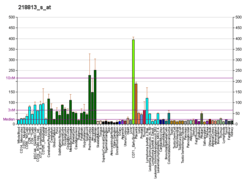
SH3GLB2
Endophilin-B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SH3GLB2 gene.[5][6]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000148341 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026860 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Pierrat B, Simonen M, Cueto M, Mestan J, Ferrigno P, Heim J (February 2001). "SH3GLB, a new endophilin-related protein family featuring an SH3 domain". Genomics. 71 (2): 222–34. doi:10.1006/geno.2000.6378. PMID 11161816.
- "Entrez Gene: SH3GLB2 SH3-domain GRB2-like endophilin B2".
- Petrelli A, Gilestro GF, Lanzardo S, Comoglio PM, Migone N, Giordano S (March 2002). "The endophilin-CIN85-Cbl complex mediates ligand-dependent downregulation of c-Met". Nature. 416 (6877): 187–90. doi:10.1038/416187a. PMID 11894096.
- Soubeyran P, Kowanetz K, Szymkiewicz I, Langdon WY, Dikic I (March 2002). "Cbl-CIN85-endophilin complex mediates ligand-induced downregulation of EGF receptors". Nature. 416 (6877): 183–7. doi:10.1038/416183a. PMID 11894095.
Further reading
- Nagase T, Nakayama M, Nakajima D, Kikuno R, Ohara O (2001). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XX. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 8 (2): 85–95. doi:10.1093/dnares/8.2.85. PMID 11347906.
- Li J, Hawkins IC, Harvey CD, Jennings JL, Link AJ, Patton JG (2003). "Regulation of alternative splicing by SRrp86 and its interacting proteins". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (21): 7437–47. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.21.7437-7447.2003. PMC 207616. PMID 14559993.
- Wan D, Gong Y, Qin W, Zhang P, Li J, Wei L, Zhou X, Li H, Qiu X, Zhong F, He L, Yu J, Yao G, Jiang H, Qian L, Yu Y, Shu H, Chen X, Xu H, Guo M, Pan Z, Chen Y, Ge C, Yang S, Gu J (2004). "Large-scale cDNA transfection screening for genes related to cancer development and progression". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (44): 15724–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404089101. PMC 524842. PMID 15498874.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Mikula M, Dzwonek A, Karczmarski J, Rubel T, Dadlez M, Wyrwicz LS, Bomsztyk K, Ostrowski J (2006). "Landscape of the hnRNP K protein-protein interactome". Proteomics. 6 (8): 2395–406. doi:10.1002/pmic.200500632. PMID 16518874.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.