Slavery in the colonial United States
Slavery in the colonial history of the United States, from 1600 to 1776, developed from complex factors, and researchers have proposed several theories to explain the development of the institution of slavery and of the slave trade. Slavery strongly correlated with Europe's American colonies' need for labor, especially for the labor-intensive plantation economies of the sugar colonies in the Caribbean, operated by Great Britain, France, Spain, and the Dutch Republic.
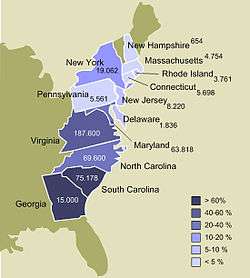
Most slaves who were ultimately brought to the Thirteen British colonies — the Eastern seaboard of what later became the United States — were imported from the Caribbean, not directly from Africa. They were taken to the Caribbean islands as a result of the Atlantic slave trade. Indigenous people were also enslaved in the North American colonies, but on a smaller scale, and Indian slavery largely ended in the late eighteenth century although the enslavement of Indigenous people did continue to occur in the Southern states until the Emancipation Proclamation issued by President Abraham Lincoln in 1863. In the English colonies, slave status for Africans became hereditary in the mid-17th century with the passage of colonial laws that defined children born in the colonies as taking the status of the mother, under the principle of partus sequitur ventrem.[2][lower-alpha 1]
Native Americans
Native Americans enslaved members of their own and other tribes before and after Europeans arrived, continuing into the 1800s; enslaved people might or might not be adopted eventually, especially if enslaved as children; and the enslavement might or might not be hereditary.[3] [4] Slaves included captives from wars and slave raids; captives bartered from other tribes, sometimes at great distances; children sold by their parents during famines; and men and women who staked themselves in gambling when they had nothing else, which put them into servitude in some cases for life.[3]
Native Americans also captured and enslaved some early European explorers and colonists, and were enslaved themselves by the colonists, starting with the Spanish in the 1500s.[3] Native Americans were enslaved by the Spanish in Florida under the encomienda system.[5] [6] New England and the Carolinas captured Native Americans in wars and distributed them as slaves.[7]

Larger societies structured as chiefdoms kept slaves as unpaid field laborers, while in band societies the ownership of enslaved captives attested to their captor's military prowess.[8] Some war captives were also subjected to ritualized torture and execution.[9] Alan Gallay and other historians emphasize differences between Native American enslavement of war captives and the European slave trading system, into which numerous native peoples were integrated.[10]
Richard White, in The Middle Ground elucidates the complex social relationships between Native American groups and the early empires, including 'slave' culture and scalping.[11] Robbie Ethridge states,
"Let there be no doubt…that the commercial trade in Indian slaves was not a continuation and adaptation of pre-existing captivity patterns. It was a new kind of slave, requiring a new kind of occupational specialty…organized militaristic slavers."[12]

One example of this militaristic slaving can be seen in Nathaniel Bacon's actions in Virginia during the late 1670s. In June 1676, the Virginia assembly granted Bacon and his men what equated to a slave-hunting license by providing that any enemy Native Americans caught were to be slaves for life. They also provided soldiers who had captured Native Americans with the right to "retain and keep all such Native American slaves or other Native American goods as they either have taken or hereafter shall take."[13] By this order, the assembly had made a public decision to enslave Native Americans. In the years to follow, other laws resulted in Native Americans being grouped with other non-Christian servants who had imported to the colonies (Negro slaves) as slaves for life.
Puritan New England, Virginia, Spanish Florida, and the Carolina colonies engaged in large-scale enslavement of Native Americans, often through the use of Indian proxies to wage war and acquire the slaves. In New England, slave raiding accompanied the Pequot War and King Philip's War but declined after the latter war ended in 1676. Enslaved Native Americans were in Jamestown from the early years of the settlement, but large-scale cooperation between English slavers and the West and Occaneechi peoples, whom they armed with guns, did not begin until the 1640s. These groups conducted enslaving raids in what is now Georgia, Tennessee, North Carolina, South Carolina, Florida, and possibly Alabama.[14] The Carolina slave trade, which included both trading and direct raids by colonists,[15] was the largest among the British colonies in North America,[16] estimated at 24,000 to 51,000 Native Americans by Gallay.[17]
Historian Ulrich Phillips argues that Africans were inculcated as slaves and the best answer to the labor shortage in the New World because Native American slaves were more familiar with the environment, and would often successfully escape into the wilderness that African slaves had much more difficulty surviving in. Also, early colonial America depended heavily on the sugar trade, which led to malaria, a disease the Africans were far less susceptible to than Native American slaves.[18]
The first enslaved Africans
Georgia
The first African slaves in what would become the present day United States of America arrived in 1526 with Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón's establishment of San Miguel de Gualdape on the current Georgia or Carolina coast.[19][20][21] They rebelled and lived with indigenous people, destroying the colony in less than 2 months.[19][22]
Georgia was the last of the Thirteen Colonies to be established and the furthest south (Florida was not one of the Thirteen Colonies). Founded in the 1730s, Georgia's powerful backers did not object to slavery as an institution, but their business model was to rely on labor from Britain (primarily England's poor) and they were also concerned with security, given the closeness of then Spanish Florida, and Spain's regular offers to enemy-slaves to revolt or escape. Despite agitation for slavery, it was not until a defeat of the Spanish by Georgia colonials in the 1740s that arguments for opening the colony to slavery intensified. To staff the rice plantations and settlements, Georgia's proprietors relented in 1751, and African slavery grew quickly. After becoming a royal colony, in the 1760s Georgia began importing slaves directly from Africa.[23]
Florida
When St. Augustine, FL, was founded in 1565, the site already had enslaved Native Americans, whose ancestors had migrated from Cuba.[3] The Spanish introduced African slaves in what is now Florida soon after they claimed the area in 1513. The Spanish settlement was sparse and they held comparatively few slaves.[24] African slaves arrived in Florida in 1539 with Hernando de Soto, and in the 1565 founding of St. Augustine, Florida.[21][22]
The Spanish promised freedom to refugee slaves from the English colonies of South Carolina and Georgia in order to destabilize English settlement.[25] [26] If the slaves converted to Catholicism and agreed to serve in a militia for Spain, they could become Spanish citizens. By 1730 the black settlement known as Fort Mose developed near St. Augustine and was later fortified. There were two known Fort Mose sites in the eighteenth century, and the men helped defend St. Augustine against the British. It is "the only known free black town in the present-day southern United States that a European colonial government-sponsored.[27] The Fort Mose Site, today a National Historic Landmark, is the location of the second Fort Mose."[27] During the nineteenth century, this site became marsh and wetlands.
In 1763, Great Britain took over Florida in an exchange with Spain after defeating France in the Seven Years' War. Spain evacuated its citizens from St. Augustine, including the residents of Fort Mose, transporting them to Cuba. As Britain developed the colony for plantation agriculture, the percentage of slaves in the population in twenty years rose from 18% to almost 65% by 1783.[28]
Virginia and Chesapeake Bay
The first recorded Africans in Virginia arrived in late August 1619. The White Lion, a privateer ship owned by Robert Rich, 2nd Earl of Warwick but flying a Dutch flag, docked at what is now Old Point Comfort (located in modern-day Hampton) with approximately 20 Africans. They were captives from the area of present-day Angola and had been seized by the British crew from a Portuguese slave ship, the "São João Bautista".[29][30] To obtain the Africans, the Jamestown colony traded provisions with the ship.[31] These individuals appear to have been treated as indentured servants, since slave laws were not passed until later, in 1641 in Massachusetts and in 1661 in Virginia.[32]
Some number of the colony's early Africans earned freedom by fulfilling a work contract or for converting to Christianity.[33] At least one of these, Anthony Johnson, in turn, acquired slaves or indentured servants for workers himself. Historians such as Edmund Morgan say this evidence suggests that racial attitudes were much more flexible in early 17th-century Virginia than they would later become.[34] A 1625 census recorded 23 Africans in Virginia. In 1649 there were 300, and in 1690 there were 950.[35] Over this period, legal distinctions between white indentured servants and "Negros" widened into lifelong and inheritable chattel-slavery for Africans.[36]
Carolinas
Until the early 18th century, enslaved Africans were difficult to acquire in the colonies that became the United States, as most were sold to the West Indies, where the large plantations and high mortality rates required continued importation of slaves. One of the first major centers of African slavery in the English North American colonies occurred with the founding of Charles Town and the Province of Carolina in 1670. The colony was founded mainly by planters from the overpopulated English sugar island of Barbados, who brought relatively large numbers of African slaves from that island to establish new plantations.[37]
To meet agricultural labor needs, colonists also practiced Indian slavery for some time. The Carolinians transformed the Indian slave trade during the late 17th and early 18th centuries by treating such slaves as a trade commodity to be exported, mainly to the West Indies. Historian Alan Gallay estimates that between 1670 and 1715, between 24,000 and 51,000 captive Native Americans were exported from South Carolina—much more than the number of Africans imported to the colonies of the future United States during the same period.[38]
New England
Slaves, African and Native American, made up a smaller part of the New England economy, which was based on yeoman farming and trades, and a smaller fraction of the population, but they were present.[39] The Puritans codified slavery in 1641.[40][41] The Massachusetts royal colony passed the Body of Liberties, which prohibited slavery in some instances, but did allow three legal bases of slavery.[41] Slaves could be held if they were captives of war if they sold themselves into slavery, were purchased from elsewhere, or if they were sentenced to slavery by the governing authority.[41] The Body of Liberties used the word "strangers" to refer to people bought and sold as slaves, as they were generally not English subjects. Colonists came to equate this term with Native Americans and Africans.[42]
New York and New Jersey
The Dutch West India Company introduced slavery in 1625 with the importation of eleven enslaved blacks who worked as farmers, fur traders, and builders to New Amsterdam (present day New York City), capital of the nascent province of New Netherland.[43] The Dutch colony expanded across the North River (Hudson River) to Bergen (in today's New Jersey). Later, slaves were also held privately by settlers in the area.[44][45] Although enslaved, the Africans had a few basic rights and families were usually kept intact. They were admitted to the Dutch Reformed Church and married by its ministers, and their children could be baptized. Slaves could testify in court, sign legal documents, and bring civil actions against whites. Some were permitted to work after hours earning wages equal to those paid to white workers. When the colony fell to the English in the 1660s, the company freed all its slaves, which created an early nucleus of free Negros in the area.[43]
The English continued to import more slaves. Enslaved Africans performed a wide variety of skilled and unskilled jobs, mostly in the burgeoning port city and surrounding agricultural areas. In 1703 more than 42% of New York City's households held slaves, a percentage higher than in the cities of Boston and Philadelphia, and second only to Charleston in the South.[46]
Midwest, Mississippi River, and Louisiana
The French introduced legalized slavery into their colonies in New France both near the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River. (They also used slave labor on their island colonies in the Caribbean: Guadeloupe and especially Saint-Domingue.) After the port of New Orleans was founded in 1718 with access to the Gulf Coast, French colonists imported more African slaves to the Illinois Country for use as agricultural or mining laborers. By the mid-eighteenth century, slaves accounted for as many as a third of the limited population in that rural area.[47]
Slavery was much more extensive in colonial Louisiana, where the French developed sugar cane plantations along the Mississippi River. Slavery was maintained during the French (1699 – 1763, and 1800 – 1803) and Spanish (1763 – 1800) periods of government. The first people enslaved by the French were Native Americans, but they could easily escape into the countryside which they knew well. Beginning in the early 18th century, the French imported Africans as laborers in their efforts to develop the colony. Mortality rates were high for both colonists and Africans, and new workers had to be imported.
Implemented in colonial Louisiana in 1724, Louis XIV of France's Code Noir regulated the slave trade and the institution of slavery in the French colonies. As a result, Louisiana and the Mobile area developed very different patterns of slavery compared to the British colonies.[48] As written, the Code Noir gave some rights to slaves, including the right to marry. Although it authorized and codified cruel corporal punishment against slaves under certain conditions, it forbade slave owners to torture slaves, to separate married couples (and to separate young children from their mothers). It required owners to instruct slaves in the Catholic faith, implying that Africans were human beings endowed with a soul, an idea that had not been acknowledged until then.[49][50][51]
The Code Noir forbade interracial marriages, but interracial relationships were formed in La Louisiane from the earliest years. In New Orleans society particularly, a formal system of concubinage, known as plaçage, developed. Usually formed between young white men and African or African-American women, these relationships were formalized with contracts that sometimes provided for freedom for a woman and her children (if she was still enslaved), education for the mixed-race children of the union, and sometimes a property settlement. The free people of color became an intermediate social caste between the whites and the mass of enslaved blacks; many practiced artisan trades, and some acquired educations and property.
Gradually in the English colonies, slavery became known as a racial caste that generally encompassed all people of African descent, even if mixed race. From the 17th century, Virginia defined all children born to enslaved mothers as born into slavery, regardless of their father's ancestry. Similarly, Virginia denied that converting a slave to Christianity was grounds for freedom. Even free people of color or mixed-race (known as mulattoes) were restricted in their rights, especially as colonies passed harsher laws after early slave revolts. During the centuries of slavery in the British colonies, many slaves were of mixed-race ancestry.[48][51]
Slave rebellions
Colonial slave rebellions before 1776, or before 1801 for Louisiana, include:
- San Miguel de Gualdape (1526)
- Gloucester County, Virginia Revolt (1663)[52]
- New York Slave Revolt of 1712
- Samba Rebellion (1731)
- Stono Rebellion (1739)
- New York Slave Insurrection of 1741
- 1791 Mina conspiracy
- Pointe Coupée conspiracy (1794)
16th century
While the British knew about Spanish and Portuguese slave trading, they did not implement slave labor in the Americas until the 17th century.[53] British travelers were fascinated by the dark-skinned people they found in West Africa; they developed mythologies that situated them in their view of the cosmos.[54]
The first Africans to arrive in England came voluntarily in 1555 with John Lok (an ancestor of the famous philosopher John Locke). Lok intended to teach them English in order to facilitate the trading of material goods with West Africa.[55] This model gave way to a slave trade initiated by John Hawkins, who captured 300 Africans and sold them to the Spanish.[56] Blacks in England were subordinate but never had the legal status of chattel slaves.[57]
In 1607, England established Jamestown as its first permanent colony on the North American continent.[58] Tobacco became the chief commodity crop of the colony, due to the efforts of John Rolfe in 1611. Once it became clear that tobacco was going to drive the Jamestown economy, more workers were needed for the labor-intensive crop. The British aristocracy also needed to find a labor force to work on its sugar plantations in the Americas. The major sources were indentured servants from Britain, Native Americans, and West Africans.[59] During this period, Barbados became an English Colony in 1624 and the Caribbean's Jamaica in 1655. These and other Caribbean colonies became the center of wealth generated from sugar cane and the focus of the slave trade for the growing English empire.[60]
The English entertained two lines of thought simultaneously toward the indigenous Native Americans. Because these people were lighter-skinned, they were seen as more European and therefore as candidates for civilization. At the same time, because they were occupying the land desired by the colonial powers, they were from the beginning, targets of potential military attack.[61]
At first, indentured servants were used as the needed labor.[62] These servants provided up to seven years of service in exchange for having their trip to Jamestown paid for by someone in Jamestown. Once the seven years were over, the indentured servant was free to live in Jamestown as a regular citizen. However, colonists began to see indentured servants as too costly, in part because the high mortality rate meant the force had to be resupplied.
17th century
In 1619, Dutch traders brought African slaves taken from a Spanish ship to Point Comfort.[63]
Several colonial colleges held enslaved people as workers and relied on them to operate.[64]
The development of slavery in 17th-century America

The laws relating to slavery and their enforcement hardened in the second half of the 17th century, and the prospects for Africans and their descendants grew increasingly dim. By 1640, the Virginia courts had sentenced at least one black servant, John Punch, to slavery.[65] In 1656 Elizabeth Key won a suit for freedom based on her father's status as a free Englishman, and his having baptized her as Christian in the Church of England. In 1662 the Virginia House of Burgesses passed a law with the doctrine of partus, stating that any child born in the colony would follow the status of its mother, bond or free. This was an overturn of a longheld principle of English Common Law, whereby a child's status followed that of the father. It enabled slaveholders and other white men to hide the mixed-race children born of their rape of slave women and removed their responsibility to acknowledge, support, or emancipate the children.
During the second half of the 17th century, the British economy improved and the supply of British indentured servants declined, as poor Britons had better economic opportunities at home. At the same time, Bacon's Rebellion of 1676 led planters to worry about the prospective dangers of creating a large class of restless, landless, and relatively poor white men (most of them former indentured servants). Wealthy Virginia and Maryland planters began to buy slaves in preference to indentured servants during the 1660s and 1670s, and poorer planters followed suit by c.1700. (Slaves cost more than servants, so initially only the wealthy could invest in slaves.) The first British colonists in Carolina introduced African slavery into the colony in 1670, the year the colony was founded, and Charleston ultimately became the busiest slave port in North America. Slavery spread from the South Carolina Lowcountry first to Georgia, then across the Deep South as Virginia's influence had crossed the Appalachians to Kentucky and Tennessee. Northerners also purchased slaves, though on a much smaller scale. Enslaved people outnumbered free whites in South Carolina from the early 1700s to the Civil War. An authoritarian political culture evolved to prevent slave rebellion and justify white slaveholding. Northern slaves typically dwelled in towns, rather than on plantations as in the South, and worked as artisans and artisans' assistants, sailors and longshoremen, and domestic servants.[66]
In 1672, King Charles II rechartered the Royal African Company (it had initially been set up in 1660), as an English monopoly for the African slave and commodities trade—thereafter in 1698, by statute, the English parliament opened the trade to all English subjects.[67] The slave trade to the mid-Atlantic colonies increased substantially in the 1680s, and by 1710 the African population in Virginia had increased to 23,100 (42% of total); Maryland contained 8,000 Africans (23% of total).[68] In the early 18th century, England passed Spain and Portugal to become the world's leading slave-trader.[67][69]
The North American royal colonies not only imported Africans but also captured Native Americans, impressing them into slavery. Many Native Americans were shipped as slaves to the Caribbean. Many of these slaves from the British colonies were able to escape by heading south, to the Spanish colony of Florida. There they were given their freedom if they declared their allegiance to the King of Spain and accepted the Catholic Church. In 1739 Fort Mose was established by African American freedmen and became the northern defense post for St. Augustine. In 1740, English forces attacked and destroyed the fort, which was rebuilt in 1752. Because Fort Mose became a haven for escaped slaves from the English colonies to the north, it is considered a precursor site of the Underground Railroad.[70]
Chattel slavery developed in British North America before the full legal apparatus that supported slavery did. During the late 17th century and early 18th century, harsh new slave codes limited the rights of African slaves and cut off their avenues to freedom. The first full-scale slave code in British North America was South Carolina's (1696), which was modeled on the colonial Barbados slave code of 1661 and was updated and expanded regularly throughout the 18th century.[71]
A 1691 Virginia law prohibited slaveholders from emancipating slaves unless they paid for the freedmen's transportation out of Virginia.[72] Virginia criminalized interracial marriage in 1691,[73] and subsequent laws abolished blacks' rights to vote, hold office, and bear arms.[72] Virginia's House of Burgesses established the basic legal framework for slavery in 1705.[74]
The Atlantic slave trade to North America
Of the enslaved Africans brought to the New World an estimated 5-7% ended up in British North America. The vast majority of slaves transported across the Atlantic Ocean were sent to the Caribbean sugar colonies, Brazil, or Spanish America. Throughout the Americas, but especially in the Caribbean, tropical disease took a large toll on their population and required large numbers of replacements. Many Africans had limited natural immunity to yellow fever and malaria; but malnutrition, poor housing, inadequate clothing allowances, and overwork contributed to a high mortality rate.
In British North America the slave population rapidly increased via the birth rate, whereas in the Caribbean colonies they did not. The lack of proper nourishment, being suppressed sexually, and poor health are possible reasons. Of the small numbers of babies born to slaves in the Caribbean, only about 1/4 survived the miserable conditions on sugar plantations.
It was not only the major colonial powers of Western Europe such as France, England, Spain, Portugal, and the Netherlands that were involved. Other countries, including Sweden and Denmark, participated in the trans-Atlantic slave trade though on a much more limited scale.
Sexual role differentiation and slavery
"Depending upon their age and gender, slaves were assigned a particular task, or tasks, that had to be completed during the course of the day."[75] In certain settings, men would participate in the hard labor, such as working on the farm, while women would generally work in the household. They would "be sent out on errands but in most cases their jobs required that they spend much of their time within their owner's household."[76] These gender distinctions were mainly applied in the Northern colonies and on larger plantations. In Southern colonies and smaller farms, however, women and men typically engaged in the same roles, both working in the tobacco crop fields for example.
Although slave women and men in some areas performed the same type of day-to-day work, "[t]he female slave...was faced with the prospect of being forced into sexual relationships for the purpose of reproduction."[77] This reproduction would either be forced between one African slave and another, or between the slave woman and the owner. Slave owners saw slave women in terms of prospective fertility. That way, the number of slaves on a plantation could multiply without having to purchase another African. Unlike the patriarchal society of white Anglo-American colonists, "slave families" were more matriarchal in practice. "Masters believed that slave mothers, like white women, had a natural bond with their children that therefore it was their responsibility - more so than that of slave fathers - to care for their offspring."[78] Therefore, women had the extra responsibility, on top of their other day-to-day work, to take care of children. Men, in turn, were often separated from their families. "At the same time that slaveholders promoted a strong bond between slave mothers and their children, they denied to slave fathers their paternal rights of ownership and authority..."[78] Biological families were often separated by sale.
Indentured servitude
Some historians, notably Edmund Morgan, have suggested that indentured servitude provided a model for slavery in 17th-century Virginia. In practice, indentured servants were teenagers in England whose father sold their labor voluntarily for a period of time (typically four to seven years), in return for free passage to the colonies, room and board and clothes, and training in an occupation. After that, they received cash, clothing, tools, and/or land, and became ordinary settlers.
The Quaker Petition Against Slavery
In 1688, four German Quakers in Germantown, a town outside Philadelphia, wrote a petition against the use of slaves by the English colonists in the nearby countryside. They presented the petition to their local Quaker Meeting, and the Meeting was sympathetic, but could not decide what the appropriate response should be. The Meeting passed the petition up the chain of authority to Philadelphia Yearly Meeting, where it continued to be ignored. It was archived and forgotten for 150 years.
The Quaker petition was the first public American document of its kind to protest slavery. It was also one of the first public declarations of universal human rights. While the petition was forgotten for a time, the idea that every human has equal rights were regularly discussed in Philadelphia Quaker society through the eighteenth century.
18th century
During the Great Awakening of the late eighteenth century, Methodist and Baptist preachers toured in the South, trying to persuade planters to manumit their slaves on the basis of equality in God's eyes. They also accepted slaves as members and preachers of new chapels and churches. The first black churches (all Baptist) in what became the United States were founded by slaves and free blacks in Aiken County, South Carolina, in 1773,[79] Petersburg, Virginia, in 1774, and Savannah, Georgia, in 1778, before the end of the Revolutionary War.[80][81]
Slavery was officially sanctioned in 1776 by the Philadelphia Yearly Meeting.
East Indian slaves
In the early 21st century, new research has revealed that small numbers of East Indians were brought to the colonies as enslaved laborers, during the period when both India and the colonies were under British control. As an example, an ad in the Virginia Gazette of Aug. 4, 1768, describes one young "East Indian" as "a well made fellow, about 5 feet 4 inches high" who had "a thin visage, a very sly look, and a remarkable set of fine white teeth." Another slave is identified as "an East India negro man" who speaks French and English.[82] Most of the Indian slaves were already converted to Christianity, were fluent in English, and took western names.[82] Their original names and homes are not known. Their descendants have mostly merged with the African-American community, which also incorporated European ancestors. Today, descendants of such East Indian slaves may have a small percent of DNA from their Asiatic ancestors but it likely falls below the detectable levels for today's DNA tests.[83]
Beginning of the anti-slavery movement
African and African American slaves expressed their opposition to slavery through armed uprisings such as the Stono Rebellion (1739) in South Carolina. More typically, they resisted through work slowdowns, tool-breaking, and running away, either for short periods or permanently. Until the Revolutionary era, almost no white American colonists spoke out against slavery. Even the Quakers generally tolerated slaveholding (and slave-trading) until the mid-18th century, although they emerged as vocal opponents of slavery in the Revolutionary era.
Further events
Late 18th and 19th century
During and following the Revolution, the northern states all abolished slavery, with New Jersey acting last in 1804. Some of these state jurisdictions enacted the first abolition laws in the entire New World.[84] In states that passed gradual abolition laws, such as New York and New Jersey, children born to slave mothers had to serve an extended period of indenture into young adulthood. In other cases, some slaves were reclassified as indentured servants, effectively preserving the institution of slavery through another name.[85]
Often citing Revolutionary ideals, some slaveholders freed their slaves in the first two decades after independence, either outright or through their wills. The proportion of free blacks rose markedly in the Upper South in this period, before the invention of the cotton gin created a new demand for slaves in the developing "Cotton Kingdom" of the Deep South.
By 1808 (the first year allowed by the Constitution to federally ban the import slave trade), all states (except South Carolina) had banned the international buying or selling of slaves. Acting on the advice of President Thomas Jefferson, who denounced the international trade as "violations of human rights which have been so long continued on the unoffending inhabitants of Africa, in which the morality, the reputation, and the best interests of our country have long been eager to proscribe", in 1807 Congress also banned the international slave trade. However, the domestic slave trade continued in the South.[86] It brought great wealth to the South, especially to New Orleans, which became the fourth largest city in the country, also based on the growth of its port. In the antebellum years, more than one million enslaved African Americans were transported from the Upper South to the developing Deep South, mostly in the slave trade. Cotton culture, dependent on slavery, formed the basis of new wealth in the Deep South.
In 1844 the Quaker petition was rediscovered and became a focus of the burgeoning abolitionist movement.
Emancipation Proclamation and end of slavery in the US
On 1 January 1863, Abraham Lincoln signed Emancipation Proclamation freeing slaves in areas in rebellion during the American Civil War when Union troops advanced south. The Thirteenth Amendment (abolition of slavery and involuntary servitude) was ratified in December 1865.
See also
- Abolitionism in the United States
- American Descendants of Slavery (ADOS)
- Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
- Emancipation Proclamation
- Timeline of abolition of slavery and serfdom
- Colonial history of the United States
- Free negro
- Grand Model for the Province of Carolina
- History of labor law in the United States
- History of slavery in Connecticut
- History of slavery in Georgia
- History of slavery in Maryland
- History of slavery in Massachusetts
- History of slavery in New Jersey
- History of slavery in New York
- History of slavery in Pennsylvania
- History of slavery in Rhode Island
- History of slavery in Virginia
- Indentured servitude in the Americas
- Slave Trade Act
- Slavery among Native Americans in the United States
- Slavery at common law
- Slavery in the British and French Caribbean
- Slavery in the Spanish New World colonies
- Slavery in the United States
References
Footnotes
- Compare: Los Angeles Times, 13 July 2003: "The 'one drop' rule (which 'deemed "black" anyone who had a drop of black blood') and the virtual outlawing of manumission and interracial marriage reinforced white privileges and closed what some historians, writing of B
Citations
- numbers from: Ira Berlin, Generations of Captivity: A History of African-American Slaves (2003).
- Oxford Journals (subscription required)
- Lauber, Almon Wheeler (1913). "Enslavement by the Indians Themselves, Chapter 1 in Indian Slavery in Colonial Times Within the Present Limits of the United States". 53 (3). Columbia University: 25–48. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Gallay, Alan (2009). "Introduction: Indian Slavery in Historical Context". In Gallay, Alan (ed.). Indian Slavery in Colonial America. Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press. pp. 1–32. Retrieved March 8, 2017.
- Guitar, Lynne, No More Negotiation: Slavery and the Destabilization of Colonial Hispaniola's Encomienda System, by Lynne Guitar, retrieved 2019-12-06
- Indian Slavery in the Americas- AP US History Study Guide from The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, 2012-03-22, retrieved 2019-12-06
- Lauber, Almon Wheeler (1913). "The Institution as Practiced by the English, Part 2 in Indian Slavery in Colonial Times Within the Present Limits of the United States". 53 (3). Columbia University. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Gallay, Alan. (2002) The Indian Slave Trade: The Rise of the English Empire in the American South 1670–1717. Yale University Press: New York. ISBN 0-300-10193-7, pg. 29
- Gallay, Alan. (2002) The Indian Slave Trade: The Rise of the English Empire in the American South 1670–1717. Yale University Press: New York. ISBN 0-300-10193-7, p. 187–90.
- "Europeans did not introduce slavery or the notion of slaves as laborers to the American South but instead were responsible for stimulating a vast trade in humans as commodities." (p. 29) "In Native American societies, ownership of individuals was more a matter of status for the owner and a statement of debasement and "otherness" for the slave than it was a means to obtain economic rewards from unfree labor. … The slave trade was an entirely new enterprise for most people of all three culture groups [Native American, European, and African]." (p. 8) Gallay, Alan. (2002) The Indian Slave Trade: The Rise of the English Empire in the American South 1670–1717. Yale University Press: New York. ISBN 0-300-10193-7, pg. 29
- White, Richard. (1991) The Middle Ground: Indians, Empires, and Republics in the Great Lakes Region. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-42460-7
- Ethridge, From Chicaza to Chickasaw (2010), p. 93.
- Morgan, Edmund (1975). American Slavery, American Freedom. New York: W.W. Norton and Company. pp. 328–329. ISBN 978-0-393-32494-5.
- Ethridge, From Chicaza to Chickasaw (2010), pp. 97–98.
- Ethridge, From Chicaza to Chickasaw (2010), p. 109.
- Ethridge, From Chicaza to Chickasaw (2010), p. 65.
- Figures cited in Ethridge, From Chicaza to Chickasaw (2010), p. 237.
- Phillips, Ulrich. American Negro Slavery (1918)
- Cameron, Guy, and Stephen Vermette; Vermette, Stephen (2012). "The Role of Extreme Cold in the Failure of the San Miguel de Gualdape Colony". The Georgia Historical Quarterly. 96 (3): 291–307. ISSN 0016-8297. JSTOR 23622193.
- Parker, Susan (2019-08-24). "'1619 Project' ignores fact that slaves were present in Florida decades before". St. Augustine Record. Retrieved 2019-12-06.
- Francis, J. Michael, Gary Mormino and Rachel Sanderson (2019-08-29). "Slavery took hold in Florida under the Spanish in the 'forgotten century' of 1492-1619". Tampa Bay Times. Retrieved 2019-12-06.
- Torres-Spelliscy, Ciara; Law, a fellow at the Brennan Center for Justice at NYU School of; Br, the author of "Political; s." (2019-08-23). "Perspective - Everyone is talking about 1619. But that's not actually when slavery in America started". Washington Post. Retrieved 2019-12-06.
- Wood, Betty; et al. "Slavery in Colonial Georgia". New Georgia Encyclopedia. Retrieved 2018-07-14.
- "Before 1861", Florida Memory
- Hankerson, Derek (2008-01-02). "The journey of Africans to St. Augustine, Florida and the establishment of the underground railway". Patriotic Vanguard. Retrieved 2019-12-06.
- Gardner, Sheldon (2019-05-20). "St. Augustine's Fort Mose added to UNESCO Slave Route Project". St. Augustine record. Retrieved 2019-12-06.
- "Fort Mose", "American Latino Heritage", National Park Service
- "Plantations", Florida Memory
- Deetz, Kelley Fanto (August 13, 2019). "400 years ago, enslaved Africans first arrived in Virginia". National Geographic. Retrieved 2019-08-25.
- Waxman, Olivia B. (August 20, 2019). "Where the Landing of the First Africans in English North America Really Fits in the History of Slavery". Time. Retrieved 2019-08-25.
- Finley, Ben (2019-08-22). "Virginia marks pivotal moment when African slaves arrived". Associated Press. Retrieved 2019-08-25.
- https://www.pbs.org/opb/historydetectives/feature/indentured-servants-in-the-us/, Indentured Servants In The U.S.
- Edmund S. Morgan, American Slavery, American Freedom: The Ordeal of Colonial Virginia (New York: Norton, 1975), pp.154–157.
- Morgan, American Slavery, American Freedom pp.327–328.
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), p. 78.
- Foner, Phillip. Slaves and Free Blacks in the Southern Colonies." History of Black Americans: From Africa to the Emergence of the Cotton Kingdom. Greenwood Press. 1975. (web archive access from October 14, 2013)
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), pp. 64–65.
- Gallay, Alan. (2002) The Indian Slave Trade: The Rise of the English Empire in the American South 1670–1717. Yale University Press: New York. ISBN 0-300-10193-7, pg. 299
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), pp. 94–95.
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), p. 103.
- Higginbotham, A. Leon (1975). In the Matter of Color: Race and the American Legal Process: The Colonial Period. Greenwood Press. ISBN 9780195027457.
- William M. Wiecek (1977). "the Statutory Law of Slavery and Race in the Thirteen Mainland Colonies of British America". The William and Mary Quarterly. 34 (2): 261. JSTOR 1925316.
- Hodges, Russel Graham (1999), Root and Branch: African Americans in New York and East Jersey, 1613-1863, Chapel Hill, North Carolina: University of North Carolina Press
- Shakir, Nancy. "Slavery in New Jersey". Slaveryinamerica. Archived from the original on 2003-10-17. Retrieved 2008-10-22.
- Karnoutsos, Carmela. "Underground Railroad". Jersey City Past and Present. New Jersey City University. Retrieved 2011-03-27.
- "The Hidden History of Slavery in New York". The Nation. ISSN 0027-8378. Retrieved 2016-10-11.
- Ekberg, Carl J. (2000). French Roots in the Illinois Country. University of Illinois Press. pp. 2–3. ISBN 0-252-06924-2.
- Martin H. Steinberg, Disorders of Hemoglobin: Genetics, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Management, pp.725-726
- Rodney Stark, "For the Glory of God: How Monotheism Led to Reformations, Science, Witch-hunts, and the End of Slavery", p.322 Note that the hardcover edition has a typographical error stating "31.2 percent"; it is corrected to 13.2 in the paperback edition. The 13.2% value is confirmed with 1830 census data.
- Cook, Samantha; Hull, Sarah (2011). The Rough Guide to the USA. Rough Guides UK. ISBN 9781405389525.
- Jones, Terry L. (2007). The Louisiana Journey. Gibbs Smith. p. 115. ISBN 9781423623809.
- Joseph Cephas Carroll, Slave Insurrections in the United States, 1800-1865, p. 13
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), p. 21. "Yet those in high places who advocated the overseas expansion of England did not propose that West Africans could, should, or would be enslaved by the English in the Americas. Indeed, West Africans scarcely figured at all in the sixteenth-century English agenda for the New World."
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), p. 23. "More than anything else it was the blackness of West Africans that at once fascinated and repelled English commentators. The negative connotations that the English had long attached to the color black were to deeply prejudice their assessment of West Africans."
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), p. 26. "It seems that these men were the first West Africans to set foot in England, and their arrival marked the beginning of a black British population. The men in question had come to England willingly. Lok's sole motive was to facilitate English trading links with West Africa. He intended that these five men should be taught English, and something about English commercial practices, and then returned home to act as intermediaries between the English and their prospective West African trading partners."
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), p. 27.
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), p. 28.
- Wilford, John Noble (13 September 1996). "Jamestown Fort, 'Birthplace' Of America in 1607, Is Found". New York Times.
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), p. 18.
- "British Involvement in the Transatlantic Slave Trade". The Abolition Project. E2BN - East of England Broadband Network and MLA East of England. 2009. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), pp. 34–39.
- Barker, Deanna. "Indentured Servitude in Colonial America". Mert Sahinoglu. Frontier Resources.
- Monroe, Mailing Address: 41 Bernard RoadFort; Us, VA 23651-1001 Phone: 757-722-FORTContact. "History & Culture - Fort Monroe National Monument (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov. Retrieved 2019-09-26.
- Wilder, Craig Steven (2014-09-02). Ebony and Ivy: Race, Slavery, and the Troubled History of America's Universities. Bloomsbury Publishing USA. ISBN 9781608194025.
- http://c.mfcreative.com/offer/us/obama_bunch/PDF/main_article_final.pdf
- Wilson, Thomas D. The Ashley Cooper Plan: The Founding of Carolina and the Origins of Southern Political Culture. Chapel Hill, N.C.: University of North Carolina Press, 2016. Chapters 1 and 4.
- "Africans in America | Part 1 | Narrative | from Indentured Servitude to Racial Slavery".
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), p. 88.
- "European traders - International Slavery Museum, Liverpool museums".
- "Aboard the Underground Railroad - Fort Mose Site". nps.gov. U.S. Department of the Interior.
- Alan Taylor, American Colonies (New York: Viking, 2001), p. 213.
- Alan Taylor, American Colonies (New York: Viking, 2001), p. 156.
- America Past and Present Online - The Laws of Virginia (1662, 1691, 1705) Archived 2008-04-21 at the Wayback Machine
- Wood, Origins of American Slavery (1997), p. 92. "In 1705, almost exactly a century after the first colonists had set foot in Jamestown, the House of Burgesses codified and systematized Virginia's laws of slavery. These laws would be modified and added to over the next century and a half, but the essential legal framework within which the institution of slavery would subsequently operate had been put in place."
- Wood, Betty (January 1, 2005). Slavery in Colonial America. Rowman and Littlefield. p. 33.
- Wood, Betty (January 1, 2005). Slavery in Colonial America. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 39.
- Hallam, Jennifer. "The Slave Experience: Men, Women, and Gender". PBS. Retrieved December 2, 2014.
- Stevenson, Brenda. "Distress and Discord in Virginia Slave Families, 1830-1860". In Joy and in Sorrow: Women, Family and Marriage in the Victorian South.
- Raboteau, Albert J. (2004). Slave Religion: The "Invisible Institution" in the Antebellum South. Oxford University Press. p. 139. ISBN 978-0-19-517413-7. Retrieved 28 May 2013.
- Edward A. Hatfield, "First African Baptist Church", New Georgia Encyclopedia, 2009
- Andrew Billingsley, Mighty Like a River: The Black Church and Social Reform (New York: Oxford University Press, 2003)
- Assisi, Francis C. (16 May 2007). "Indian Slaves in Colonial America". India Currents. Archived from the original (reprint) on 27 November 2012. Retrieved 2013-02-19.
- Estes, Roberta (2012). "East India Indians in Early Colonial Records". Native Heritage Project.
- Foner, Eric (2010). The Fiery Trial: Abraham Lincoln and American Slavery. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. p. 14.
- Edgar J. McManus, A History of Negro Slavery in New York, Syracuse University Press, 1966
- Dumas Malone, Jefferson and the President: Second Term, 1805-1809 (1974) pp. 543-4
Sources
- Ethridge, Robbie Franklyn (2010). From Chicaza to Chickasaw: The European invasion and the transformation of the Mississippian world, 1540-1715. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 978-0-8078-3435-0.
- Wood, Betty. The Origins of American Slavery. New York: Hill and Wang, 1997. ISBN 978-0-8090-1608-2.
Further reading
- Aptheker, Herbert. American Negro Slave Revolts. 50th Anniversary edition. New York: International Publishers, 1993. ISBN 0717806057
- Berlin, Ira. Many Thousands Gone: The First Two Centuries of Slavery in North America. Cambridge: Belknap Press of Harvard University, 1998.
- Genovese, Eugene D. Roll, Jordan, Roll: The World the Slaves Made. New York: Pantheon, 1974.
- Gutman, Herbert G. The Black Family in Slavery and Freedom, 1750–1925. New York: Pantheon, 1976.
- Huggins, Nathan. Black Odyssey: The African-American Ordeal in Slavery. New York: Pantheon, 1990.
- Jewett, Clayton E. and John O. Allen; Slavery in the South: A State-By-State History (Greenwood Press, 2004)
- Levine, Lawrence W. Black Culture and Black Consciousness: Afro-American Folk Thought from Slavery to Freedom. New York: Oxford University Press, 1977.
- McManus, Edgar J. A History of Negro Slavery in New York, Syracuse University Press, 1966
- Morgan, Edmund S. American Slavery, American Freedom: The Ordeal of Colonial Virginia. New York: Norton, 1975.
- Olwell, Robert. Masters, Slaves, & Subjects: The Culture of Power in the South Carolina Low Country, 1740–1790 (1998).
- Schwalm, Leslie A. A Hard Fight for We: Women's Transition from Slavery to Freedom in South Carolina. Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1997.
- Snyder, Terri L. The Power to Die: Slavery and Suicide in British North America. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2015.
- White, Deborah Gray. Ar'n't I a Woman? Female Slaves in the Plantation South. New York: Norton, 1985.
- Williams, Eric, Capitalism and Slavery. 4th edition, 1975.
- Wood, Betty. Slavery in Colonial America, 1619-1776 (2005)
- Wood, Betty. Slavery In Colonial Georgia, 1730-1775 (2007)
- Wood, Peter H. Black Majority: Negroes in Colonial South Carolina from 1670 through the Stono Rebellion (1974).
External links
- Immigrant Servants Database
- Slavery and the slave trade collaboration by UNESCO, Colonial Williamsburg and others
