Treaty of Passarowitz
The Treaty of Passarowitz or Treaty of Požarevac was the peace treaty signed in Požarevac (Serbian Cyrillic: Пожаревац, German: Passarowitz), a town in the Ottoman Empire (modern Serbia), on 21 July 1718 between the Ottoman Empire on one side and Austria of the Habsburg Monarchy and the Republic of Venice on the other.[1]
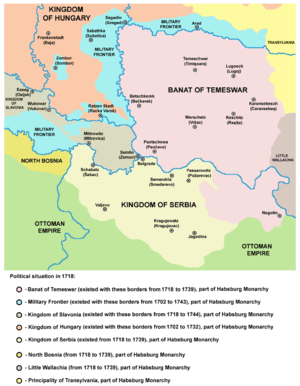 The central Balkans in 1718. Territories passed from the Turks to the Habsburg Monarchy were:
Territory passed from Wallachia to the Habsburg Monarchy: Lesser Wallachia (Oltenia)
| |
| Context |
|
|---|---|
| Signed | 21 July 1718 |
| Location | Passarowitz, Habsburg Kingdom of Serbia (now Požarevac, Serbia) |
| Mediators | |
| Parties | |

Background
Between 1714 and 1718, the Ottomans had been successful against Venice in Greece and Crete (Ottoman–Venetian War) but had been defeated at Petrovaradin (1716) by the Austrian troops of Prince Eugene of Savoy (Austro-Turkish War of 1716–1718).

Terms
The treaty reflected the military situation. The Ottoman Empire lost the Banat and southeastern Syrmia, central part of present-day Serbia (from Belgrade to south of Kruševac), and a tiny strip of northern Bosnia, while part of Wallachia (an autonomous Ottoman vassal) known as the Lesser Wallachia (Oltenia) was also ceded to the Habsburg Monarchy.
Venice renounced the Peloponnese peninsula (known as the Morea at the time), gained by the Treaty of Karlowitz, as well as its last remaining outposts in Crete and islands of Aegina and Tinos, retaining only the Ionian Islands (with Ottoman-occupied Kythera added to them) and the cities of Preveza and Arta on the Epirote mainland. In Dalmatia, it made some small advances, taking the areas of Imotski and Vrgorac in the hinterland.
Aftermath
The result of the treaty was the restoration of Habsburg administration over much of the territory of present-day Serbia, which they had temporarily occupied during the Great Turkish War between 1688 and 1690, and the effective establishment of the Kingdom of Serbia as a crown land. Following Passarowitz, a Habsburg crown land known as the Banat of Temeswar was also established.[2]
After another Austro-Turkish war, the 1739 Treaty of Belgrade made the Ottoman Empire regain northern Bosnia, Habsburg Serbia (including Belgrade) and southern parts of the Banat of Temeswar, and Lesser Wallachia (Oltenia) was returned to Wallachia.
See also
References
- Ingrao, Samardžić & Pešalj 2011.
- Ćirković 2004, p. 151.
Sources
- Hochedlinger, Michael (2013). Austria's Wars of Emergence: War, State and Society in the Habsburg Monarchy, 1683-1797. London & New York: Routledge.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ćirković, Sima (2004). The Serbs. Malden: Blackwell Publishing.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ingrao, Charles; Samardžić, Nikola; Pešalj, Jovan, eds. (2011). The Peace of Passarowitz, 1718. West Lafayette: Purdue University Press.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Treaty of Passarowitz. |
- "Treaty of Passarowitz". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Text of treaty in English
