Survey parties to the Northern Territory 1864–1870
A number of survey parties to the Northern Territory were involved in attempts to found a settlement in the Northern Territory during the years 1864–1870. This article describes attempts by the South Australian Government to found a settlement in the Northern Territory, and the people who took part in those ventures. It includes lists of all known participants.
Background
In 1863, the part of New South Wales to the north of South Australia between the 129th and 138th parallels of longitude East was annexed to South Australia, by letters patent, as the "Northern Territory of South Australia", which was abbreviated to the Northern Territory (6 July 1863).[1] The South Australian Government, with the Wakefield plan for colonisation of South Australia as a basis, believed that European settlement of the Northern Territory could be achieved in much the same way: by selling "off the plan" parcels of land to investors, and a great deal of money would go into Government coffers, which would be used for infrastructure, thus attracting further investment. All that was required was another Col. William Light, another George Gawler and a location for the new capital, which from the start was to be named "Palmerston".
Finniss expedition to Adam Bay 1864
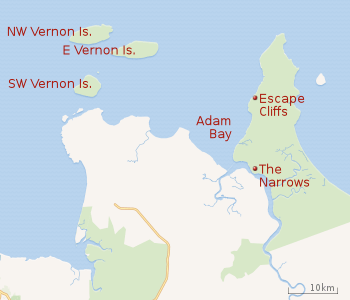 |
The first requirement for such a settlement was a safe harbour, and from previous explorers' experience, one stood out: Adam Bay, into which the Adelaide River flows, a river navigable for a considerable distance, where all kinds of wharfs and berths could be erected. There was little land at the mouth for buildings, but no doubt suitable areas would be found upstream.
Boyle Travers Finniss, a career public servant with some surveying experience, was put in charge of a body of some 40 officers and men, and whose task it was to establish a camp at a site of his choosing and mark out some 1000 town sites and a similar number of rural sites.
Finniss was not obliged to settle at Adam Bay; he chose it in preference to Port Darwin or Port Patterson on account of its harbour and the Adelaide River, which is navigable for a great distance inland, ignoring the lack of building materials, the low-lying boggy nature of the country. He chose two settlement sites; Escape Cliffs on the east coast of the bay, and The Narrows, a short distance up the Adelaide River, where there was a good landing for boats, and planned a connecting road of 6 miles (10 km).[2]
No substantial building was ever erected, apart from the Government Resident's house, in front of which he daily drilled his Guard, to the delight of the natives, who mimicked their exercises.[3]
No surveying could be done in first dry season due to insufficient manpower;[4] much of the stores never made it under cover, and much manpower was wasted keeping a lookout for marauding Aborigines. The Protector of Aborigines, Dr. Goldsmith, was refused membership of a party sent to recover stolen property, which turned into a reprisal, then after some horses were speared, refused inclusion in an armed party led by Finniss's son, when many shots were fired and at least one Aborigine killed.
Morale was low from the start. Only the Government Resident (Finniss) and a few favourites refused to admit that the choice of site was a huge mistake. Jealousies developed between various sections of the workforce as to who was getting preferential treatment or having the more odious duties to perform, the Government Resident and Surgeon (Sweet) were seen going off on "jaunts" with "favorites". Jealousies erupted and operations stumbled from crisis to crisis. The number of staff was augmented somewhat to replace those whose year's contract had expired; Finniss was recalled to answer accusations levelled against him, and others at the same time as witnesses or to answer charges related to the murder of several Aborigines. Some resigned and found their own way back to Adelaide. Many, whose one-year contract was over, returned at the same time.
Manton, left in charge of the depleted party, reported that it was certain there was no land within a hundred miles worth surveying, and they could do nothing more than protect themselves and their stores from the natives. In October 1866 Government ordered a recall of Manton and his men, along with those remaining of McKinlay's party on the steamer Eagle, Captain Hill, which left 11 January 1867, transhipped to the Rangatira at Sydney, and arrived at Port Adelaide 2 February 1867.
Personnel
| Name | Job/position | Depart Adelaide | Depart Adam Bay | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R. Arthur | in charge of stock | Ellen Lewis May 1866 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| J. Railton Atkinson | chainman | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Bengal May 1865, | Sacked by Finniss. From Surabaya to Singapore with Cottrell, died in India. |
| William Patrick Auld | labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Bengal May 1865 in charge of Sgt. Potter | killed aboriginal man 8 September 1864 near Chambers Bay, Northern Territory |
| Job Austin | visitor | South Australian October 1864 (privately) Bengal March 1865 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | later with Goyder expedition, OT |
| William N. de Bathe | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | William Nicholson M. de Bathe (c. 1846 – 4 December 1868) was son of horse breeder James Bathe, owner of Graham's Castle, Prospect. | |
| Samuel Baker | labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | died 28 March 1868 |
| Jacob Bauer | visitor, agent for land purchasers[5] | South Australian October 1864 (privately) | accompanied by wife Eliza and ten-year-old son. Drowned 12 October 1866 after falling from boat[6] | |
| Henry Baumgurtel | labourer, miner | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| S. Beard | in charge of stock | Ellen Lewis May 1866 | ||
| Robert Beard | visitor | South Australian October 1864 (privately) Bengal March 1865 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 Eagle January 1867 ? | later with Goyder expedition |
| J. J. Benham | Bengal March 1865 | Eagle January 1867 | ||
| J. W. O. Bennett | Draftsman | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | with Goyder expedition, speared to death |
| John Bohn | labourer and able seaman | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Beatrice November 1864? Bengal May 1865?[7] | |
| Bastin Boucaut | labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | died of fever 16 September 1864; brother of Sir J. P. Boucaut | |
| Thomas Brennan | blacksmith | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Charles Bright[8] | Reporter for The Argus | South Australian October 1864 | South Australian December 1864 | |
| Edward Burford | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Robert Charles Burton | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | joined McKinlay's party July 1866 later with Goyder expedition, OT |
| Stephen Chandler | labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | witness to murder of Aborigine 8 September 1864; died 29 March 1866 after drunken fight |
| G. C. Christie | visitor | South Australian October 1864 (privately) Bengal March 1865 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | returned in poor health |
| John Cleland | Bengal March 1865 | Eagle January 1867 | joined McKinlay's party July 1866 | |
| George Thomas Cottrell | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Bengal May 1865, thence to Singapore with Atkinson | |
| John Cowie | shoemaker and labourer, cook | Henry Ellis April 1864 | South Australian December 1864 | |
| James Davis | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Forlorn Hope May 1865 | |
| John Davis | Assistant Storekeeper | Henry Ellis April 1864 Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 Eagle January 1867 | |
| Firmin Deacon | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Bengal May 1865 | |
| James Deslandes | in charge of stock | Ellen Lewis May 1866 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| William Dougall | more info needed | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | tried with Auld for murder of Aborigine 8 September 1864.[9] |
| James Douglas | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | later with Goyder expedition |
| C. Dutton | in charge of stock | Ellen Lewis May 1866 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| John Dyer | labourer and bullock-driver | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| G. F. Edmunds | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Bengal May 1865 | |
| R. H. Edmunds | Surveyor | South Australian October 1864 | Beatrice August 1866 | joined McKinlay's party as surveyor and deputy leader November 1865[10] |
| Francis Edwards | labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Forlorn Hope May 1865 | |
| Joseph Atkinson Ewart | in charge of stock | Ellen Lewis May 1866 | Eagle January 1867 | Son of prominent hotelier, member of Stuart's 5th expedition.[11][12] later with Goyder expedition. |
| B. T. Finniss | leader and Government Resident | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Frederick Robe "Fred" Finniss | chainman | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | son of the Government Resident |
| R. E. Fisher | in charge of stock | Ellen Lewis May 1866 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| Walter Fisher | in charge of stock | Ellen Lewis May 1866 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| Michael Edward Fitch | chainman and Able Seaman | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | later with Goyder expedition, OT, Post Office |
| David Francis | crew of Bengal? | fell out of boat Julia 18 January 1865 when making her fast at The Narrows, swept away in swift-moving water | ||
| James Gilbert | labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Bengal May 1865 | |
| Thomas Sherlock Gillman | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Francis Edward Goldsmith | Surgeon and Protector of Aborigines | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Bengal May 1865 | resigned |
| C. W. Grainer | visitor | South Australian October 1864 (privately) | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | returned in poor health |
| D. Gray | in charge of stock | Ellen Lewis May 1866 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| Charles Hake | labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Forlorn Hope May 1865 | |
| Arthur R. Hamilton | Junior Surveyor | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Forlorn Hope May 1865 | |
| James Hill | in charge of stock | Ellen Lewis May 1866 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| Frank W. Hood | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| John Absalom Howe | carpenter | Henry Ellis April 1864 | South Australian December 1864 | |
| Charles S. Hulls | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | joined McKinlay's party November 1865[10] |
| David Johnson | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | joined McKinlay's party July 1866 later with Goyder expedition |
| George Kersley | staff member | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | later with Goyder expedition |
| Stephen King, jun. | Storekeeper and Superintendent of Stock | South Australian October 1864 | Bengal May 1865 on sick leave Ellen Lewis December 1865? | later with Goyder expedition |
| Thomas King | labourer and able seaman | Henry Ellis April 1864 | South Australian December 1864 | |
| E. C. Kirby | visitor | South Australian October 1864 (privately) | ||
| John G. Kirby | labourer, in charge of stock | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| R. M. Lewis | in charge of stock | Ellen Lewis May 1866 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| F. H. Litchfield | labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | died 1867 |
| J. V. Lloyd | visitor | South Australian October 1864 (privately) Bengal March 1865 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Charles William Machell[13] | chainman and Able Seaman | Henry Ellis April 1864 | perhaps same person as "Mitchell" on Beatrice November 1864 | |
| W. Mann | visitor | South Australian October 1864 | ||
| James Thomas Manton | Engineer and Surveyor | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| Henry Martin | labourer / in charge of stock | South Australian October 1864 Ellen Lewis May 1866 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 Eagle January 1867 ? | |
| Gilbert R. McMinn | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | later with Goyder expedition |
| William McMinn | chainman | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Forlorn Hope May 1865 | |
| William Moorshead | carpenter | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Owen Morris | Eagle January 1867 | joined McKinlay's party July 1866[14] | ||
| William S. Murray | seaman, labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Charles Edwin Neal | staff | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | later with Goyder expedition |
| H. D. Packard | Surveyor | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | accompanied by wife Mary Packard and their four-month-old daughter (Mary made history by in December 1866 giving birth to a daughter in the Top End) |
| Francis James "Frank" Packard | chainman | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| William Pearson | Surveyor | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Bengal May 1865 | on sick leave |
| Charles Pennycuick | more info needed | Beatrice November 1864 | dismissed by Finniss September? 1864 for "joining Ward clique"[4] | |
| Sgt. William Potter | police trooper | Ellen Lewis 1865 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| W. Read | chainman and Able Seaman | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Bengal May 1865 | later on OT, killed by crocodile |
| J. F. Roberts[15] | labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Bengal May 1865 | later with Goyder expedition, OT |
| James Ross | labourer, in charge of stock | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| W. Rowland | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| Jeremiah Ryan | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | joined McKinlay party November 1865[10] later with Goyder expedition |
| John Ryan | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Chris. Schmidt | staff | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| J. Dodson de Skelton | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | South Australian December 1864 | |
| Alfred Smith | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| William Smith | labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Bengal May 1865 | |
| Jefferson P. Stow | visitor, agent for land purchasers[5] | South Australian October 1864 | Forlorn Hope May 1865 | criticised frivolous use of Beatrice[16] |
| Wycliffe Stow | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | returned in poor health |
| Edward Strawbridge | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| John Stuckey | visitor, agent for land purchasers[5] | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Henry Thomas "Harry" Styles | labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | South Australian December 1864 | |
| G. Thompson | in charge of stock | Ellen Lewis May 1866 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| Alfred John Tod | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| Edward "Ned" Tuckwell | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | joined McKinlay party November 1865[10] later with Goyder expedition |
| John Varley | mason | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Frederick Wadham | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | returned in poor health, died 6 July 1878 |
| James Wadham | Junior Surveyor | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Yatala November 1864 | brother to at least one other Wadham[17] A niece, Bertha Mary Wadham (1863–1936), was mother of Sir Howard Florey |
| John Wadham | carpenter | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | sick with scurvy, died 30 May 1866 |
| W. H. Walker | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Alaric Ward | labourer | Henry Ellis April 1864 | killed an Aborigine at Escape Cliffs August 1864, himself speared and bludgeoned to death 31 July 1865 (listed on Ellen Lewis December 1865) | |
| Ebenezer Ward | Clerk in charge, Accountant, and Postmaster | Henry Ellis April 1864 | South Australian December 1864 | dismissed by Finniss September? 1864 for insubordination |
| R. J. (R. A?) Ware | labourer, cook | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Bengal May 1865 | ill at the same time as Pearson |
| George T. Warland | labourer, in charge of stock | South Australian October 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Richard Watson | Draftsman | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| John White | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Forlorn Hope May 1865 | |
| Eddowes J. Wilson | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | died of apoplexy 11 December 1864 | |
| D. B. Wiltshire | chainman and Able Seaman | Henry Ellis April 1864 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Clement Young | Postmaster and Clerk | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| John Young | labourer | South Australian October 1864 | Eagle January 1867 | joined McKinlay party November 1865[10] accidental death aboard Rangatira 1 February 1867[18] |
(for Legend see below following sub-section)
McKinlay expedition 1866
The Finniss expedition, which had left Adelaide with high expectations had, with each depressing report from the Territory, become a drag on Government, who decided what was needed was a small exploration party, unencumbered by such mundane tasks as erecting buildings and maintaining and protecting stores, to make a clear decision as to where the fertile land was, and where the capital should be. To that end they appointed John McKinlay to lead a party of twelve, to receive all support from the Finniss party, but to go where they might. Their ship also carried instructions to Finniss to return to Adelaide to answer criticisms of his administration. McKinlay did not receive the support he expected from Finniss's successor Manton, and did not commence exploration until 20 January, when rain interfered with his travels. They never reached Cape Hawkesbury, the Roper or the Victoria. Their lowest point came in June 1866 (not the Wet Season as sometimes reported)[19] when McKinlay, Edmunds and party, having one by one slaughtered their horses for food, were trapped in boggy land by the East Alligator River. Weak and malnourished with no chance of making it back to camp alive, they killed their two remaining horses for jerky and built a raft 21 by 9 by 4 feet (6.4 m × 2.7 m × 1.2 m) of horses' hides around a structure of green branches, and on 29 June started paddling down to the sea, and arrived back at Escape Cliffs on 5 July 1866.[20]
After recovering from their ordeal they made several coastal expeditions, visiting Anson Bay, the Daly River and Port Darwin.[5] He returned to Adelaide to a hero's welcome, despite having achieved nothing, though he did report having seen some good land near Anson Bay,[21] and thought Port Darwin had many advantages, but lacked fresh water.
Personnel
| Name | Job/position | Depart Adelaide | Depart Adam Bay | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Robert Charles Burton | Eagle January 1867 | joined July 1866 from Manton's party[14] later with Goyder expedition | ||
| John Cleland | Eagle January 1867 | joined 1866 from Manton's party[14] | ||
| David Collier | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Eagle January 1867 | ||
| Thomas Bagnold Crispe | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Eagle January 1867 | ||
| John Davis | storekeeper | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Eagle January 1867 | |
| R. H. Edmunds | surveyor and deputy leader | Beatrice August 1866 | joined from Finniss's party November 1865[10] | |
| Thomas Gilbanks (often Gillbanks) | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Eagle January 1867 | In charge of party after departure of McKinlay | |
| Thomas Glen | bushman | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Beatrice August 1866 | Brother-in-law of McKinlay |
| John Horner | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Eagle January 1867 | ||
| Charles S. Hulls | Eagle January 1867 | joined from Finniss's party November 1865[10] | ||
| David Johnston (often Johnson) | Eagle January 1867 | joined 1866 from Manton's party[14] later with Goyder expedition | ||
| George Gibson Mayo | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Beatrice August 1866 | ||
| John McKinlay | leader | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Beatrice August 1866 | |
| Dr. J. Stokes Millner | Surgeon and Protector of Aborigines | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Eagle January 1867 | with Goyder expedition |
| G. P. Morris | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Eagle January 1867 | ||
| Owen Morris | Eagle January 1867 | joined 1866 from Manton's party[14] | ||
| William Potter | Police trooper | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Ellen Lewis December 1865 | |
| Jeremiah Ryan | Eagle January 1867 | Joined from Finniss's party November 1865[10] | ||
| Francis William Thring | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Eagle January 1867 | Stuart's third officer on his two longest expeditions. | |
| Edward "Ned" Tuckwell | Eagle January 1867 | joined from Finniss's party November 1865[10] | ||
| Samuel Watts | Ellen Lewis September 1865 | Eagle January 1867 | ||
| John Young | labourer | Eagle January 1867 | joined McKinlay party November 1865[10] accidental death aboard Rangatira 1 February 1867[18] |
- Legend
- Leaving SA
- Henry Ellis April 1864 Henry Ellis, ship, 412 tons; Capt. Phillips left Port Adelaide 23 April 1864, arrived Adam Bay 20 June 1864[22]
- Government schooner Yatala, Humbert, left Port Adelaide 18 May 1864. Capt. Humbert was dismissed by Finniss October 1864.[23]
- South Australian October 1864 steamer South Australian, 435 tons, J. Pain, left Port Adelaide 29 October 1864 arrived Adam Bay December 1864[24] with 47 passengers, including 40 Government appointees.
- Surveying schooner Beatrice 93 tons, Hutchinson R.N., left Port Adelaide 9 April 1864 for Northern Territory. Arrived Adam Bay. Returned from Koepang with supplies 1 October 1864, returned Port Adelaide 14 December 1864.
- Lt. Frederick Howard R.N. succeeded Commander Hutchison as officer in charge January 1865; left Port Adelaide 18 February 1865 arrived Adam Bay 8 April 1865 with pay for men, took Auld to Port Darwin for brief exploration.[25] explored Adelaide River May 1865,[26] September 1865 exploring Victoria River, then to Koepang for provisions;[27] Sourabaya for supplies December 1865; Departed Adam Bay August 1866 arrived Port Adelaide arrived with McKinlay and three or four other passengers 26 September 1866.
- Bengal March 1865 Bengal left Port Adelaide 3 March 1865 with 6 passengers[28] arrived Adam Bay 21 April 1865.
- Ellen Lewis September 1865 336 tons, Stephen Hellon master. John McKinlay and party of 12 left Port Adelaide 25 September 1865, arrived Adam Bay 5 November 1865.
- Ellen Lewis May 1866 Ellen Lewis left Port Adelaide May 1866 for Adam Bay with stock and 11 passengers.
- Leaving NT
- Beatrice November 1864 Beatrice left Adam Bay 9 November 1864,[29] arrived Port Adelaide 14 December 1864.
- Yatala November 1864 Yatala left Adam Bay 9 November 1864[29]
- South Australian December 1864 South Australian left Adam Bay c. 10 December 1864 with Ward, King, five others[30]
- Bengal May 1865 Swedish barque Bengal, Peterson master, left Adam Bay 6 May 1865 for Surabaya with 13 passengers; two transshipped to Singapore; the rest by Douglas to Melbourne, thence to Adelaide.
- Forlorn Hope May 1865 seven men left Adam Bay 6 May 1865 on an open sailing boat, dubbed Forlorn Hope, purchased from skipper of Bengal
- Schooner Beatrice left Adam Bay for Adelaide
- Ellen Lewis December 1865 Ellen Lewis left Adam Bay 1 December 1865, arrived Port Adelaide 13 February 1866 with Finniss, Litchfield and 30 others.[31][32][33]
- Beatrice August 1866 Beatrice left Adam Bay 14 August 1866, arrived Port Adelaide via Koepang 26 September; McKinlay and three or four passengers only.
- Eagle January 1867 Steamer Eagle, Captain Hill, left Adam Bay 11 January 1867, transhipped to Rangatira at Sydney; arrived Adelaide February 1867.[34][35]
Cadell expedition 1867
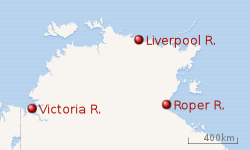 |
In January 1867, realising they had no alternative site chosen for the capital, the South Australian Government instructed Captain Francis Cadell to assemble a party to investigate the coast of the Northern Territory, to choose areas suitable for agriculture, and a site for the settlement. Cadell and a few associates left for Sydney, where he engaged the wooden steamer Eagle for six months, with the option of extending for another three or six. There he also hired a crew (preferring not to employ South Australians)[36] which would have included a number of woodcutters to feed the steamer's voracious boilers once the coal had been consumed. He had the ship refitted in Brisbane, and on 20 April the party of 26 men left for Victoria River.[37] Cadell had an interesting nine months' expedition and made several useful findings, including the true nature of Flinders' Probable Islands in Arnhem Bay. He named the strait between Elcho Island and the mainland Cadell Strait after himself and the mainland peninsula Napier Peninsula after his surveyor. He discovered the mouth of the Roper River,[38] and the condition (untouched) of the Escape Cliffs settlement. They visited Koepang for re-provisioning. They also returned to Burketown, Queensland at least once for the same reason.[38] He took only 20 horses, so was unable to investigate far inland, and made no strong recommendation for the site of the capital, though his choice ultimately fell on the Liverpool River, in Arnhem Land.[39]
A. T. Saunders (1854–1940), South Australia's noted amateur historian and critic of Cadell the self-publicist and influence-peddler, had little to say on this page in his history. One contemporary newspaper editor however, held nothing back in his satire on Cadell's pomposity.[40]
Personnel
| Name | Job/position | Depart Adelaide | Joined Sydney | Returned Adelaide | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Francis Cadell | Leader | Coorong February 1867 | Aldinga February 1868 | ||
| John M. Creed | Surgeon | information needed | supported charges of Cadell's cruelty.[41] | ||
| George Fraser | blacksmith | information needed | accidentally shot himself dead c. September 1867[39] | ||
| R. Hodges | Coorong February 1867 | on a previous Cadell exploration party[42] | |||
| M. Mason | Coorong February 1867 | ||||
| T. Morris | Coorong February 1867 | on a previous Cadell exploration party[42] | |||
| Francis Napier | surveyor/engineer | information needed | Died 1875 without death notice or obituary, but clearly a favorite of Cadell.[43] Author of Voyage from NSW to the North Coast of Australia, 1867[38] | ||
| G. Philcox | Coorong February 1867 |
No information has been found on Hodges, Mason and Philcox, who have also been listed as Hodge, Massen and J Philcox[44] and nothing on the 20-odd from Sydney and Brisbane.
- Legend
Coorong February 1867 Left Port Adelaide 26 February 1867 on Coorong for Sydney, where he chartered steamer Eagle and light draught steamer firefly; picked up a surgeon and exploring party
He returned to Sydney by Eagle 21 January 1868, paid off his workers, disposed of stores, remained in Sydney while the Duke of Edinburgh was in town, then by the Aldinga to Adelaide on 13 February 1868. No mention was made of any associates, but the South Australian public was wearied of the continued waste of money on "frolics" in the Territory, and by Cadell in particular.
Goyder expedition 1869
After four years of hearing nothing but reports of lack of progress in surveying land they had paid for, land-order-holders in England and Australia (mostly speculators with no intention of ever settling in the Territory) began agitating for a refund of their money, with interest, and would not be mollified by explanations of the difficulties involved, and the expense to which the Colonial Government had been put. In March 1868 it was decided to offer a refund with interest to those who wanted out, and to those who were prepared to hang on for an extra year, a sweetener in the increase of the plot size from 160 to 240 acres (later increased to 320).[45] Public tenders were called for the surveying of 420,000 acres, which The Advertiser cynically reckoned would result in no, or exceedingly inflated, bids and would therefore be undertaken by the Surveyor-General's department.[46] The outcome was a little of both: George Goyder (the Surveyor-General) offered to organise and lead the expedition, and survey 420,000 acres (1,700 km2) receiving his usual salary plus a bonus of £3,000 for successful completion within a year at a cost of £25,000, not counting shipping costs. Parliament leapt at the proposal, such was Goyder's reputation for integrity, energy and vision. The fact that the South Australian Government was losing no time and grudging no expenditure on a successful outcome, and putting their best man in charge of the venture, restored much confidence in the investors in Northern Territory property.[47]
Goyder's plan was to appoint six 1st Class Surveyors of his choosing; they would appoint their own 2nd Class Surveyors and Cadets, and where possible the "arms and legs": the chainmen, trenchers, cook and stock handlers, otherwise these appointments would be made by Goyder from men he knew. He agreed with the purchase of horses and cattle from Brisbane, but rejected suggestions that any men should be picked up there; he wanted men he knew and who respected him. They would land at Port Darwin and work their way towards the fertile lands of the Upper Adelaide and Victoria Rivers.[48] He insisted on all provisions being supplied in Adelaide to his specifications (10,000 lbs beef and mutton prepared by the Melbourne Meat Preservation Company (S. S. Ritchie's process), rather than relying on store cattle and sheep.[49] He also ordered 20 tons of dry-ground flour, being less affected by tropical conditions than the moist-ground flour used by bakers).[5] and personally inspected by him.
Goyder gave strict instructions to his men that for their own safety, interactions with the natives should be strictly limited: none to be allowed in the camp; strictly no touching Aboriginal women under any circumstances, the greatest source of animosity; never to go out alone, and not to leave the camp unarmed; to use firearms as a last resort and to aim at a person only when one's own life was in peril. To respect Aboriginal property, and not to engage in any form of retribution. Two men, Hardy and Greene, ignored this last injunction and smashed several of their canoes and pushed two others into the current, for no good reason, and received a dressing-down from the Surveyor-General.
The men worked hard and efficiently and the whole of the surveying job was completed by August 1869.
Personnel
Includes some information on those of Goyder's parties who remained or returned to the NT to participate in Charles Todd's Overland Telegraph (OT) Line construction.
| Name | Job/position | Left Port Adelaide | Left Port Darwin | Left Adelaide for OT project | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| George Sydney Aldridge[50] | Surveyor, Cadet, 2nd Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | ||
| James Henry Aldridge [51] | Chainman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | OT cadet under Knuckey & C. Giles | |
| C. Almers | carpenter | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT under Knuckey and C. Giles | |
| George A. Armstrong | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| Job Austin | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT labourer under Harvey & Roberts |
| William Barlow | Assistant Photographer | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| Robert W. Barrow | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| George Bayfield | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Govt Resident's staff as teamster, OT as teamster. Friend of Deane and engaged to his sister Ny. | ||
| Robert Beard | In Charge of Horses | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | had been on Finniss's 1864 expedition | |
| Tom Bee | Surveyor, Cadet, 1st Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | Born 4 July 1850 in Brompton, England, educated at AEI, worked on OT under McMinn & Musgrave, later postmaster several SA towns, died 21 November 1919 in Millicent, South Australia.[52] |
| David Landel Beetson | Surveyor, Cadet, 2nd Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | acted as land selection agent,[53] prospected for gold, had (with S. King and C. Schmidt) first private house in Palmerston, insolvent, died in WA. | |
| Frederick John Bennett[5] | Wellsinker | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| J. W. O. Bennett | Draftsman | Moonta December 1868 | Bennett and William Guy speared by Aborigines 24 or 25 May 1869. Bennett died 28 May, the day after Dr Peel removed, under chloroform, broken spear point which had passed into chest cavity.[54] Buried on Fort Hill, Darwin. | ||
| Michael Bennett | Teamster | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| Edwin S. Berry | Draftsman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| Henry John Boord | Police trooper | Govt Resident's staff; became publican, Windmill Hotel, Nailsworth, Commercial Hotel Grenfell Street, died 27 July 1885, aged 41 | |||
| Henry S. Bosworth | Chainman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| Joseph Brans | Boatman/labourer | Gulnare February 1869 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Appointed to Govt Resident's staff | |
| J. S. Brooking | Surveyor, Cadet, 1st Class | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Deputy Surveyor-General of W.A., retired 1896, died November 1916. | |
| Joseph Brooks | Photographer and Draftsman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | perhaps poundkeeper near Balaklava | |
| Philip Henry Burden | Surveyor, Cadet, 2nd Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | In 1875 draftsman with Surveyor-General's Dept. | |
| Martin Burke | Trencher | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| James Burton | Coxswain | Gulnare February 1869 | Omeo December 1871 | Govt. Resident's staff; later with OT under A. J. Mitchell | |
| R. C. Burton | Staff | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | overseer with OT. An American, he was later with W.A. Government | |
| Thomas Cherry | Chainman | Moonta December 1868 | labourer on Govt. Resident's staff | ||
| Robert Collard | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | labourer on Govt. Resident's staff, then joined OT party | ||
| William Collett | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Omeo August 1870 | OT laborer under Harvey & Roberts |
| William Cook | not known | Gulnare February 1869 | appointed Port Darwin's Pilot and Harbor Master June 1892 | ||
| W. H. Cornish[55] | Chainman | Moonta December 1868 | later had career with Survey Department | ||
| Walter Dalwood | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Moonta March 1869[56] | sent back to Adelaide as invalid,[5] but he was also wanted for bigamy (jailed).[57] died July 1894 | |
| Daniel Dominick Daly (signed himself D. Daniel Daly) | Surveyor, 2nd Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | nephew of Sir Dominick Daly | |
| George Price Deane | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Omeo December 1871 | stockman on Govt. Resident's staff, later with OT under A. J. Mitchell | |
| James Divine | Officers' cook | Kohinoor December 1869 | Joined by wife and three children; appointed to Govt Resident's staff | ||
| David Donley (also Donnolly) | Steward,[5] Chief Cook and repairer of instruments | Moonta December 1868 | joined Gulnare as cook April 1869[5] | ||
| James Hereford Douglas | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | ||
| F. Drought | Police corporal | Govt Resident's staff | |||
| Henry Edwards | Chainman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Returned to NT with wife and children January 1870 per Kohinoor | |
| T. Edwards | labourer | labourer on Govt. Resident's staff | |||
| Joseph Atkinson Ewart | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT laborer under Harvey & Roberts, later resident of Roper River area,[58] killed himself by pistol shot at Wandi, Northern Territory, on 17 May 1901.[59] |
| William John Hillary Farrant | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT laborer under Woods & Jarvis |
| William Fisher | Chainman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Omeo August 1870 | OT wireman under Knuckey & C. Giles |
| Michael Edward Fitch | boatman | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT laborer under McMinn & Musgrave | |
| Paul Foelsche | Inspector of Police | Kohinoor December 1869 | NT Government appointment | ||
| Michael Francis | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Omeo August 1870 | OT cook under Knuckey & C. Giles |
| Donald Fraser | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| Charles Fry | Teamster | Moonta December 1868 | Appointed to Govt Resident's staff; joined by wife and three children per Kohinoor January 1870. Died in Gothenburg disaster | ||
| Adam Gaire | Cook | Moonta December 1868 | |||
| R. Gallattly | Cook | Kohinoor December 1869 | Govt Resident's staff, temporary replacement for Paul Hoppa | ||
| William John Gepp[60] | Veterinary surgeon, farrier and blacksmith | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Had own business 1893 | |
| John Gerald | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Omeo August 1870 | John Gerrald was OT labourer under Woods & Jarvis |
| C. Giles, jun. | Surveyor, Cadet, 1st Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869[61] Gulnare January 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT leader under Knuckey |
| G. W. Goyder | Surveyor-General | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| Charles Newton Greene | Surveyor, Cadet, 1st Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | ||
| William Gunn | Trencher | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| William Guy | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | speared in buttock by Aborigines at Fred's Pass May 1869 in same attack that killed Bennett. Guy, treated by Dr Peel, recovered. | |
| Dennis Haire (also Heir) | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| William M. Hardy | Draftsman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | ||
| William Harvey | Surveyor, 1st Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT Inspector w/ Roberts |
| H. Hatch | more info needed | Kohinoor February 1870 | on Bengal August 1871 for OT | ||
| Robert Hayball | Teamster | Moonta December 1868 | Appointed to Govt Resident's staff as a labourer. Joined by wife and children January 1870 per Kohinoor | ||
| William Brelsford Hayes | Gardener | Moonta December 1868 | Govt. Resident's staff. Died 18 June 1878 at Palmerston two months after being acquitted of attempting to shoot at a native. | ||
| Richard Hazard | Cook | Moonta December 1868 | Hazard, a "coloured"[5] man aged 42, died (of pneumonia?) at Fort Point 9 August, 1869, buried alongside Bennett[62] | ||
| Patrick Healey | Trencher | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| Henry Hemming | Staff | Moonta December 1868 | worked with Goyder before, later prospector.[63] | ||
| Alex. Hicks | Staff | Moonta December 1868 | |||
| Richard Hinton | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| W. W. Hoare[64] | Doctor's Assistant | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Watercolour illustrations of Schultze's specimens. Returned to England[65] | |
| William Hodge | labourer | Kohinoor December 1870 | Govt Resident's staff | ||
| William George Holland | Staff | Moonta December 1868 | |||
| Wilhelm Ludwig Homeyer | Staff | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | A friend of Richard Schomburgk, he advocated cultivation of wattles[66] | |
| F. W. "Frank" Hood | Staff | Moonta December 1868 | Appointed NT Government Accountant, Postmaster, Storekeeper | ||
| R. A. Horn | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | station manager brother of T. S. Horn. | |
| T. S Horn | Trencher | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| Matthew Houston | Chainman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| William Houston | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT labourer under Knuckey & C. Giles |
| W. Howe, sen. | more info needed | Gulnare September 1869[61] | |||
| George R. Hughes | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT labourer under Knuckey & C. Giles |
| Henry H. Irwin | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | ||
| David Johnston (often Johnson) | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT laborer under McMinn & Musgrave |
| Renney Kappler | Police trooper | Govt Resident's staff | |||
| Michael Keeley | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| George Kelley | Cook | ''Kohinoor December 1869 | Govt Resident's staff? | ||
| J. G. Kelly | Ship's carpenter | Govt Resident's staff | |||
| Pat. Kelly | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT labourer under Knuckey & C. Giles |
| Alexander "Alick" Kennedy | Staff | Moonta December 1868 | Moonta March 1869[56] | Sacked by Goyder for deserting his post and disobeying orders[54] | |
| George Kersley | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Omeo August 1870 | OT cook under Woods & Jarvis |
| Stephen King, jun. | Surveyor, 2nd Class | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| R. R. Knuckey | Surveyor, 2nd Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Omeo August 1870 | OT inspector w/ C. Giles |
| Heinrich or Henry Ralfs Krüss[67] | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT labourer under McMinn & Musgrave |
| Peter Krüss | Teamster | Moonta December 1868 | died in NT January 1874 while member of a prospecting party[68] | ||
| J. M. Lambell | Accountant and Postmaster | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo December 1871 | OT under A. J. Mitchell |
| Charles Laycock | Cook | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Omeo August 1870 | OT cook under Knuckey & C. Giles |
| Arthur Frederick Lines (1845–1914) | Chainman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | A. H. Smith married his sister. daughter of Oscar J. Lines. | |
| Charles Lines | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | not clearly related to A. F. Lines | |
| John Loudon (not London) | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| Thomas Loveday | Trencher | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| R. J. Loveday, jun | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| Cornelius Lowther | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | boatman/labourer on Govt. Resident's staff | |
| John Lowther | Trencher | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | boatman/labourer on Govt. Resident's staff, OT under Knuckey & C. Giles |
| Hugh Campbell MacCallum bka H. C. McCallum | cadet Surveyor | more info needed | Acted as secretary to Goyder, who suffered rheumatism. Appointed to Govt. Resident's staff | ||
| J. Massey | Police trooper | Govt Resident's staff | |||
| Donald McAulay | Wellsinker | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| J. McIntyre | teamster/labourer | Govt Resident's staff | |||
| Terence McIntyre | Wellsinker | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | ||
| Alexander L. McKay | Surveyor, Cadet, 1st Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | Died in Gothenburg disaster | |
| Alexander McKenzie | Cook | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT under Beckwith & Wills |
| George Galbraith McLachlan | Surveyor, 1st Class | Moonta December 1868 | Appointed to Govt Resident's staff. Died of lung disease 19 March 1873, at Port Darwin | ||
| Gilbert R. McMinn | Surveyor, 1st Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | OT inspector with C. Musgrave | |
| James McPherson | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| A. E. Millar (also Miller) | not known | Gulnare February 1869 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| Charles A. Miller (also Millar) | not known | Gulnare February 1869 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| James A. Miller | boatman? | Gulnare February 1869 | boatman/labourer on Govt. Resident's staff | ||
| J. Stokes Millner | Surgeon, Protector of Aborigines | Kohinoor December 1869 | Appointed to Govt Resident's staff, whole family died in Gothenburg disaster | ||
| W. Whitfield Mills | Surveyor, 2nd Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | on Elder Scientific Exploring Expedition, 1891–1892, prospector in W.A. | |
| Alex James Mitchell | Surveyor, 1st Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Omeo December 1871 | later with OT. Described by Edwin Smith as brilliant but erratic,[5] he had four or five children by Annie Sloper Cornish, then in 1877 eloped bigamously to America.[69] |
| E. Martin Moyse | Wellsinker | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| Patrick Molloy (often Mulloy) | Teamster | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | OT teamster under Woods & Jarvis | |
| W. Charles Musgrave | Chainman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Omeo August 1870 | OT sub-inspector under McMinn; died in Gothenburg disaster |
| Charles Edwin Neal | Stockman | Kohinoor December 1869 | Govt Resident's staff appointment? | ||
| Thomas Neate | Axeman/Mason | Moonta December 1868 | Omeo December 1871 | Govt Resident's staff, later with OT under A. J. Mitchell | |
| North Smith | more info needed | Kohinoor February 1870 | |||
| John G. Nottage | Store Assistant | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| James Oborn | Teamster | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| H. D. Packard | Surveyor, Cadet, 1st Class | Moonta December 1868 | Appointed surveyor on Govt Resident's staff. Mrs Packard and children arrived by Kohinoor January 1870. | ||
| John Harrison Packard[69] | Chainman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | brother of H. D. Packard, became prominent surveyor | |
| Charles J. Palmer | Teamster | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT teamster under Woods & Jarvis, died on the OT. |
| Dr. Robert Peel | Surgeon | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| John Penrose | blacksmith | Kohinoor December 1869 | Govt Resident's staff appointment | ||
| William "Billy" Plaisted | Chainman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | mason/labourer in Govt Resident's staff | |
| Robert Price | Teamster | Moonta December 1868 | |||
| R. Rice | teamster/labourer | Govt. Resident's staff | |||
| George Richards | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| Alexander "Paddy" Ringwood[70] | Draftsman | Moonta December 1868 | Govt Resident's staff, worked on OT, later meteorologist under C. Todd | ||
| Edward Cecil Rix | Doctor's assistant | Kohinoor December 1869 | Govt Resident's staff; medical officer to OT | ||
| J. F. Roberts | Surveyor, Cadet, 2nd Class | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT sub-inspector under Harvey |
| Jas. Robinson | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT labourer under McMinn & Musgrave |
| William Rowe, jun. | Staff | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT saddler under Knuckey & C. Giles |
| William Rowe, sen. | In Charge of Horses | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| Edward J. Ryan | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | labourer on Govt. Resident's staff | ||
| Jeremiah "Jerry" Ryan | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | stockman on Govt. Resident's staff | |
| Michael C. Ryan | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| Walter L. Samson | Staff | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | ||
| T. Sayers (also Sayer) | Blacksmith | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| Alfred Schultze | Assistant Botanist | Moonta December 1868 | son of Frederick | ||
| Frederick Schultze[71] | Botanist | Moonta December 1868 | Stayed on by request of Government Resident. | ||
| Andrew Smith | not known | Gulnare February 1869 | |||
| Arthur Henry Smith | Surveyor, 1st Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | brother-in-law of Goyder; made bathetic suicide attempt in 1868,[72] died 24 September 1909 in Perth, WA. | |
| Edwin Mitchell Smith[73] | Surveyor, 2nd Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | ||
| H. Q. Smith | Police trooper | Govt Resident's staff | |||
| John W. Smith | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT laborer under Harvey & Roberts |
| Charles Spencely | Cook | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Appointed Govt Resident's staff but returned with wife and children per Kohinoor 1870 | |
| N.? Wm? Spooner | Goyder's boatman[74] | Gulnare February 1869 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| C. W. L. Sprigg | Surveyor, Cadet, 2nd Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare January 1870 | with public service when he died 1875 | |
| William Stanborough | Chainman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT labourer under Woods & Jarvis |
| Thomas Stevens | Steward,[5] Cook | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| Robert Rowland Stevenson | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| William George Stretton | Police trooper | Govt Resident's staff, career public servant[75] | |||
| Joseph Middlemore Thomas | Surveyor, 2nd Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | with Lands Titles Office until retirement 1904[76] | |
| Edward "Ned" Tuckwell | Mechanic | Moonta December 1868 | Appointed to Govt Resident's staff. Joined by wife and four children per Kohinoor January 1870 | ||
| (Samuel) Grosvenor Walters | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo December 1871 | OT under A. J. Mitchell |
| Alfred Warren | Trencher | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | Omeo August 1870 | OT head teamster under Knuckey & C. Giles |
| Benjamin Wells | assistant carpenter | Govt Resident's staff | |||
| Charles Frederick Wells | Surveyor, Cadet, 2nd Class | Moonta December 1868 | Omeo December 1871 | Govt Resident's staff, later with OT under A. J. Mitchell | |
| R. Wells | Carpenter | Moonta December 1868 | |||
| David Wilson | Teamster | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| Frederick M. Wilson | Axeman | Moonta December 1868 | Kohinoor February 1870 | ||
| A. T. Woods[77] | Surveyor, 1st Class | Moonta December 1868 | Gulnare September 1869 | Omeo August 1870 | OT inspector w/ Jarvis |
- Legend
- Leaving SA
- Moonta December 1868 Ship Moonta, 627 tons,[78] T. Barneson, departed Port Adelaide 23 December 1868,[79] but was held up three days at North Arm before getting underway,[80] arrived Port Darwin 5 February 1869.
- Schooner Sea Ripple 126 tons, T. Bicknell, intended as a link between Darwin and Koepang, and for exploration purposes, should have left Adelaide with building materials in January 1869 but was condemned as unsuited to the region. Gulnare was purchased in her place.[81] Of course Goyder and party had no knowledge of these delays and feared the worst.
- Gulnare February 1869 Schooner Gulnare, 150 tons, Capt. Samuel W. Sweet (also a noted photographer), left Adelaide 12 February 1869 arrived Port Darwin 27 March 1869.
- Gulnare left Adelaide 23 June 1869 for Koepang and Port Darwin, arrived 23 August 1869. No passengers, though with the sudden revival of interest in the Territory, many put their names forward.[82]
- Kohinoor December 1869 Barque Kohinoor, 280 tons, Capt. Bicknell, left Adelaide 16 December 1869 with settlers,[83] arrived Port Darwin 21 January 1870
- Omeo August 1870 Steamer Omeo chartered by Darwent & Dalwood officers S. King, W. McMinn, Burton, E M Bagot had contract for distributing provisions from depot at Mount Margaret, Harvey Bacon had a store 200 miles to north.. 5 gangs (from north) Harvey, A T Woods, Beckwith, McMinn, Knuckey; each 120 miles of line.[84]
- Omeo December 1871 Steamer Omeo chartered by Charles Todd.[85]
- Leaving NT
- Moonta March 1869 Moonta left Port Darwin 4 March, arrived Port Wallaroo 23 April with curios and botanical samples, poss. passengers: Dalwood, Kennedy.
- Gulnare left 30 April 1869 for Koepang and Adelaide, arriving 7 June 1869.[86]
- Gulnare September 1869 Gulnare left Port Darwin 28 September 1869 arrived Adelaide 15 November 1869.[61] Donley part of crew, may have left ship at Port Adelaide.
- Gulnare January 1870 Gulnare, Capt. Sweet, left Port Darwin 21 January 1870 arrived Port Adelaide 27 March 1870 with 12 officers and 7 men.[87]
- Kohinoor February 1870 Kohinoor, Thomas Bicknell, left Port Darwin 6 February 1870 arrived Port Adelaide 10 April 1870.[88]
1868 article about Daly's administration
From an article entitled "The Administration of Sir Dominick Daly, K.B." in the Adelaide Register, dated 28 February 1868:
SETTLEMENT
From the close of Stuart's first overland journey in 1859 little doubt seems to have been entertained by his fellow-colonists as to his ultimate success. So enthusiastic was our then Governor, Sir Richard MacDonnell, about the capabilities of the newly-discovered country that he applied to the Colonial Office for its immediate annexation to South Australia. The Duke of Newcastle replied that it was too soon to speak of that until the practicability of the overland route had been demonstrated. During the next few years additional evidence was discovered, not only by Stuart himself, but by Burke and Wills, McKinlay, Landsborough, and other contemporary explorers. The Duke of Newcastle was applied to a second time, not in the interests of South Australia, however, but of Queensland. Ignoring altogether the large share of credit due to South Australian explorers, and the prior claim of the South Australian Government, he offered the whole of the north coast to Queensland, the then pet colony of Downing-street. She had the modesty to confess that one-half of the white elephant would be enough for her, and so a line was drawn at the west side of the Gulf of Carpentaria. South Australia repeated her request for Arnheim's Land, unfortunately with success. The Waterhouse Ministry, before they retired from office in July, 1863, had the satisfaction of hearing from the Duke of Newcastle that their resolutions passed in Executive Council on the undesirability of annexing the whole of Northern Australia to Queensland had carried conviction to his mind. All that portion between the 129th and 138th degrees of east longitude was to be handed over to the "temporary guardianship" of South Australia. So ended the prologue to our Northern Territory melodrama. The first act must needs open with a Ministerial crisis, and in the transformation scene those who had opposed annexation became its executive, while some of its official originators enrolled themselves in the opposition. Among the founders of the Adam Bay settlement were a Chief Secretary (Mr. Ayers), a Treasurer (Captain Hart), and a Commissioner of Crown Lands (Mr. Glyde), who on the shady side of the House had spoken against annexation as a very equivocal benefit. They had deprecated the ambition of the Waterhouse Government in proposing to send stock overland, and within twelve months they shipped from Port Adelaide a full-blown colony, with Government Resident, Secretary, guard of honour and valet-de-chambre for His Excellency, Police and Police Inspectors, Surveyors and Surveyor Generals, labourers and gentlemen farmers — altogether a perfect specimen of a ready-made municipality. But hothouse colonization did not suit the climate of Adelaide River. Disgusted with two years' experience of it, we tried a little exploring again, and Mr. McKinlay spent a pleasant winter on the East Alligator River at the expense of the Northern Territory Fund. To complete the programme of dilettante colonization our only further requirement was a marine survey à la Marco Polo, which Captain Cadell has given us. Now we can turn round and conscientiously say to the land-order-holders — the would-be cotton-planters and paddy-cultivators of Adam Bay — that we have done our best for them in that particular direction. Had the Duke of Newcastle been alive, with what gusto might the land-order-holders have poured their grievances into his sympathetic ear ; what invidious comparisons might they not have drawn between the Queensland style of settlement and our own ! There on one side of the boundary is Escape Cliffs, with its abandoned stores hid away under tarpaulins, and "the old Chief Mira" as special constable keeping guard over them. On the other side is Burke Town, a flourishing depot for the squatting stations on the Plains of Promise. From Queensland stock has been allowed to eat its way gradually down the Flinders, the Cloncurry, and the Albert Rivers. It has not only cost nothing to the Brisbane Government, but has been a large source of profit to the country. From South Australia not a single head of cattle has entered Arnheim's Land, unless by sea, and after eating its head off half a dozen times over on the voyage, seventy thousand pounds spent on a four years' infatuation, and the net result is— two hundred pounds worth of marine stores left on Escape Cliffs as a souvenir of the Finniss regime ! If history could be expunged as easily as Parliamentary votes, the words "Northern Territory" would never more be seen in our annals.[89]
References
- Territorial evolution of Australia – 6 July 1863
- "Topics of the Day". The South Australian Advertiser. VII (1994). South Australia. 16 December 1864. p. 2. Retrieved 22 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Adam Bay Settlement". Sydney Mail. VI (266). New South Wales, Australia. 5 August 1865. p. 11. Retrieved 7 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory". South Australian Register. XXVIII (5658). South Australia. 16 December 1864. p. 2. Retrieved 22 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- Goyder Kerr, Margaret The Surveyors Rigby, Adelaide 1971 ISBN 978-0-85179-287-3 (Mrs Kerr was a grand-daughter of G. W. Goyder).
- "The Northern Territory Party". South Australian Register. XXXI (6320). South Australia. 5 February 1867. p. 2. Retrieved 25 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory Expedition". The South Australian Advertiser. VIII (2185). South Australia. 31 July 1865. p. 3. Retrieved 21 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Anecdotal Photographs: Charles Bright". Table Talk (386). Victoria, Australia. 18 November 1892. p. 4. Retrieved 22 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory Murder Case". South Australian Weekly Chronicle. VIII (393). South Australia. 17 February 1866. p. 7. Retrieved 5 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Arrival of the Ellen Lewis". The Adelaide Express. III (674). South Australia. 14 February 1866. p. 2. Retrieved 1 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia. "increased his party by five . . . numbering 14" explanation needed
- "South Australia". The Melbourne Leader. X (264). Victoria, Australia. 19 January 1861. p. 11. Retrieved 23 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Mr Stuart's Party". South Australian Register. XXV (4455). South Australia. 25 January 1861. p. 2. Retrieved 23 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Late C. W. Machell". The Bunyip (1, 075). South Australia. 8 May 1885. p. 2. Retrieved 23 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Northern Territory". South Australian Register. XXX (6212). South Australia. 29 September 1866. p. 2. Retrieved 21 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Late Mr. Le M. F. Roberts". The Register (Adelaide). LXXV (19, 840). South Australia. 14 June 1910. p. 8. Retrieved 22 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory". The Adelaide Express. III (641). South Australia. 6 January 1866. p. 3. Retrieved 2 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "North Australia". South Australian Register. XXVIII (5603). South Australia. 13 October 1864. p. 2. Retrieved 22 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia. John c. 1828; Fred c. 1831; James c. 1833
- "Victoria". The South Australian Advertiser. South Australia. 5 February 1867. p. 3. Retrieved 23 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "McKinlay". Adelaide Observer. LIV (2, 912). South Australia. 24 July 1897. p. 33. Retrieved 1 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Mr. McKinlay's Exploration". The South Australian Advertiser. South Australia. 29 September 1866. p. 7. Retrieved 28 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Arrival of the Beatrice". Kapunda Herald And Northern Intelligencer. II (101). South Australia. 28 September 1866. p. 2. Retrieved 28 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Shipping Intelligence". South Australian Register. XXVIII (5456). South Australia. 25 April 1864. p. 2. Retrieved 21 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory". South Australian Register. XXVIII (5657). South Australia. 15 December 1864. p. 3. Retrieved 2 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia. diary also has good accounts of Ward's, Goldsmith's sackings
- "Departure of the Northern Territory Expedition". South Australian Register. XXVIII (5618). South Australia. 31 October 1864. p. 3. Retrieved 21 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Northern Territory Despatches". The South Australian Advertiser. VIII (2202). South Australia. 19 August 1865. p. 3. Retrieved 1 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory". South Australian Register. XXIX (5976). South Australia. 27 December 1865. p. 4. Retrieved 2 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "News from the Northern Territory". The Adelaide Express. III (627). South Australia. 18 December 1865. p. 3. Retrieved 2 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Shipping News". The South Australian Advertiser. VII (2060). South Australia. 6 March 1865. p. 2. Retrieved 21 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory". South Australian Weekly Chronicle. VII (335). South Australia. 7 January 1865. p. 5. Retrieved 23 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Steamer South Australian". The South Australian Advertiser. VII (2007). South Australia. 3 January 1865. p. 2. Retrieved 22 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Arrival of the Ellen Lewis". South Australian Register. XXX (6017). South Australia. 14 February 1866. p. 2. Retrieved 28 May 2019 – via National Library of Australia.Complaint to Capt. Hellon by 34 passengers
- "Advertising". South Australian Register. XXX (6017). South Australia. 14 February 1866. p. 1. Retrieved 29 May 2019 – via National Library of Australia. letter to Capt Hellon requesting stop at Koepang
- "The News from the Northern Territory". South Australian Register. XXX (6026). South Australia. 24 February 1866. p. 3. Retrieved 21 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia. perhaps a better list
- "The Northern Territory Expedition". South Australian Register. XXXI (6319). South Australia. 4 February 1867. p. 2. Retrieved 21 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Abandonment of the Adam Bay Settlement". The Australasian. II (44). Victoria, Australia. 2 February 1867. p. 22. Retrieved 22 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Captain Cadell's Mission". The South Australian Advertiser. South Australia. 6 March 1867. p. 2. Retrieved 27 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Despatches on Northern Territory". Adelaide Observer. XXV (1339). South Australia. 1 June 1867. p. 2. Retrieved 27 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Voyage of the "Eagle"". The Daily Telegraph (10896). New South Wales, Australia. 25 April 1914. p. 15. Retrieved 27 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Despatches from Captain Cadell". The Express and Telegraph. IV (1, 155). South Australia. 2 October 1867. p. 2. Retrieved 26 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Ulysses of the Northern Territory". South Australian Register. XXXII (6651). South Australia. 29 February 1868. p. 2. Retrieved 29 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "To the Editor of the Herald". The Sydney Morning Herald (15, 275). New South Wales, Australia. 11 March 1887. p. 9. Retrieved 29 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory Expedition". South Australian Register. XXXI (6337). South Australia. 25 February 1867. p. 2. Retrieved 27 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "To the Editor". The Sydney Morning Herald. XXXIX (6292). New South Wales, Australia. 6 August 1858. p. 4. Retrieved 4 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Shipping News". The Express and Telegraph. IV (973). South Australia. 27 February 1867. p. 2. Retrieved 28 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "A Northern Territory Policy at Last". South Australian Register. XXXII (6661). South Australia. 12 March 1868. p. 2. Retrieved 30 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Advertiser". The South Australian Advertiser. XI (3109). South Australia. 1 October 1868. p. 2. Retrieved 1 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory". The South Australian Advertiser. XI (3124). South Australia. 19 October 1868. p. 2. Retrieved 1 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory Survey". The South Australian Advertiser. XI (3126). South Australia. 21 October 1868. p. 2. Retrieved 4 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia. This article includes a list of all tenders for the work.
- "The Northern Territory Expedition". South Australian Register. XXXII (6900). South Australia. 17 December 1868. p. 2. Retrieved 5 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Obituary". The Chronicle (Adelaide). LIV (2, 766). South Australia. 26 August 1911. p. 42. Retrieved 14 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "A Veteran Sportsman". The Advertiser (Adelaide). South Australia. 12 November 1925. p. 14. Retrieved 14 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Obituary". The South Eastern Times. South Australia. 25 November 1919. p. 2. Retrieved 21 June 2020 – via Trove.
- "Advertising". The South Australian Advertiser. South Australia. 21 March 1870. p. 1. Retrieved 16 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- G.W. Goyder. "Northern Territory Survey Expedition, 1868-70; Diary kept by the Surveyor General Jan 1 to Sep 18 1869" (PDF). Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- "Death of H. H. Cornish". South Australian Register. LIII (12, 951). South Australia. 17 May 1888. p. 5. Retrieved 16 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "News from the Northern Territory". The Express and Telegraph. VI (1, 626). South Australia. 24 April 1869. p. 1. Retrieved 24 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Police Courts". South Australian Register. XXXIII (7019). South Australia. 8 May 1869. p. 3. Retrieved 24 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Northern Territory Times". Northern Territory Times And Gazette. II (89). Northern Territory, Australia. 17 July 1875. p. 1. Retrieved 23 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Wandi Tragedy". Northern Territory Times And Gazette. XXII (1438). Northern Territory, Australia. 31 May 1901. p. 3. Retrieved 23 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Death of Mr W. J. Gepp". The Mail (Adelaide). 3 (150). South Australia. 27 March 1915. p. 3. Retrieved 17 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Arrival of the Gulnare from the Northern Territory". South Australian Register. XXXIII (7182). South Australia. 15 November 1869. p. 2. Retrieved 24 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia. 34 names listed including "Jerrold", which is yet a mystery
- "Mr Goyder's Official Despatches". The South Australian Advertiser. South Australia. 16 November 1869. p. 2. Retrieved 24 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "A Prospector's Tragic Death". Adelaide Observer. LIX (3, 166). South Australia. 7 June 1902. p. 34. Retrieved 13 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "William Webster Hoare". DAAO. Retrieved 23 June 2019.
- "Concerning People". The Register (Adelaide). LXXXII (22, 167). South Australia. 24 November 1917. p. 6. Retrieved 16 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Wattle Culture". South Australian Register. XLVII (11, 259). South Australia. 14 December 1882. p. 1. Retrieved 19 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Late H. R. Kruss". The Advertiser (Adelaide). XLIII (13, 277). South Australia. 8 May 1901. p. 7. Retrieved 16 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia. Footballer Hermy Kruss was a son.
- "Mining Intelligence". The Express and Telegraph. XI (3, 099). South Australia. 24 February 1874. p. 3. Retrieved 16 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "No title". Glen Innes Examiner And General Advertiser. 5 (157). New South Wales, Australia. 10 October 1877. p. 4. Retrieved 18 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Week". South Australian Weekly Chronicle. XXVII (1, 389). South Australia. 4 April 1885. p. 11. Retrieved 18 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- Lon Wallis and Ray Dundon. "Frederick Schultze". Top End Plant Society. Retrieved 17 June 2019.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- "General News". The Express and Telegraph. V (1, 461). South Australia. 3 October 1868. p. 2. Retrieved 15 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Death of Mr. E. M. Smith". The Advertiser (Adelaide). South Australia. 22 April 1929. p. 11. Retrieved 19 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Parliament". South Australian Register. XXXVI (7720). South Australia. 12 August 1871. p. 5. Retrieved 16 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Death of Mr Stretton". The Advertiser. LXII (19108). South Australia. 10 January 1920. p. 7. Retrieved 16 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Concerning People". The Register (Adelaide). LXXV (19, 865). South Australia. 13 July 1910. p. 6. Retrieved 16 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Late Mr A. T. Woods". South Australian Register. LVII (14, 359). South Australia. 19 November 1892. p. 5. Retrieved 19 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Northern Territory Expedition". South Australian Register. XXXII (6897). South Australia. 14 December 1868. p. 3. Retrieved 13 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Going On Board". The South Australian Advertiser. XI (3191). South Australia. 6 January 1869. p. 4. Retrieved 7 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory". The Adelaide Observer. XXVII (1439). South Australia. 1 May 1869. p. 10. Retrieved 24 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory". South Australian Register. XXXIII (6938). South Australia. 2 February 1869. p. 5. Retrieved 6 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Summary for England". Evening Journal (Adelaide). I (141). South Australia. 19 June 1869. p. 2. Retrieved 6 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory Staff". The Evening Journal (Adelaide). I (294). South Australia. 18 December 1869. p. 3. Retrieved 13 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia. It is not clear which of these appointments travelled by Kohinoor.
- "The Overland Telegraph". South Australian Register. XXXV (7434). South Australia. 10 September 1870. p. 5 (Supplement to the South Australian Register.). Retrieved 14 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Overland Telegraph Expedition". The Evening Journal (Adelaide). III (903). South Australia. 19 December 1871. p. 2. Retrieved 15 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Northern Territory". South Australian Register. XXXIII (7044). South Australia. 7 June 1869. p. 3. Retrieved 6 July 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Shipping Intelligence". South Australian Register. XXXIV (7281). South Australia. 14 March 1870. p. 4. Retrieved 28 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "Shipping Intelligence". South Australian Register. XXXIV (7305). South Australia. 11 April 1870. p. 4. Retrieved 17 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- "The Administration of Sir Dominick Daly, K.B." South Australian Register. XXXII (6650). South Australia. 28 February 1868. p. 2. Retrieved 29 June 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
Further reading
- Cross, Jack (2011) Great Central State: The Foundation of the Northern Territory Wakefield Press.
- Substantial sections of this work are free to view on-line.