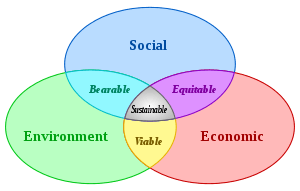
Sustainable consumption
Sustainable consumption (SC) is the use of material products, energy and immaterial services in such a way that it minimizes the impact on the environment, so that human needs can be met not only in the present but also for future generations. [1] Consumption refers not only to individuals and households, but also to governments, business, and other institutions. Sustainable consumption is closely related to sustainable production and sustainable lifestyles. "A sustainable lifestyle minimizes ecological impacts while enabling a flourishing life for individuals, households, communities, and beyond. It is the product of individual and collective decisions about aspirations and about satisfying needs and adopting practices, which are in turn conditioned, facilitated, and constrained by societal norms, political institutions, public policies, infrastructures, markets, and culture.". [2]
Sustainable Consumption, then, would also include analyses of efficiency, infrastructure, and waste, as well as access to basic services, green and decent jobs and a better quality of life for all.[3] It shares a number of common features with and is closely linked to the terms sustainable production and sustainable development. Sustainable consumption as part of sustainable development is a prerequisite in the worldwide struggle against sustainability challenges such as climate change, resource depletion, famines or environmental pollution.
Sustainable development as well as sustainable consumption rely on certain premises such as:
- Effective use of resources, and minimisation of waste and pollution
- Use of renewable resources within their capacity for renewal
- Fuller product life-cycles
- Intergenerational and intragenerational equity
The Oslo definition
The definition proposed by the 1994 Oslo Symposium on Sustainable Consumption defines it as "the use of services and related products which respond to basic needs and bring a better quality of life while minimizing the use of natural resources and toxic materials as well as emissions of waste and pollutants over the life cycle of the service or product so as not to jeopardize the needs of future generations."[4]
Strong and weak sustainable consumption
In order to achieve sustainable consumption, two developments have to take place: it requires both an increase in the efficiency of consumption as well as a change in consumption patterns and reductions in consumption levels in industrialized countries as well as rich social classes in developing countries which have also a large ecological footprint and give examples for increasing middle classes in developing countries.[5] The first prerequisite is not sufficient on its own and can be named weak sustainable consumption. Here, technological improvements and eco-efficiency support a necessary reduction in resource consumption. Once this aim has been met, the second prerequisite, the change in patterns and reduction of levels of consumption is indispensable. Strong sustainable consumption approaches also pay attention to the social dimension of well-being and assess the need for changes based on a risk-averse perspective.[6] In order to achieve what can be termed strong sustainable consumption, changes in infrastructures as well as the choices customers have are required. In the political arena, weak sustainable consumption has been discussed whereas strong sustainable consumption is missing from all debates.[7]
The so-called attitude-behaviour or values-action gap describes a significant obstacle to changes in individual customer behavior. Many consumers are well aware of the importance of their consumption choices and care about environmental issues, however, most of them do not translate their concerns into their consumption patterns as the purchase-decision making process is highly complicated and relies on e.g. social, political and psychological factors. Young et al. identified a lack of time for research, high prices, a lack of information and the cognitive effort needed as the main barriers when it comes to green consumption choices.[8]
Notable conferences and programs
- 1992 - At the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) the concept of sustainable consumption was established in chapter 4 of the Agenda 21.[9]
- 1995 – SC was requested to be incorporated by UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) into the UN Guidelines on Consumer Protection.
- 1997 – A major report on SC was produced by the OECD.[10]
- 1998 – United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) started a SC program and SC is discussed in the Human Development Report of the UN Development Program (UNDP).[11]
- 2002 – A ten-year program on sustainable consumption and production (SCP) was created in the Plan of Implementation at the World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD) in Johannesburg.[12]
- 2003 - The "Marrakesh Process" was developed by co-ordination of a series of meetings and other "multi-stakeholder" processes by UNEP and UNDESA following the WSSD.[13]
- 2018 - Third International Conference of the Sustainable Consumption Research and Action Initiative (SCORAI) in collaboration with the Copenhagen Business School.[14]
See also
- Collaborative consumption
- Sustainable consumer behavior
- Durable goods
- Overconsumption
- Degrowth
References
- Our common future. World Commission on Environment and Development. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 1987. ISBN 978-0192820808. OCLC 15489268.CS1 maint: others (link)
- Vergragt, P.J. et al (2016) Fostering and Communicating Sustainable Lifestyles: Principles and Emerging Practices, UNEP– Sustainable Lifestyles, Cities and Industry Branch, http://www.oneearthweb.org/communicating-sustainable-lifestyles-report.html , page 6.
- "Sustainable consumption and production". United Nations Sustainable Development. Retrieved 2018-08-15.
- Source: Norwegian Ministry of the Environment (1994) Oslo Roundtable on Sustainable Production and Consumption.
- Meier, Lars; Lange, Hellmuth, eds. (2009). The New Middle Classes. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9938-0. ISBN 978-1-4020-9937-3.
- Lorek, Sylvia; Fuchs, Doris (2013). "Strong Sustainable Consumption Governance - Precondition for a Degrowth Path?". Journal of Cleaner Production. 38: 36–43. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.08.008.
- Fuchs, Doris; Lorek, Sylvia (2005). "Sustainable Consumption Governance: A History of Promises and Failures". Journal of Consumer Policy. 28 (3): 261–288. doi:10.1007/s10603-005-8490-z.
- Young, William (2010). "Sustainable Consumption: Green Consumer Behaviour when Purchasing Products" (PDF). Sustainable Development (18): 20–31.
- United Nations. "Agenda 21" (PDF).
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (1997) Sustainable Consumption and Production, Paris: OECD.
- United Nations Development Program (UNDP) (1998) Human Development Report, New York: UNDP.
- United Nations (UN) (2002) Plan of Implementation of the World Summit on Sustainable Development. In Report of the World Summit on Sustainable Development, UN Document A/CONF.199/20*, New York: UN.
- United Nations Department of Social and Economic Affairs (2010) Paving the Way to Sustainable Consumption and Production. In Marrakech Process Progress Report including Elements for a 10-Year Framework of Programmes on Sustainable Consumption and Production (SCP). [online] Available at: http://www.unep.fr/scp/marrakech/pdf/Marrakech%20Process%20Progress%20Report%20-%20Paving%20the%20Road%20to%20SCP.pdf [Accessed: 6/11/2011].
- "Third International Conference of the Sustainable Consumption Research and Action Initiative (SCORAI)". CBS - Copenhagen Business School. 2018-03-07. Retrieved 2020-02-21.