Venus figurines
A Venus figurine is any Upper Palaeolithic statuette portraying a woman, usually carved in the round.[1] Most have been unearthed in Europe, but others have been found as far away as Siberia, and distributed across much of Eurasia.

Most date from the Gravettian period (26,000–21,000 years ago).[1] However, findings are not limited to this period; for example, the Venus of Hohle Fels dates back at least 35,000 years to the Aurignacian era, and the Venus of Monruz dates back about 11,000 years to the Magdalenian. Such figurines were carved from soft stone (such as steatite, calcite or limestone), bone or ivory, or formed of clay and fired. The latter are among the oldest ceramics known to historians. In total, over 200 such figurines are known;[2] virtually all of modest size, between about 3 cm and 40 cm in height.[3] These figurines are recognised as some of the earliest works of prehistoric art.
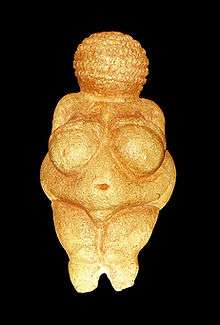
Most have small heads, wide hips, and legs that taper to a point. Arms and feet are often absent, and the head is usually small and faceless. Various figurines exaggerate the abdomen, hips, breasts, thighs, or female anatomy, although many found examples do not reflect these typical characteristics. Depictions of hairstyles can be detailed, and especially in Siberian examples, clothing or tattoos may be indicated.[4]
The original cultural meaning and purpose of these artefacts is not known. It has frequently been suggested that they may have served a ritual or symbolic function. There are widely varying and speculative interpretations of their use or meaning: they have been seen as religious figures,[5] an expression of health and fertility, grandmother goddesses or as self-depictions by female artists.[6]
History of discovery
The Vénus impudique, which was the figurine that gave the whole category its name, was the first Palaeolithic sculptural representation of a woman to be discovered in modern times. It was found in 1864 by Paul Hurault, 8th Marquis de Vibraye at Laugerie-Basse in the Vézère valley. This valley is one of the many important Stone Age sites in and around the commune of Les Eyzies-de-Tayac-Sireuil in Dordogne, southwestern France. The figurines were mostly discovered in settlement contexts, both in open-air sites and caves.[1] The Magdalenian Venus from Laugerie-Basse is headless, footless, armless, and displays a strongly emphasised female reproductive system.[7]
Four years later, Salomon Reinach published an article about a group of soapstone figurines from the caves of Balzi Rossi. The famous Venus of Willendorf was excavated in 1908 from a loess deposit in the Danube valley located in Austria. Since then, hundreds of similar figurines have been discovered from the Pyrenees Mountains to the plains of Siberia.
In September 2008, archaeologists from the University of Tübingen discovered a 6 cm figurine carved from a mammoth's tusk. This figurine was later called the Venus of Hohle Fels and can be dated to at least 35,000 years ago. It represents the earliest known sculpture of this type and the earliest known work of figurative art.[8]
Recent finds in Palestine and Syria have expanded the discoveries further East and deeper into the mists of time. A recent discovery of a goddess figure found at Golen Heights, Israel has been dated to at least 230,000 BCE. The Venus of Berekhat Ram, a possible human artifact, was found sandwiched between layers of volcanic ash dated to 230,000-700,000 BCE. during the Acheulean culture of the Lower Paleolithic period of the old Stone Age. The discovery at Berekhat Ram was followed by another discovery of a similar allegedly human created object in Morocco — the Venus of Tan-Tan—dated to the Middle Acheulean period, between 300,000 and 500,000 years. [Pre-dates humans using tools? ]
Name
Upper Palaeolithic female figurines are collectively described as "Venus figurines" in reference to the Roman goddess of beauty Venus. This decision was made because prehistorians of the early 20th century assumed the figurines represented an ancient ideal of beauty.
The expression, "Venus", was first used in the mid-nineteenth century by the Marquis de Vibraye, who discovered an ivory figurine and named it La Vénus impudique or Venus Impudica ("immodest Venus").[9] The Marquis then contrasted the ivory figurine to the Aphrodite Of Knidos, a Greco-Roman sculpture depicting Venus covering her naked body with both her hands.[9]
The use of the name is metaphorical as there is no link between the ancient figurines and the Roman goddess Venus; although they have been interpreted as representations of a primordial female goddess. The term has been criticised for being a reflection of Western ideas rather than reflecting the beliefs of the sculptures' original owners, but the original names are unknown as well so the term Venus has persisted.[10]
Like many prehistoric artefacts, the exact cultural meaning of these figures may never be known. Archaeologists speculate, however, that they may be symbolic of security and success, fertility, or a mother goddess.[11] The female figures are a part of Upper Palaeolithic art, specifically the category of Palaeolithic art known as portable art.
Figure details

The majority of Venus figurines are depictions of women, and follow artistic conventions of the times. Most of the figurines display the same body shape with the widest point at the abdomen and the female reproductive organs exaggerated. Oftentimes other details, such as the head and limbs, are neglected or absent which leads the figure to be abstracted to the point of simplicity. The heads are often of relatively small size and devoid of detail. Some may represent pregnant women, while others show no indication of pregnancy.[13]
The Venus of Willendorf and the Venus of Laussel (a rock relief rather than a figurine) bear traces of having been externally covered in red ochre. The significance of this is not clear, but is traditionally assumed to be religious or ritual in nature. Some human bodies from the Palaeolithic era are found similarly covered, so it is assumed this colour had a significant meaning in their culture even though we do not know what.[14]
All generally accepted Palaeolithic female figurines are from the Upper Palaeolithic. Although they were originally mostly considered part of the Aurignacian culture, the majority are now associated with the Gravettian and Solutrean cultures.[15] In these periods, the more rotund figurines are predominant. Within the Magdalenian cultures, the forms become finer with more detail and the styling of said figures started to become similar within areas of close contact.
Interpretation
.jpg)
There have been many differing interpretations of the figurines since their discovery[1] one of which comes from Helen Benigni. In her book, Emergence of the Goddess, she argues that the consistency in design of these featureless, large-breasted, often pregnant figures throughout a wide region and over a long period of time suggests they represent an archetype of a female Supreme Creator. Neolithic, Bronze Age, and Iron Age inhabitants likely connected women as creators innately tied to the cycles of nature. Through this, it was believed that women's birth and menstrual cycles aligned with lunar cycles and tides.[16]
It has been suggested that because of the way these figures are depicted, such as the large breasts and lack of feet and faces, these statues were made by women looking at their own bodies, as the perspective of their bodies they would have had mirrors that of the figurines, and they likely did not have access to mirrors.[17]
It has been suggested that they may be a sign of an earlier prevalence of steatopygia, now associated principally to women of certain African or Andamanese ancestry. However the Venuses do not qualify as steatopygian, since they exhibit an angle of approximately 120 degrees between the back and the buttocks, while steatopygia is diagnosed by modern medical standards at an angle of about 90 degrees only.[18]
Later female figurines and continuity
Some scholars suggest a direct continuity between Palaeolithic female figurines and later examples of female depictions from the Neolithic or Bronze Age.[21]
A female figurine which has 'no practical use and is portable' and has the common elements of a Venus figurine (a strong accent or exaggeration of female sex linked traits, and the lack of complete lower limbs) may be considered to be a Venus figurine, even if archaeological evidence suggests it was produced after the main Palaeolithic period. Some figurines matching this definition originate from the Neolithic era and into the Bronze Age. The period and location in which a figurine was produced helps guide archaeologists to reach conclusions as to whether the art piece found can be defined as a Venus figurine or not. For example, ceramic figurines from the late ceramic Neolithic may be accepted as Venus figurines, while stone figurines from later periods are not. This is a matter of ongoing debate given the strong similarity between many figurines from the Palaeolithic, Neolithic and beyond. A reworked endocast of a brachiopod from around 6000 BCE in Norway has been identified as a late Venus figurine.[22]
This means that a given female figurine may or may not be classified as a Venus figure by any given archaeologist, regardless of its date, though most archaeologists disqualify figurines which date later than the Palaeolithic, even though their purpose could have been the same.
Notable figurines
See also
- List of Stone Age art
- Matriarchal religion
- When God Was A Woman
Notes
- Fagan, Brian M., Beck, Charlotte, "Venus Figurines", The Oxford Companion to Archaeology, 1996, Oxford University Press, ISBN 9780195076189 pp. 740–741
- Holloway
- Fagan, 740
- "Clothing of figurines may be record of Ice Age tribes' skills". old.post-gazette.com. Retrieved 2019-11-13.
- Beck, 207-208
- William Haviland, Harald Prins, Dana Walrath, Bunny McBride, Anthropology: The Human Challenge, 13th edition, 2010, Cengage Learning, ISBN 0495810843, 9780495810841,google books; Cook; Beck, 205-208
- White, Randall (December 2008). "The Women of Brassempouy: A Century of Research and Interpretation" (PDF). Journal of Archaeological Method and Theory. 13 (4): 250–303. doi:10.1007/s10816-006-9023-z.
- Cressey, Daniel (13 May 2009). "Ancient Venus rewrites history books". Nature. News. doi:10.1038/news.2009.473.
- Beck, 202-203
- Dr. Beth Harris & Dr. Steven Zucker (27 May 2012). Nude Woman (Venus of Willendorf), c. 28,000-25,000 B.C.E. (youtube video). Smarthistory, Art History at Khan Academy. Event occurs at 0:21. Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- Soffer, O.; Adovasio, J. M.; Hyland, D. C. (Summer 2000). "The "Venus" Figurines: Textiles, Basketry, Gender, and Status in the Upper Paleolithic". Current Anthropology. 41 (4): 511–537. doi:10.1086/317381. ISSN 0011-3204.
- The body used is the local loess, with only traces of clay; there is no trace of surface burnishing or applied pigment. Pamela B. Vandiver, Olga Soffer, Bohuslav Klima and Jiři Svoboda, "The Origins of Ceramic Technology at Dolni Věstonice, Czechoslovakia", Science, New Series, 246, No. 4933 (November 24, 1989:1002-1008).
- Sandars, 29; Fagan, 740-741; Cook; Beck, 203-213, who analyses attempts to classify the figures.
- Sandars, 28
- Fagan, 740-741; Beck, 203
- Benigni, Helen, ed. 2013. The Mythology of Venus: Ancient Calendars and Archaeoastronomy. Lanham, Maryland : University Press Of America.
- Cook; McDermott, LeRoy. 1996. "Self-representation in Upper Paleolithic Female Figurines". Current Anthropology 37 (2). [University of Chicago Press, Wenner-Gren Foundation for Anthropological Research]: 227–75. JSTOR
- Softpedia, Stefan Anitei. "What is Steatopygia?". news.softpedia.com/. Retrieved 4 September 2016.
- "Site officiel du musée du Louvre". cartelfr.louvre.fr.
- "Figure féminine - Les Musées Barbier-Mueller". www.musee-barbier-mueller.org.
- Walter Burkert, Homo Necans (1972) 1983:78, with extensive bibliography, including P.J. Ucko, who contested the identification with mother goddesses and argues for a plurality of meanings, in Anthropomorphic Figurines of Predynastic Egypt and Neolithic Crete with Comparative Material from the Prehistoric Near East and Mainland Greece (1968).
- Tidemann, Grethe. "Venus fra Svinesund". Uniforum. University of Oslo. Retrieved 11 December 2014.
References
- Beck, Margaret, in Ratman, Alison E. (ed.), Reading the Body: Representations and Remains in the Archaeological Record, 2000, University of Pennsylvania Press, ISBN 0812217098, 9780812217094, google books
- Cook, Jill, Venus figurines, Video with Dr Jill Cook, Curator of European Prehistory, British Museum
- Fagan, Brian M., Beck, Charlotte, "Venus Figurines", The Oxford Companion to Archaeology, 1996, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0195076184, 9780195076189, google books
- Sandars, Nancy K. (1968), Prehistoric Art in Europe. Penguin: Pelican, now Yale, History of Art. (nb 1st ed.)
Further reading
- Abramova, Z., 1962: Paleolitičeskoe iskusstvo na territorii SSSR, Moskva : Akad. Nauk SSSR, Inst. Archeologii, 1962
- Abramova, Z., 1995: L'Art paléolithique d'Europe orientale et de Sibérie., Grenoble: Jérôme Millon.
- Cohen, C. : La femme des origines - images de la femme dans la préhistoire occidentale, Belin - Herscher (2003) ISBN 2-7335-0336-7
- Conard N., 2009: A female figurine from the basal Aurignacian deposits of Hohle Fels Cave in southwestern Germany. Nature, 2009; 459 (7244): 248 DOI: 10.1038/nature07995
- Cook, Jill 2013. Ice Age Art: the Arrival of the Modern Mind; London: British Museum Press. ISBN 978-0-7141-2333-2
- Delporte, Henri 1993. L'image de la femme dans l'art préhistorique, éd. Picard. (ISBN 2-7084-0440-7)
- Dixson, Alan F., and Barnaby Dixson. 2011. "Venus Figurines of the European Paleolithic: Symbols of Fertility or Attractiveness?" Journal of Anthropology 2011 [sic]: 1-11.
- Gvozdover, M., 1995: Art of the mammoth hunters: the finds from Avdeevo, (Oxbow Monograph 49), Oxford: Oxbow.
- Schlesier, Karl H. 2001. "More on the 'Venus' Figurines." Current Anthropology 42: 410-12.
- Soffer O., Adovasio J., Hyland D., 2000: The 'Venus' Figurines - Textiles, Basketry, Gender, and Status in the Upper * Paleolithic, Current Anthropology Volume 41, Number 4, August–October 2000
- Rau, S., Naumann D., Barth M., Mühleis Y., Bleckmann C., 2009: Eiszeit: Kunst und Kultur, Thorbecke, 2009, 396p. ISBN 978-3-7995-0833-9
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Venus figurines. |