Principate
The Principate is the name sometimes given to the first period of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in 284 AD, after which it evolved into the so-called Dominate.
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of ancient Rome |
| Periods |
|
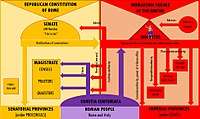
| Roman Constitution |
| Precedent and law |
|
|
| Assemblies |
| Ordinary magistrates |
| Extraordinary magistrates |
| Titles and honours |
|
The Principate is characterised by the reign of a single emperor (princeps) and an effort on the part of the early emperors, at least, to preserve the illusion of the formal continuance, in some aspects, of the Roman Republic.[1][2][3]
Etymology
It is etymologically derived from the Latin word princeps, meaning chief or first, the political regime dominated by such a political leader, whether or not he is formally head of state and/or head of government. This reflects the principate emperors' assertion that they were merely "first among equals" among the citizens of Rome.
History
The title, in full, of princeps senatus / princeps civitatis ("first amongst the senators" / "first amongst the citizens") was first adopted by Octavian Caesar Augustus (27 BC–AD 14), the first Roman "emperor" who chose, like the assassinated dictator Julius Caesar, not to reintroduce a legal monarchy. Augustus's purpose was probably to establish the political stability desperately needed after the exhausting civil wars by a de facto dictatorial regime within the constitutional framework of the Roman Republic as a more acceptable alternative to, for example, the early Roman Kingdom.
The title itself derived from the position of the princeps senatus, traditionally the oldest member of the Senate who had the right to be heard first on any debate. Although dynastic pretenses crept in from the start, formalizing this in a monarchic style remained politically unthinkable.
Often, in a more limited and precise chronological sense, the term is applied either to the Empire (in the sense of the post-Republican Roman state) or specifically the earlier of the two phases of "Imperial" government in the ancient Roman Empire, extending from when Augustus claimed auctoritas for himself as princeps until Rome's military collapse in the West (fall of Rome) in 476, leaving the Byzantine Empire sole heir, or, depending on the source, up to the rule of Commodus, of Maximinus Thrax or of Diocletian. Afterwards, Imperial rule in the Empire is designated as the dominate, which is subjectively more like an (absolute) monarchy while the earlier Principate is still more 'Republican'.
Under this "Principate stricto sensu", the political reality of autocratic rule by the Emperor was still scrupulously masked by forms and conventions of oligarchic self-rule inherited from the political period of the 'uncrowned' Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) under the motto Senatus Populusque Romanus ("The Senate and people of Rome") or SPQR. Initially, the theory implied the 'first citizen' had to earn his extraordinary position (de facto evolving to nearly absolute monarchy) by merit in the style that Augustus himself had gained the position of auctoritas.
Imperial propaganda developed a paternalistic ideology, presenting the princeps as the very incarnation of all virtues attributed to the ideal ruler (much like a Greek tyrannos earlier), such as clemency and justice, and in turn placing the onus on the princeps to play this designated role within Roman society, as his political insurance as well as a moral duty. What specifically was expected of the princeps seems to have varied according to the times; Tiberius, who amassed a huge surplus for the city of Rome, was criticized as a miser, but Caligula was criticized for his lavish spending on games and spectacles.
Generally speaking, it was expected of the Emperor to be generous but not frivolous, not just as a good ruler but also with his personal fortune (as in the proverbial "bread and circuses" – panem et circenses) providing occasional public games, gladiators, horse races and artistic shows. Large distributions of food for the public and charitable institutions were also means that served as popularity boosters while the construction of public works provided paid employment for the poor.
Redefinition under Vespasian
With the fall of the Julio-Claudian dynasty in AD 68, the principate was redefined in formal terms under the Emperor Vespasian in AD 69. The position of princeps became a distinct entity within the broader – formally still republican – Roman constitution. While many of the cultural and political expectations remained, the princeps was no longer a position extended on the basis of merit, or auctoritas, but on a firmer basis, allowing Vespasian and future emperors to designate their own heir without those heirs having to earn the position through years of success and public favor.
Under the Antonine dynasty, it was the norm for the Emperor to appoint a successful and politically promising individual as his successor. In modern historical analysis, this is treated by many authors as an "ideal" situation: the individual who was most capable was promoted to the position of princeps. Of the Antonine dynasty, Edward Gibbon famously wrote that this was the happiest and most productive period in human history, and credited the system of succession as the key factor.
Dominate
This first phase evolved into the so-called dominate. Starting with the Emperor Diocletian, an oriental type of style like dominus ("Lord", "Master", suggesting the citizens became servi, servants or slaves) gradually became current, though not legal, but there was no clear constitutional turning point. This trend is also said to have been established by the Emperor Septimius Severus; while the Severan dynasty began to use the terminology of the Dominate in reference to the emperor, the various emperors and their usurpers throughout the 3rd century appealed to the people as both military dominus and political princeps.
After the Crisis of the Third Century almost resulted in the Roman Empire's political collapse, Diocletian replaced the one-headed principate with the tetrarchy (c. AD 300, two Augusti ranking above two Caesares), in which the vestigial pretense of the old Republican forms was largely abandoned. The title of princeps was abandoned – like the territorial unity of the Empire – in favor of dominus, and the position of the emperor(s), especially in the Western Roman Empire, was entirely dependent on their control of the armed forces.
The dominate developed more and more, especially in the Eastern Roman Empire, along the lines of an oriental absolute monarchy, where the subjects, and even diplomatic allies, could be termed servus or the corresponding Greek term doulos, ("servant/slave") to express the exalted position of the Emperor as second only to God, and on earth to none.
References
- "Principate - government". britannica.com. Archived from the original on 2016-10-11.
- A history of Rome, M. Cary & H.H. Scullard, ISBN 0333278305
- SPQR; Mary Beard, ISBN 9781846683800
- Digital Reproduction of diagram found in The Anchor Atlas of World History, Vol. 1 (From the Stone Age to the Eve of the French Revolution) Paperback – December 17, 1974 by Werner Hilgemann, Hermann Kinder, Ernest A. Menze (Translator), Harald Bukor (Cartographer), Ruth Bukor (Cartographer)
Sources
- Alston, Richard. 1998. Aspects of Roman History. AD 14–117. London: Routledge.
- Aparicio Pérez, Antonio. 2009. “Taxation in Times of the Principate.” Gerión 27:1: 207-217.
- Bleicken, Jochen. 1978. Prinzipat und Dominat. Gedanken zur Periodisierung der römischen Kaiserzeit. Wiesbaden: Fr. Stein.
- Flaig, Egon. 2011. “The Transition from Republic to Principate: Loss of Legitimacy, Revolution, and Acceptance.” In The Roman Empire in Context: Historical and Comparative Perspectives, Edited by Jóhann Páll Arnason and Kurt A. Raaflaub. Ancient World, 67-84. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell.
- Gallia, Andrew B. 2012. Remembering the Roman Republic: Culture, Politics and History under the Principate. Cambridge; New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Gibson, A. G. G., ed. 2013. The Julio-Claudian Succession: Reality and Perception of the Augustan model. Mnemosyne. Supplements; 349. Leiden: Brill.
- Harlow, Mary and Laurence, Ray. 2017. “Augustus Senex: Old Age and the Remaking of the Principate.” Greece and Rome 64.2: 115-131.
- Kousser, Rachel Meredith. 2005. “From Conquest to Civilization: The Rhetoric of Imperialism in the Early Principate.” In A Tall Order: Writing the Social History of the Ancient World: Essays in Honor of William V. Harris, Edited by Jean-Jacques Aubert and Zsuzsanna Várhelyi. Beiträge zur Altertumskunde; 216, 185-202. München: Saur.
- Melounová, Markéta. 2012. “Trials with Religious and Political Charges from the Principate to the Dominate.” Series archaeologica et classica 17.2: 117-130.
- Raaflaub, Kurt A, Mark Toher, and G. W Bowersock. 1990. Between Republic and Empire: Interpretations of Augustus and His Principate. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Williams, Kathryn Frances. 2009. “Tacitus' Germanicus and the Principate.” Latomus 68.1: 117-130.
External links
| Library resources about Principate |