S100P
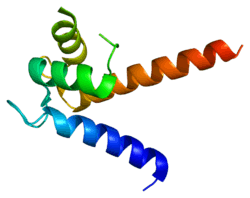
S100 calcium-binding protein P (S100P) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the S100P gene.[3][4][5]
Function
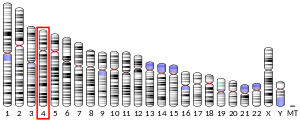
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100 genes include at least 13 members which are located as a cluster on chromosome 1q21; however, this gene is located at 4p16. This protein, in addition to binding Ca2+, also binds Zn2+ and Mg2+. This protein may play a role in the etiology of prostate cancer.[5]
Interactions
S100P has been shown to interact with EZR [6] and RAGE.[7] The interactions between S100P and RAGE are disrupted by cromolyn[8] and pentamidine.[7]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000163993 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Engelkamp D, Schäfer BW, Mattei MG, Erne P, Heizmann CW (Aug 1993). "Six S100 genes are clustered on human chromosome 1q21: identification of two genes coding for the two previously unreported calcium-binding proteins S100D and S100E". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 90 (14): 6547–51. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.14.6547. PMC 46969. PMID 8341667.
- Schäfer BW, Wicki R, Engelkamp D, Mattei MG, Heizmann CW (Jun 1995). "Isolation of a YAC clone covering a cluster of nine S100 genes on human chromosome 1q21: rationale for a new nomenclature of the S100 calcium-binding protein family". Genomics. 25 (3): 638–43. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(95)80005-7. PMID 7759097.
- "Entrez Gene: S100P S100 calcium binding protein P".
- Koltzscher M, Neumann C, König S, Gerke V (Jun 2003). "Ca2+-dependent binding and activation of dormant ezrin by dimeric S100P". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 14 (6): 2372–84. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-09-0553. PMC 194886. PMID 12808036.
- Penumutchu SR, Chou RH, Yu C (2014-08-01). "Structural insights into calcium-bound S100P and the V domain of the RAGE complex". PLOS ONE. 9 (8): e103947. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0103947. PMC 4118983. PMID 25084534.
- Penumutchu SR, Chou RH, Yu C (Oct 2014). "Interaction between S100P and the anti-allergy drug cromolyn". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 454 (3): 404–409. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.10.048. PMID 25450399.
Further reading
- Schäfer BW, Heizmann CW (1996). "The S100 family of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins: functions and pathology". Trends Biochem. Sci. 21 (4): 134–40. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(96)80167-8. PMID 8701470.
- Emoto Y, Kobayashi R, Akatsuka H, Hidaka H (1992). "Purification and characterization of a new member of the S-100 protein family from human placenta". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 182 (3): 1246–53. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(92)91865-N. PMID 1540168.
- Becker T, Gerke V, Kube E, Weber K (1992). "S100P, a novel Ca(2+)-binding protein from human placenta. cDNA cloning, recombinant protein expression and Ca2+ binding properties". Eur. J. Biochem. 207 (2): 541–7. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17080.x. PMID 1633809.
- Gribenko AV, Makhatadze GI (1998). "Oligomerization and divalent ion binding properties of the S100P protein: a Ca2+/Mg2+-switch model". J. Mol. Biol. 283 (3): 679–94. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2116. PMID 9784376.
- Koltzscher M, Gerke V (2000). "Identification of hydrophobic amino acid residues involved in the formation of S100P homodimers in vivo". Biochemistry. 39 (31): 9533–9. doi:10.1021/bi000257+. PMID 10924150.
- Harvell JD, Fulton R, Jones CD, Terris DJ, Warnke RA (2001). "Composite dendritic cell neoplasm (NOS) and small lymphocytic lymphoma". Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 8 (4): 322–8. doi:10.1097/00022744-200012000-00010. PMID 11127925.
- Gribenko AV, Hopper JE, Makhatadze GI (2002). "Molecular characterization and tissue distribution of a novel member of the S100 family of EF-hand proteins". Biochemistry. 40 (51): 15538–48. doi:10.1021/bi0114731. PMID 11747429.
- Gribenko AV, Guzmán-Casado M, Lopez MM, Makhatadze GI (2003). "Conformational and thermodynamic properties of peptide binding to the human S100P protein". Protein Sci. 11 (6): 1367–75. doi:10.1110/ps.0202202. PMC 2373636. PMID 12021435.
- Filipek A, Jastrzebska B, Nowotny M, Kuznicki J (2002). "CacyBP/SIP, a calcyclin and Siah-1-interacting protein, binds EF-hand proteins of the S100 family". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (32): 28848–52. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203602200. PMID 12042313.
- Zhang H, Wang G, Ding Y, Wang Z, Barraclough R, Rudland PS, Fernig DG, Rao Z (2003). "The crystal structure at 2A resolution of the Ca2+ -binding protein S100P". J. Mol. Biol. 325 (4): 785–94. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(02)01278-0. PMID 12507480.
- Nowotny M, Spiechowicz M, Jastrzebska B, Filipek A, Kitagawa K, Kuznicki J (2003). "Calcium-regulated interaction of Sgt1 with S100A6 (calcyclin) and other S100 proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (29): 26923–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211518200. PMID 12746458.
- Koltzscher M, Neumann C, König S, Gerke V (2004). "Ca2+-dependent binding and activation of dormant ezrin by dimeric S100P". Mol. Biol. Cell. 14 (6): 2372–84. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-09-0553. PMC 194886. PMID 12808036.
- Arumugam T, Simeone DM, Schmidt AM, Logsdon CD (2004). "S100P stimulates cell proliferation and survival via receptor for activated glycation end products (RAGE)". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (7): 5059–65. doi:10.1074/jbc.M310124200. PMID 14617629.
- Jin G, Wang S, Hu X, Jing Z, Chen J, Ying K, Xie Y, Mao Y (2004). "Characterization of the tissue-specific expression of the s100P gene which encodes an EF-hand Ca2+-binding protein". Mol. Biol. Rep. 30 (4): 243–8. doi:10.1023/A:1026311423326. PMID 14672411.
- Sato N, Fukushima N, Matsubayashi H, Goggins M (2004). "Identification of maspin and S100P as novel hypomethylation targets in pancreatic cancer using global gene expression profiling". Oncogene. 23 (8): 1531–8. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207269. PMID 14716296.
- Lee YC, Volk DE, Thiviyanathan V, Kleerekoper Q, Gribenko AV, Zhang S, Gorenstein DG, Makhatadze GI, Luxon BA (2005). "NMR structure of the Apo-S100P protein". J. Biomol. NMR. 29 (3): 399–402. doi:10.1023/B:JNMR.0000032617.88899.4b. PMID 15213440.