hold to enlist in the Continental Army.
Revolutionary War

During the American Revolutionary War, Burr took part in Colonel Benedict Arnold's expedition to Quebec, an arduous trek of more than 300 miles (480 km) through the frontier of Maine. Arnold was deeply impressed by Burr's "great spirit and resolution" during the long march, and he sent Burr up the Saint Lawrence River when they reached Quebec City to contact General Richard Montgomery, who had taken Montreal, and escort him to Quebec. Montgomery then promoted Burr to captain and made him an aide-de-camp. Burr distinguished himself during the Battle of Quebec on December 31, 1775, where he attempted to recover Montgomery's corpse after he had been killed.[12]
In the spring of 1776, Burr's stepbrother Matthias Ogden helped him to secure a place on George Washington's staff in Manhattan, but he quit within two weeks on June 26 to be on the battlefield; there was more honor to be gained in battle than in the "insular world of the commander's staff," according to historian Nancy Isenberg.[13] General Israel Putnam took Burr under his wing, and Burr saved an entire brigade from capture after the British landing in Manhattan by his vigilance in the retreat from lower Manhattan to Harlem. Washington failed to commend his actions in the next day's General Orders, however, which was the fastest way to obtain a promotion. Burr was already a nationally known hero, but he never received a commendation. According to Ogden, he was infuriated by the incident, which may have led to the eventual estrangement between him and Washington.[14][15] Nevertheless, Burr defended Washington's decision to evacuate New York as "a necessary consequence." It was not until the 1790s that the two men found themselves on opposite sides in politics.[16]
Burr was promoted to lieutenant colonel in July 1777 and assumed virtual leadership of Malcolm's Additional Continental Regiment.[17] There were approximately 300 men under Colonel William Malcolm's nominal command, but Malcolm was frequently called upon to perform other duties, leaving Burr in charge.[17] The regiment successfully fought off many nighttime raids into central New Jersey by Manhattan-based British troops who arrived by water. Later that year, Burr commanded a small contingent during the harsh winter encampment at Valley Forge, guarding "the Gulph," an isolated pass that controlled one approach to the camp. He imposed discipline and defeated an attempted mutiny by some of the troops.[18]
Burr's regiment was devastated by British artillery on June 28, 1778 at the Battle of Monmouth in New Jersey and he suffered heat stroke.[19] In January 1779, he was assigned to Westchester County, New York in command of Malcolm's Regiment, a region between the British post at Kingsbridge, Bronx and that of the Americans about 15 miles (24 km) to the north. This district was part of the larger command of General Alexander McDougall, and there was much turbulence and plundering by lawless bands of civilians and by raiding parties of ill-disciplined soldiers from both armies.[20]
In March 1779, due to continuing bad health, Burr resigned from the Continental Army.[21] He renewed his study of law. Technically, he was no longer in the service, but he remained active in the war; he was assigned by General Washington to perform occasional intelligence missions for Continental generals, such as Arthur St. Clair. On July 5, 1779, he rallied a group of Yale students at New Haven, Connecticut, along with Captain James Hillhouse and the Second Connecticut Governor's Guards, in a skirmish with the British at the West River.[22] The British advance was repulsed, forcing them to enter New Haven from Hamden, Connecticut.[22]
Marriage to Theodosia Bartow Prevost
Burr met Theodosia Bartow Prevost in August 1778 while she was married to Jacques Marcus Prevost, a Swiss-born British officer in the Royal American Regiment.[23] In Prevost's absence, Burr began regularly visiting Theodosia at The Hermitage, her home in New Jersey.[24] Although she was ten years older than Burr, the constant visits provoked gossip, and by 1780 the two were openly lovers.[25] In December 1781, she learned that Prevost had died in Jamaica of yellow fever.[26]
Theodosia and Aaron Burr were married in 1782, and they moved to a house on Wall Street in Lower Manhattan.[27] After several years of severe illness, Theodosia died in 1794 from stomach or uterine cancer. Their only child to survive to adulthood was Theodosia Burr Alston, born in 1783.
Law and politics
Despite his wartime activities, Burr finished his studies and was admitted to the bar at Albany, New York in 1782, the year of his marriage. He began practicing law in New York City the following year, after the British evacuated the city.[27]
Burr served in the New York State Assembly from 1784 to 1785. In addition, he continued his military service as lieutenant colonel and commander of a regiment in the militia brigade commanded by William Malcolm.[28] He became seriously involved in politics in 1789, when George Clinton appointed him as New York State Attorney General. He was also Commissioner of Revolutionary War Claims in 1791. In 1791, he was elected by the legislature as a Senator from New York, defeating incumbent General Philip Schuyler. He served in the Senate until 1797.
Burr ran for president in the 1796 election and received 30 electoral votes, coming in fourth behind John Adams, Thomas Jefferson, and Thomas Pinckney.[29] He was shocked by this defeat, but many Democratic-Republican electors voted for Jefferson and no one else, or for Jefferson and a candidate other than Burr.[30] Jefferson and Burr were again candidates for president and vice president during the election of 1800. Jefferson ran with Burr in exchange for Burr working to obtain New York's electoral votes for Jefferson.[30]
President John Adams appointed Washington as commanding general of U.S. forces in 1798, but he rejected Burr's application for a brigadier general's commission during the Quasi-War with France. Washington wrote, "By all that I have known and heard, Colonel Burr is a brave and able officer, but the question is whether he has not equal talents at intrigue."[31] Burr was elected to the New York State Assembly in 1798 and served there through 1799.[1] During this time, he cooperated with the Holland Land Company in gaining passage of a law to permit aliens to hold and convey lands.[32] National parties became clearly defined during Adam's Presidency, and Burr loosely associated himself with the Democratic-Republicans, though he had moderate Federalist allies such as Senator Jonathan Dayton of New Jersey.
New York City politics
Burr quickly became a key player in New York politics, more powerful in time than Hamilton due largely to the power of the Tammany Society (which became Tammany Hall). Burr converted it from a social club into a political machine to help Jefferson reach the Presidency, particularly in populous New York City.[33]
In September 1799, Burr fought a duel with John Barker Church, whose wife Angelica was the sister of Hamilton's wife Elizabeth. Church had accused Burr of taking a bribe from the Holland Company in exchange for his political influence. Burr and Church fired at each other and missed, and afterward Church acknowledged that he was wrong to have accused Burr without proof. Burr accepted this as an apology, and the two men shook hands and ended the dispute.[34]
In 1799, Burr founded the Bank of the Manhattan Company, and the enmity between him and Hamilton may have arisen from how he did so. Prior to the establishment of Burr's bank, the Federalists held a monopoly on banking interests in New York via the federal government's Bank of the United States and Hamilton's Bank of New York. These banks financed operations of large business interests owned by aristocratic members of the city. Hamilton had prevented the formation of rival banks in the city. Small businessmen relied on tontines to buy property and establish a voting voice (at this time voting was based upon property rights). Burr solicited support from Hamilton and other Federalists under the guise that he was establishing a badly needed water company for Manhattan. He secretly changed the application for a state charter at the last minute to include the ability to invest surplus funds in any cause that did not violate state law,[35] and dropped any pretense of founding a water company once he had gained approval. Hamilton and other supporters believed that he had acted dishonorably in deceiving them. Meanwhile, construction was delayed on a safe water system for Manhattan, and writer Ron Chernow suggests that the delay may have contributed to deaths during a subsequent malaria epidemic.[36]
Burr's Manhattan Company was more than a bank; it was a tool to promote Democratic-Republican power and influence, and its loans were directed to partisans. By extending credit to small businessmen, who then obtained enough property to gain the franchise, the bank was able to increase the party's electorate. Federalist bankers in New York responded by trying to organize a credit boycott of Democratic-Republican businessmen. Partisanship escalated.
The presidential election of 1800
In the 1800 city elections, Burr combined the political influence of the Manhattan Company with party campaign innovations to deliver New York's support for Jefferson.[37] In 1800, New York's state legislature was to choose the presidential electors, as they had in 1796 (for John Adams). Before the April 1800 legislative elections, the State Assembly was controlled by the Federalists. The City of New York elected assembly members on an at-large basis. Burr and Hamilton were the key campaigners for their respective parties. Burr's Democratic-Republican slate of assemblymen for New York City was elected, giving the party control of the legislature, which in turn gave New York's electoral votes to Jefferson and Burr. This drove another wedge between Hamilton and Burr.[38]
Burr enlisted the help of Tammany Hall to win the voting for selection of Electoral College delegates. He gained a place on the Democratic-Republican presidential ticket in the 1800 election with Jefferson. Though Jefferson and Burr won New York, he and Burr tied for the presidency overall, with 73 electoral votes each. Members of the Democratic-Republican Party understood they intended that Jefferson should be president and Burr vice president, but the tied vote required that the final choice be made by the House of Representatives, with each of the 16 states having one vote, and nine votes required for election.[39]
Publicly, Burr remained quiet, and refused to surrender the presidency to Jefferson, the great enemy of the Federalists. Rumors circulated that Burr and a faction of Federalists were encouraging Republican representatives to vote for him, blocking Jefferson's election in the House. However, solid evidence of such a conspiracy was lacking and historians generally gave Burr the benefit of the doubt. In 2011, however, historian Thomas Baker discovered a previously unknown letter from William P. Van Ness to Edward Livingston, two leading Democratic-Republicans in New York.[40] Van Ness was very close to Burr—serving as his second in the later duel with Hamilton. As a leading Democratic-Republican, Van Ness secretly supported the Federalist plan to elect Burr as president and tried to get Livingston to join.[40] Livingston apparently agreed at first, then reversed himself. Baker argues that Burr probably supported the Van Ness plan: "There is a compelling pattern of circumstantial evidence, much of it newly discovered, that strongly suggests Aaron Burr did exactly that as part of a stealth campaign to compass the presidency for himself."[41] The attempt did not work, due partly to Livingston's reversal, but more to Hamilton's energetic opposition to Burr. Jefferson was elected president, and Burr vice president.[42][43]
Vice presidency

Burr was never trusted by Jefferson. He was effectively shut out of party matters. As vice president, Burr earned praise from some enemies for his even-handed fairness and his judicial manner as President of the Senate; he fostered some practices for that office that have become time-honored traditions.[44] Burr's judicial manner in presiding over the impeachment trial of Justice Samuel Chase has been credited as helping to preserve the principle of judicial independence that was established by Marbury v. Madison in 1803.[45] One newspaper wrote that Burr had conducted the proceedings with the "impartiality of an angel, but with the rigor of a devil".[46]
Burr's farewell speech in March 1805 moved some of his harshest critics in the Senate to tears. But it was never recorded in full, and has been preserved only in short quotes and descriptions of the address, which defended the United States of America's system of government.
Duel with Alexander Hamilton
| Wikisource has original texts related to: |
When it became clear that Jefferson would drop Burr from his ticket in the 1804 election, the Vice President ran for Governor of New York instead. Burr lost the election to little known Morgan Lewis, in what was the largest margin of loss in New York's history up to that time.[47] Burr blamed his loss on a personal smear campaign believed to have been orchestrated by his party rivals, including New York governor George Clinton. Alexander Hamilton also opposed Burr, due to his belief that Burr had entertained a Federalist secession movement in New York.[48] In April, the Albany Register published a letter from Dr. Charles D. Cooper to Philip Schuyler, which relayed Hamilton's judgment that Burr was "a dangerous man, and one who ought not be trusted with the reins of government", and claiming to know of "a still more despicable opinion which General Hamilton has expressed of Mr. Burr".[49] In June, Burr sent this letter to Hamilton, seeking an affirmation or disavowal of Cooper's characterization of Hamilton's remarks.[50]
Hamilton replied that Burr should give specifics of Hamilton's remarks, not Cooper's. He said he could not answer regarding Cooper's interpretation. A few more letters followed, in which the exchange escalated to Burr's demanding that Hamilton recant or deny any statement disparaging Burr's honor over the past 15 years. Hamilton, having already been disgraced by the Maria Reynolds adultery scandal and mindful of his own reputation and honor, did not. According to historian Thomas Fleming, Burr would have immediately published such an apology, and Hamilton's remaining power in the New York Federalist party would have been diminished.[51] Burr responded by challenging Hamilton to a duel, personal combat under the formalized rules for dueling, the code duello.

Dueling had been outlawed in New York; the sentence for conviction of dueling was death. It was illegal in New Jersey as well, but the consequences were less severe. On July 11, 1804, the enemies met outside Weehawken, New Jersey, at the same spot where Hamilton's oldest son had died in a duel just three years prior. Both men fired, and Hamilton was mortally wounded by a shot just above the hip.[52]
The observers disagreed on who fired first. They did agree that there was a three-to-four-second interval between the first and the second shot, raising difficult questions in evaluating the two camps' versions.[53] Historian William Weir speculates that Hamilton might have been undone by his own machinations: secretly setting his pistol's trigger to require only a half pound of pressure as opposed to the usual 10 pounds. Burr, Weir contends, most likely had no idea that the gun's trigger pressure could be reset.[54] Louisiana State University history professors Nancy Isenberg and Andrew Burstein concur with this. They note that "Hamilton brought the pistols, which had a larger barrel than regular dueling pistols, and a secret hair-trigger, and were therefore much more deadly,"[55] and conclude that "Hamilton gave himself an unfair advantage in their duel, and got the worst of it anyway."[55]
David O. Stewart, in his biography of Burr, American Emperor, notes that the reports of Hamilton's intentionally missing Burr with his shot began to be published in newspaper reports in papers friendly to Hamilton only in the days after his death.[56] But Ron Chernow, in his biography, Alexander Hamilton, states Hamilton told numerous friends well before the duel of his intention to avoid firing at Burr. Additionally, Hamilton wrote a number of letters, including a Statement on Impending Duel With Aaron Burr[57] and his last missives to his wife dated before the duel,[58] which also attest to his intention. The two shots, witnesses reported, followed one another in close succession, and none of those witnesses could agree as to who fired first. Prior to the duel proper, Hamilton took a good deal of time getting used to the feel and weight of the pistol (which had been used in the duel at the same Weehawken site in which his 19-year-old son had been killed), as well as putting on his glasses in order to see his opponent more clearly. The seconds placed Hamilton so that Burr would have the rising sun behind him, and during the brief duel, one witness reported, Hamilton seemed to be hindered by this placement as the sun was in his eyes.
Each man took one shot, and Burr's shot fatally injured Hamilton, while Hamilton's shot missed. Burr's bullet entered Hamilton's abdomen above his right hip, piercing Hamilton's liver and spine. Hamilton was evacuated to the Manhattan home of a friend, William Bayard Jr., where he and his family received visitors including Episcopal bishop Benjamin Moore, who baptized Hamilton before he died the following day. Burr was charged with multiple crimes, including murder, in New York and New Jersey, but was never tried in either jurisdiction.
He fled to South Carolina, where his daughter lived with her family, but soon returned to Philadelphia and then to Washington to complete his term as vice president. He avoided New York and New Jersey for a time, but all the charges against him were eventually dropped. In the case of New Jersey, the indictment was thrown out on the basis that, although Hamilton was shot in New Jersey, he died in New York.
Conspiracy and trial
After Burr left the vice-presidency at the end of his term in 1805, he journeyed to the Western frontier, areas west of the Allegheny Mountains and down the Ohio River Valley eventually reaching the lands acquired in the Louisiana Purchase. Burr had leased 40,000 acres (16,000 ha) of land—known as the Bastrop Tract—along the Ouachita River, in present-day Louisiana, from the Spanish government. Starting in Pittsburgh and then proceeding to Beaver, Pennsylvania, and Wheeling, Virginia, and onward he drummed up support for his planned settlement, whose purpose and status were unclear.[59]
His most important contact was General James Wilkinson, Commander-in-Chief of the U.S. Army at New Orleans and Governor of the Louisiana Territory. Others included Harman Blennerhassett, who offered the use of his private island for training and outfitting Burr's expedition. Wilkinson would later prove to be a bad choice.[60]
Burr saw war with Spain as a distinct possibility. In case of a war declaration, Andrew Jackson stood ready to help Burr, who would be in position to immediately join in. Burr's expedition of about eighty men carried modest arms for hunting, and no war materiel was ever revealed, even when Blennerhassett Island was seized by Ohio militia.[61] The aim of his "conspiracy", he always avowed, was that if he settled there with a large group of armed "farmers" and war broke out, he would have a force with which to fight and claim land for himself, thus recouping his fortunes. However, war did not come as Burr expected: the 1819 Adams–Onís Treaty secured Florida for the United States without a fight, and war in Texas did not occur until 1836, the year Burr died.
After a near-incident with Spanish forces at Natchitoches, Wilkinson decided he could best serve his conflicting interests by betraying Burr's plans to President Jefferson and to his Spanish paymasters. Jefferson issued an order for Burr's arrest, declaring him a traitor before any indictment. Burr read this in a newspaper in the Territory of Orleans on January 10, 1807. Jefferson's warrant put Federal agents on his trail. Burr twice turned himself in to Federal authorities, and both times judges found his actions legal and released him.
Jefferson's warrant, however, followed Burr, who fled toward Spanish Florida. He was intercepted at Wakefield, in Mississippi Territory (now in the state of Alabama), on February 19, 1807. He was confined to Fort Stoddert after being arrested on charges of treason.[62]

Burr's secret correspondence with Anthony Merry and the Marquis of Casa Yrujo, the British and Spanish ministers at Washington, was eventually revealed. He had tried to secure money and to conceal his true designs, which was to help Mexico overthrow Spanish power in the Southwest. Burr intended to found a dynasty in what would have become former Mexican territory.[44] This was a misdemeanor, based on the Neutrality Act of 1794, which Congress passed to block filibuster expeditions against US neighbors, such as those of George Rogers Clark and William Blount. Jefferson, however, sought the highest charges against Burr.
In 1807, Burr was brought to trial on a charge of treason before the United States Circuit court at Richmond, Virginia. His defense lawyers included Edmund Randolph, John Wickham, Luther Martin, and Benjamin Gaines Botts.[63] Burr had been arraigned four times for treason before a grand jury indicted him. The only physical evidence presented to the Grand Jury was Wilkinson's so-called letter from Burr, which proposed the idea of stealing land in the Louisiana Purchase. During the Jury's examination, the court discovered that the letter was written in Wilkinson's own handwriting. He said he had made a copy because he had lost the original. The Grand Jury threw the letter out as evidence, and the news made a laughingstock of the general for the rest of the proceedings.
The trial, presided over by Chief Justice of the United States John Marshall, began on August 3. Article 3, Section 3 of the United States Constitution requires that treason either be admitted in open court, or proven by an overt act witnessed by two people. Since no two witnesses came forward, Burr was acquitted on September 1, in spite of the full force of the Jefferson administration's political influence thrown against him. Burr was immediately tried on a misdemeanor charge and was again acquitted.[64]
Given that Jefferson was using his influence as president in an effort to obtain a conviction, the trial was a major test of the Constitution and the concept of separation of powers. Jefferson challenged the authority of the Supreme Court, specifically Chief Justice Marshall, an Adams appointee who clashed with Jefferson over John Adams' last-minute judicial appointments. Jefferson believed that Burr's treason was obvious. Burr sent a letter to Jefferson in which he stated that he could do Jefferson much harm. The case as tried was decided on whether Aaron Burr was present at certain events at certain times and in certain capacities. Thomas Jefferson used all of his influence to get Marshall to convict, but Marshall was not swayed.
Historians Nancy Isenberg and Andrew Burstein write that Burr:
was not guilty of treason, nor was he ever convicted, because there was no evidence, not one credible piece of testimony, and the star witness for the prosecution had to admit that he had doctored a letter implicating Burr.[55]
David O. Stewart, on the other hand, insists that while Burr was not explicitly guilty of treason according to Marshall's definition, evidence exists that links him to treasonous crimes. For example, Bollman admitted to Jefferson during an interrogation that Burr planned to raise an army and invade Mexico. He said that Burr believed that he should be Mexico's monarch, as a republican government was not right for the Mexican people.[65] Many historians believe the extent of Burr's involvement may never be known.
Exile and return
By the conclusion of his trial for treason, despite an acquittal, all of Burr's hopes for a political comeback had been dashed, and he fled America and his creditors for Europe.[66] Dr. David Hosack, Hamilton's physician and a friend to both Hamilton and Burr, loaned Burr money for passage on a ship.[67]
Burr lived in self-imposed exile from 1808 to 1812, passing most of this period in England, where he occupied a house on Craven Street in London. He became a good friend, even confidant, of the English Utilitarian philosopher Jeremy Bentham, and on occasion lived at Bentham's home. He also spent time in Scotland, Denmark, Sweden, Germany, and France. Ever hopeful, he solicited funding for renewing his plans for a conquest of Mexico, but was rebuffed. He was ordered out of England and Napoleon Bonaparte refused to receive him,[44] although one of his ministers held an interview concerning Burr's goals for Spanish Florida or the British possessions in the Caribbean.
After returning from Europe, Burr used the surname "Edwards", his mother's maiden name, for a while to avoid creditors. With help from old friends Samuel Swartwout and Matthew L. Davis, Burr returned to New York and his law practice. Later he helped the heirs of the Eden family in a financial lawsuit. By the early 1820s, the remaining members of the Eden household, Eden's widow and two daughters, had become a surrogate family to Burr.[68]
Later life and death

Despite financial setbacks, Burr lived out the remainder of his life in New York in relative peace,[69] until 1833, when his second marriage failed after four months, soon followed by medical difficulties.
Marriage to Eliza Jumel
On July 1, 1833, at age 77, Burr married Eliza Jumel, a wealthy widow who was 19 years younger. They lived together briefly at her residence which she had acquired with her first husband, the Morris-Jumel Mansion in the Washington Heights neighborhood in Manhattan.[70] Listed on the National Register of Historic Places, it is now preserved and open to the public.[71]
Soon after the marriage, she realized her fortune was dwindling due to Burr's land speculation losses.[72] She separated from Burr after four months of marriage. For her divorce lawyer, she chose Alexander Hamilton Jr.,[73] and the divorce was officially completed on September 14, 1836, coincidentally the day of Burr's death.[74]
Death
Burr suffered a debilitating stroke in 1834,[75] which rendered him immobile. In 1836, Burr died on Staten Island in the village of Port Richmond, in a boardinghouse that later became known as the St. James Hotel.[76] He was buried near his father in Princeton, New Jersey.[77]
Children and parenthood
In addition to his daughter Theodosia, Burr was the father of at least three other biological children, and he adopted two sons. Burr also acted as a parent to his two stepsons by his wife's first marriage, and he became a mentor or guardian to several protégés who lived in his home.
Burr's daughter Theodosia
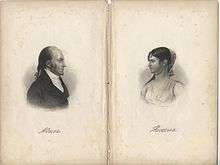
Theodosia Burr was born in 1783, and was named after her mother. She was the only child of Burr's marriage to Theodosia Bartow Prevost who survived to adulthood. A second daughter, Sally, lived to the age of three.[78]
Burr was a devoted and attentive father to Theodosia.[78] Believing that a young woman should have an education equal to that of a young man, Burr prescribed a rigorous course of studies for her which included the classics, French, horsemanship, and music.[78] Their surviving correspondence indicates that he affectionately treated his daughter as a close friend and confidante as long as she lived.
Theodosia became widely known for her education and accomplishments. In 1801, she married Joseph Alston of South Carolina.[79] They had a son together, Aaron Burr Alston, who died of fever at age ten. During the winter of 1812–1813, Theodosia was lost at sea with the schooner Patriot off the Carolinas, either murdered by pirates or shipwrecked in a storm.
Stepchildren and protégés
Upon Burr's marriage, he became stepfather to the two teenage sons of his wife's first marriage. Augustine James Frederick Prevost (called Frederick) and John Bartow Prevost had both joined their father in the Royal American Regiment in December 1780, at the ages of 16 and 14.[23] When they returned in 1783 to become citizens of the United States,[23] Burr acted as a father to them: he assumed responsibility for their education, gave both of them clerkships in his law office, and frequently was accompanied by one of them as an assistant when he traveled on business.[80] John was later appointed by Thomas Jefferson to a post in the Territory of Orleans as the first judge of the Louisiana Supreme Court.[81]

Burr served as a guardian to Nathalie de Lage de Volude (1782–1841) from 1794 to 1801, during Theodosia's childhood. The young daughter of a French marquis, Nathalie had been taken to New York for safety during the French Revolution by her governess Caroline de Senat.[82] Burr opened his home to them, allowing Madame Senat to tutor private students there along with his daughter, and Nathalie became a companion and close friend to Theodosia.[83] While traveling to France for an extended visit in 1801, Nathalie met Thomas Sumter Jr., a diplomat and the son of General Thomas Sumter.[82] They married in Paris in March 1802, before returning to his home in South Carolina. From 1810 to 1821, they lived in Rio de Janeiro,[84] where Sumter served as the American ambassador to Portugal during the transfer of the Portuguese Court to Brazil.[85] One of their children, Thomas De Lage Sumter, was a Congressman from South Carolina.[82]
In the 1790s, Burr also took the painter John Vanderlyn into his home as a protégé,[86] and provided him with financial support and patronage for 20 years.[87] He arranged Vanderlyn's training by Gilbert Stuart in Philadelphia, and sent him in 1796 to the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris where he remained for six years.[88]
Adopted and acknowledged children
Burr adopted two sons, Aaron Columbus Burr and Charles Burdett, during the 1810s and 1820s after the death of his daughter Theodosia. Aaron (né Aaron Burr Columbe) was born in Paris in 1808 and arrived in America around 1815, and Charles was born in 1814.[68][89][90]
Both of the boys were reputed to actually be Burr's biological sons. A Burr biographer described Aaron Columbus Burr as "the product of a Paris adventure", conceived presumably during Burr's exile from the United States between 1808 and 1814.[90]
In 1835, the year before his death, Burr acknowledged two young daughters whom he had fathered late in his life, by different mothers. Burr made specific provisions for his surviving daughters in a will dated January 11, 1835, in which he left "all the rest and residue" of his personal estate, after other specific bequests, to six year old Frances Ann (born c. 1829), and two year old Elizabeth (born c. 1833).[91]
Unacknowledged children
Among some families of color that claim descent from Burr, there is an oral tradition that he fathered two illegitimate children with an East Indian woman who worked as a servant or governess in his household in Philadelphia during his first marriage.[92][93] According to these family histories, the woman was named either Mary Emmons or Eugénie Beauharnais, and she came from Calcutta to Haiti or Saint-Domingue, where she lived and worked before being brought to Philadelphia.[93] Both of the children married into Philadelphia's "Free Negro" community in which their families became prominent:
- Louisa Charlotte Burr (b. 1788) worked most of her life as a domestic servant in the home of Elizabeth Powel Francis Fisher, a prominent Philadelphia society matron, and later in the home of her son Joshua Francis Fisher.[92] She was married to Francis Webb (1788–1829), a founding member of the Pennsylvania Augustine Education Society, secretary of the Haytien Emigration Society formed in 1824, and distributor of Freedom's Journal from 1827 to 1829.[92] After his death, Louisa remarried and became Louisa Darius.[92] Her youngest son Frank J. Webb wrote the 1857 novel The Garies and Their Friends.[92]
- John Pierre Burr (c. 1792–1864) became a member of Philadelphia's Underground Railroad and served as an agent for the abolitionist newspaper The Liberator. He worked in the National Black Convention movement and served as chairman of the American Moral Reform Society.[94]
One contemporary of John Pierre Burr identified him as a natural son of Burr in a published account,[95] but Burr's surviving letters and documents provide no evidence of any woman matching the description of Mary or Eugénie and do not mention or allude to Louisa or Jean Pierre. No source suggests that Burr acknowledged them as his children, in contrast to his adoption or acknowledgement of other children born later in his life.
In 2018, Louisa and John were acknowledged by the Aaron Burr Association as the children of Burr after a DNA test showed a familial link between descendants of Burr and descendants of John Pierre.[96][97]
Character
Aaron Burr was a man of complex character who made many friends, but also many powerful enemies. He may be the most controversial of the Founding Fathers of the United States.[98] He was indicted for murder after the death of Hamilton, but never prosecuted;[99] he was reported by acquaintances to be curiously unmoved by Hamilton's death, expressing no regret for his role in the result. He was arrested and prosecuted for treason by President Jefferson, but acquitted.[100] Contemporaries often remained suspicious of Burr's motives to the end of his life, continuing to view him as untrustworthy at least since his role in the founding of the Bank of Manhattan.
In his later years in New York, Burr provided money and education for several children, some of whom were reputed to be his own natural children. To his friends and family, and often to complete strangers, he could be kind and generous. The wife of the struggling poet Sumner Lincoln Fairfield recorded in her autobiography that in the late 1820s, their friend Burr pawned his watch to provide for the care of the Fairfields' two children.[101] Jane Fairfield wrote that, while traveling, she and her husband had left the children in New York with their grandmother, who proved unable to provide adequate food or heat for them. The grandmother took the children to Burr's home and asked his help: "[Burr] wept, and replied, 'Though I am poor and have not a dollar, the children of such a mother shall not suffer while I have a watch.' He hastened on this godlike errand, and quickly returned, having pawned the article for twenty dollars, which he gave to make comfortable my precious babes."[101]
By Fairfield's account, Burr had lost his religious faith before that time; upon seeing a painting of Christ's suffering, Burr candidly told her, "It is a fable, my child; there never was such a being."[102]
Burr believed women to be intellectually equal to men, and hung a portrait of Mary Wollstonecraft over his mantel. The Burrs' daughter, Theodosia, was taught dance, music, several languages, and learned to shoot from horseback. Until her death at sea in 1813, she remained devoted to her father. Not only did Burr advocate education for women, upon his election to the New York State Legislature, he submitted a bill to allow women to vote.
Conversely, Burr was considered a notorious womanizer. In addition to cultivating relationships with women in his social circles, Burr's personal journals indicate that he was a frequent patron of prostitutes during his travels in Europe; he recorded brief notes of dozens of such encounters, and the amounts he paid. He described "sexual release as the only remedy for his restlessness and irritability".[103]
In 1784 as a New York state assemblyman, Burr unsuccessfully sought to abolish slavery immediately following the American Revolutionary War.[104] The legislature in 1799 finally abolished slavery in New York. John Quincy Adams wrote in his diary when Burr died: "Burr's life, take it all together, was such as in any country of sound morals his friends would be desirous of burying in quiet oblivion."[105] Adams' father, President John Adams, had frequently defended Burr during his life. At an earlier time, he wrote, Burr "had served in the army, and came out of it with the character of a knight without fear and an able officer".[106]
Gordon S. Wood, a leading scholar of the revolutionary period, holds that it was Burr's character that put him at odds with the rest of the "founding fathers", especially Madison, Jefferson, and Hamilton. He believed that this led to his personal and political defeats and, ultimately, to his place outside the golden circle of revered revolutionary figures. Because of Burr's habit of placing self-interest above the good of the whole, those men thought that Burr represented a serious threat to the ideals for which they had fought the revolution. Their ideal, as particularly embodied in Washington and Jefferson, was that of "disinterested politics", a government led by educated gentlemen who would fulfill their duties in a spirit of public virtue and without regard to personal interests or pursuits. This was the core of an Enlightenment gentleman, and Burr's political enemies thought that he lacked that essential core. Hamilton thought that Burr's self-serving nature made him unfit to hold office, especially the presidency.
Although Hamilton considered Jefferson a political enemy, he believed him a man of public virtue. Hamilton conducted an unrelenting campaign in the House of Representatives to prevent Burr's election to the presidency and gain election of his erstwhile enemy, Jefferson. Hamilton characterized Burr as greatly immoral, "unprincipled ... voluptuary", and deemed his political quest as one for "permanent power". He predicted that if Burr gained power, his leadership would be for personal gain, but that Jefferson was committed to preserving the Constitution.[107]
Legacy
Although Burr is often remembered primarily for his duel with Hamilton, his establishment of guides and rules for the first impeachment trial set a high bar for behavior and procedures in the Senate chamber, many of which are followed today.[108]
A lasting consequence of Burr's role in the election of 1800 was the Twelfth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which changed the way in which vice presidents were chosen. As was obvious from the 1800 election, the situation could easily arise where the vice president, as the defeated presidential candidate, could not work well with the president. The Twelfth Amendment required that electoral votes be cast separately for president and vice president.[109]
Furthermore, the electioneering methods pioneered by Burr during the election of 1800 (such as door-to-door canvassing) remain the standard to this day in election campaigns all over the world.
Representation in literature and popular culture
- Burr appears as a character of worldly sophistication in Harriet Beecher Stowe's 1859 historical romance The Minister's Wooing.[lower-alpha 1]
- Edward Everett Hale's 1863 story "The Man Without a Country" is about a fictional co-conspirator of Burr's in the Southwest and Mexico, who is exiled for his crimes.[lower-alpha 2]
- Charles Felton Pidgin's 1902 novel The Climax is an alternate history where no Hamilton duel occurred, and Burr later becomes president.[lower-alpha 3]
- My Theodosia (1945) by author Anya Seton is a fictional interpretation about the life of Theodosia Burr, daughter of Aaron Burr.
- "The Aaron Burr Story" (1965), a second-season episode of the television series Daniel Boone, starred Leif Erickson as ex–Vice President Aaron Burr trying to organize an army to take over the western states.[lower-alpha 4]
- Gore Vidal's Burr: A Novel (1973) is the first in chronology of his Narratives of Empire series.[lower-alpha 5]
- James Thurber's story, "A Friend to Alexander", in his collection My World and Welcome To It (1969), portrayed the Burr–Hamilton rivalry in the twentieth century.[lower-alpha 6]
- Eudora Welty's story, "First Love", in her Selected Stories of Eudora Welty (Modern Library, 1992) related the romance of Burr's Western expedition.[lower-alpha 7]
- In the comic book, The Flash, "The Man of Destiny!", a 1975 backup story featuring Green Lantern, stars Burr. It reveals that Burr was recruited by aliens to act as a leader for an interplanetary society in chaos.[lower-alpha 8]
- In Michael Kurland's The Whenabouts of Burr,[lower-alpha 9] the protagonists chase across various alternate universes trying to recover the US Constitution, which has been stolen and replaced by an alternate signed by Aaron Burr.
- In Orson Scott Card's alternate history / fantasy novel, Seventh Son (1987), a character states that "... Aaron Burr got to be governor of Suskwahenny, before Daniel Boone shot him dead in ninety-nine."[lower-alpha 10]
- A 1993 "Got Milk?" commercial directed by Michael Bay features a historian obsessed with the study of Aaron Burr—he owns the guns and the bullet from the duel (see Aaron Burr (advertisement)).
- In 2000, the PBS television series American Experience presented an episode titled "The Duel", re-enacting the events that led to the Burr–Hamilton duel.[104]
- In Alexander C. Irvine's novel, A Scattering of Jades (2002), Burr is shown to take part in a plot to bring an ancient Aztec deity into power, as if to explain his interest in Mexico.[lower-alpha 11]
- The Lonely Island's "Lazy Sunday" lyrics quotes the line "you can call us Aaron Burr from the way we're dropping Hamiltons", as they spend a large number of ten-dollar bills, a reference to Burr killing or "dropping" Hamilton at their duel.[lower-alpha 12]
- In the alternate history short story, "The War of '07" by Jayge Carr, collected in the anthology Alternate Presidents, Burr is elected President over Thomas Jefferson in 1800, establishes an alliance with Napoleon Bonaparte, and creates a family dictatorship. He serves as president for a total of nine terms. Upon his death in 1836, he is succeeded by his grandson Aaron Burr Alston, who previously served as his Vice President.[lower-alpha 13]
- A 2011 short dramatic film recounts Burr's life as having become "a casualty of history". It was a selection at the 2011 New York Film Festival as well numerous other US festivals.[lower-alpha 14]
- In the gaslamp fantasy roleplaying game Castle Falkenstein, Burr is the founder and seemingly immortal President for Life of the pirates' republic of Orleans and the lover of Marie Laveau, although he has not been seen in public in more than 25 years at the time the game is set.[lower-alpha 15]
- Burr is a principal character in the 2015 Broadway musical Hamilton, written by Lin-Manuel Miranda and inspired by historian Ron Chernow's 2004 biography of Hamilton.[lower-alpha 16] The role of Burr was originated by Leslie Odom Jr., who won the 2016 Tony Award for Best Actor in a Musical for his work in the role. In Hamilton, Burr is both the principal narrator, and a sympathetic yet increasingly antagonistic foil to Hamilton. He is portrayed as ambitious but indecisive, preferring to smile and gladhand rather than make any strong commitment or action—a character trait that Hamilton constantly questions and calls Burr out on.
Notes
- Office of Art and Archives.
- Wheelan, Joseph (2006). Jefferson's Vendetta: the Pursuit of Aaron Burr and the Judiciary. PublicAffairs. ISBN 0786716894.
- "The Election of 1800". Lehrman Institute.
- Unger, Harlow Giles (2014). John Marshall: the Chief Justice Who Saved the Nation. Hachette Books. ISBN 978-0306822216.
- Wheelan, Joseph (2006). Jefferson's Vendetta: the Pursuit of Aaron Burr and the Judiciary. PublicAffairs. ISBN 0786716894.
- Chisholm 1911, p. 861–862.
- "Aaron Burr Reeve". Litchfield Historical Society. Retrieved May 21, 2018.
- "Burr, Aaron". www.historycentral.com.
- "Aaron Burr Jr. (1756–1836) < Biographies < American History From Revolution To Reconstruction and beyond". www.let.rug.nl.
- "History". The American Whig–Cliosophic Society. Princeton University. 2016. Archived from the original on April 6, 2016.
- Isenberg 2007, pp. 9–16.
- Isenberg 2007, pp. 22–28.
- Isenberg 2007, pp. 33–34.
- Lomask 1979, p. 82.
- Schachner 1961, p. 37.
- Isenberg 2007, pp. 34, 36.
- Isenberg 2007, pp. 37–38.
- Parmet & Hecht 1967, p. 42.
- Isenberg 2007, p. 46.
- Burr 1837, p. 159.
- Parton 1861, p. 120.
- Parton 1861, pp. 124–125.
- Williams 1973, pp. 16–17.
- "The House Where Aaron Burr Courted Theodosia". The New York Times. September 1, 1977. Archived from the original on May 17, 2019.
- Isenberg 2007, p. 69–70.
- Isenberg 2007, p. 70.
- Parmet & Hecht 1967, p. 57.
- Documents of the Senate of the State of New York 1902, p. 108.
- Members of the electoral college in the 18th century cast two ballots but did not specify an office. The first-place finisher overall became president and the runner-up vice president. They did not run on a "ticket" and were often opponents.
- Isenberg 2007, p. 153.
- Lomask 1979, p. 215.
- Steiner 1907.
- Myers 1901, pp. 14–16.
- Chernow 2004, pp. 589–591.
- Allen, p. 12.
- Chernow 2004, pp. 585–590.
- Murphy 2008, pp. 233–266.
- Elkins 1995, p. 733.
- Paulsen 2017, p. 53.
- Baker 2011, pp. 553–598.
- Baker 2011, p. 556.
- Ferling 2004.
- Sharp 2010.
- Chisholm 1911, p. 862.
- McDonald 1992.
- Lamb 1921, p. 500.
- Stewart 2011, p. 29.
- Kerber 1980, p. 148.
- Fleming 1999, p. 233.
- Fleming 1999, p. 284.
- Fleming 1999, pp. 287–289.
- Buescher 2010.
- Ellis 2000, pp. 20–47.
- Weir 2003.
- Isenberg & Burstein 2011.
- Stewart 2011.
- Hamilton 1804a.
- Hamilton 1804b.
- McFarland 1979, p. 62.
- Parmet & Hecht 1967, p. 259.
- Parmet & Hecht 1967, p. 268.
- Pickett 1900.
- Wandell & Minnigerode 1925, p. 182.
- Hoffer 2008.
- Stewart 2011, pp. 213–214.
- Isenberg 2007, p. 380.
- Leitch 1978, pp. 261–262.
- Isenberg 2007, p. 397.
- Isenberg 2007, pp. 396–397.
- Oppenheimer 2015, pp. 165–169.
- Ward 2000, p. 39.
- Brown 1901, pp. 3–4.
- Beyer 2017, p. 163.
- Nolan 1980, pp. 41–43.
- Koeppel 2001, p. 183.
- Walsh 2009.
- Beveridge 2000, p. 538.
- James 1971, p. 270.
- Chisholm 1911, p. 861.
- Burr 1837, p. 252; Isenberg 2007, p. 76.
- Wymond 1921, p. 113; New York Gen. & Bio. Record 1881, p. 28.
- Tisdale 2001.
- Schachner 1961; Burr 1837, p. 387 n.1.
- Tisdale 2001, pp. 83-90.
- Bureau of Public Affairs.
- Isenberg 2007, pp. 158–159.
- National Gallery.
- National Gallery; Kip 1867, pp. 228–229.
- Lomask 1982, pp. 387–388.
- Schachner 1961, p. 513.
- Oppenheimer 2015, p. 165–169; Stillwell 1928, p. 66.
- Maillard 2013, pp. 261–300.
- Willson 2000, p. 123 n.11.
- Willson 2000, p. 123 n.11; Ballard 2011, pp. 68, 271.
- Pickard 1895, p. 224.
- Holpuch, Amanda (August 24, 2019). "Aaron Burr, vice-president who killed Hamilton, had children of color". The Guardian. Retrieved August 24, 2019.
- "Aaron Burr — villain of 'Hamilton' — had a secret family of color, new research shows". The Washington Post.
- Isenberg 2007.
- Berkin et al. 2013, p. 200.
- Newmyer 2012, p. 182.
- Fairfield 1860, p. 89.
- Fairfield 1860, p. 82.
- Stewart 2011, p. 278.
- PBS 2000.
- Sharp 1993, p. 262.
- Adams 1856, p. 123.
- Ferling 2004, p. 180.
- Daschle & Robbins 2013, p. 174.
- Bailey 2007, p. 196.
- References in popular culture
- Stowe, Harriet Beecher (1869) [1st pub. Derby and Jackson: 1859]. The Minister's Wooing. London: Sampson Low, Son, & Marston.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Hale, Edward Everett (1889) [1st pub. The Atlantic Monthly Dec. 1863]. The Man Without a Country: And Other Tales. Boston: Roberts Brothers.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Feeley, Gregory (September 6, 2004). "The Way It Wasn't". The Weekly Standard.
- NBC (October 28, 1965). "The Aaron Burr Story". Daniel Boone. Season 2. Episode 7. National Broadcasting Company.
- Vidal, Gore (2011) [1st pub. 1973]. Burr: A Novel. Knopf Doubleday. ISBN 978-0307798411.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Thurber, James (1969). My World and Welcome to It. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. ISBN 0156623447.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Jöttkandt, Sigi (2010). "In the Self's Temporary Lodgings: Eudora Welty". First Love: A Phenomenology of the One. re.press.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "The Man of Destiny!". The Flash. DC Comics (231). February 1975.
- Kurland, Michael (1975). The Whenabouts of Burr. DAW.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Card, Orson Scott (2003) [1st pub. 1987]. Seventh Son: The Tales of Alvin Maker. Macmillan. ISBN 978-1429964937.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Irvine, Alexander C. (2003). A Scattering of Jades. Macmillan. ISBN 978-0765340986.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Lazy Sunday (feat. Chris Parnell)". Lyrics. The Lonely Island. 2009. Retrieved February 22, 2015.
- Carr, Jayge (1992). "The War of '07". In Resnick, Mike (ed.). Alternate Presidents. Tor Books.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- O'Keefe, Dana (2012). "Aaron Burr, Part 2". Vimeo. Retrieved February 22, 2015.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bolme, Edward; Parks, Jim; Quintanar, Derek; Schumann, Mark; Cambias, James; Floch, Eric; Hyatt, Angela; Rosen, Barrie; Williams, Chris (1996). Six-Guns & Sorcery. Castle Falkenstein. Berkeley, CA: R. Talsorian Games.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wood, Gordon S. (January 14, 2016). "Federalists on Broadway". New York Review of Books. pp. 10–13.
References
- Adams, John; Adams, Charles Francis (1856). "To James Lloyd. Quincy, 17 February 1815". The Works of John Adams, Second President of the United States. 10. Boston, MA: Little, Brown and Co.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Adamson, Bruce Campbell (1988). For Which We Stand: The Life and Papers of Rufus Easton. Aptos, CA: Self-published.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Allen, Oliver E. (1993). The Tiger: The Rise and Fall of Tammany Hall. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company. ISBN 0-201-62463-X.
- Bailey, Jeremy D. (2007). Thomas Jefferson and Executive Power. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1139466295.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Baker, Thomas N. (Winter 2011). "'An Attack Well Directed': Aaron Burr Intrigues for the Presidency". Journal of the Early Republic. University of Pennsylvania Press. 31 (4): 553–598. doi:10.1353/jer.2011.0073. JSTOR 41261652.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Berkin, Carol; Miller, Christopher L.; Cherny, Robert W.; Gormly, James L.; Egerton, Douglas R. & Woestman, Kelly (2013) [1st pub. Houghton Mifflin: 1995]. Making America: A History of the United States (Brief 6th ed.). Boston, MA: Wadsworth, Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1133317692.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Beveridge, Albert J. (2000). The Life of John Marshall: Conflict and Construction 1800–1815. Beard Books. p. 538. ISBN 978-1-58798-049-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Beyer, Rick (2017). Rivals Unto Death: Alexander Hamilton and Aaron Burr. Hachette Books. p. 163. ISBN 978-0-316-50496-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bray, Samuel (2005). "Not Proven: Introducing a Third Verdict". University of Chicago Law Review. 72 (4). SSRN 1339222.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Brown, Maria Ward (1901). The Life of Dan Rice. Long Branch, NJ: Self-published.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Buescher, John (November 11, 2010). "Burr-Hamilton Duel". Ask a Historian. Teachinghistory.org. Archived from the original on October 29, 2014.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Burr, Aaron (1837). Davis, Matthew Livingston (ed.). Memoirs of Aaron Burr: With Miscellaneous Selections from His Correspondence. New York: Harper & Brothers. p. 387 n.1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Chernow, Ron (2004). Alexander Hamilton. New York: Penguin. ISBN 978-1-1012-0085-8.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Collins, Paul (2013). Duel with the Devil. Crown.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Daschle, Tom; Robbins, Charles (2013). The U.S. Senate: Fundamentals of American Government. New York: Thomas Dunne Books. ISBN 978-1250027559.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Documents of the Senate of the State of New York. 9. Albany, NY: J. B. Lyon Company. 1902.
- Elkins, Stanley; McKitrick, Eric (1995). The Age of Federalism.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ellis, Joseph J. (2000). Founding Brothers: The Revolutionary Generation. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 978-0375405440.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Fairfield, Jane (1860). The Autobiography of Jane Fairfield. Boston: Bazin and Ellsworth.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ferling, John (2004). Adams vs. Jefferson: The Tumultuous Election of 1800. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-516771-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Fleming, Thomas (1999). Duel: Alexander Hamilton, Aaron Burr, and the Future of America. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0465017379.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Hamilton, Alexander. "Statement on Impending Duel with Aaron Burr (28 June–10 July 1804)". Founders Online.
- Hamilton, Alexander. "To Elizabeth Hamilton from Alexander Hamilton, 10 July 1804". Founders Online (letter).
- Hoffer, Peter Charles (2008). The Treason Trials of Aaron Burr. U. Press of Kansas.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ip, Greg (October 5, 2005). "Aaron Burr fans find unlikely ally in black descendant". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. Archived from the original on December 3, 2008.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Isenberg, Nancy (2007). Fallen Founder: The Life of Aaron Burr. Penguin Publishing Group. ISBN 978-1-101-20236-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Isenberg, Nancy; Burstein, Andrew (January 4, 2011). "What Michele Bachmann doesn't know about history". Salon.com. Archived from the original on December 11, 2014.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- James, Edward T.; James, Janet Wilson; Boyer, Paul S., eds. (1971). "Burr, Theodosia". Notable American Women, 1607–1950: A Biographical Dictionary. Harvard University Press. p. 270. ISBN 978-0-674-62734-5.
- Kerber, Linda K. (1980) [1st pub. 1970]. Federalists in Dissent: Imagery and Ideology in Jeffersonian America. New York: Cornell University Press. ISBN 0801492122.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Kip, William Ingraham (February 1867). "Recollections of John Vanderlyn, the Artist". The Atlantic Monthly. Boston: Ticknor and Fields. 19.
- Koeppel, Gerard T. (2001). Water for Gotham: A History. Princeton University Press. p. 183. ISBN 0-691-08976-0.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Lamb, Martha J. (1921) [1st pub. A.S. Barnes: 1877]. History of the City of New York: Its Origin, Rise and Progress. 3. New York: Valentine's Manual.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Leitch, Alexander (1978). A Princeton Companion. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1400870011.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Lomask, Milton (1979). Aaron Burr: The Years from Princeton to Vice President, 1756–1805. Aaron Burr. 1. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Lomask, Milton (1982). Aaron Burr: The Conspiracy and Years of Exile, 1805–1836. Aaron Burr. 2. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Maillard, Mary (2013). "'Faithfully Drawn from Real Life': Autobiographical Elements in Frank J. Webb's The Garies and Their Friends". Pennsylvania Magazine of History and Biography. 137 (3): 261–300. doi:10.5215/pennmaghistbio.137.3.0261. JSTOR 10.5215/pennmaghistbio.137.3.0261.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- McDonald, Forrest (June 14, 1992). "The Senate Was Their Jury". Review. New York Times. Archived from the original on December 10, 2014.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- McFarland, Philip (1979). Sojourners. New York: Atheneum.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Murphy, Brian Phillips (2008). "'A Very Convenient Instrument': The Manhattan Company, Aaron Burr, and the Election of 1800". William and Mary Quarterly. 65 (2).CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Myers, Gustavus (1901). The History of Tammany Hall. Gustavus Myers. p. 15.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Vanderlyn, John". National Gallery of Art. Archived from the original on January 18, 2018.
- The New York Genealogical and Biographical Record. New York Genealogical and Biographical Society. 1881–1882.
- Newmyer, R. Kent (2012). The Treason Trial of Aaron Burr: Law, Politics, and the Character Wars of the New Nation. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1107022188.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Nolan, Charles J. (1980). Aaron Burr and the American Literary Imagination. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press. ISBN 978-0313212567.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Office of Art and Archives (n.d.). "Burr, Aaron". Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. U.S. Congress. Archived from the original on December 7, 2014.
- Bureau of Public Affairs. "Thomas Sumter Jr. (1768–1840)". Office of the Historian. United States Department of State. Archived from the original on October 18, 2012.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Oppenheimer, Margaret (2015). The Remarkable Rise of Eliza Jumel: A Story of Marriage and Money in the Early Republic. Chicago Review Press. ISBN 978-1-61373-383-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Parmet, Herbert S. & Hecht, Marie B. (1967). Aaron Burr: Portrait of an Ambitious Man. Macmillan.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Parton, James (1861). The Life and Times of Aaron Burr. New York: Mason Brothers. p. 124.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Timeline of Events leading up to the Duel – 1756–1804". The American Experience: The Duel. PBS. Archived from the original on October 24, 2014.
- Paulsen, Michael Stokes; Paulsen, Luke (2017). The Constitution: An Introduction. Basic Books. ISBN 9780465093298.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Pickard, Samuel Thomas (1895). Life and Letters of John Greenleaf Whittier. Cambridge, MA: The Riverside Press.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Pickett, Albert James (1900) [1st pub. Walker and James:1851]. "The Arrest of Aaron Burr in Alabama". History of Alabama. Birmingham, AL: The Webb Book Co. pp. 488–502.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Schachner, Nathan (1961) [1937]. Aaron Burr: A Biography. A. S. Barnes. Archived from the original on January 17, 2018.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Sharp, James Roger (1993). American Politics in the Early Republic: The New Nation in Crisis. Yale University Press. ISBN 0300065191.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Sharp, James Roger (2010). The Deadlocked Election of 1800: Jefferson, Burr, and the Union in the Balance.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Steiner, Bernard C. (1907). The Life and Correspondence of James McHenry: Secretary of War under Washington and Adams. Cleveland, OH: Burrows Brothers.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Steiner, Dale R. (1987). Of Thee We Sing: Immigrants and American History. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. ISBN 978-0155673854.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Stewart, David O. (2011). American Emperor: Aaron Burr's Challenge to Jefferson's America. New York: Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-1439160329.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Stillwell, John E. (1928). The History of the Burr Portraits, Their Origin, Their Dispersal and Their Reassemblage. New York? : s.n.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Tisdale, Thomas (2001). A Lady of the High Hills: Natalie Delage Sumter. Univ. of South Carolina Press. ISBN 978-1-57003-415-2.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Walsh, Kevin (November 1, 2009). "Port Richmond Avenue, Staten Island". Forgotten New York. Archived from the original on December 8, 2014.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wandell, Samuel H.; Minnigerode, Meade (1925). Aaron Burr. New York: G. P. Putnam's Sons.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ward, Candace, ed. (2000). New York City Museum Guide (2nd ed.). New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0486410005.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Weir, William (2003). Written with Lead: America's Most Famous and Notorious Gunfights from the Revolutionary War to Today. Cooper Square Press. ISBN 978-0-8154-1289-2.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Williams, Edward G. (January 1973). "The Prevosts of the Royal Americans". Western Pennsylvania Historical Magazine (PDF). 56 (1): 16–17. Archived from the original on November 5, 2016. Retrieved May 21, 2019.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Willson, Joseph (2000). Winch, Julie (ed.). The Elite of Our People: Joseph Willson's Sketches of Black Upper-Class Life in Antebellum Philadelphia. Pennsylvania State University Press. ISBN 0-271-04302-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wymond, John; Dart, Henry Plauché, eds. (January 1921) [March 1, 1913]. "Celebration of the Centenary of the Supreme Court of Louisiana". The Louisiana Historical Quarterly. Louisiana Historical Society. 4 (1).
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. 4 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 861–862.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
Further reading
- Abernethy, Thomas Perkins. "Aaron Burr in Mississippi". Journal of Southern History 1949 15 (1): 9–21. ISSN 0022-4642
- Adams, Henry, History of the United States, vol. iii. New York, 1890. (For the traditional view of Burr's conspiracy.)
- Alexander, Holmes Moss. Aaron Burr: The Proud Pretender. 1937; Reprinted by Greenwood-Heinemann Publishing, 1973.
- Barbagallo, Tricia (March 10, 2007). "Fellow Citizens Read a Horrid Tale" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 19, 2009. Retrieved June 4, 2008.
- Brands, H. W. The Heartbreak of Aaron Burr (American Portraits Series) (2012).
- Burr, Aaron. Political Correspondence and Public Papers of Aaron Burr. Mary-Jo Kline and Joanne W. Ryan, eds. 2 vol. Princeton University Press, 1983. 1311 pp.
- Cheetham, James (1803). Nine Letters on the Subject of Aaron Burr's Political Defection: With an Appendix. Denniston & Cheetham.
- Cheetham, James. A view of the political conduct of Aaron Burr, esq., vice-president of the United States. (1802)
- Burdett, Charles. Margaret Moncrieffe: The First Love of Aaron Burr. Available from the University of Michigan, 1860.
- Clark, Alan J., Cipher Code of Dishonor: Aaron Burr, an American Enigma. Bloomington, IN: AuthorHouse, 2005.
- Clark, Daniel. Proofs of the Corruption of Gen. James Wilkinson, and of His Connexion With Aaron Burr: A Full Refutation of His Slanderous Allegations in Relation to ... of the Principal Witness Against Him (1809). Reprinted by University Press of the Pacific, 2005.
- Clemens, Jere. (Hon.), The Rivals: A Tale of the Times of Aaron Burr and Alexander Hamilton. (1860) online edition
- Cohalan, John P., The Saga of Aaron Burr. (1986)
- Cote, Richard N., Theodosia Burr Alston: Portrait of a Prodigy. (2002)
- Faulkner, Robert K. "John Marshall and the Burr Trial". Journal of American History 1966 53(2): 247–258. ISSN 0021-8723
- Ford, Worthington Chauncey. "Some Papers of Aaron Burr" Proceedings of the American Antiquarian Society 29(1): 43–128. 1919
- Freeman, Joanne B. "Dueling as Politics: Reinterpreting the Burr-Hamilton Duel". William and Mary Quarterly 53(2) (1996): 289–318. ISSN 0043-5597
- Harrison, Lowell. 1978. "The Aaron Burr Conspiracy". American History I Illustrated 13:25.
- Jenkinson, Isaac. Aaron Burr: His Personal and Political Relations with Thomas Jefferson and Alexander Hamilton. (1902)
- Jillson, Willard Rouse (October 1943). "Aaron Burr's Trial for Treason, at Frankfort, 1806". Filson Club History Quarterly. 17 (4). Archived from the original on May 2, 2012. Retrieved December 6, 2011.
- Kennedy, Roger G. Burr, Hamilton, and Jefferson: A Study in Character. New York: Oxford University Press, 1999.
- Künstler, Laurence S. The Unpredictable Mr. Aaron Burr (1974).
- Larson, Edward J. A Magnificent Catastrophe: The Tumultuous Election of 1800, America's First Presidential Campaign. New York: Free Press, 2007.
- McCaleb, Walter Flavius, The Aaron Burr Conspiracy: A History Largely from Original and Hitherto Unused Sources, New York, 1903.
- McCaleb, Walter Flavius, A New Light on Aaron Burr (date unknown)
- Melton, Buckner F. Jr. Aaron Burr: Conspiracy to Treason. New York: John Wiley, 2002. online edition
- Missouri History Museum, Aaron Burr papers
- Robertson, David. Reports of the Trials of Colonel Aaron Burr (Late Vice President of the United States) for Treason and for Misdemeanor ... Two Volumes (report taken in shorthand) (1808)
- Rogow, Arnold A. A Fatal Friendship: Alexander Hamilton and Aaron Burr (1998).
- Rorabaugh, William J. "The Political Duel in the Early Republic: Burr v. Hamilton". Journal of the Early Republic 1995 15(1): 1–23. ISSN 0275-1275
- Slaughter, Thomas P. "Review Essay: Conspiratorial Politics: The Public Life of Aaron Burr". Conspiratorial Politics.
- Stewart, David O., "Burr, Ogden, and Dayton: The Original Jersey Boys", Smithsonian, August 12, 2011.
- Todd, Charles Burr. The True Aaron Burr: A Biographical Sketch (1902). New York, A.S. Barnes & Company. Available from Internet Archive.
- Vail, Philip. The Great American Rascal: The Turbulent Life of Aaron Burr (1973).
- Van Ness, William Peter. An Examination of the Various Charges Exhibited Against Aaron Burr, Vice-President of the United States: and a Development of the Characters and Views of His Political Opponents. (1803) Available through Haithi Trust
- Wells, Colin. "Aristocracy, Aaron Burr, and the Poetry of Conspiracy". Early American Literature (2004).
- Wheelan, Joseph. Jefferson's Vendetta: The Pursuit of Aaron Burr and the Judiciary. New York: Carroll & Graff, 2005.
- Wilson, Samuel M. (January 1936). "The Court Proceedings of 1806 in Kentucky Against Aaron Burr and John Adair". Filson Club History Quarterly. 10 (1). Archived from the original on April 25, 2012. Retrieved November 29, 2011.
- Wood, Gordon S. (2006) Revolutionary Characters. New York: Penguin.


