Substrate presentation
Substrate presentation is a biological process that activates a protein. The protein is sequestered away from its substrate and then activated by release and exposure of the protein to its substrate.[1][2] A substrate is typically the substance on which an enzyme acts but can also be a protein surface to which a ligand binds. The substrate is the material acted upon. In the case of an interaction with an enzyme, the protein or organic substrate typically changes chemical form. Substrate presentation differs from allosteric regulation in that the enzyme need not change its conformation to begin catalysis.
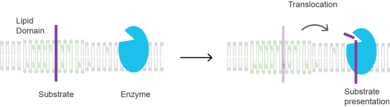
Types
SARS-CoV-2
(Furin) (producing cell, replication). When cells are loaded with cholesterol furin traffics to GM1 lipid rafts where it is localized with the palmitoylated spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 and primes it for viral entry[3].
(ACE2) (target Cell, viral entry), the receptor for SARS-CoV-2 ACE2 traffics SARS-CoV-2 to GM1 lipid rafts where it is endocytosed and exposed to cathepsin for cleavage and optimal cells fusion[4]. In low cholesterol ACE2 traffics the virus to TMPRSS2 which also cleaves and allows viral entry but through a surface mechanism that is much less efficient. The sensitivity of ACE2 to cholesterol is thought to contribute to less severe COVID19 symptoms in children.
Amyloid Precursor Protein
Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is cleaved by beta and gamma secretase to yield a 40-42 amino acid peptide responsible for beta amyloid plaques associated with Alzheimers disease. The enzymes are regulated by substrate presentation.[5] The substrate APP is palmitoylated and moves in and out of GM1 lipid rafts in response to astrocyte cholesterol. Cholesterol delivered by apolipoprotein E (ApoE) drives APP to associate with GM1 lipid rafts. When cholesterol is low the protein traffics to the disordered region and is cleaved by alpha secretase to produce a non amylogenic product. The enzymes do not appear to response to cholesterol, only the substrate moves.
Hydrophobicity drives the partitioning of molecules. In the cell, this gives rise to compartmentalization within the cell and within cell membranes. For lipid rafts, palmitoylation regulates raft affinity for the majority of integral raft proteins.[6] Raft regulation is regulated by cholesterol signaling.
Phospholipase D2
(PLD2) is a well-defined example of an enzyme activated by substrate presentation.[7] The enzyme is palmitoylated causing the enzyme to traffic to GM1 lipid domains or "lipid rafts". The substrate of phospholipase D is phosphatidylcholine (PC) which is unsaturated and is of low abundance in lipid rafts. PC localizes to the disordered region of the cell along with the polyunsaturated lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). PLD2 has a PIP2 binding domain. When PIP2 concentration in the membrane increases, PLD2 leaves the GM1 domains and binds to PIP2 where it then gains access to its substrate PC and commences catalysis based on substrate presentation. Presumably, the enzyme is capable of catalyzing a reaction in a lipid raft but lacks a substrate for activity.

Mechanisms of activation
sequestration
Phase separation, endometriosis, vesicle formation, organelle trafficking Either the substrate of the enzyme can move. Movement is typically the disruption of palmitate mediated localization. For proteins that are both palmitoylated and bind PIP2, increasing the concentration of PIP2 favors trafficking of the enzyme out of lipid rafts to PIP2. PIP2 is primarily polyunsaturated which causes the lipid to localize away from lipid rafts and allows the PIP2 to oppose palmitate mediated localization.[8]
Regulation
Cholesterol
Cholesterol and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) regulate lipid raft formation, hence the biological function of rafts. When saturated lipids and cholesterol increase in the membrane, lipid rafts increase their affinity for palmitoylated proteins[9]. PUFAs have the opposite effect, they fluidize the membrane.
PUFAs
PUFAs may also increase the concentration of signaling lipids. The arachidonic acid, a very common PUFA in the brain, incorporates into PC[10]. Arachidonyl PC is a preferred substrate of PLD likely increasing the amount of PA in a cell. Regulation of raft function by cholesterol effectively regulates substrate presentation and the many palmitoylated proteins that utilize substrate presentation as a mechanism of activation. While speculative, the profound effect of cholesterol and PUFAs on human health is likely through physiological regulation of lipid raft function in cells.
Role in Biology
mechanosensation
Mechanical force (shear or swell) can independently disrupt the packing and resultant affinity of palmitate to lipid rafts. This disruption also causes PLD2 to favor trafficking to PIP2 domains. [11]
anesthesia
General anesthetic propofol and inhaled anesthetics xeon, chloroform, isoflurane, diethyl ether disrupt lipid raft function including palmitate mediated localization of PLD2 to lipid rafts.[12][13] Activation of PLD then activates TREK-1 channels. The membrane mediated PLD2 activation could be transferred to an anesthetic insensitive homolog TRAAK, rending the channel anesthetic sensitive.
References
- Petersen, EN; Pavel, MA; Wang, H; Hansen, SB (28 October 2019). "Disruption of palmitate-mediated localization; a shared pathway of force and anesthetic activation of TREK-1 channels". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1862 (1): 183091. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.183091. PMC 6907892. PMID 31672538.
- Robinson, CV; Rohacs, T; Hansen, SB (September 2019). "Tools for Understanding Nanoscale Lipid Regulation of Ion Channels". Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 44 (9): 795–806. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2019.04.001. PMC 6729126. PMID 31060927.
- Wang, Hao; Yuan, Zixuan; Pavel, Mahmud Arif; Hansen, Scott B. (29 May 2020). "The role of high cholesterol in age-related COVID19 lethality". bioRxiv: 2020.05.09.086249. doi:10.1101/2020.05.09.086249.
- Wang, Hao; Yuan, Zixuan; Pavel, Mahmud Arif; Hansen, Scott B. (29 May 2020). "The role of high cholesterol in age-related COVID19 lethality". bioRxiv: 2020.05.09.086249. doi:10.1101/2020.05.09.086249.
- Wang, Hao; Kulas, Joshua A.; Ferris, Heather A.; Hansen, Scott B. (18 June 2020). "Regulation of amyloid processing in neurons by astrocyte-derived cholesterol". bioRxiv: 2020.06.18.159632. doi:10.1101/2020.06.18.159632.
- Levental, I; Lingwood, D; Grzybek, M; Coskun, U; Simons, K (21 December 2010). "Palmitoylation regulates raft affinity for the majority of integral raft proteins". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (51): 22050–4. Bibcode:2010PNAS..10722050L. doi:10.1073/pnas.1016184107. PMC 3009825. PMID 21131568.
- Petersen, EN; Chung, HW; Nayebosadri, A; Hansen, SB (15 December 2016). "Kinetic disruption of lipid rafts is a mechanosensor for phospholipase D." Nature Communications. 7: 13873. Bibcode:2016NatCo...713873P. doi:10.1038/ncomms13873. PMC 5171650. PMID 27976674.
- Hansen, SB (May 2015). "Lipid agonism: The PIP2 paradigm of ligand-gated ion channels". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 1851 (5): 620–8. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.01.011. PMC 4540326. PMID 25633344.
- Levental, I; Lingwood, D; Grzybek, M; Coskun, U; Simons, K (21 December 2010). "Palmitoylation regulates raft affinity for the majority of integral raft proteins". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (51): 22050–4. Bibcode:2010PNAS..10722050L. doi:10.1073/pnas.1016184107. PMID 21131568.
- Petersen, E. Nicholas; Gudheti, Manasa; Pavel, Mahmud Arif; Murphy, Keith R.; Ja, William W.; Jorgensen, Erik M.; Hansen, Scott B. (5 September 2019). "Phospholipase D Transduces Force to TREK-1 Channels in a Biological Membrane". bioRxiv 10.1101/758896.
- Petersen, EN; Pavel, MA; Wang, H; Hansen, SB (28 October 2019). "Disruption of palmitate-mediated localization; a shared pathway of force and anesthetic activation of TREK-1 channels". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1862 (1): 183091. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.183091. PMC 6907892. PMID 31672538.
- Petersen, EN; Pavel, MA; Wang, H; Hansen, SB (1 January 2020). "Disruption of palmitate-mediated localization; a shared pathway of force and anesthetic activation of TREK-1 channels". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1862 (1): 183091. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.183091. PMID 31672538.
- Pavel, Mahmud Arif; Petersen, E. Nicholas; Wang, Hao; Lerner, Richard A.; Hansen, Scott B. (19 June 2019). "Studies on the mechanism of membrane mediated general anesthesia". bioRxiv 10.1101/313973.