Polyisoprene
Polyisoprene is a collective name for polymers that are produced by polymerization of isoprene. In principle, four different isomers can form. Cis-1,4-polyisoprene, which is also called isoprene rubber, is a major ingredient of natural rubber. Trans-1,4-polyisoprene is a major ingredient of gutta-percha. Annual worldwide production of polyisoprene was 13,000 kilotonne in 2007.[1]

Property
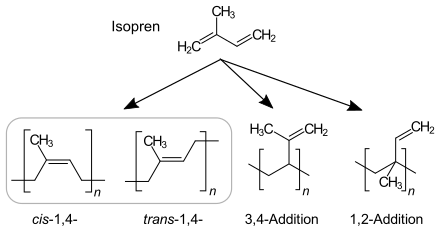
The percentage of repeating units of polyisoprene comprising each type of polymer bond is dependent on the reaction mechanism.
Anionic chain polymerization, which is initiated by n-Butyllithium, produces cis-1,4-polyisoprene dominant polyisoprene. 90–92% of repeating units are cis-1,4-, 2–3% trans-1,4- and 6–7% 3,4-units.[2]
Coordinative chain polymerization: With Ziegler–Natta catalyst TiCl4/Al(i-C4H9)3, more pure Cis-1,4-polyisoprene is formed. Natural rubber is more pure cis-1,4-polyisoprene. With Ziegler–Natta catalyst VCl3/Al(i-C4H9)3, trans-dominant polyisoprene is formed.[3]
1,2 and 3,4 dominant polyisoprene is produced MoO2Cl2 catalyst supported by phosphorus ligand and Al(OPhCH3)(i-Bu)2 co-catalyst.[4]
Usage
Natural Gutta-percha and synthesized trans-1,4-polyisoprenes are used for golf balls. Natural rubber and synthesized cis-1,4-polyisoprene are used for elastomer.
Polyisoprene condoms provide an alternative to traditional latex condoms.
See also
References
- Sebastian Koltzenburg, Michael Maskos, Oskar Nuyken, Polymere: Synthese, Eigenschaften und Anwendungen, Springer, Berlin, 2012, S. 424.
- Jürgen Falbe, Manfred Regitz (Hrsg.): CD Römpp Chemie Lexikon, Thieme, Stuttgart, 1995.
- Bernd Tieke, Makromolekulare Chemie, 3. Auflage, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2014, S. 149.
- 1,2- and 3,4-rich polyisoprene synthesized by Mo(VI)-based catalyst with phosphorus ligand Polymer Science Series B September 2016, Volume 58, Issue 5, pp 495–502