Urea nitrate
Urea nitrate is a fertilizer-based high explosive that has been used in improvised explosive devices in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iraq, and various other terrorist acts elsewhere in the world, like the 1993 World Trade Center bombings.[2] It has a destructive power similar to better-known ammonium nitrate explosives, with a velocity of detonation between 11,155 ft/s (3,400 m/s) and 15,420 ft/s (4,700 m/s).[3]
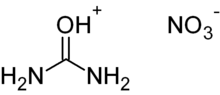 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.276 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
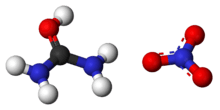
| CH5N3O4 | |
| Molar mass | 123.068 g/mol |
| Density | 1.67±0.011 g/cm3 [1] |
| Melting point | 157–159 °C (315–318 °F; 430–432 K) |
| 167.2±0.5 mg/mL [1] | |
| Solubility | Ethanol 14.2±0.1 mg/mL
Methanol 54.8±0.9 mg/mL Acetone 10.4±0.2 mg/mL [1] |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | Very low |
| Friction sensitivity | Very low |
| Detonation velocity | 4700 m/s |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   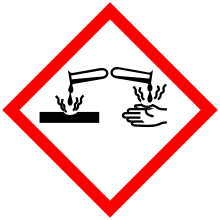 |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H201, H271, H301, H304, H314, H332 |
| P220, P233, P260, P250, P305+351+338 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Urea nitrate is produced in one step by reaction of urea with nitric acid. This is an exothermic reaction, so steps must be taken to control the temperature.
Urea nitrate explosions may be initiated using a blasting cap.[3]
Chemistry
Urea contains a carbonyl group. The more electronegative oxygen atom pulls electrons away from the carbon forming a greater electron density around the oxygen, giving the oxygen a partial negative charge and forming a polar bond. When nitric acid is presented, it ionizes. A hydrogen cation contributed by the acid is attracted to the oxygen and forms a covalent bond [electrophile H+]. The electronegative NO3− ion then is attracted to the positive hydrogen ion. This forms an ionic bond and hence the compound urea nitrate.
(NH2)2CO (aq) + HNO3 (aq) → (NH2)2COHNO3 (s)
The compound is favored by many amateur explosive enthusiasts as a principal explosive for use in larger charges. In this role it acts as a substitute for ammonium nitrate based explosives. This is due to the ease of acquiring the materials necessary to synthesize it, and its greater sensitivity to initiation compared to ammonium nitrate based explosives.
References
- Oxley, Jimmie & Smith, James & Vadlamannati, Sravanthi & Brown, Austin & Zhang, Guang & Swanson, Devon & Canino, Jonathan. (2013). Synthesis and Characterization of Urea Nitrate and Nitrourea. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics. 38. 10.1002/prep.201200178.
- Aaron Rowe (18 September 2007). "Chem Lab: Spray-On Test for Improvised Explosives". Wired.
- "Explosives - ANFO (Ammonium Nitrate - Fuel Oil)". GlobalSecurity.org.
Further reading
- Almog J, Burda G, Shloosh Y, Abramovich-Bar S, Wolf E, Tamiri T (November 2007). "Recovery and detection of urea nitrate in traces". J. Forensic Sci. 52 (6): 1284–90. doi:10.1111/j.1556-4029.2007.00551.x. PMID 17868267.
- Mr.X (July 2008). "Improvised Urea Nitrate". aware eZine Gamma. Archived from the original on 2008-09-20. Retrieved 2008-11-11.
.jpg)
