Pontic–Caspian steppe
The Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe, or Ukrainian steppe is the vast steppeland stretching from the northern shores of the Black Sea (called Euxeinos Pontos [Εὔξεινος Πόντος] in antiquity) as far east as the Caspian Sea, from Dobruja in the northeastern corner of Bulgaria and southeastern Romania, through Moldova and eastern Ukraine across Russian Northern Caucasus, Southern and lower Volga regions to western Kazakhstan, forming part of the larger Eurasian steppe, adjacent to the Kazakh steppe to the east. It is a part of the Palearctic temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome.
| Pontic–Caspian steppe | |
|---|---|
 The steppe in Azov-Syvash National Nature Park, Ukraine, with reintroduced horses. | |
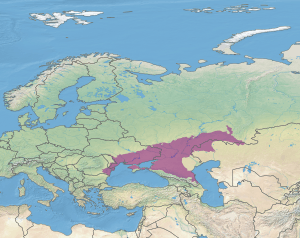 The steppe extends roughly from the Dniepr River to the Ural River | |
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Palearctic |
| Biome | Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands |
| Geography | |
| Area | 994,000 km2 (384,000 sq mi) |
.jpg)

The area corresponds to Cimmeria, Scythia, and Sarmatia of classical antiquity. Across several millennia the steppe was used by numerous tribes of nomadic horsemen, many of which went on to conquer lands in the settled regions of Europe, Western Asia, and Southern Asia.
The term Ponto-Caspian region is used in biogeography of the flora and fauna of these steppes, including animals from the Black Sea, Caspian Sea, and Azov Sea. Genetic research has identified this region as the most probable place where horses were first domesticated.[1]
According to the most prevalent theory in Indo-European studies called the Kurgan hypothesis, the Pontic–Caspian steppe was the homeland of the speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language.[2][3][4][5]
Geography and ecology
The Pontic steppe covers an area of 994,000 square kilometres (384,000 sq mi) of Europe, extending from Dobrudja in the northeastern corner of Bulgaria and southeastern Romania, across southern Moldova, Ukraine, through Russia and northwestern Kazakhstan to the Ural Mountains. The Pontic steppe is bounded by the East European forest steppe to the north, a transitional zone of mixed grasslands and temperate broadleaf and mixed forests.
To the south, the Pontic steppe extends to the Black Sea, except the Crimean and western Caucasus mountains' border with the sea, where the Crimean Submediterranean forest complex defines the southern edge of the steppes. The steppe extends to the western shore of the Caspian Sea in the Dagestan region of Russia, but the drier Caspian lowland desert lies between the Pontic steppe and the northwestern and northern shores of the Caspian. The Kazakh Steppe bounds the Pontic steppe to the east.
The Ponto-Caspian seas are the remains of the Turgai Sea, an extension of the Paratethys which extended south and east of the Urals and covering much of today's West Siberian Plain in the Mesozoic and Cenozoic.
Prehistoric cultures
- Linear Pottery culture 5500–4500 BC
- Cucuteni-Trypillian culture 5300–2600 BC
- Khvalynsk culture 5000–3500 BC
- Sredny Stog culture 4500–3500 BC
- Yamna/Kurgan culture 3500–2300 BC
- Catacomb culture 3000–2200 BC
- Srubna culture 1600–1200 BC
- Novocherkassk culture 900–650 BC
Historical peoples and nations
- Cimmerians 12th–7th centuries BC
- Dacians 11th century BC – 3rd century AD
- Scythians 8th–4th centuries BC
- Sarmatians 5th century BC – 5th century AD
- Ostrogoths 3rd–6th centuries
- Huns and Avars 4th–8th centuries
- Bulgars (Onogurs) 4th–7th century[6]
- Alans 5th–11th centuries
- Eurasian Avars 6th–8th centuries
- Göktürks 6th–8th centuries
- Sabirs 6th–8th centuries
- Khazars 6th–11th centuries
- Pechenegs 8th–11th centuries
- Kipchaks and Cumans 11th–13th centuries
- Mongol Golden Horde 13th–15th centuries
- Cossacks, Kalmyks, Crimean Khanate, Volga Tatars, Nogais and other Turkic states and tribes 15th–18th centuries
- Russian Empire 18th–20th centuries
- Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus 19th-20th centuries
- Soviet Union 20th century
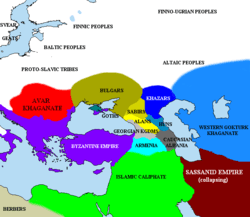 The Pontic steppe in c. 650
The Pontic steppe in c. 650 Zaporozhian Cossacks fighting Tatars from the Crimean Khanate—late 19th-century painting
Zaporozhian Cossacks fighting Tatars from the Crimean Khanate—late 19th-century painting
See also
- Black Sea-Caspian Steppe
- Forest steppe
- Crimean–Nogai raids into East Slavic lands
- Eurasian Steppe
- Haplogroup R1a1 (Y-DNA)
- Haplogroup R1b1 (Y-DNA)
- Kurgan hypothesis
- Late Glacial Maximum
- Steppe Route
- Tarim mummies
- Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands
- Kurgan stelae
References
- "Mystery Of Horse Domestication Solved?". sciencedaily.com. Retrieved 3 April 2018.
- David W. Anthony (2010-07-26). The Horse, the Wheel, and Language: How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes Shaped the Modern World. Princeton University Press. ISBN 9781400831104.
- Haak, Wolfgang; Lazaridis, Iosif; Patterson, Nick; Rohland, Nadin; Mallick, Swapan; Llamas, Bastien; Brandt, Guido; Nordenfelt, Susanne; Harney, Eadaoin; Stewardson, Kristin; Fu, Qiaomei; Mittnik, Alissa; Bánffy, Eszter; Economou, Christos; Francken, Michael; Friederich, Susanne; Pena, Rafael Garrido; Hallgren, Fredrik; Khartanovich, Valery; Khokhlov, Aleksandr; Kunst, Michael; Kuznetsov, Pavel; Meller, Harald; Mochalov, Oleg; Moiseyev, Vayacheslav; Nicklisch, Nicole; Pichler, Sandra L.; Risch, Roberto; Guerra, Manuel A. Rojo; Roth, Christina; Szécsényi-Nagy, Anna; Wahl, Joachim; Meyer, Matthias; Krause, Johannes; Brown, Dorcas; Anthony, David; Cooper, Alan; Alt, Kurt Werner; Reich, David (10 February 2015). "Massive migration from the steppe is a source for Indo-European languages in Europe". bioRxiv. 522 (7555): 207–211. arXiv:1502.02783. Bibcode:2015Natur.522..207H. bioRxiv 10.1101/013433. doi:10.1038/NATURE14317 (inactive 2020-05-29). PMC 5048219. PMID 25731166. Retrieved 3 April 2018.
- Allentoft, Morten E.; Sikora, Martin; Sjögren, Karl-Göran; Rasmussen, Simon; Rasmussen, Morten; Stenderup, Jesper; Damgaard, Peter B.; Schroeder, Hannes; Ahlström, Torbjörn; Vinner, Lasse; Malaspinas, Anna-Sapfo; Margaryan, Ashot; Higham, Tom; Chivall, David; Lynnerup, Niels; Harvig, Lise; Baron, Justyna; Casa, Philippe Della; Dąbrowski, Paweł; Duffy, Paul R.; Ebel, Alexander V.; Epimakhov, Andrey; Frei, Karin; Furmanek, Mirosław; Gralak, Tomasz; Gromov, Andrey; Gronkiewicz, Stanisław; Grupe, Gisela; Hajdu, Tamás; et al. (2015). "Population genomics of Bronze Age Eurasia". Nature. 522 (7555): 167–172. Bibcode:2015Natur.522..167A. doi:10.1038/nature14507. PMID 26062507.
- Mathieson, Iain; Lazaridis, Iosif; Rohland, Nadin; Mallick, Swapan; Llamas, Bastien; Pickrell, Joseph; Meller, Harald; Guerra, Manuel A. Rojo; Krause, Johannes; Anthony, David; Brown, Dorcas; Fox, Carles Lalueza; Cooper, Alan; Alt, Kurt W.; Haak, Wolfgang; Patterson, Nick; Reich, David (14 March 2015). "Eight thousand years of natural selection in Europe". bioRxiv: 016477. doi:10.1101/016477. Retrieved 3 April 2018 – via biorxiv.org.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2013-12-24.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eurasian Steppe. |
- "Pontic steppe". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- Google maps: Pontic-Caspian steppe