Test and validation centre, Wegberg-Wildenrath
The Test and validation centre, Wegberg-Wildenrath (German: Prüf- und Validationscenter Wegberg-Wildenrath) is a railway test centre owned by Siemens Mobility near Wildenrath in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.[1]
| Test and validation centre, Wegberg-Wildenrath (connection and T1 Oval, T3 track) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Test and validation centre, Wegberg-Wildenrath (T2 Oval, T3/4/5 track) Urban Rail (Blue) - T2 Oval | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


History
The centre is located on the site of the former RAF Wildenrath British military airfield. After the airfield closed in 1992, it was taken over by Siemens who opened the test and validation centre in June 1997. By 2007, the railway test tracks had taken over considerable areas of the airfield, with all but the western threshold and overrun of the runway obliterated. The north-east dispersal is completely taken over by sidings, workshops and loops. Of the southern dispersals, the central and eastern are bisected by the main railway oval test track.
There are ovals of track for testing trains, and various electrification systems. The test track is connected to the rest of the German railway network by the German portion of the Iron Rhine freight railway, branching off near Wegberg.[2]
Testing
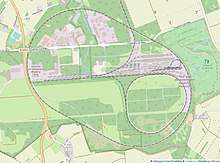
As well as Siemens the test tracks are also used by competitors such as Alstom and Bombardier Transportation.[1]
There are standard gauge and metre gauge tracks.[2] The facility is used for technical acceptance tests and approvals of locomotives,[3] rolling stock and trams[4] under operating conditions, and personnel training. It has been equipped for trials with Galileo.[5]
References
- "Independent testing at Wildenrath". Railway Gazette International. 1 September 2002.
- "Railway tests and test infrastructure right in the heart of Europe" (PDF). Siemens Mobility.
- "Siemens Vectron revealed". www.railcolor.net. 29 June 2010.
- "Next-generation Citadis tram on test". Railway Gazette International. 5 September 2008.
- "Siemens railway test site equipped for Galileo trials". Railway Gazette International. 10 August 2009.
External links
- Test- and Validationcenter Wegberg-Wildenrath, Siemens Mobility
- Railway tests and test infrastructure right in the heart of Europe, Siemens Mobility
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Siemens Test Centre Wegberg-Wildenrath. |