Spanish Virgin Islands
The Spanish Virgin Islands, (Spanish: Islas Vírgenes Españolas) formerly called the Passage Islands (Spanish: Islas del Pasaje) and also known as the Puerto Rican Virgin Islands (Spanish: Islas Vírgenes de Puerto Rico, Islas Vírgenes Puertorriqueñas), primarily consisting of the islands of Culebra and Vieques, are part of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, and are located east of the main island of Puerto Rico in the Caribbean.[1]
| Spanish: Islas Vírgenes de Puerto Rico / Islas Vírgenes Españolas | |
|---|---|
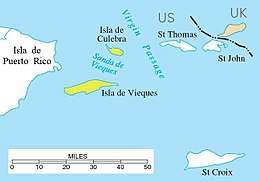 Location of the Spanish Virgin Islands (yellow) between Puerto Rico (left) and Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands | |
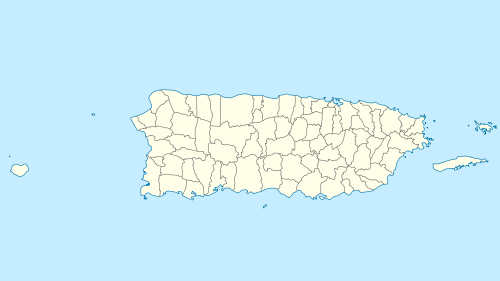 Spanish Virgin Islands / Puerto Rican Virgin Islands  Spanish Virgin Islands / Puerto Rican Virgin Islands  Spanish Virgin Islands / Puerto Rican Virgin Islands | |
| Geography | |
| Coordinates | 18°13′36.27″N 65°20′18.38″W |
| Archipelago | Virgin Islands |
| Adjacent bodies of water | Caribbean sea |
| Area | 165.1 km2 (63.7 sq mi) |
| Administration | |
| Territory | Puerto Rico |
| Municipality | Culebra and Vieques |
| Largest settlement | Isabel Segunda (pop. 1459) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 11,119 |
| Pop. density | 67.35/km2 (174.44/sq mi) |
History
Like Puerto Rico, the islands belonged to Spain until 1898. On September 19, 1898, the United States took possession of the islands after the signing of the armistice that ended military operations in the Spanish-American war. The islands, along with the islands of Puerto Rico, Mona, Monito, Desecheo, and other smaller islands adjacent to the island of Puerto Rico, were formally ceded by Spain to the United States with the signing of the Treaty of Paris on December 10, 1898.
Geography

Puerto Rican tourist literature uses the name Spanish Virgin Islands, but most general maps and atlases do not treat these islands as part of the Virgin Islands archipelago. They are mostly referred to as "Islas Municipio"[2] with Vieques being called "Isla Nena".[3] As part of Puerto Rico, the Passage Islands are part of a territory of the United States, and they belonged to Spain before the Spanish–American War in 1898. Spanish remains the predominant language, although English is also common.
The principal islands of the group are Culebra and Vieques, with multiple associated smaller islands and islets. Other islands that are close to the shore of Puerto Rico include: Icacos Island, Cayo Lobo, Cayo Diablo, Palomino Island, Palominito Island, Isla de Ramos, Isla Pineiro, Cayo Lobo. Near Culebra there is Cayo Luis Peña.
Culebra's smaller island, Cayo Norte, is part of Culebra National Wildlife Refuge.[4] Much of Vieques is part of Vieques National Wildlife Refuge, formerly a U.S. Navy facility.[5]
References
- Howorth, Michael (January 1999). "For the Beauty of It". Yachting. p. 44. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- "Grave la flota que sirve a las islas municipio". El Nuevo Dia (in Spanish). August 25, 2019.
- "Directorio de Municipios de Puerto Rico". PR GOV (in Spanish).
- U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service. "Culebra National Wildlife Refuge" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 14, 2006. Retrieved March 7, 2007.
- U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service. "Vieques National Wildlife Refuge" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 4, 2006. Retrieved March 7, 2007.