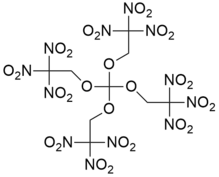
Trinitroethylorthocarbonate
Trinitroethylorthocarbonate also known as TNEOC is an oxidizer with excellent chemical stability. Its explosion point is 238 °C, and it begins to be decomposed at 200 °C. Its explosion heat is 5.797 J/g and specific volume is 694 L/kg.[1] Its structure is closely related to that of trinitroethylorthoformate (TNEOF). Both are highly explosive and very shock-sensitive, and may be dissolved in nitroalkanes to reduce their shock-sensitivity.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8N12O28 | |
| Molar mass | 732.219 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Melting point | 161 °C (322 °F; 434 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Liu, Jiping (2015). Liquid Explosives. Springer. pp. 5, 6, 8, 136, 309. ISBN 9783662458471. Retrieved 26 March 2016.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.