Proflavine
Proflavine, also called proflavin and diaminoacridine, is an acriflavine derivative, a disinfectant bacteriostatic against many gram-positive bacteria. It has been used in the form of the dihydrochloride and hemisulfate salts as a topical antiseptic, and was formerly used as a urinary antiseptic.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
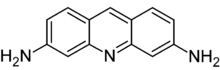
| IUPAC name
acridine-3,6-diamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.976 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H11N3 | |
| Molar mass | 209.252 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Proflavine is also known to have a mutagenic effect on DNA by intercalating between nucleic acid base pairs. It differs from most other mutagenic components by causing basepair-deletions or basepair-insertions and not substitutions. In the presence of light, proflavine can induce double-stranded breaks in DNA.[1]
Proflavine absorbs strongly in the blue region at 445 nm (in water at pH 7) with molar extinction coefficient of c. 40,000.[2]
References
- Gatasheh, Mansour K; Kannan, S; Hemalatha, K; Imrana, N (2017). "Proflavine an acridine DNA intercalating agent and strong antimicrobial possessing potential properties of carcinogen". Karbala International Journal of Modern Science. 3 (4): 272–278. doi:10.1016/j.kijoms.2017.07.003.
- Sarre, Peter J. (2006). "The Diffuse Interstellar Bands: A Major Problem in Astronomical Spectroscopy". Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy. 238 (1): 1–10. arXiv:astro-ph/0608113. Bibcode:2006JMoSp.238....1S. doi:10.1016/j.jms.2006.03.009.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.