Wide area network
A wide area network (WAN) is a telecommunications network that extends over a large geographical area for the primary purpose of computer networking. Wide area networks are often established with leased telecommunication circuits.[1]

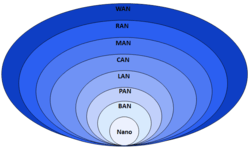
| Computer network types by spatial scope |
|---|
 |
Business, as well as education and government entities use wide area networks to relay data to staff, students, clients, buyers and suppliers from various locations across the world. In essence, this mode of telecommunication allows a business to effectively carry out its daily function regardless of location. The Internet may be considered a WAN.[2]
Similar types of networks are personal area networks (PANs), local area networks (LANs), campus area networks (CANs), or metropolitan area networks (MANs) which are usually limited to a room, building, campus or specific metropolitan area, respectively.
Design options
The textbook definition of a WAN is a computer network spanning regions, countries, or even the world.[3] However, in terms of the application of computer networking protocols and concepts, it may be best to view WANs as computer networking technologies used to transmit data over long distances, and between different LANs, MANs and other localised computer networking architectures. This distinction stems from the fact that common LAN technologies operating at lower layers of the OSI model (such as the forms of Ethernet or Wi-Fi) are often designed for physically proximal networks, and thus cannot transmit data over tens, hundreds, or even thousands of miles or kilometres.
WANs do not just necessarily connect physically disparate LANs. A CAN, for example, may have a localized backbone of a WAN technology, which connects different LANs within a campus. This could be to facilitate higher bandwidth applications or provide better functionality for users in the CAN.[4]
WANs are used to connect LANs and other types of networks together so that users and computers in one location can communicate with users and computers in other locations. Many WANs are built for one particular organization and are private. Others, built by Internet service providers, provide connections from an organization's LAN to the Internet. WANs are often built using leased lines. At each end of the leased line, a router connects the LAN on one side with a second router within the LAN on the other. Leased lines can be very expensive. Instead of using leased lines, WANs can also be built using less costly circuit switching or packet switching methods. Network protocols including TCP/IP deliver transport and addressing functions. Protocols including Packet over SONET/SDH, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and Frame Relay are often used by service providers to deliver the links that are used in WANs. X.25 was an important early WAN protocol, and is often considered to be the "grandfather" of Frame Relay as many of the underlying protocols and functions of X.25 are still in use today (with upgrades) by Frame Relay.[5]
Academic research into wide area networks can be broken down into three areas: mathematical models, network emulation, and network simulation.
Performance improvements are sometimes delivered via wide area file services or WAN optimization.
Private networks
Of the approximately four billion addresses defined in IPv4, about 18 million addresses in three ranges are reserved for use in private networks. Packets addresses in these ranges are not routable in the public Internet; they are ignored by all public routers. Therefore, private hosts cannot directly communicate with public networks, but require network address translation at a routing gateway for this purpose.
Reserved private IPv4 network ranges[6] Name CIDR block Address range Number of addresses Classful description 24-bit block 10.0.0.0/8 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 16777216 Single Class A. 20-bit block 172.16.0.0/12 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 1048576 Contiguous range of 16 Class B blocks. 16-bit block 192.168.0.0/16 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 65536 Contiguous range of 256 Class C blocks.
Since two private networks, e.g., two branch offices, cannot directly interoperate via the public Internet, the two networks must be bridged across the Internet via a virtual private network (VPN) or an IP tunnel, which encapsulates packets, including their headers containing the private addresses, in a protocol layer during transmission across the public network. Additionally, encapsulated packets may be encrypted for the transmission across public networks to secure the data.
Connection technology
Many technologies are available for wide area network links. Examples include circuit-switched telephone lines, radio wave transmission, and optical fiber. New developments in technologies have successively increased transmission rates. In ca. 1960, a 110 bit/s (bits per second) line was normal on the edge of the WAN, while core links of 56 kbit/s to 64 kbit/s were considered fast. As of 2014, households are connected to the Internet with dial-up, asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL), cable, WiMAX, 4G[7] or fiber. The speeds that people can currently use range from 28.8 kbit/s through a 28K modem over a telephone connection to speeds as high as 100 Gbit/s using 100 Gigabit Ethernet.
The following communication and networking technologies have been used to implement WANs.
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode
- Cable modem
- Dial-up internet
- Digital subscriber line
- Fiber-optic communication
- Frame Relay
- ISDN
- Leased line
- SD-WAN
- Synchronous optical networking
- X.25
400-gigabit Ethernet
AT&T conducted trials in 2017 for business use of 400-gigabit Ethernet.[8] Researchers Robert Maher, Alex Alvarado, Domaniç Lavery, and Polina Bayvel of University College London were able to increase networking speeds to 1.125 terabits per second.[9] Christos Santis, graduate student Scott Steger, Amnon Yariv, Martin and Eileen Summerfield developed a new laser that potentially quadruples transfer speeds with fiber optics.[10]
See also
- Cell switching
- Internet area network (IAN)
- Label switching
- Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN)
- Wide area application services
- Wide area file services
- Wireless WAN
References
- "A WAN Is a Wide Area Network. Here's How They Work". Lifewire. Retrieved 2017-04-21.
- Groth, David and Skandler, Toby (2005). Network+ Study Guide, Fourth Edition. Sybex, Inc. ISBN 0-7821-4406-3.
- Forouzan, Behrouz (2012-02-17). Data Communications and Networking. McGraw-Hill. p. 14. ISBN 9780073376226.
- "Campus Area Networks (CAN). Computer and Network Examples". conceptdraw.com.
- "Frame relay". techtarget.com.
- Y. Rekhter; B. Moskowitz; D. Karrenberg; G. J. de Groot; E. Lear (February 1996). Address Allocation for Private Internets. Network Working Group IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1918. BCP 5. RFC 1918.
- "Welcome to the GitHub API Development and Support Board!". github.community. 2018-11-07. Retrieved 2019-07-26.
- "AT&T Completes Industry-Leading 400 Gb Ethernet Testing, Establishing A Future Network Blueprint for Service Providers and Businesses". www.att.com. September 8, 2017.
- Maher, Robert; Alvarado, Alex; Lavery, Domaniç; Bayvel, Polina (11 February 2016). "Increasing the information rates of optical communications via coded modulation: a study of transceiver performance". Scientific Reports. 6 (1): 21278. doi:10.1038/srep21278. PMC 4750034. PMID 26864633.
- "A New Laser for a Faster Internet - Caltech". Cal Tech.
External links
- Cisco - Introduction to WAN Technologies
- "What is WAN (wide area network)? - Definition from WhatIs.com", SearchEnterpriseWAN, retrieved 2017-04-21